4. entropy + Gibbs free energy
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
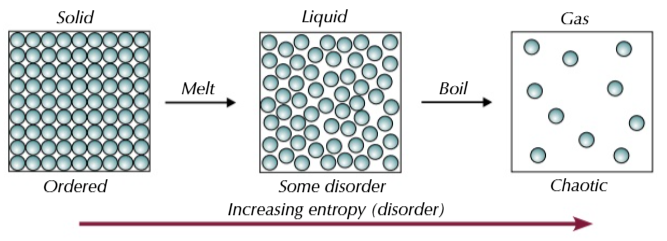
entropy
the measure of the number of ways that particles can be arranged and the number of ways that the energy can be shared out between the particles
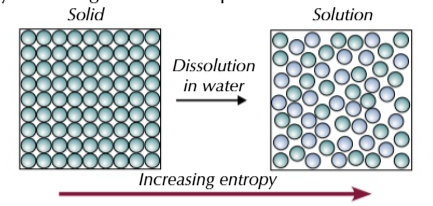
dissolution
dissolving a solid also increases its entropy as dissolved particles can move freely as they are no longer held in place
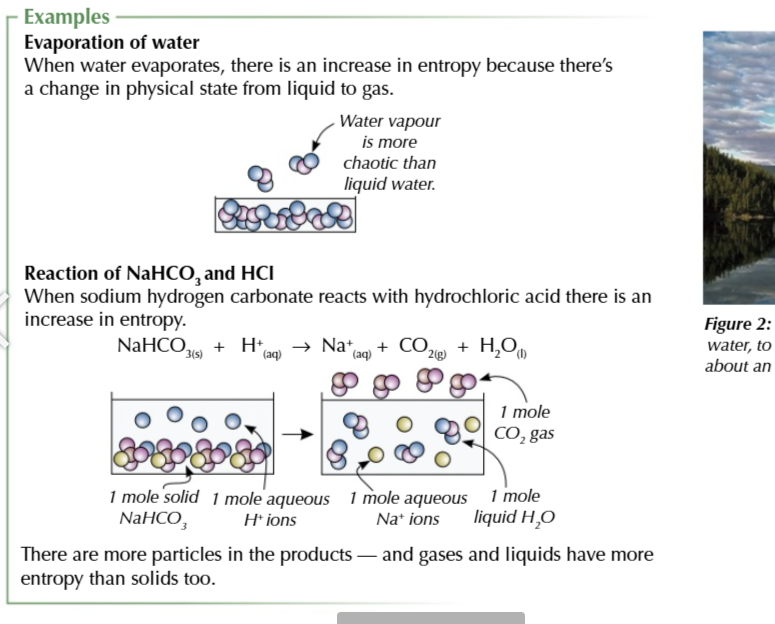
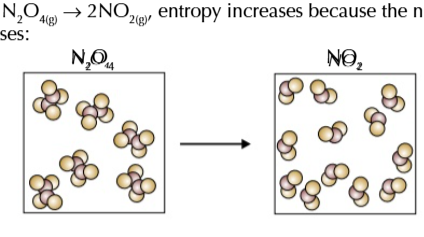
more particles means more entropy
the more particles there are the more ways they and their energy can be arranged
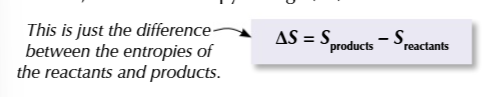
calculating entropy change
products - reactants
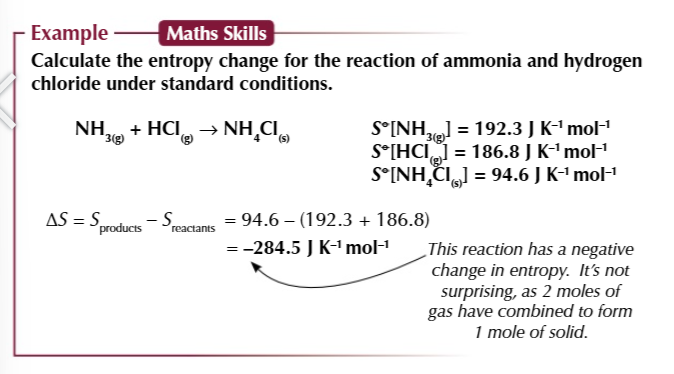
free energy change
is a measure used to predict whether a reaction is feasible
a reaction is feasible when
ΔG is negative or equal to 0
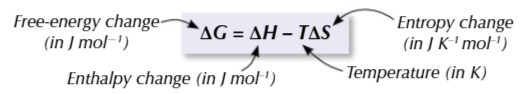
negative ΔG doesn’t guarantee a reaction will occur or tell you about its rate
the reaction may only be theoretically feasible,
with an extremely high activation energy
or have such a slow rate you wouldn’t be able to notice tis happening at all

