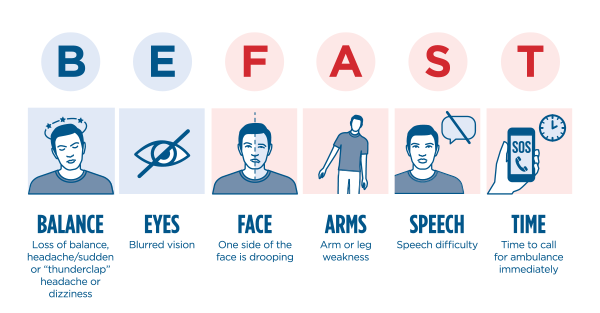
Neuropathology
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:36 PM on 10/31/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
1
New cards
What is Dementia?
Is not a specific disease, but is progressive and is worse with time. It is not a normal aging progress and occurs in older people. Loss of cognitive functioning occurs.
2
New cards
What causes Dementia?
- Neuron degeneration ➡️ neurons die, oxidative stress causes damage from ROS waste on neuroglia
- Atherosclerosis ➡️ decrease in blood flow ➡️ ischemia ➡️ hypoxia ➡️ infarction
- Brain tissue compression ➡️ CHRONIC, epidural or subdural hematoma or a tumor
- Brain trauma ➡️ repeated blows to the head (boxers, football players)
- Genetic predisposition ➡️ linked to genetic abnormality, NOT FAMILIAL
- Atherosclerosis ➡️ decrease in blood flow ➡️ ischemia ➡️ hypoxia ➡️ infarction
- Brain tissue compression ➡️ CHRONIC, epidural or subdural hematoma or a tumor
- Brain trauma ➡️ repeated blows to the head (boxers, football players)
- Genetic predisposition ➡️ linked to genetic abnormality, NOT FAMILIAL
3
New cards
What is Alzheimers Disease?
A progressive neurological disorder effecting memory, thinking skills, the inability to carry out simplest tasks.
4
New cards
Alzheimers is the most common what?
Most common type of dementia
➡️ (Alzheimers Dementia)
➡️ (Alzheimers Dementia)
5
New cards
Late Onset Alzheimers
- 95% common
- Not genetic or linked to any gene
- Sporadic = most common
- Alteration of apolipoprotien E ➡️ high cholesterol increases risk for Alz.
- Not genetic or linked to any gene
- Sporadic = most common
- Alteration of apolipoprotien E ➡️ high cholesterol increases risk for Alz.
6
New cards
Early Onset Alzheimers
- FAMILIAL
- 5% rare
- Diagnosed in early 30-40s
- Caused by Trisomy 21/Down Syndrome
- 5% rare
- Diagnosed in early 30-40s
- Caused by Trisomy 21/Down Syndrome
7
New cards
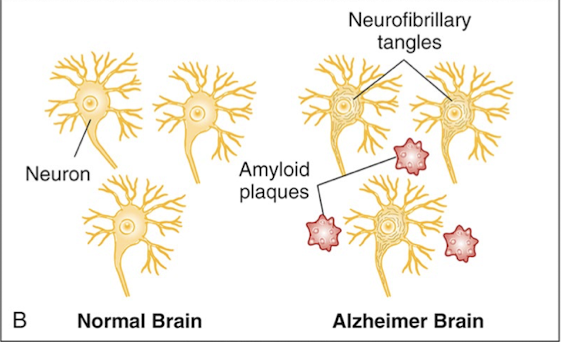
Cause of Alzheimers
- Extracellular deposition of β-amyloid (Senile neuritic plaques)
- Intracellular accumulation of tau protein (Neurofibrillary tangles)
- Intracellular accumulation of tau protein (Neurofibrillary tangles)
8
New cards
Alzheimers S&S
- Extends 10-20 years
- Behavioral changes
- Forgetfulness ➡️ progressive memory loss
⭐️Telltale sign: Patients forgetting to pay their bills, or forgetting their everyday routine tasks
- Behavioral changes
- Forgetfulness ➡️ progressive memory loss
⭐️Telltale sign: Patients forgetting to pay their bills, or forgetting their everyday routine tasks
9
New cards
Alzheimers Diagnostics
No definite clinical diagnostic tests, only based on a series of questions and if the patient meets the criteria
10
New cards
Alzheimers Treatment
- No specific treatment
- Anticholinesterase drugs
- Aducanumab
- Team approach
- Anticholinesterase drugs
- Aducanumab
- Team approach
11
New cards
What is Parkinson's Disease?
