Genetics: Linkage, Recombination, and Gene Mapping in Eukaryotes (CH7)
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
121 Terms
Principle of segregation
Alleles separate during meiosis.
Independent assortment
Alleles at one locus sort independently from alleles at another locus.
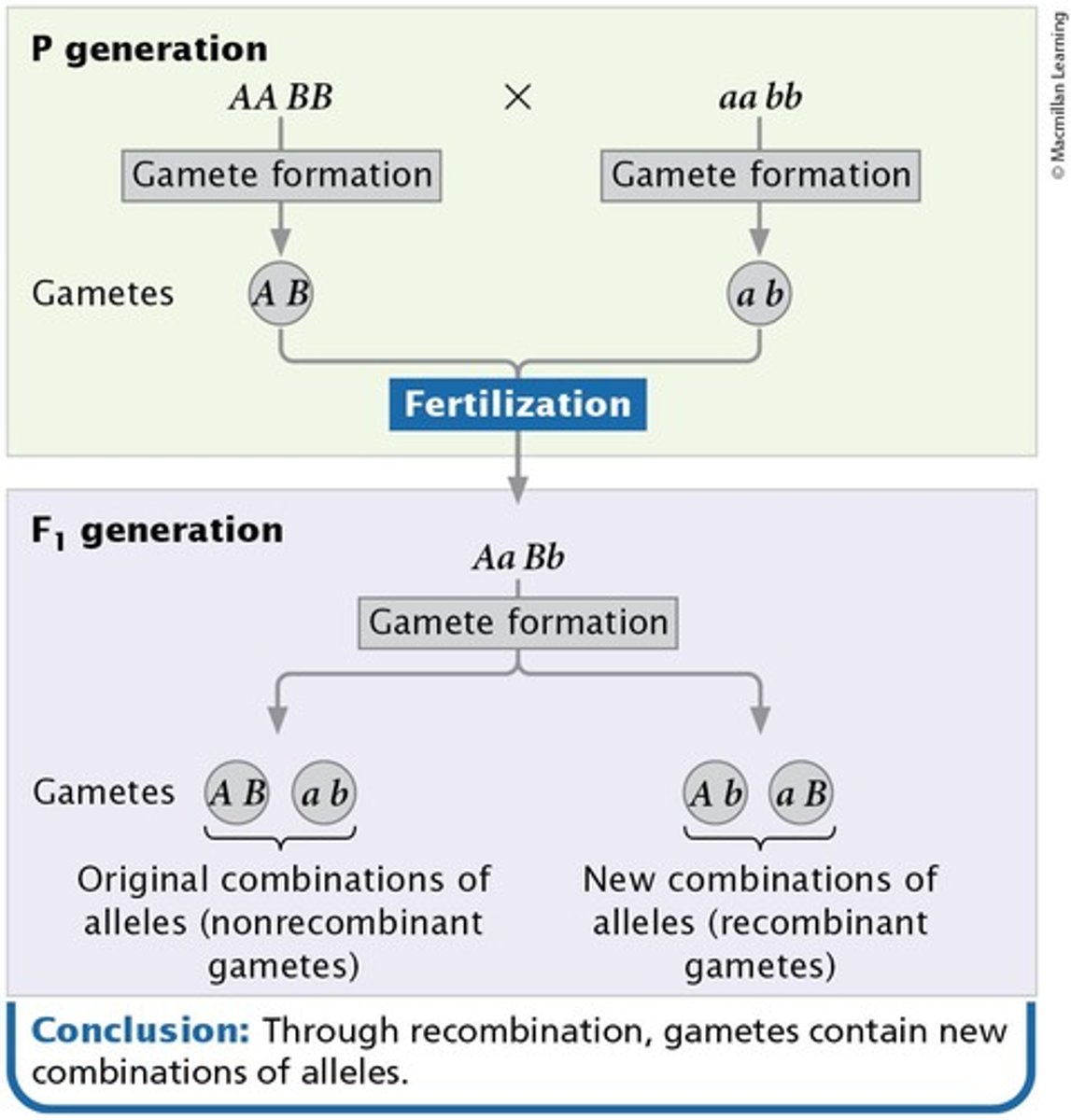
Recombination
Alleles sort into new combinations.
