NPB101: Neurophysiology Part 1
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A Basic Overview of the Central Nervous System
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
Glial Cells
Are support cells
Transduction
all the stimuli are of different “flavors” (different modalities)
Transduction examples
Hear: sound waves hit air and travel through cochlea then you will do transduction
Light waves: light bounce to your eye, your retina, the photoreceptors will transduce it
AP is an ____ signal
electrical
In Transduction you want to convert everything to an _____ signal
electrical
Cant detect microwaves why?
We don’t have the receptor for it!
The NS (nervous system) _____ & _____ signals
processes & integrates
T/F: the NS controls only voluntary activities
False, the NS control both voluntary and involuntary activities
The NS functions with ____ regulation
homeostatic
The NS functions with higher ____ function
cognitive
T/F: We only use 10% of our brain
FALSE! We use 100% of our brain 10% would mean we would be functionally DEAD!
What are the parts of the Central Nervous System (CNS)?
Brain
Spinal Cord
Retina
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Afferent Division sensories
Somatic
Visceral
Special
What is the afferent division?
The afferent division bring info to the CNS (they are sensory in nature)
T/F: the Visceral sensory is involuntary
This is true because we aren’t actively controlling this function
Efferent Division motors
Somatic: control GI tract (involuntary)
Autonomic
Sympathetic
Parasympathetic
Enteric
The efferent divison brings ___ to the ____
info, organs
Somatic motor
Voluntary movement (like moving hand)
T/F: Autonomic is voluntary
False it is involuntary
Autonomic motor
Sympathetic: involuntary, influenced by stimuli, fight or flight, stress
Parasympathetic: involuntary, rest and safety
Enteric: NS of your GI tract
T/F: The Somatic motor from Efferent Division is involuntary
True it is involuntary
T/F: Sympathetic from Autonomic motor from Efferent Division is involuntary
True, you do not have control over it
T/F: You are not influenced by stimuli that activates sympathetic actions from autonomic motor
False, you are influences by stimuli that activates sympathetic action from autonomic motor and this can be being scared (fast heart beat) when receiving a pop quiz
The ___ communication in our NS is the ____
main, neuron
What two cells do myelination?
A) Astrocytes and Schwann cells
B) Oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells
C) Microglia and astrocytes
D) Ependymal cells and oligodendrocytes
B) Oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells
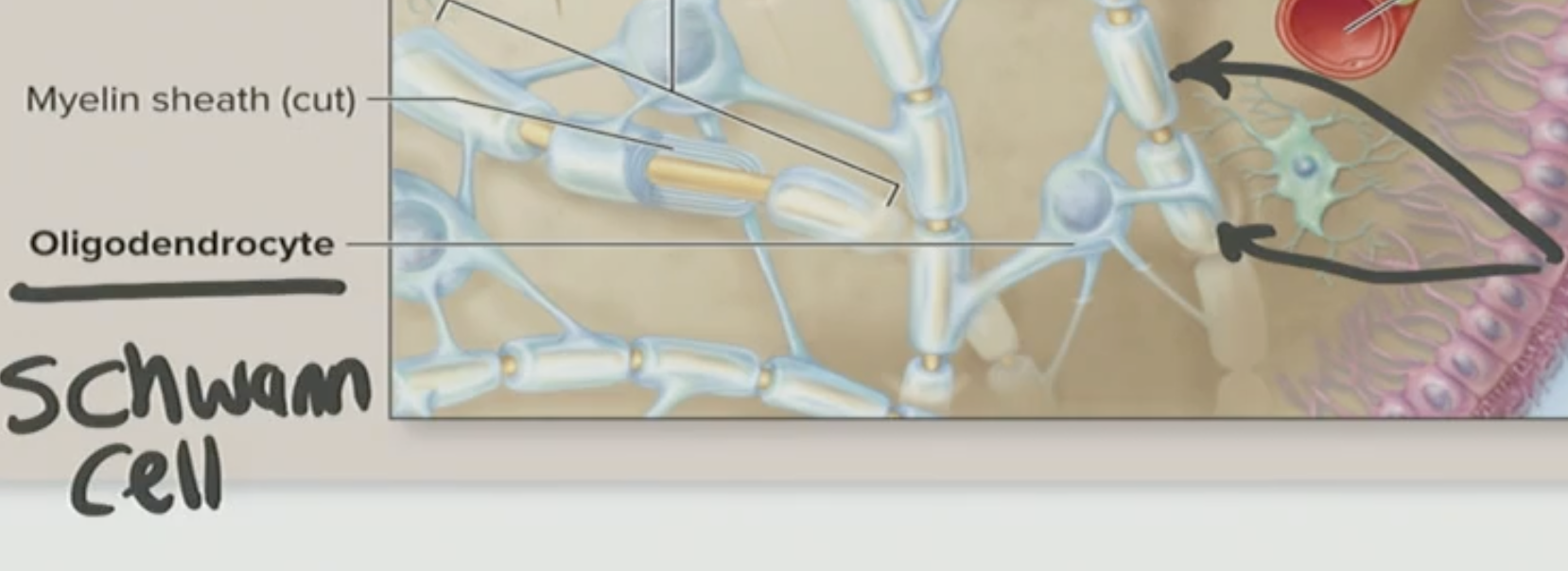
Astrocytes
The most idea environment for our neurons, they regulate Brain ECF
Ependymal cell
produce cerebral fluid
Where are Ependymal cells created?