Progressive, neurodegenerative disease of the melanin-containing dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra, pars compacta
⭐️Severe degeneration of the basal ganglia
- Caused in older patients 50-60s
⭐️Severe degeneration of the basal ganglia
- Caused in older patients 50-60s
12
New cards
Primary Parkinsons
⭐️ Idiopathic: no idea what causes it
- Majority of the population diagnosed with this type
- Majority of the population diagnosed with this type
13
New cards
Secondary Parkinsons
Caused by something else
Ex: Environmental factors, anti-psychotics, pseudo-parkinsonism
Ex: Environmental factors, anti-psychotics, pseudo-parkinsonism
14
New cards
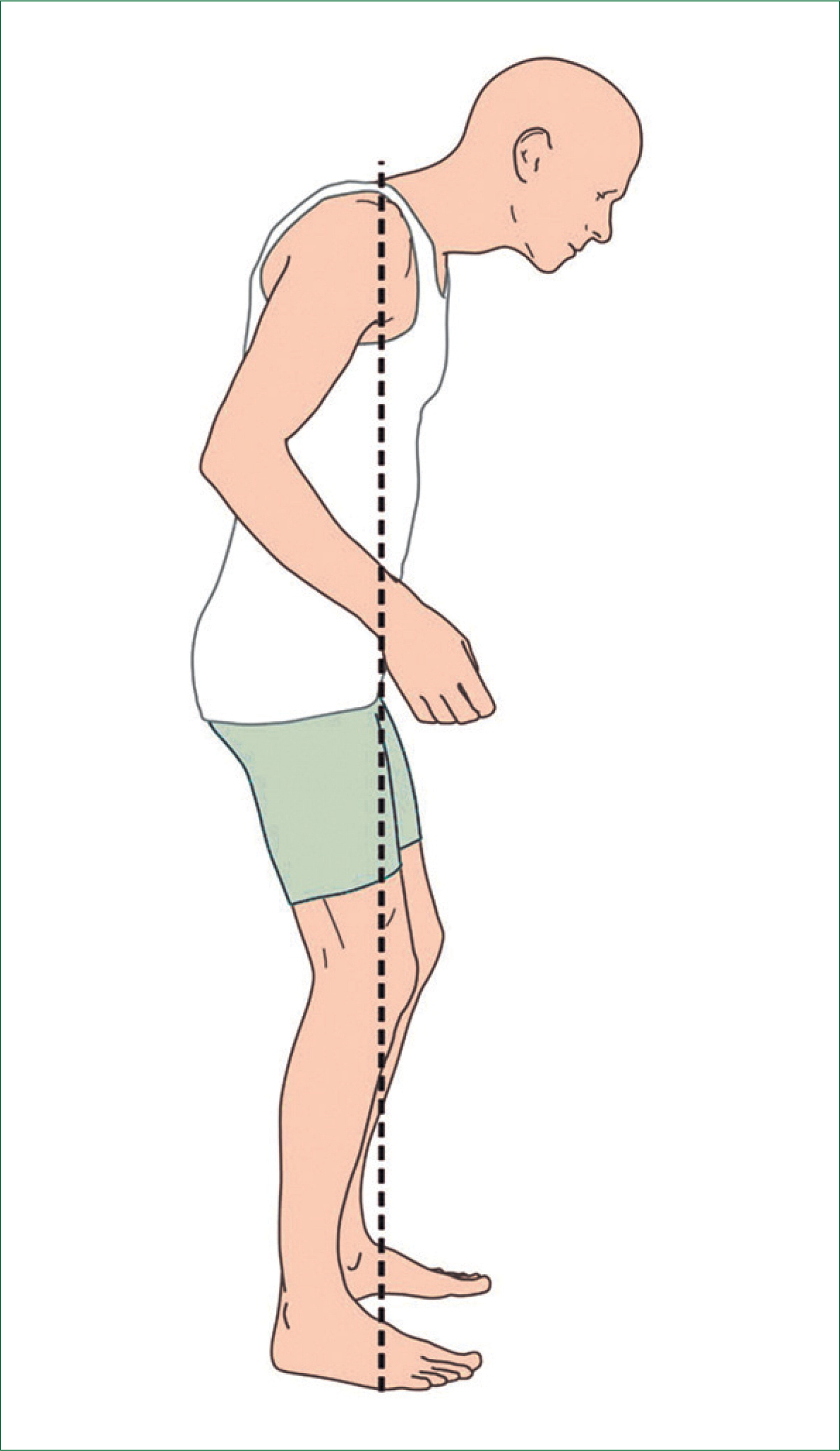
Parkinsons S&S
⭐️ RESTING TREMOR
- Stooped posture & rigidity
- Pill rolling tremor
- Cockwheel rigidity (slow wind up and rapid action)
- Masked facies (the face is frozen)
- Short shuffling steps
⭐️ In early stages of parkinsons, patients will often hide their resting tremor in their hands
- Stooped posture & rigidity
- Pill rolling tremor
- Cockwheel rigidity (slow wind up and rapid action)
- Masked facies (the face is frozen)
- Short shuffling steps
⭐️ In early stages of parkinsons, patients will often hide their resting tremor in their hands
15
New cards
Parkinsons Diagnosis
No diagnostic tests, based on S&S
16
New cards
Parkinsons Treatment
💊 Dopamine agonist (Levodopa)
💊 MAOB inhibitor
💊 Anticholinerdic drugs
💊 Amantadine
⭐️ Team approach
💊 MAOB inhibitor
💊 Anticholinerdic drugs
💊 Amantadine
⭐️ Team approach
