all of p8
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
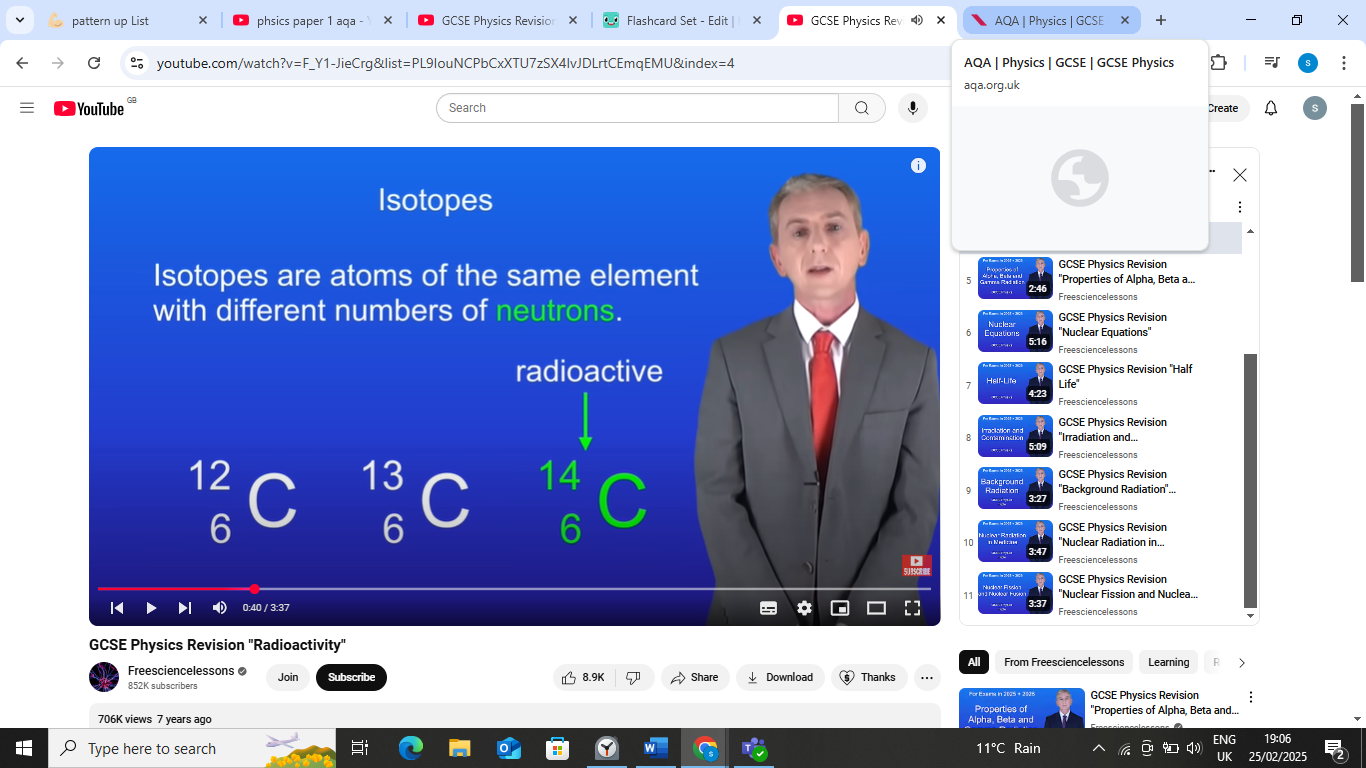
what is carbon 14
carbon 14 is a radioactive isotope
whats radioactive decay
radioactive decay is when some isotopes have an unstable nucleus,to become stable nucleus gives out radiation
what type of procss is radioactive decay?
radioactive decay is a totally random process
whats activity
activity is the rate at which a source of unstable nuclei decay
whats activity measured in
activity is measured in Bq becquerel
how many bq = 1 decay per sec
1bq=1decay per sec
what object do you use to measure activity
geiger muller tube
count rate
the count rate is number of decays recorded each second by a detector
what do alpha particles consist of,whats it the same as
alpha particles consist of 2 protons 2 neutrons so its the same as a nucleus of a helium atom
whats a beta particle
whats it ejected from
a beta particle is a electron ejected from the nucleus at very high speed,beta partcile formed inside the nucleus when a neutron changes into a proton and electron
what is gamma rays a type of?