Ependymal cells are in the choroid plexus in the ventricles
T/F: Oligodendrocytes are the most important type of glial cells
False, while they are important for the formation of myelin, Astrocytes are the most important as they regulate environments like for brain ECF
Neurons are ____ cells
communication
Afferent neurons do ____ pathways
sensory
Efferent neurons do ____ pathways
motor
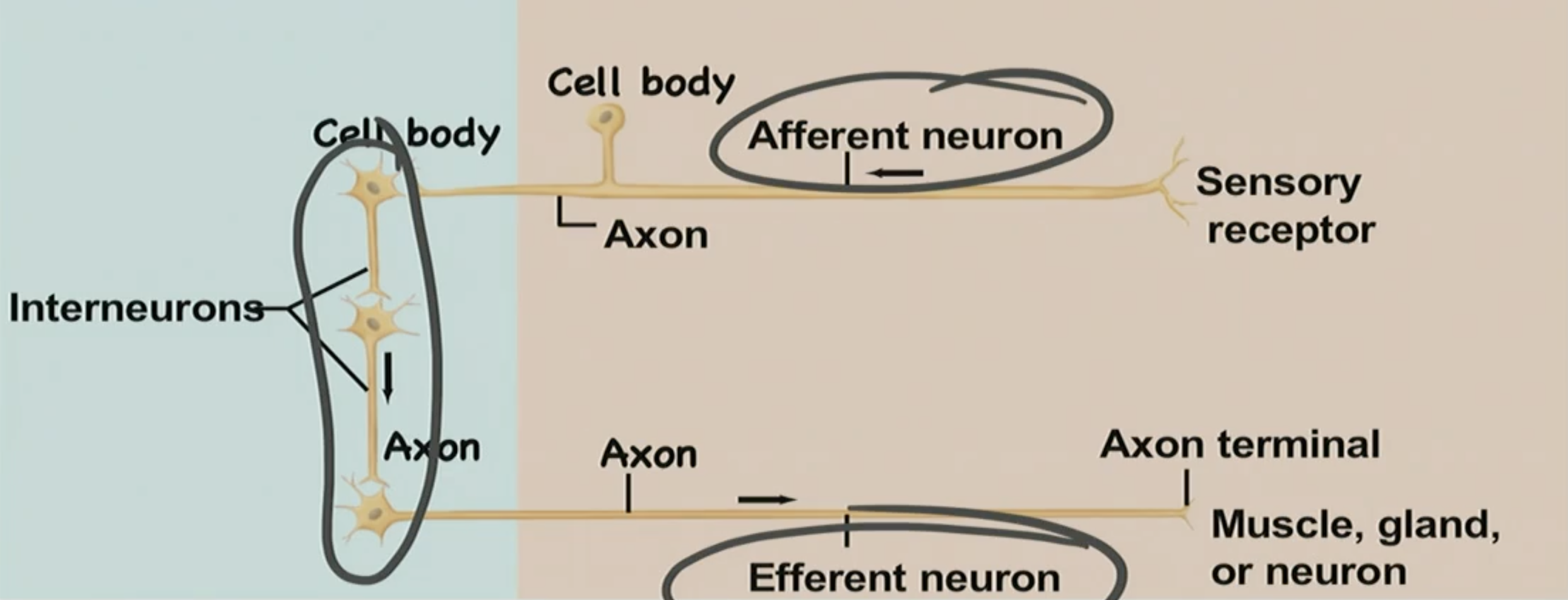
Interneurons
make all the decisions
T/F: Interneurons don’t do much processing
False, interneurons do a tremendous amount of processing
Nerve tract
take a bunch of neurons and get their axons and put it in a big bundle
Most ___ processes are ____ into nerves
neuronal, bundles
How do we protect out Spinal column/brain?
We protect our spinal column/brain with the meninges
What does the Meninges cover specifically
The meninges covers the CNS
The Meninges
Protection layers of the spinal and brain
What is flowing in between the layers of meninges and the bone?
Cerebrospinal Fluid
Cerebrospinal Fluid
Shock Absorber
Allows exchange between the brain ECF and blood
How is Cerebrospinal fluid a shock absorber?