17
New cards
What is Huntingtons Disease?
Progressively debilitating neurodegenerative inherited disease
⭐️Autosomal dominant disorder, caused by 1 bad gene, chromosome 4
- Does not manifest until the 30-40s (younger)
⚠️ Progressive atrophy of the brain
⭐️Autosomal dominant disorder, caused by 1 bad gene, chromosome 4
- Does not manifest until the 30-40s (younger)
⚠️ Progressive atrophy of the brain
18
New cards
Pathophysiology of Huntingtons
- Hyperkinetic disorder
- Involves the basal ganglia & frontal cortex
- Depletion of GABA in the basal nuclei
- Levels of ACH in brain appear reduced
- Involves the basal ganglia & frontal cortex
- Depletion of GABA in the basal nuclei
- Levels of ACH in brain appear reduced
19
New cards
Huntingtons S&S
- Mood swings
- Restlessness
- Choreiform movements
- Restlessness
- Choreiform movements
20
New cards
Huntington diagnostics?
- DNA analysis
⭐️ A familial genetic abnormality, and can be tested for
⭐️ A familial genetic abnormality, and can be tested for
21
New cards
Huntington treatment?
⚠️ NO SPECIFIC TREATMENT
- Symptomatic therapies only
- Symptomatic therapies only
22
New cards
Huntington's mortality rate caused by?
Most patients don't die from the neurologic disease:
- Infections
- Heart disease
⚠️ Suicide: the more common cause, only a 5 year life expectancy given when diagnosed
- Infections
- Heart disease
⚠️ Suicide: the more common cause, only a 5 year life expectancy given when diagnosed
23
New cards
What is Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)?