gamma rays are type of electromagnetic radiation from the nucleus
4 types of radiation
alpha,beta,gamma,neutron
size of alpha,range iin air for alpha particles,
alpha particles are large,they can travel 5cm in air before colliding with air particles and stop
range iin air for beta particles,
beta particles travel further,reach 15cm in air before stopped
range iin air for gamma particles,
gamma radiation travels several meters in air before stopping
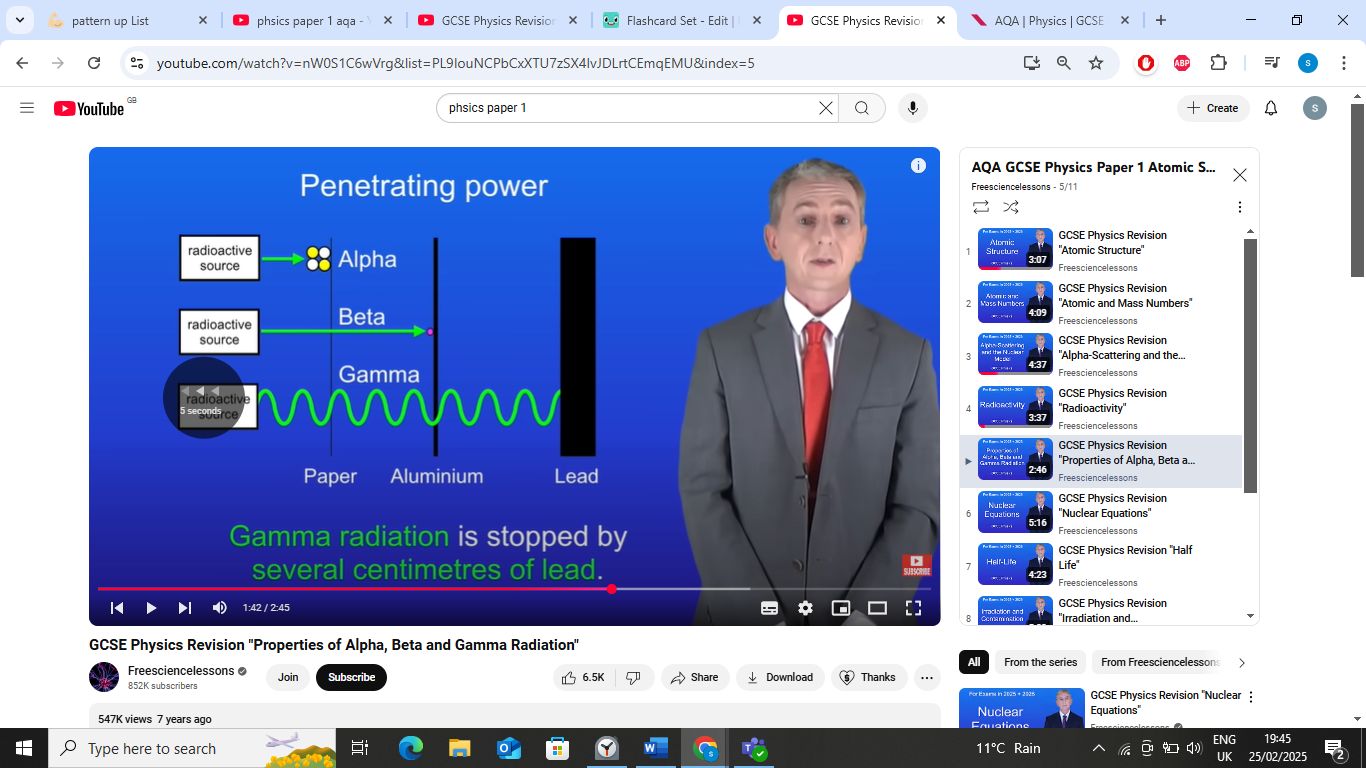
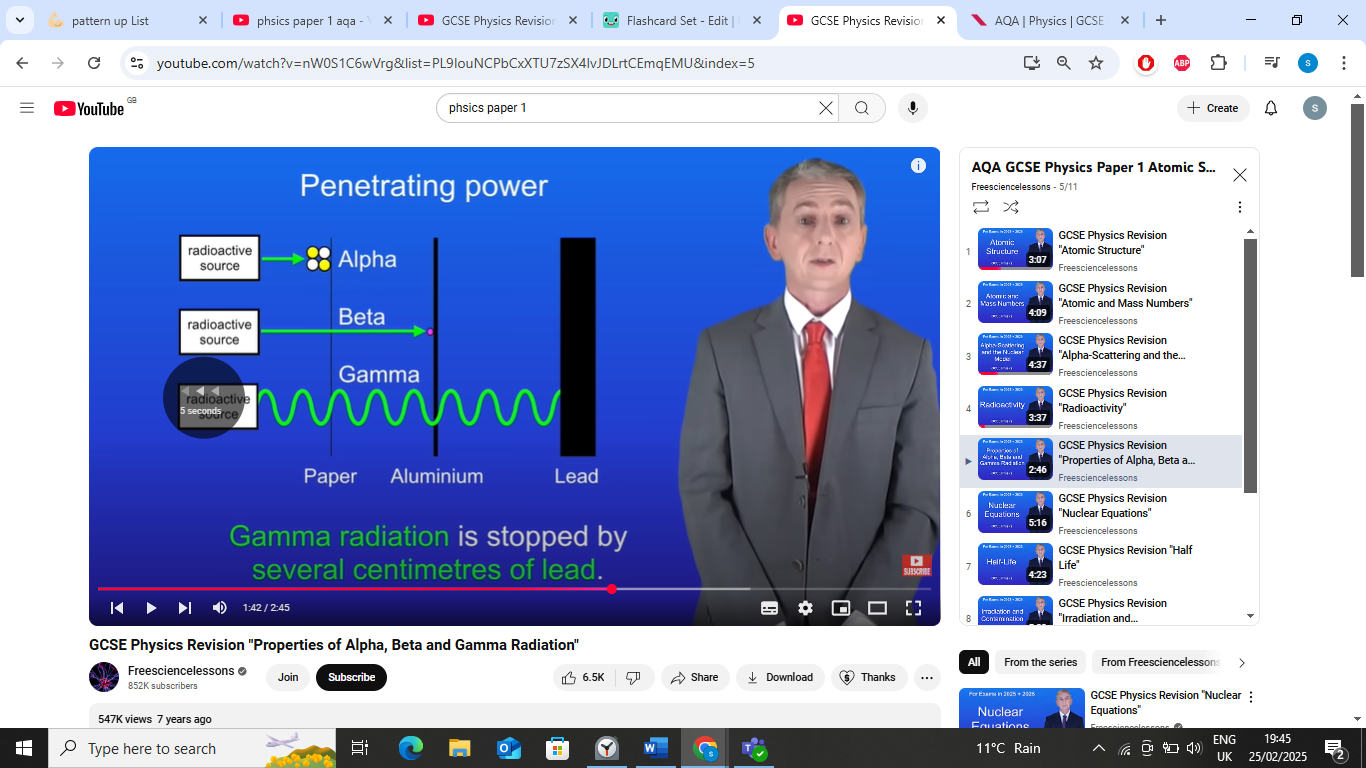
penetrating power- alpha particles
alpha particles stopped by single sheet of paper,
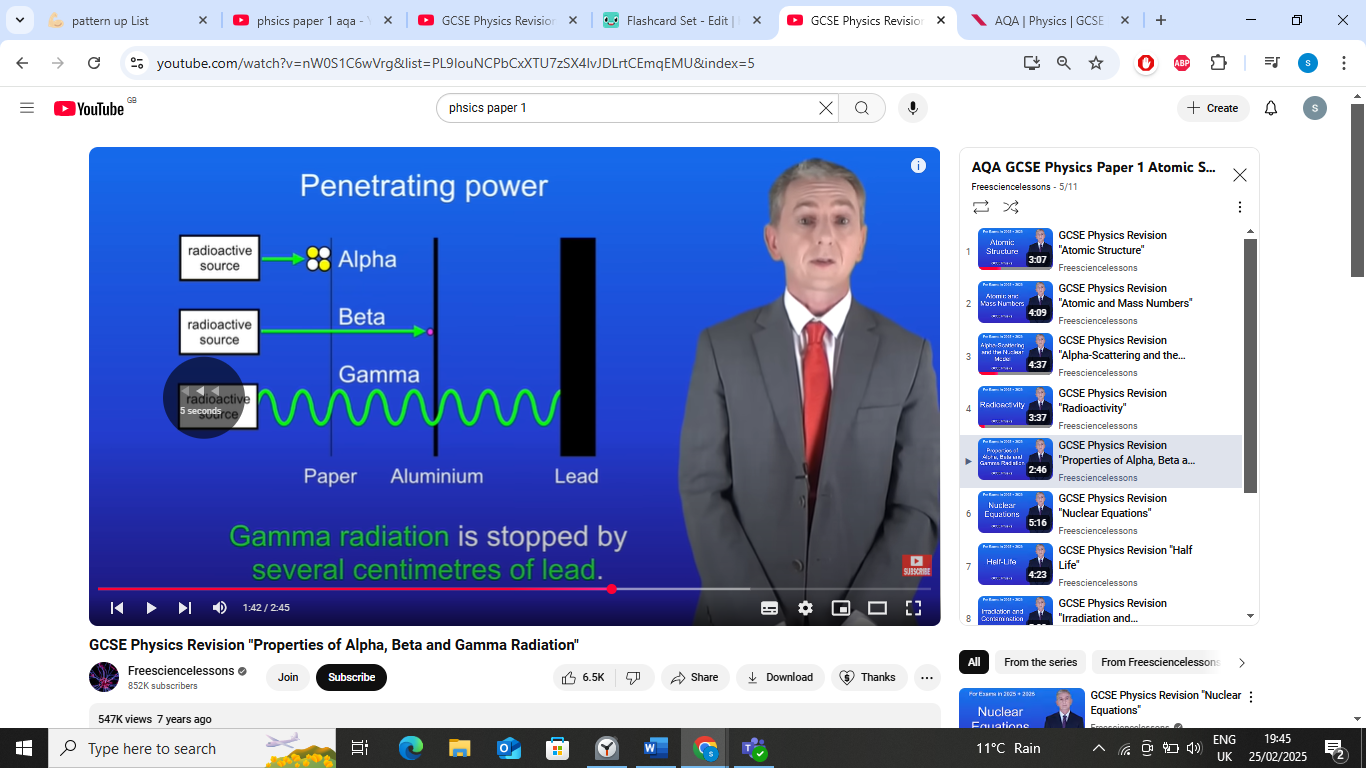
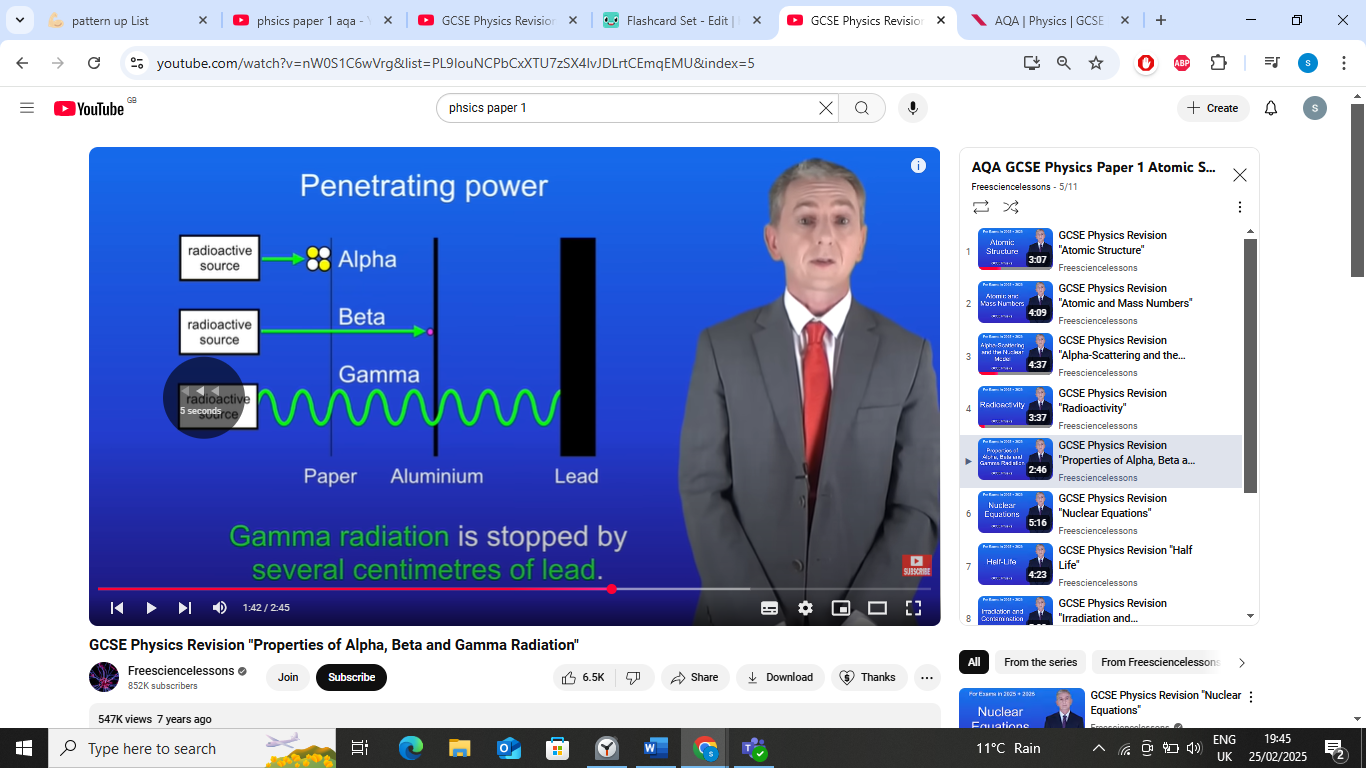
penetrating power- beta particles
beta particles stopped by few mm of aluminium,
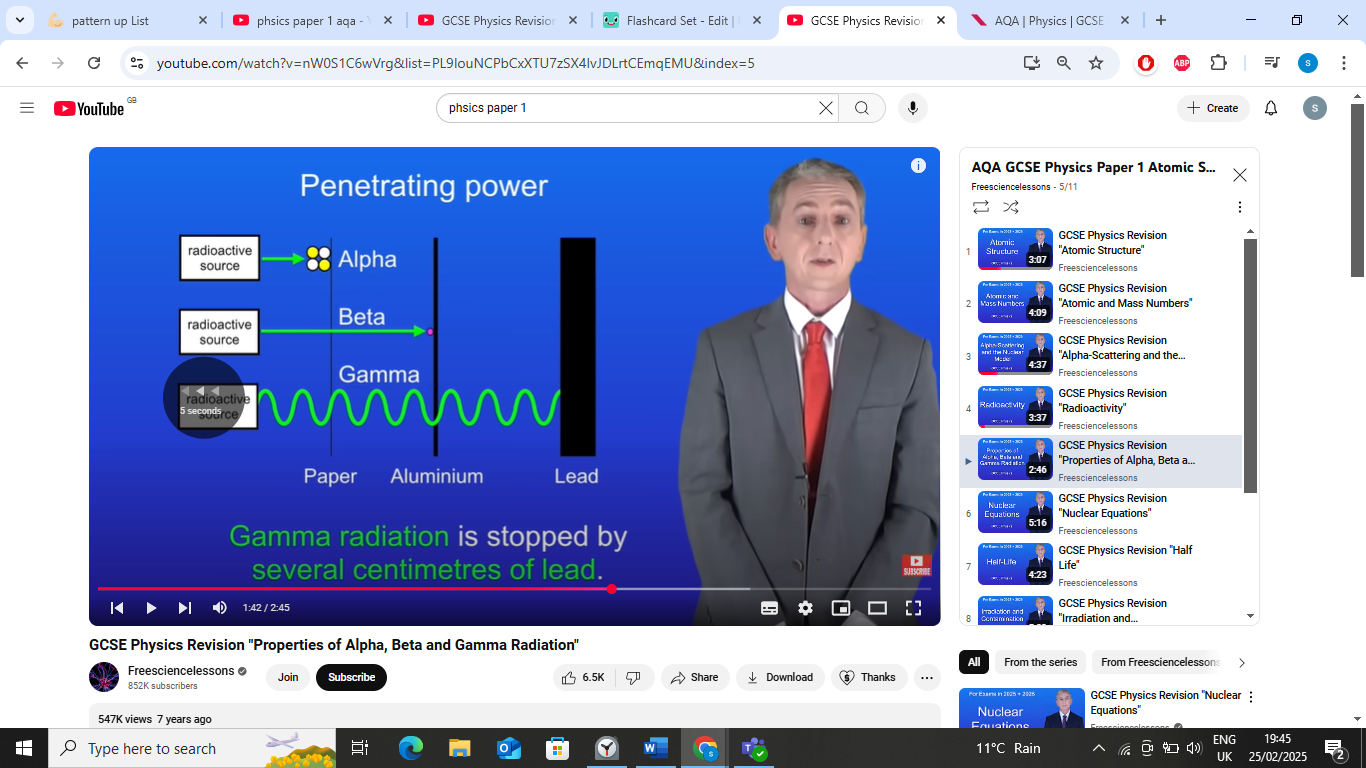
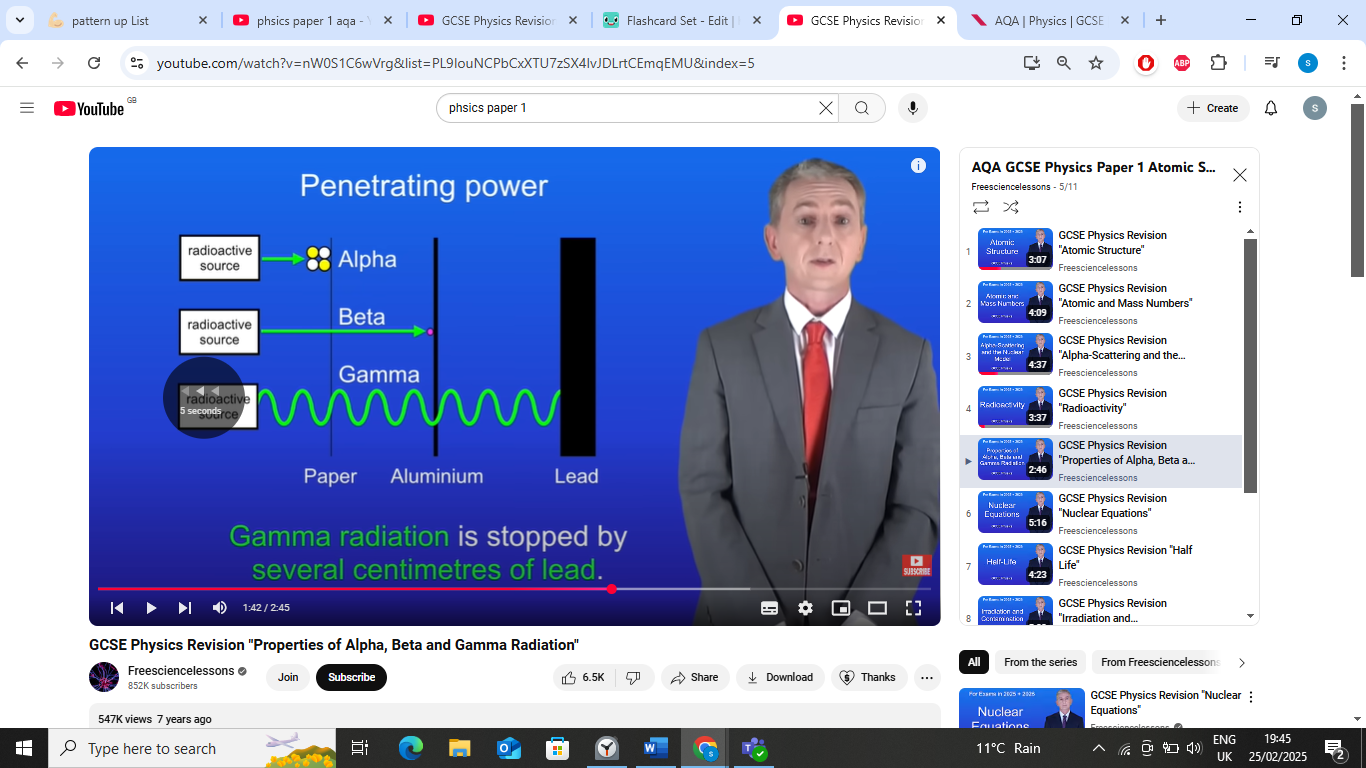
penetrating power- gamma particles
gamma radiation stopped by several cm of lead
when radiation collides with atom