Well if you wack your head the fluid absorb a bit of that pressure
How does the Cerebrospinal Fluid allow exchange between the brain ECF and blood?
This is homeostatically regulated as we move stuff between the blood and it goes into the cerebrospinal fluid and then into the brain ECF, so like a mediator: ensure brain ECF is pristine
What do we keep producing the Cerebrospinal Fluid?
A) The Choroid Plexus
B) The Arachnoid Villi
C) The Pia Mater
D) Ependymal cells
D) Ependymal cells
T/F: Cerebrospinal fluid gets discarded and remade
False, Cerebrospinal fluid is recycled: ventricles where ependymal cells are crank out this spinal fluid that goes into our ventricles and drains down the spinal cord and comes back up from spinal cord and then comes on the outside of the brain and drains back into the blood
Blood Brain Barrier info below
Flashcards 48-63
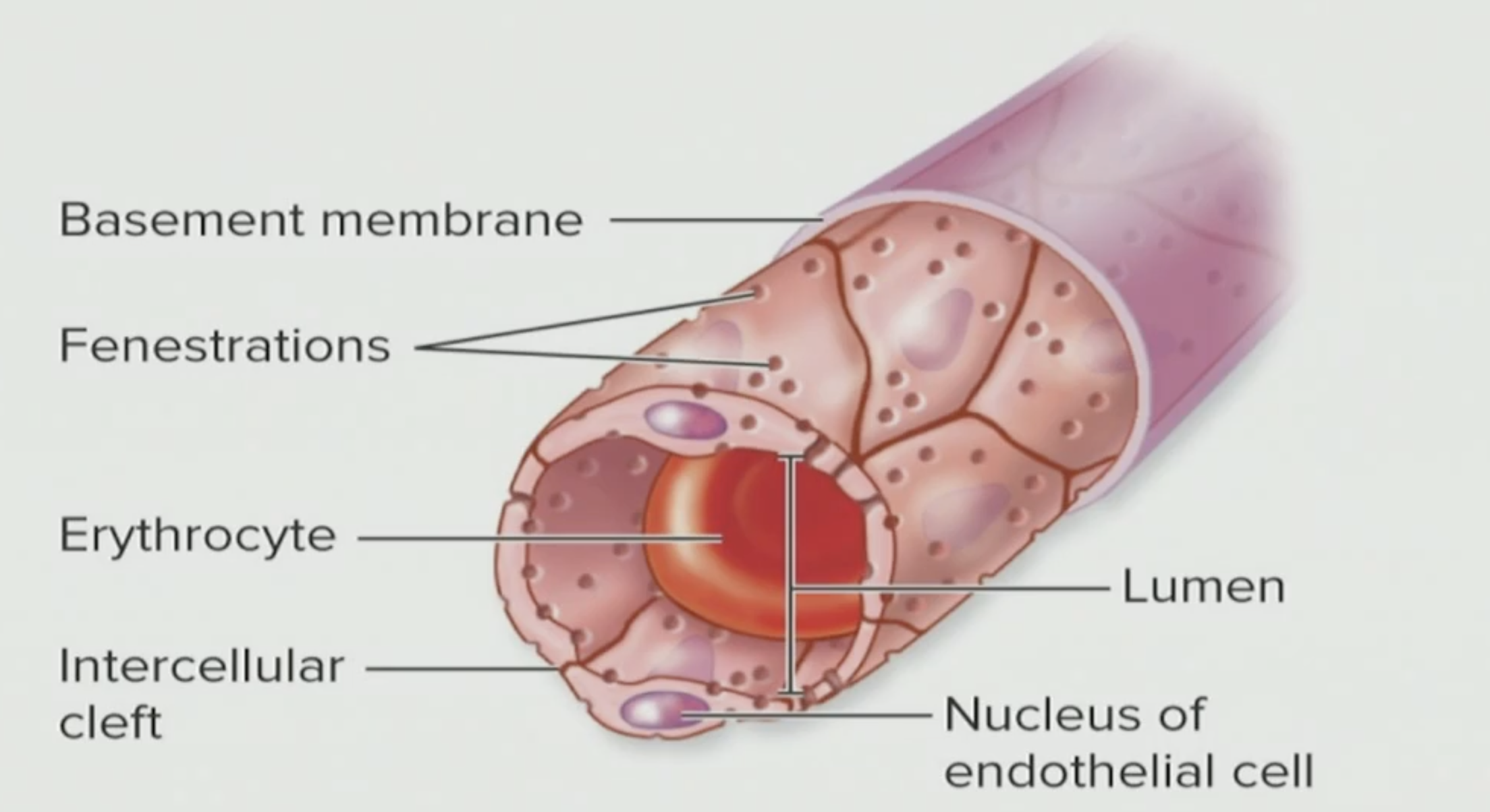
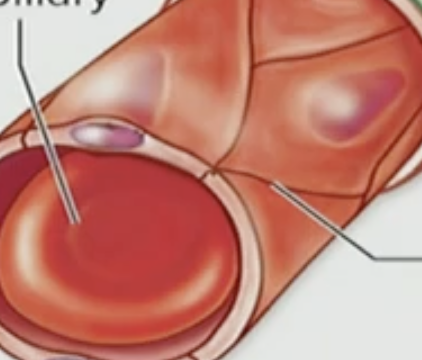
What is this?