exothermic reactions and POSITIVE ENTROPY change
these reactions are feasible at any temperature
endothermic reactions and has a NEGATIVE ENTROPY change
these reactions are not feasible at any temperature
if the reaction is endothermic and entropy is positive
the reaction will only be feasible above a certain temperature

if the reaction is exothermic and enthropy is is positive
reaction is only feasible below a certain temperature

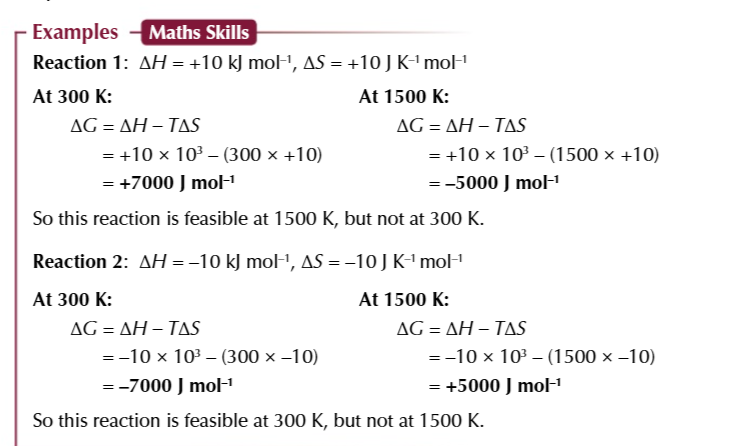
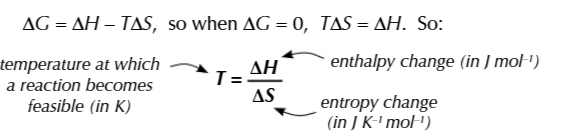
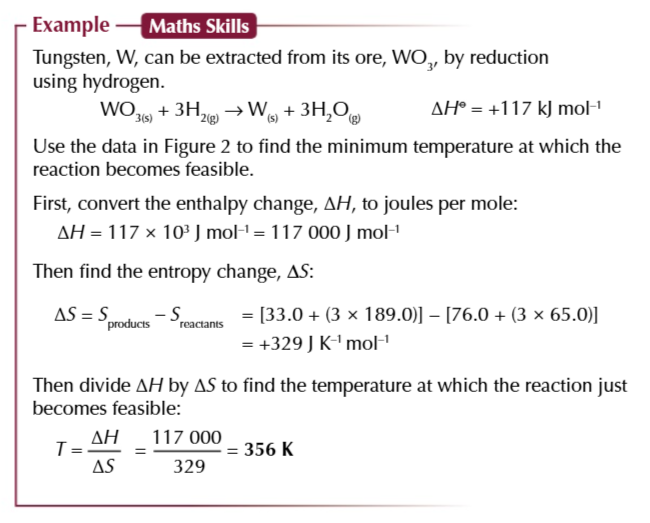
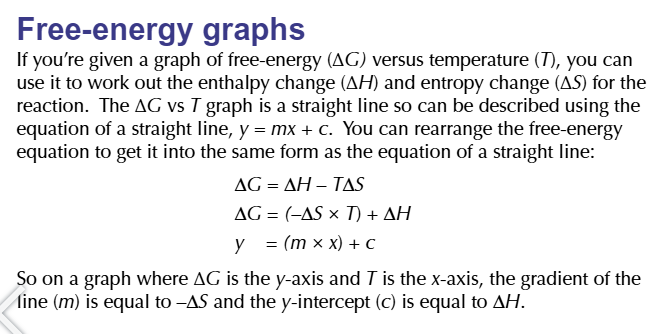
when ΔG is 0
a reaction is JUST feasible

variation in ionisation energy, FROM STRONGEST TO WEAKEST
O2+>O> O- >O2-
CATION>NEUTRAL ELEMENT>ANION