when radiation collides with atoms,it causes the atoms to lose electrons and form ions
ionising power of alpha
alpha particles very strong ionising
ionising power of beta
,beta particles quite strongly ionising,
ionising power of gamma
gamma radiation weakly ionising
what do radiactive isotopes release
radiactive isotopes release radiation from the nucleus of their atoms,
why scientists cant predict when nucleus decays
scientists cant predict when nucleus decays as the decay is a random process
whats half lfie
the half life of a radio active isotope is half the time it takes for the number of nuclei of the isotope in a sample to halve
whats half life in term of count rate
the half life is also time taken for the count rate or activity from a sample containing the isotope to fall to half its initial level
radiactiove isotope has half life of 15 days an inistal count rate of 200 counts pr sec determine the count rate after 45 days
45/15 =3
half 200 3 times
200/2, 100/2,50/2=25
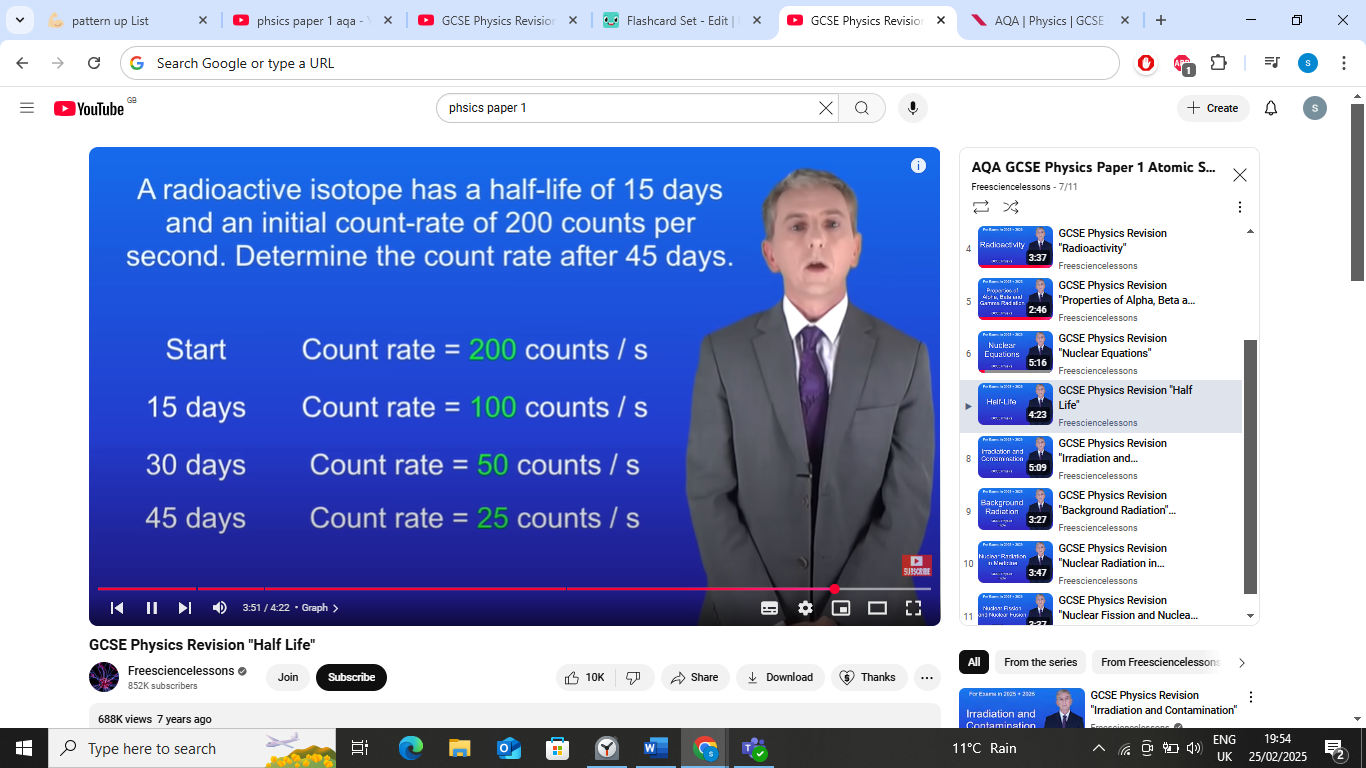
radioactive isotopes do what from their nuclei
radioactive isotopes emit and decay radiation from their nuclei
what does ionising radiation cause
ionising radiation can increase risk of cancer in humans
whats irridation
irraditation is exposing an object to nucler radiation (alpha,beta,gamma,neutrons)
one precautiion to protect against alpha radiation
one precaution is sheilding- gloves can protect against alpha radiation
how can beta and gamma radiation can be reduced
beta and gamma radiation can be reduced by using lead apron
another sheilding
lead walls,lead glass screen protect us from it
radiation monsiter
radiation monitor measures how much radiation received
what do we do if someone received to much radiation
if someone received to much radiation we can stop them from working with raidoactive isotopes
radioactive contamination
radioactive contamination when unwanted radioactive isotopes end up on other materials