Fenestrated Capillary
Fenestrated
A bunch of holes inside it; holes
Capillary
Exchange material between your blood and the tissue
Where are Fenestrated Capillaries located?
Outside of the CNS
T/F: Fenestrated Capillaries keep all the material inside
False, most are actually leaky, look at the pores
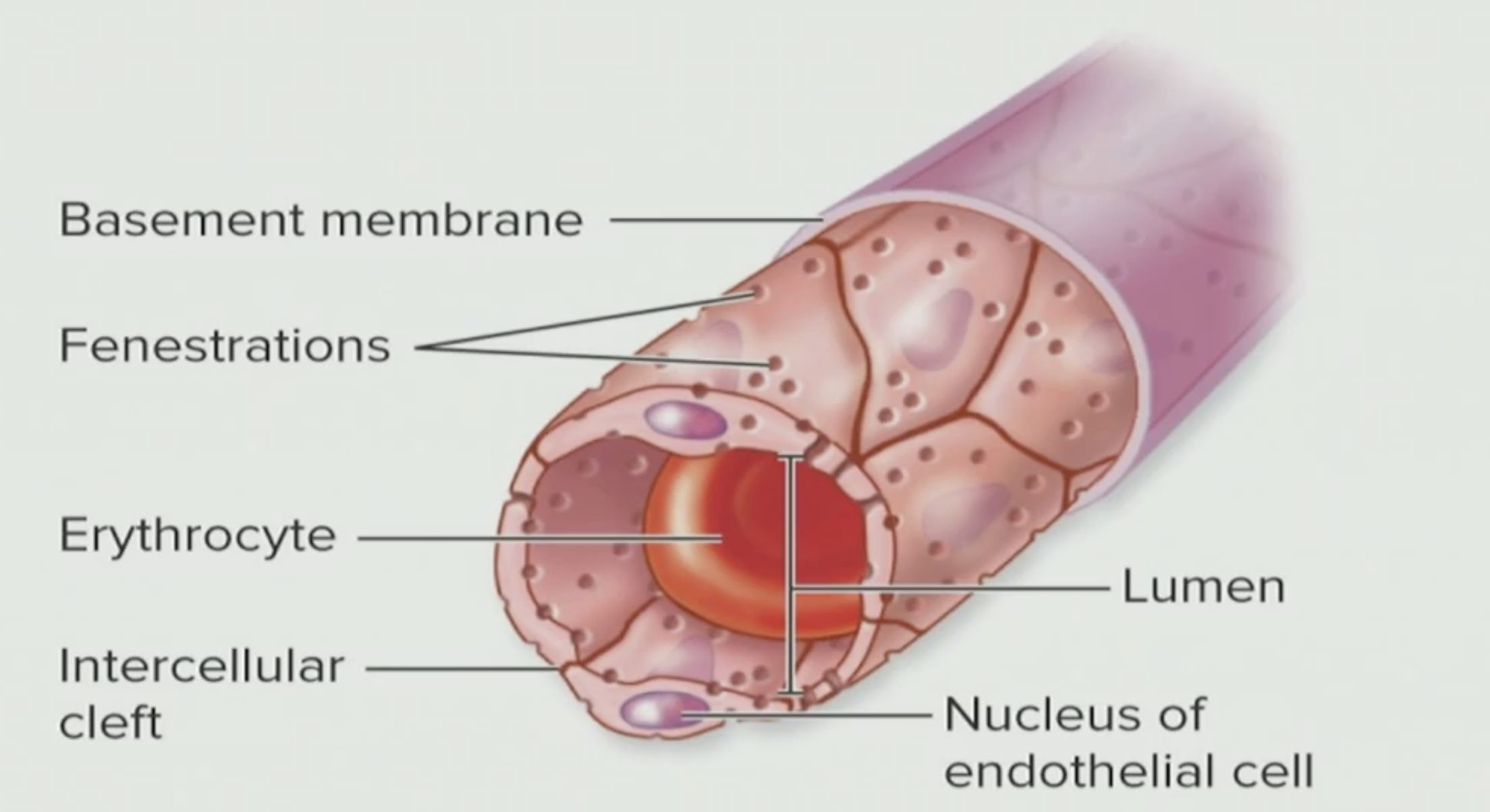
T/F: Anything in our blood is stuck and cannot go to the ECF
False, it can actually cruise on through out of the liquid of our blood (plasma) and into the ECF
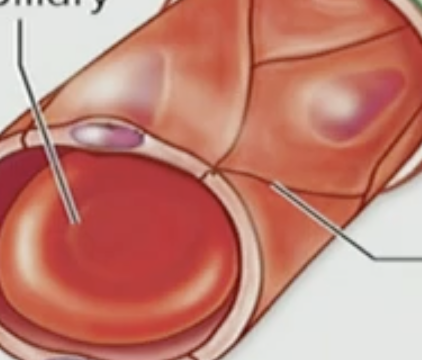
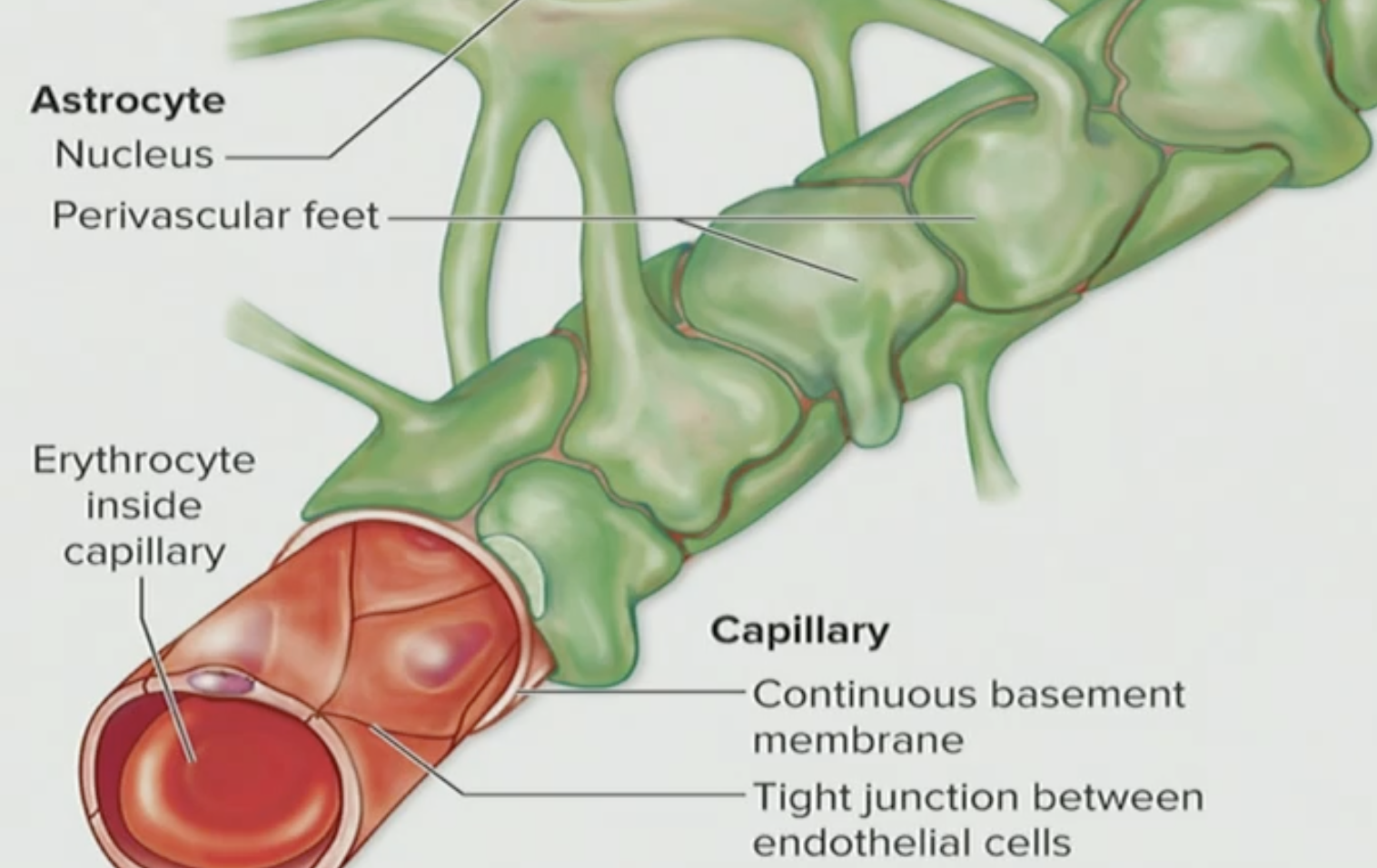
What kind of cells are these?
