Algebra II - 2nd Semester Exam Study Guide
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Matching Formulas and Properties - 35 points
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Adding Functions
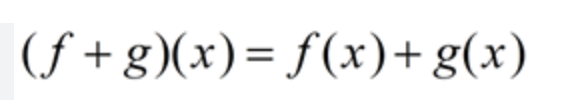
Change of Base
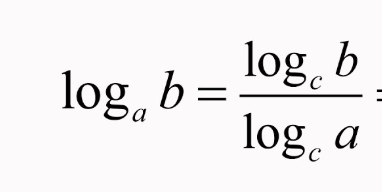
Common Logarithm
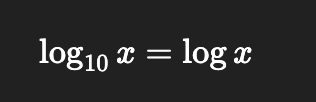
Compound Continuously
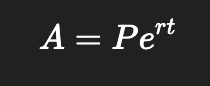
Conjugates
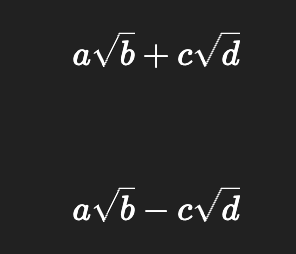
Dividing Functions
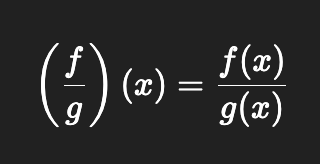
e
aprox. 2.718
Exponential Decay
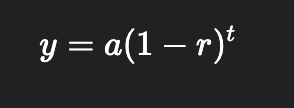
Exponential Function
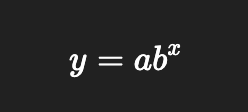
Exponential Growth

Arithmetic Sequences
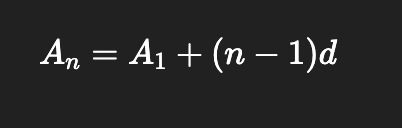
Geometric Sequences
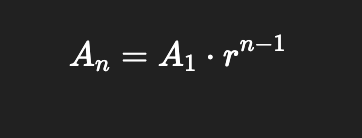
Sum of a finite arithmetic sequences
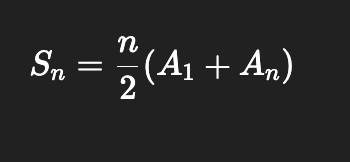
Sum of a finite geometric sequences
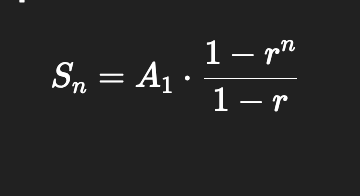
Multiplying Functions
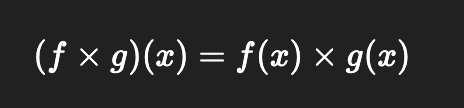
Natural base exponential function
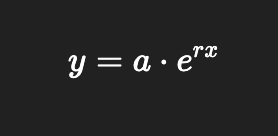
Natural Logarithm
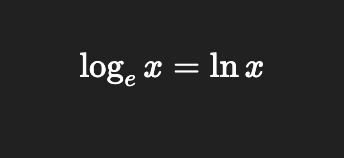
Negative Exponent
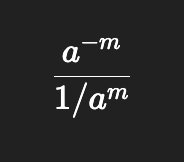
Power of a power
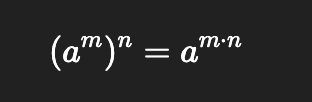
Power of a product
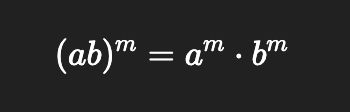
Power of a quotient
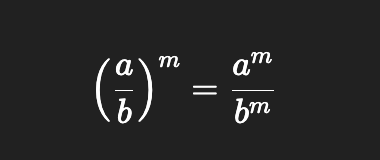
Power property
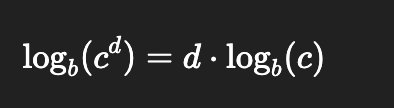
Product of powers
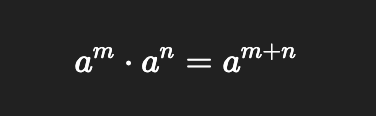
Product Property
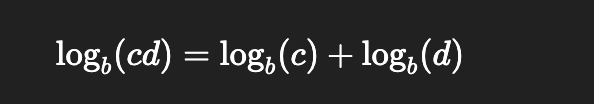
Product Property of radicals
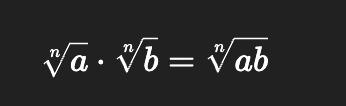
Quotient of powers
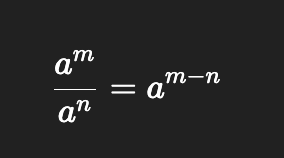
Quotient property
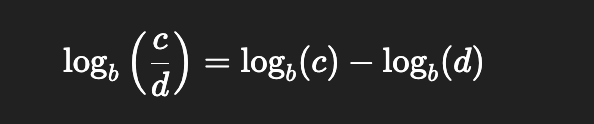
Quotient property of radicals
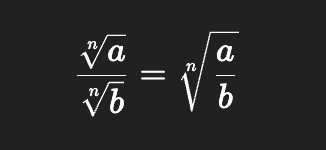
Radical function
√x
Rational Function
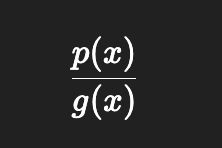
Substracting functions
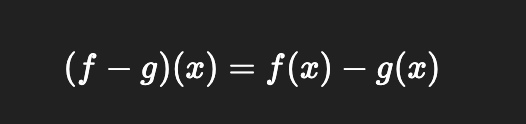
Arithmetic sequence
- a list of ordered numbers where to difference between one term to the next is constant
Compound interest
- interest that is based on an initial amount once accumulated interest
Common difference
- represents the constant different between one term to the next
Common ratio
- represents the common multiplier between any term to the next
Explicit rule
shows how An acts as a function to solve for terms at any position
Exponential equations
- have a variable in the exponent
Extraneous solutions
- Extra solutions that dont work
Finite sequence
- a list with a limited number of ordered numbers
Finite series
- limited number of terms added together
Geometric sequence
- a list of ordered numbers where the ratio of any term to the next term is constant
Horizontal line test
- if you put the horizontal line through a function and it passes through only once then the inverse is a function
Infinite sequence
- a list with an unlimited number of ordered numbers
Infinite series
unlimited number of terms added together
Inverse functions
- reflect over the line y = x
Logarithms
- the opposite of exponential function
Partial sum
the sum of the first n terms that are given in an infinite series
Recursive rule
- shows how An is related to the revious terms given the beginning term
Term
the position of a number in a sequence
Radical function
domain and range : f(x) = √x
x>=0
y>=0
Cube root function
domain and range f(x)=3√x
all real numbers
Rational function
f(x) = 1/x