why radioactive contamination is hazardous
radioactive contamination is hazardous cuz radioactive atoms decay and emit ionising radiation
how hazardous is alpha radiation
its strongly ionising but easily stopped by dead cells on skin surface,alpha emmiters can be dangerous if inhaled or swallowed
how hazardous is beta radiation
beta radiation is quite ionising so penetrates into the body
how hazardous is gamma radiation
gamma radiation is weakly ionising penetrates the body but likely to pass straight through
whats peer review
scientists explored effects of radiation on humans,they are published and shared with other scientists to alllow findings to be checked
2 natural resourcesof backround radiation
radioactive rock,
cosmic rays from space,
2 manmade resourcesof backround radiation
fall out from nuclear weapons testing,
nuclear accidents
radiactive rock
certain rocks are radiactive like granite cornwall in uk this can be major source of background radiation
cosmic rays
cosmic rays are very high energy particles that travel through space and crash into the earths atmosphere
fall out from nuclear weapons testing,
nuclear weapons testing released radioactive isotopes into the environment for decades
nculear accidents
radioactive isotopes are released by accidents at nuclear power stations
your exposure to background radiation is affected by 2 things
your exposure to background radiation is affected by location and job for e.g
in cornwall they have ltos of granite
airline pilots exposed to high levels of cosmic radiation
dose of radiation measured what
dose of radiation measured in sv
to checkfunction of throid gland,paitent does waht
to checkfunction of throid gland,paitent drinks solution of radioactive iodine
radiaciotve iodine emits what and then
radiaciotve iodine emits gamma radiation and passes out of the body and can be detected