Endothelial cells
T/F: The endothelial cells are pretty loose
False, endothelial cells are actually pretty cemented together (tightly packed)
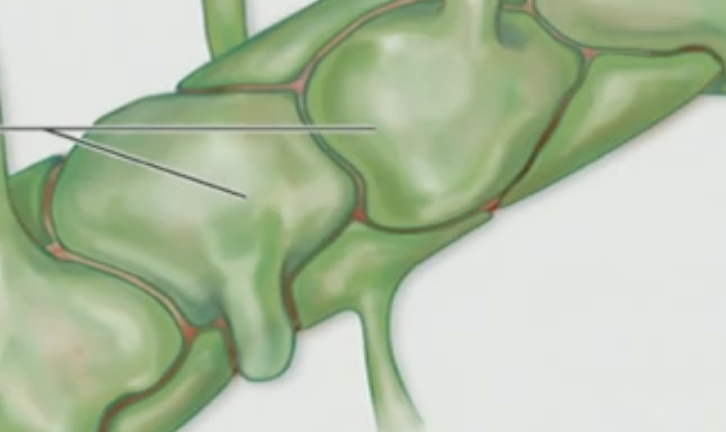
What kind of cells are these?
Astrocyte
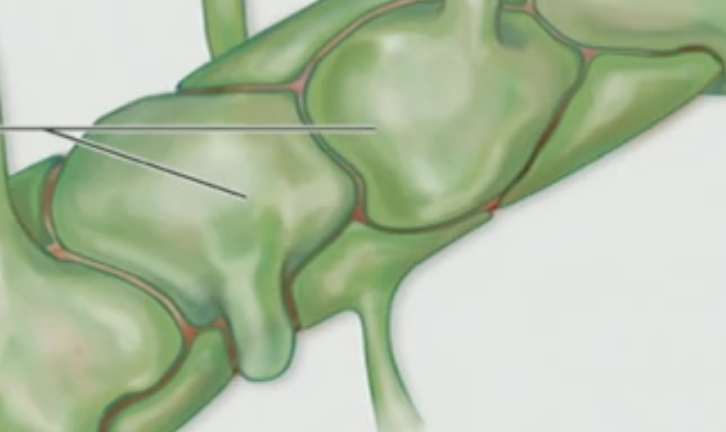
Astrocytes are what type of cells?