Dihybrid cross
A genetic cross between individuals that differ in two traits.
Expected ratio in dihybrid cross
9:3:3:1 ratio.
Nonindependent assortment
Occurs when two genes are linked.
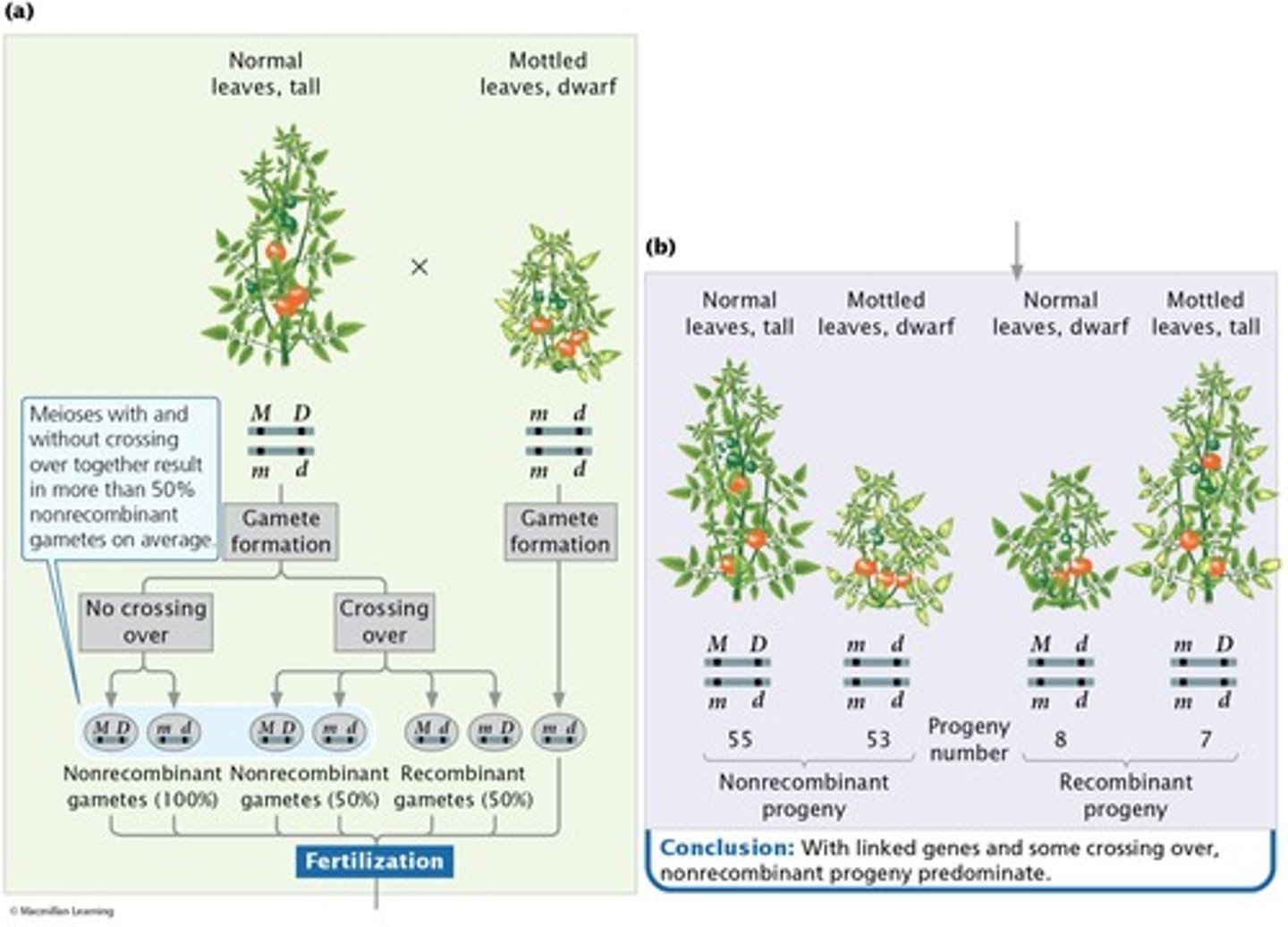
Complete linkage
Leads to nonrecombinant gametes and nonrecombinant progeny.