Rapidly progressive & fatal neurodegenerative disease of the upper and lower motor neurons
⭐️Aka "Lou Gehrigs disease"
⭐️Aka "Lou Gehrigs disease"
24
New cards
Pathophysiology of ALS?
⚠️ NOT CLEAR
- SOD1 gene mutation
- Damage to glutamate uptake channels in astrocytes
- Military vets (specifically Gulf War veterans) at risk (not sure why!!)
- Athletes, repeated trauma increases risk
⭐️Cognition & sensory is UNIMPAIRED
⚠️Death due to respiratory failure
- SOD1 gene mutation
- Damage to glutamate uptake channels in astrocytes
- Military vets (specifically Gulf War veterans) at risk (not sure why!!)
- Athletes, repeated trauma increases risk
⭐️Cognition & sensory is UNIMPAIRED
⚠️Death due to respiratory failure
25
New cards
ALS treatment?
⚠️ No specific treatment
- Stem cell therapy under investigation
💊 Riluzole (Rilutek) slows further damage to neurons
💊 Edavarone lowers the toxic environment and scavenges for free radicals
⭐️ Team approach
⚠️Like Parkinsons, patients decline very rapidly
- Stem cell therapy under investigation
💊 Riluzole (Rilutek) slows further damage to neurons
💊 Edavarone lowers the toxic environment and scavenges for free radicals
⭐️ Team approach
⚠️Like Parkinsons, patients decline very rapidly
26
New cards
Hemorrhage
Increased intracranial pressure (ICP) will cause local ischemia and generalized symptoms; blood compresses the brain
27
New cards
Arteriovenous malformation
When artery and a vein connects, high O2 blood in arteries are mixed with low O2 veins
28
New cards
Transient Ischemic Attacks (TIAs)
Transient episode of neurologic dysfunction caused by focal brain, spinal cord or retinal ischemia without acute infarction
⭐️ Decrease in blood flow, NO neuronal cell death
- REVERSIBLE
- Most commonly caused by atherosclerosis
♀ Women are protected by estrogen until menopause
⭐️ Decrease in blood flow, NO neuronal cell death
- REVERSIBLE
- Most commonly caused by atherosclerosis
♀ Women are protected by estrogen until menopause
29
New cards
TIA S&S
⚠️ IS A WARNING SIGN, can lead to a stroke if not treated
- Are difficult to diagnose after the attack, directly related to the location of ischemia
- Visual disturbances
- Numbness & paresthesia
- Transient aphasia or confusion
- Are difficult to diagnose after the attack, directly related to the location of ischemia
- Visual disturbances
- Numbness & paresthesia
- Transient aphasia or confusion
30
New cards
TIA Diagnostics
- MRI (preferred) or a CT
- Carotid doppler
- Angiography
- Carotid doppler
- Angiography
31
New cards
TIA Management
- DECREASE RISKS
- Initiate in stroke prevention therapy
- Initiate in stroke prevention therapy
32
New cards
Cerebrovascular Accidents (CVAs)
A CVA (stroke) is an infarction of brain tissue that results from a lack of blood
- There are 2 types:
- Ischemic: occlusion of a cerebral blood vessel
- Hemorrhagic: rupture of cerebral vessel
⚠️ 5 minutes of ischemia → irreversible neuronal damage
- There are 2 types:
- Ischemic: occlusion of a cerebral blood vessel
- Hemorrhagic: rupture of cerebral vessel
⚠️ 5 minutes of ischemia → irreversible neuronal damage
33
New cards
CVA Risk Factors?