if the scan showsthe thyroid too much or little absorbed iodine what do doctors do
if the scan showsthe thyroid too much or little absorbed iodine ,doctors use this to diognose the paitents condition
1st step of using tracer
tracer must emit radiation that can pass out the body and be detected
2nd step of using tracer
the tracer must not be strongly ionising to minimise damage to body tissue
1st step of using tracer
the tracer must not decay into another radioactive isotope
last step of using tracer
the tracer must have a short half life so its not present in the body for along time
what radiotherapy
certain cancers can be destroyed using ionising radiation this is radiotherapy
how is radiotherapy process
gamma rays pass into the body,destroys the tumour
radiotherapy con
healthy issue may be damaged as radiation passes through the body
e.g of radiactive in the body instead of out: a paitent has radiactive rods inserted in his body to treat prostate cancer advantage.benefit
the radiation targets precisily to the tumour so less damage to healthy tissue
when a uranium nucleus absorbs a neutron it triggers the nuclus to undergo fission(split),
when the nucleus splits it forms 2 smalleer nuclei (daughter nuclei)
it emits 2 or 3 neutrons and gamma radiation,energy released during the fission reaction,all fision products have kinetic energy
neutrons can now be absorbed by more uranium nuclei and trigger fission again which is a chain reaction
a controlled chain reaction is used to release what and whats the explosion in a nuclear weapon is caused by
a controlled chain reaction is used to release energy in a nuclear reactior
,the explosion in a nuclear weapon is caused by an uncontrolled fission chain reaction
whats nuclear fusion
in nucleear fusion 2 light nuclei like hydrogen join to form heavier nucleus some mass of nuclei convert to energy which is released as radiation
what is nuclear fusion not?
nuclear fusion is not a chain reaction but fission is