Crossing over
Leads to recombinant gametes and recombinant progeny.
Recombinant gametes
Gametes that result from crossing over between linked genes.
Testcross
A cross between a homozygote and a heterozygote.
Frequency of recombinant gametes
Is half the frequency of crossing over.
Crossover frequency
Crossover occurs in about 50% of meiosis.
Largest possible recombination frequency
0.5.
Homozygous progeny
Progeny that are homozygous for a trait.
Heterozygous progeny
Progeny that are heterozygous for a trait.
Chromatids
The two identical halves of a replicated chromosome.
Linked genes
Genes that are located close together on the same chromosome and tend to be inherited together.
Mendel's laws
Principles of inheritance that describe how traits are passed from parents to offspring.
Genotype AaBb
The genotype of F1 progeny from a cross between AAbb and aaBB.
Nonrecombinant progeny
Progeny that exhibit the parental combinations of traits.
Progeny phenotypic ratio
1AB:1ab
Progeny phenotypic ratio (if genes A and B are completely linked)
1AB:1Ab:1aB:1ab
Maximum percentage of recombinant gametes (if genes A and B are not linked)
50%
Recombination frequency formula
Recombination frequency = (Number of recombinant progeny/Total number of progeny) × 100%
Coupling configuration
Wild-type alleles are found on one chromosome; mutant alleles are found on the other chromosome.
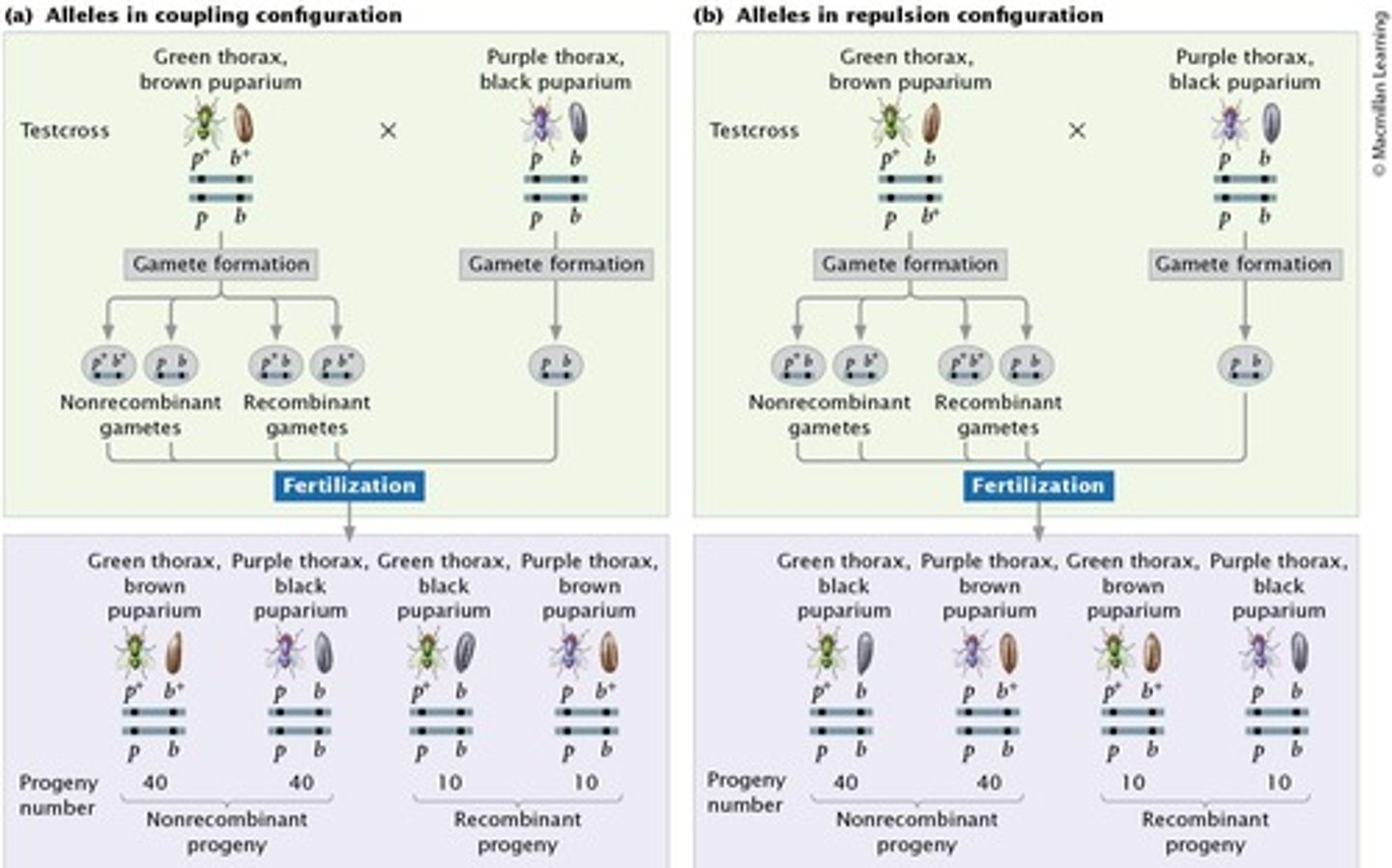
Repulsion configuration
Wild-type allele and mutant allele are found on the same chromosome.
Testcross progeny example
AaBb x aabb 🡪 10 AaBb, 40 aaBb, 40 Aabb, and 10 aabb.
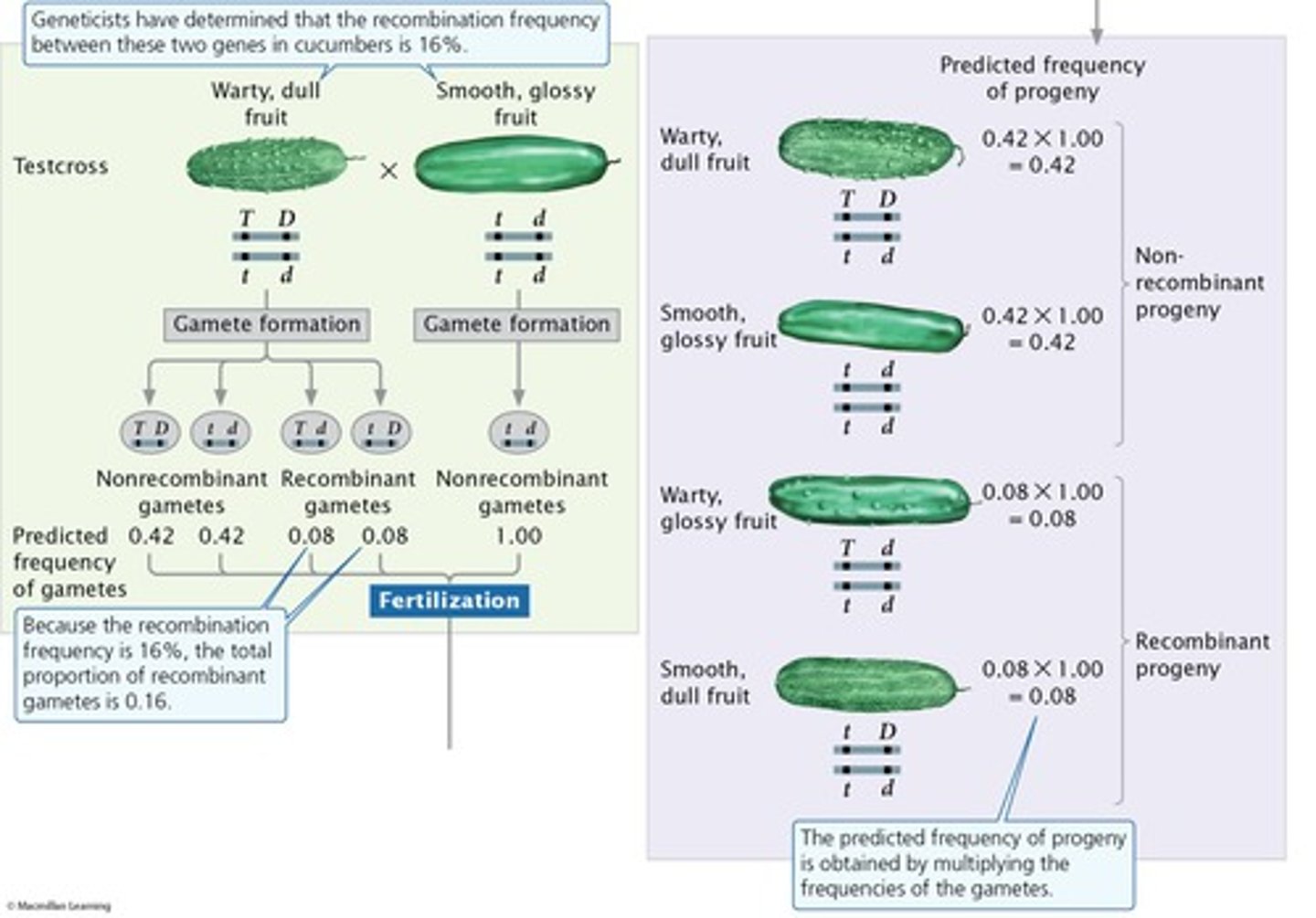
Recombination frequency from progeny numbers
0
Gene order for three linked genes
A B C
Recombination frequency between genes A and B
10.2%
Double-crossover progeny total
4 and 6
Total number of progeny from the cross
1000
Progeny numbers from cross AB/ab×ab/ab
72 AB/ab, 68 ab/ab, 17 Ab/ab, and 21 aB/ab
Maximum percentage of recombinant gametes (if a single crossover occurs)
100%
Progeny phenotypic ratio (if genes A and B are not linked)
9AB:3Ab:3aB:1ab
Walter Sutton's chromosome theory of inheritance
Genes are physically located on chromosomes.
Nettie Stevens and Edmund Wilson's research
Sex was associated with a specific chromosome in insects.
Calvin Bridges's research
Nondisjunction of X chromosomes was related to the inheritance of eye color in Drosophila.
Harriet Creighton and Barbara McClintock's contribution
Intrachromosomal recombination was the result of physical exchange between chromosomes.
Evidence for genes on chromosomes
Barbara McClintock and Harriet Creighton provided evidence that genes are located on chromosomes.
Organism studied by McClintock and Creighton
Corn.
Supported theory by McClintock and Creighton
Chromosomal theory of inheritance.
Gene mapping with recombination frequencies
Genetics maps determined by recombinant frequency.
Map unit
CentiMorgans.
Genetic map vs physical map
Genetic maps are based on rates of recombination; physical maps are based on physical distances.
Most likely order of linked genes R, S, and T
S T R.
Requirement for topoisomerase II in crossing over
Supports the theory that crossing over is due to stress.
Testing for Independent Assortment
McClintock and Creighton provided evidence that genes are located on chromosomes.
Distance between R and S
22 m.u.
Distance between S and T
8 m.u.
Distance between R and T
14 m.u.
Concept Check 3
How does a genetic map differ from a physical map?
Answer to Concept Check 3
Genetic maps are based on rates of recombination. Physical maps are based on physical distances.