- African Americans at higher risk
- 5th COD in the US
- Leading cause of disability
- 5th COD in the US
- Leading cause of disability
34
New cards
Thrombus CVA
→ Atherosclerosis in cerebral artery
→ Onset is gradual may be preceded by TIAs; occurs at rest
→ Localized, less permanent damage
→ Minimal ICP
→ Onset is gradual may be preceded by TIAs; occurs at rest
→ Localized, less permanent damage
→ Minimal ICP
35
New cards
Embolus CVA
→ Atherosclerosis of carotid artery of systemic source (heart)
→ Onset is sudden ⚠️
→ Minimal ICP
→ Localized unless multiple emboli present
→ Onset is sudden ⚠️
→ Minimal ICP
→ Localized unless multiple emboli present
36
New cards
Hemorrhage CVA
→ Hypertension, arteriosclerosis (poorly controlled hypertension)
→ Onset is sudden, occurs with activity ⚠️
→ High ICP
→ Widespread and severe, and often fatal (subarachnoid is most fatal)
→ Onset is sudden, occurs with activity ⚠️
→ High ICP
→ Widespread and severe, and often fatal (subarachnoid is most fatal)
37
New cards
CVA S&S
- Depends on location of obstruction and also the size of the artery involved
- Abrupt onset of hemiparesis, hemisensory deficits
- 👀 Loss of vision in one or both eyes, double vision
- Nystagmus
- Dysarthia
- Facial droop
- Ataxia
- Vertigo (rarely in isolation)
- Aphasia
- Headaches (HEMORRHAGIC ONLY)
- Sudden decrease in level of consciousness (Hemorrhagic can cause as well)
- Abrupt onset of hemiparesis, hemisensory deficits
- 👀 Loss of vision in one or both eyes, double vision
- Nystagmus
- Dysarthia
- Facial droop
- Ataxia
- Vertigo (rarely in isolation)
- Aphasia
- Headaches (HEMORRHAGIC ONLY)
- Sudden decrease in level of consciousness (Hemorrhagic can cause as well)
38
New cards
NIHSS
NIH Stroke Scale
- Assists with rapid diagnosis
- Predicts size and severity
- Predict short and long term outcomes
- Assists with rapid diagnosis
- Predicts size and severity
- Predict short and long term outcomes
39
New cards
Treatment of CVAs
💊 Fibrinolytic tPA
💊 Antiplatelet: aspirin
💊 Glucocorticoids
💊 Blood pressure control
- Mechanical thrombectomy
- Supportive treatment
❗️TREAT UNDERLYING PROBLEMS TO PREVENT RECURRENCES
💊 Antiplatelet: aspirin
💊 Glucocorticoids
💊 Blood pressure control
- Mechanical thrombectomy
- Supportive treatment
❗️TREAT UNDERLYING PROBLEMS TO PREVENT RECURRENCES
40
New cards
Prevention of CVAs
💊 Aspirin
- Healthier diet, reduced hyperlipidemia
💊 Antihypertensive
- Control diabetes type 2
- 🚭 STOP SMOKING!!
- Exercise
- Lifestyle changes
- Healthier diet, reduced hyperlipidemia
💊 Antihypertensive
- Control diabetes type 2
- 🚭 STOP SMOKING!!