Glial cells
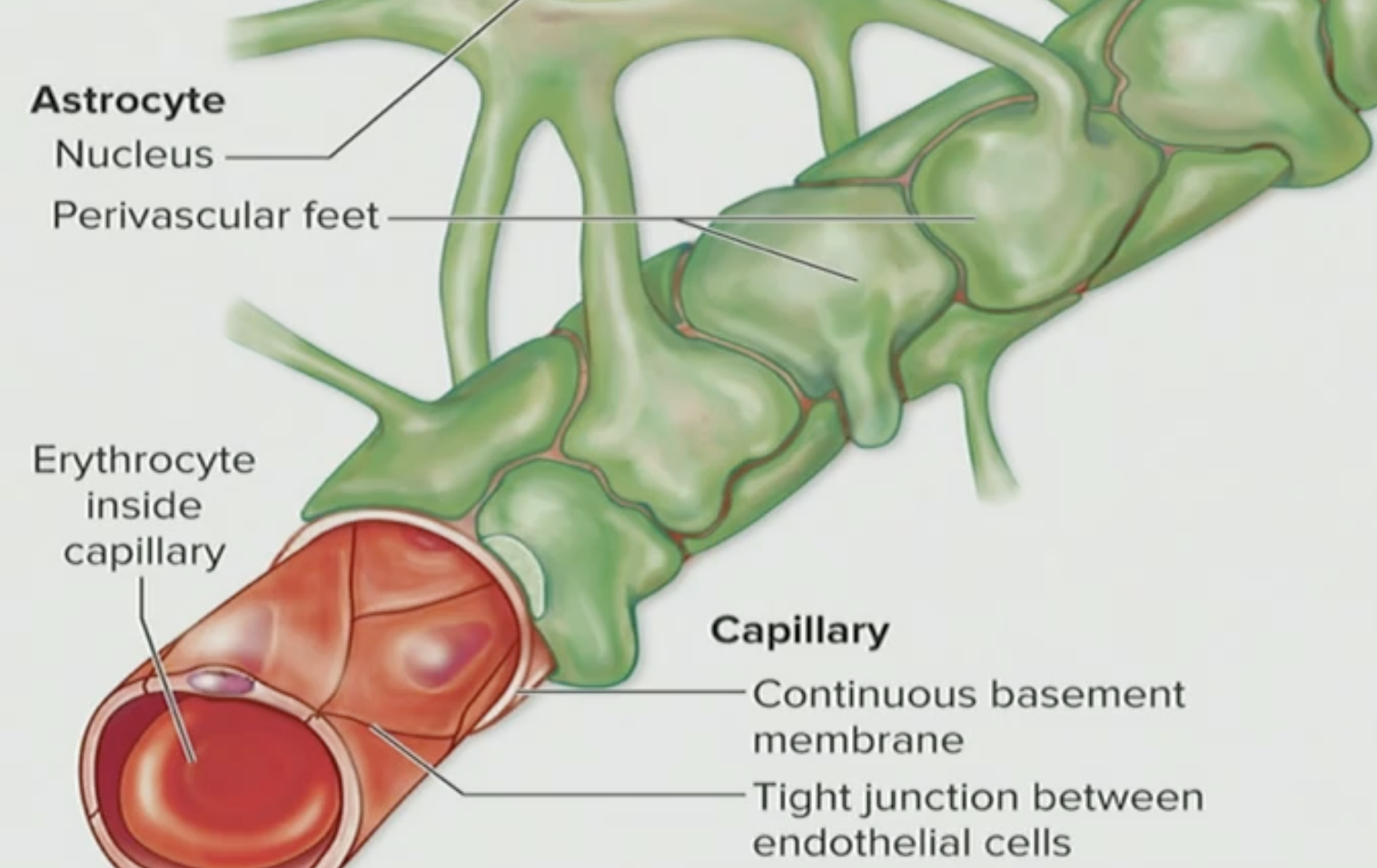
What do these two tissues do together
They are transport mechanisms as the regulate & prevent things from going directly to the blood into the brain ECF
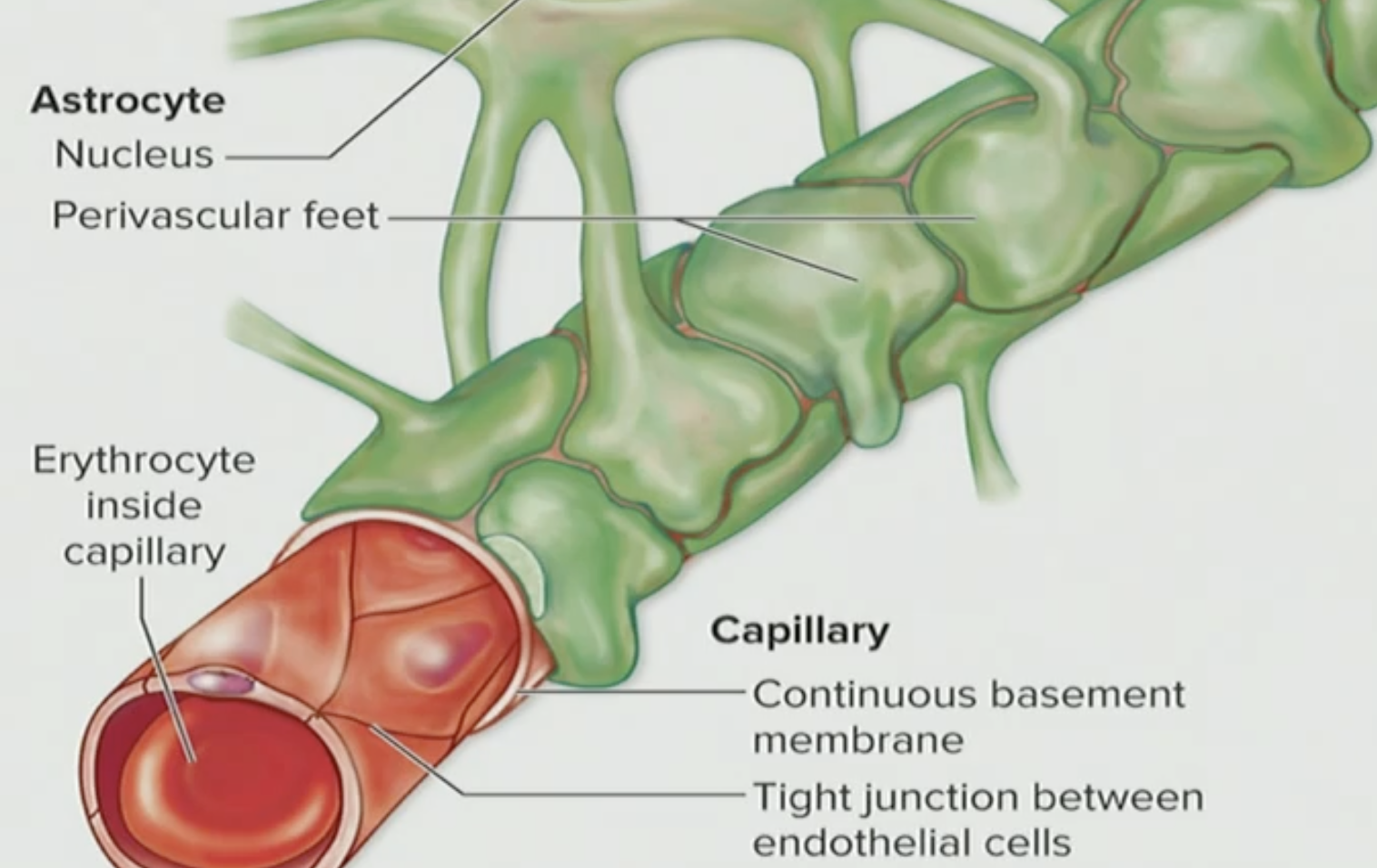
Where are these located?