Recombination frequency
The percentage of offspring that exhibit a recombinant phenotype due to crossing over during meiosis.
Two-Point Testcross
A genetic mapping method used to determine the distance between two linked genes based on recombination frequency.
Three-Point Testcross
A more efficient mapping technique that allows for the determination of the order of three linked genes in a single set of progeny.
Double crossover progeny
Offspring resulting from two crossover events between linked genes, leading to a combination of alleles different from the parental types.
Gene order determination
The process of establishing the sequence of genes on a chromosome based on crossover data from progeny.
Middle locus
The gene that is located between two other genes in a three-point testcross.
Crossover progeny
Offspring that result from the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during meiosis.
Single crossover
A crossover event that occurs between two loci on the same chromosome, resulting in recombinant offspring.
Concept Check 4
An exercise to write the genotypes of all recombinant and nonrecombinant progeny expected from a three-point cross.
Concept Check 5
An exercise to identify the middle locus in a three-point testcross based on the genotypes of progeny.
Progeny genotype
The genetic constitution of the offspring resulting from a cross, which can be recombinant or nonrecombinant.
Steps in determining gene order
A systematic approach to establish the sequence of genes in a three-point cross.
Mapping distances
The measurement of the distance between genes on a chromosome, often expressed in centimorgans (cM) based on recombination frequency.
Recombinant phenotype
A phenotype that arises from the combination of alleles that differ from those of the parental generation due to recombination.
Figure 7.13
A diagram illustrating the process of determining gene order in a three-point testcross.
Figure 7.14
A diagram showing the location of crossovers in a three-point testcross.
A, B, C loci
The specific locations of genes being studied in a three-point testcross.
All classes of progeny
Refers to considering nonrecombinant, single-crossover, and double-crossover progeny when determining gene order.
nonrecombinant
Progeny that do not show recombination of alleles.
single-crossover
A type of genetic recombination where two chromatids exchange segments at one location.
double-crossover
A type of genetic recombination where two separate exchanges occur between chromatids.
coefficient of coincidence
The ratio of the number of observed double crossovers to the number of expected double crossovers.
interference
The phenomenon where the occurrence of one crossover event affects the likelihood of another crossover event occurring nearby.
negative interference
Indicates that more double crossovers took place than expected based on single-crossover frequencies.
positive interference
Indicates that fewer double crossovers took place than expected based on single-crossover frequencies.
mathematical mapping functions
Functions that relate recombination frequencies to actual physical distances between genes.
Poisson distribution
A statistical distribution that predicts the probability of multiple rare events.
mapping human genes
The process of determining the locations of genes on human chromosomes.
expected double crossovers
The predicted number of double crossover events based on recombination frequencies.
observed double crossovers
The actual number of double crossover events recorded in a genetic experiment.
crossover
The exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during meiosis.
locus
The specific physical location of a gene on a chromosome.
gene order
The arrangement of genes on a chromosome, which can be determined through testcrosses.
effects of multiple crossovers
The impact that multiple crossover events have on the genetic mapping and recombination frequency.
crossovers
Events during meiosis where homologous chromosomes exchange segments.
total progeny
The total number of offspring produced in a genetic cross.
recombination rates
The frequency at which recombination occurs between genes.
Mapping with molecular markers
A technique used to identify specific locations of genes on chromosomes.
RFLPs
Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms, a method used in genetic mapping.
Genomewide association studies
Studies that look for associations between genetic variants and traits across the genome.
Haplotype
A combination of alleles at multiple loci that are transmitted together.
Linkage disequilibrium
The non-random association of alleles at different loci.
Somatic-cell hybridization
A method used to determine which chromosome contains a gene of interest.
Deletion mapping
A technique that reveals the chromosomal locations of genes by observing deletions.
Physical mapping through molecular analysis
Determining the physical locations of genes on chromosomes using molecular techniques.
In situ hybridization
A technique used to locate specific DNA sequences within a chromosome.