- Exercise
- Lifestyle changes
41
New cards
Meningitis
Bacterial, viral or fungal infection of the meninges of the brain
Bacterial: more fatal
Viral (aseptic): more common
Fungal: happens in immunocompromised patients
Bacterial: more fatal
Viral (aseptic): more common
Fungal: happens in immunocompromised patients
42
New cards
Meningitis S&S
- High fever with chills
- Stiff neck
- Headache
- Confusion & sleepiness
- Vomiting (from pain)
- Dislike/pain from bright lights
⚠️ Sometimes red or purple spots or bruises on the skin: OMINOUS SIGN OF DIC
- Stiff neck
- Headache
- Confusion & sleepiness
- Vomiting (from pain)
- Dislike/pain from bright lights
⚠️ Sometimes red or purple spots or bruises on the skin: OMINOUS SIGN OF DIC
43
New cards
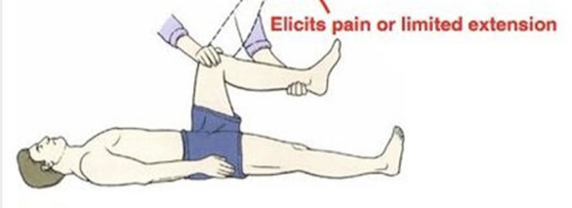
Kernig Sign
Extension of the knee is painful or limited in extension
44
New cards
Brudzinski Sign
Passive flexion of neck, causes a hip & knee flexes
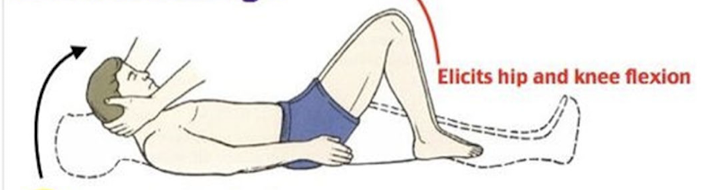
45
New cards
Pathophysiology of Meningitis
- Hematogenous: by blood
- Direct contiguous spread (ex: sinusitis)
🦠 Organisms:
- Neisseria meningiditis (gram -)
- Streptococcus pneumonia (gram +)
- Direct contiguous spread (ex: sinusitis)
🦠 Organisms:
- Neisseria meningiditis (gram -)
- Streptococcus pneumonia (gram +)
46
New cards
Meningitis diagnostics
- Lumbar puncture/spinal tap
⭐️ Culture before you treat, high morbidity rate
⭐️ Culture before you treat, high morbidity rate
47
New cards
Bacterial spinal tap
- increased PMNs & neutrophils
- decreased glucose (bacteria eats)
- decreased glucose (bacteria eats)
48
New cards
Viral spinal tap
- increased lymphocytes
- normal glucose
- normal glucose
49
New cards
Fungal/TB spinal tap
- increased lymphocytes
- decreased glucose
- decreased glucose
50
New cards
Meningitis treatment?
- Rapid diagnosis and Tx essential to prevent morbidity and mortality
- Aggressive antimicrobial therapy
💊 Glucocorticoids
💉 Vaccines are available
- Aggressive antimicrobial therapy
💊 Glucocorticoids
💉 Vaccines are available
51
New cards
What is Multiple Sclerosis?
Progressive, inflammatory, demyelinating disease of the central nervous system
⚠️ AUTOIMMUNE
⚠️ Impacts
- Impacts women more than men
- Appears 20-40 years of age; 40 years is the limit, but has been seen developing in older people
- Over time, neural degeneration becomes irreversible; function is lost
⚠️ AUTOIMMUNE
⚠️ Impacts
- Impacts women more than men
- Appears 20-40 years of age; 40 years is the limit, but has been seen developing in older people
- Over time, neural degeneration becomes irreversible; function is lost
52
New cards
Multiple Sclerosis Pathophysiology
Inflammation ➡️ Destruction of myelin sheath ➡️ Demyelination ➡️ Scar formation ➡️ Plaque formation
- Targets oligodendrocytes in the CNS
- Targets oligodendrocytes in the CNS
53
New cards
Multiple Sclerosis S&S
- Paresthesia
- Weakness
- Blurred vision
- Double vision
- Urinary incontinence
- Loss of coordination
- Dysarthia
- Weakness
- Blurred vision
- Double vision
- Urinary incontinence
- Loss of coordination
- Dysarthia
54
New cards
Multiple Sclerosis Diagnostics
MRI for diagnosis & monitoring; can see the plaque on the brain and determine the severity
55
New cards
Multiple Sclerosis Treatment
- No definitive treatment; not a one size fits all treatment
- Tx is tailored to the patient, what works for one might not work for another
- Tx is tailored to the patient, what works for one might not work for another