Endothelial cells and Astrocytes are located in most regions of the CNS
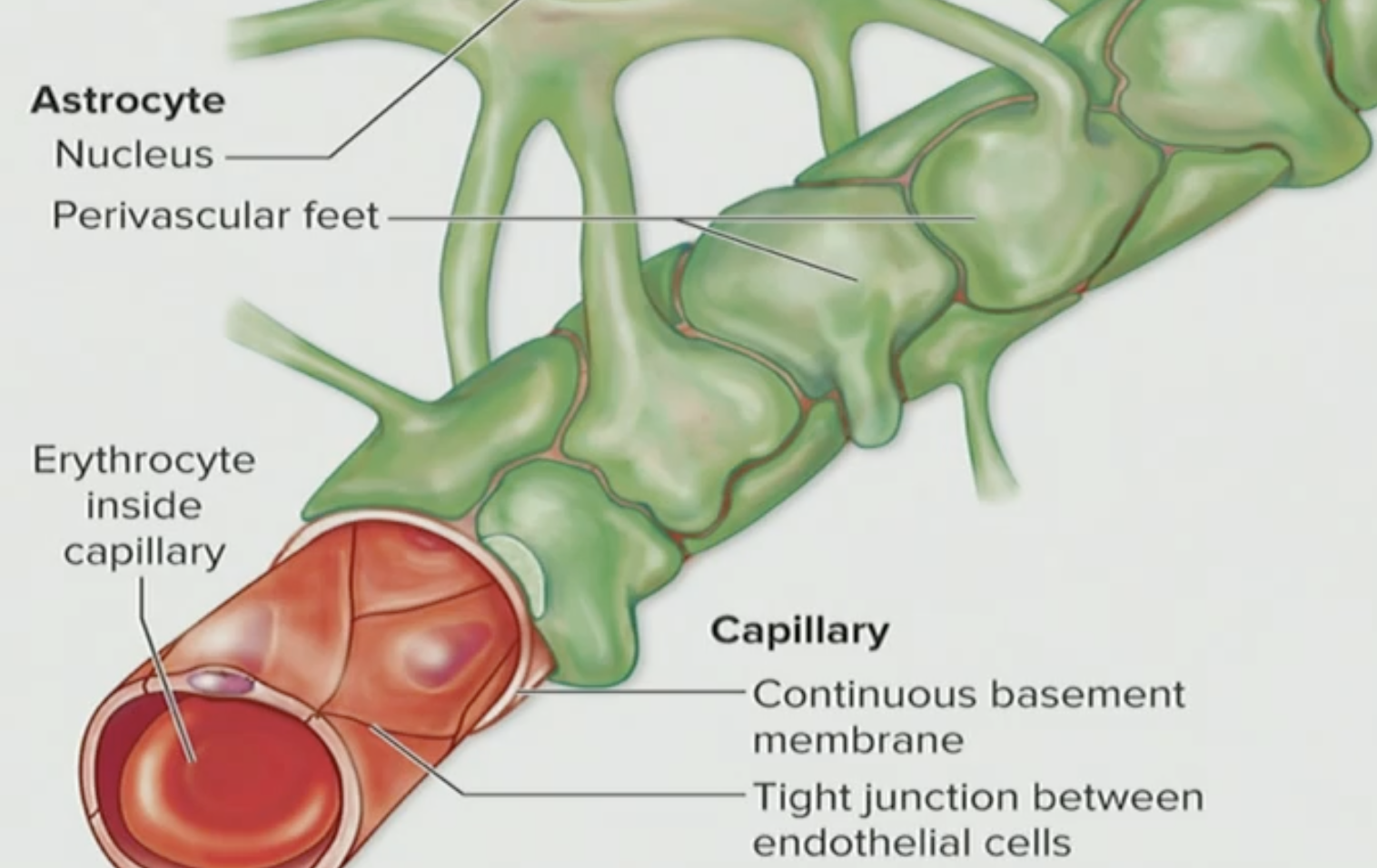
Are these capillaries leaky?
NO they are not leaky, they are actually tight junctions
T/F: Endothelial tissues and Astrocytes are a preventative barrier
True, they prevent blood from going into the brain ECF
T/F: The brain ECF doesn’t matter what state it is in (ex: bad or good)
False, It definitely does matter, brain ECF needs to be in pristine condition
T/F: Substances only enter the brain via transport process through endothelial cells only
False, substances can enter the brain via transport process through the endothelial cells and astrocytes