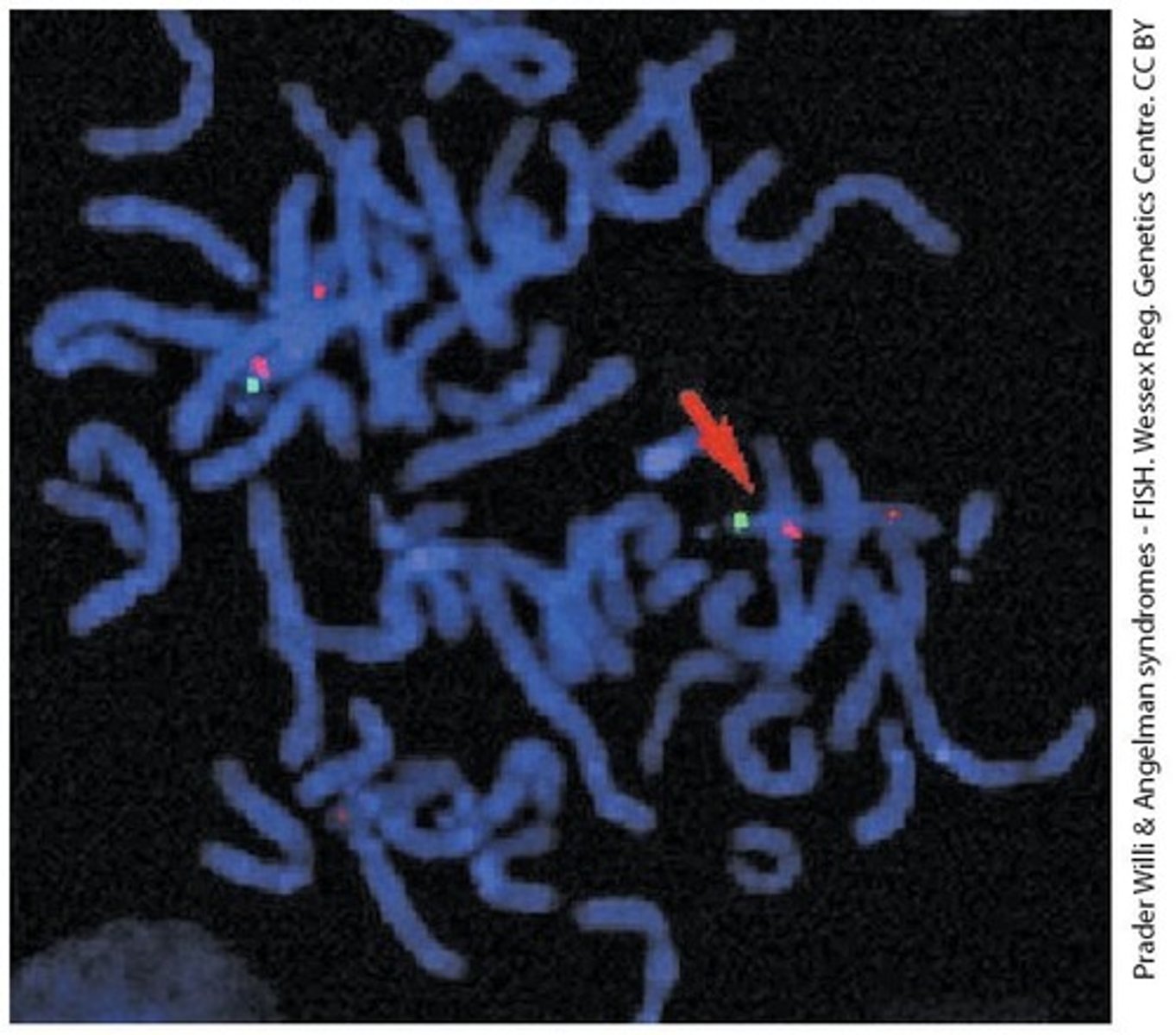
Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH)
A method that uses a single-stranded complementary DNA probe to identify specific DNA sequences.