BISC 4165 - Microbio Lab FINAL (Week 8-13)
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
What does “PCR” stand for?
polymerase chain reaction
What is the purpose of PCR?
Create millions of copies of specific DNA sequences
cheap and easy way to amplify a DNA sequence of interest (often to diagnose disease)
What does homology mean?
similarity between DNA sequences, specifically the presence of shared or conserved regions » recombination can occur
What is GenBank?
a genetic sequence database from the national institute of health (NIH)
What is a BLAST search?
Basic Local Alignment Search Tool is used to compare a DNA or protein sequence against a database of sequences to find regions of similarity and identify potential homologs or related sequences
Draw a diagram of a positive reaction in an ELISA test that you expect for an ELISA assay to detect patient antibodies.
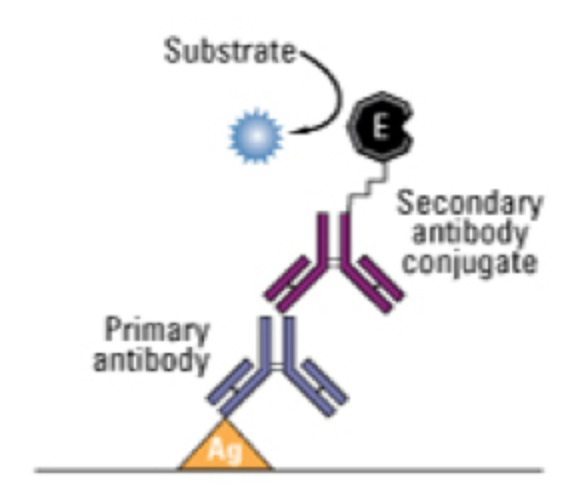
What is the function of the secondary antibody and chromogen in an ELISA?
The secondary antibody binds to the first body. It is conjugated with a chromogenic enzyme, which is what elicits a color change during the ELISA assay.
What might cause some positive results to be lighter color than others?
Lighter color = less antigen in sample
Why do you need to wash the wells between each step during the ELISA?
Washing the wells removes unbound antibodies
ELISA testing is most commonly used tool to diagnose ___ infections
HIV
ELISA can give a false negative if a patient is recently infected. How can a patient with HIV be infected but still give a negative result in an ELISA?
There have not been enough antibodies produced against the HIV, so it cannot be detected by ELISA.
What interactions occur to cause the visible agglutination in the BD BBL Staphyloslide Latex Test (rapid staph test)
Latex particles coated with human fibrinogen and IgG will bind to any staph containing bound coagulase or protein A. This will result in visible clumping or agglutination.
What is coagulase?
Coagulase is a clumping factor that converts fibrinogen to fibrin
What test is used to detect coagulase?
Coagulase test - Bacteria is incubated in liquid plasma treated with anticoagulant at 37 degrees C. If clotting occurs, the sample is coagulase positive. This can also be done on a slide
How is the catalase test performed?
The bacteria is exposed to hydrogen peroxide. If bubbles form (molecular oxygen), it indicated that catalase is present. Catalase breaks down hydrogen peroxide into oxygen.
Identify 3 ways you can distinguish between staph and strep species in lab
Staphylococcus:
1. Resistant to penicillin
2. Catalase (+)
3. Can grow on high salt media (halotolerant)
Streptococcus:
1. Sensitive to penicillin
2. Catalase (-)
3. Inhibited on high salt media
Identify 2 ways you can distinguish staph. aureus and staph epidermis in lab
S. aureus
1. ferments mannitol (yellow/gold)
2. Coagulase (+)
S. epi
1. does not ferment mannitol (red)
2. Coagulase (-)
Describe beta hemolytic bacterial colonies on blood agar.
complete lysis of red blood cells » clear zone around colonies
Describe alpha hemolytic bacterial colonies on blood agar.
green or brown pigmented halos
Describe gamma hemolytic bacterial colonies on blood agar.
no change to agar or colony
Describe lysis of alpha hemolysis.
partial lysis
Describe lysis of beta hemolysis.
complete lysis
Describe lysis of gamma hemolysis.
no lysis of RBC
What type of hemolysis is produced by S. Pyogenes?
beta hemolysis
What type of hemolysis is produced by S. Pneumoniae?
alpha hemolysis
What type of hemolysis is produced by Viridans Streptococci?
gamma hemolysis
Why is it not advisable to open the blood agar plates of oral cultures for extended time periods around other students?
Some bacteria cause opportunistic infections.
Some individuals have bacteria that are part of their normal microbiota that others don't have.
Describe the principles the rapid strep test is based on
Allows for a quick diagnosis of S. pyogenes (Group A Strep). Uses a sandwich immunoassay to detects group A Strep antigens. The test strip is coated with antibodies, which will bind the antigens. Then, a second antibody conjugated with chromogen is bound.
Your patient has a positive throat culture for group A strep but negative rapid group A strep rapid test. What could have caused these discrepant results?
Improper sample collection or storage
Low antigen concentration
Which test is quicker: culturing strep on BAP or an immunoassay?
Immunoassay
What type of assay is the QuickVue Flu test?
Lateral flow immunoassay
Which types of influenza virus does the QuickVue flu test detect?
Type A and B
Organisms that secrete the enzyme urease can change the pH of the environment. Will this increase or decrease pH?
Urease breaks down urea into ammonia and carbon dioxide, which increases pH (more basic).
It creates an alkaline environment.
Interpret a TSI test with an acid butt (yellow), alkaline slant (red)
glucose fermented
Interpret a TSI test with an acid throughout medium, butt and slant (yellow)
glucose and lactose or sucrose fermented
Interpret a TSI test with gas bubble in butt, medium is cracked
H2 and CO2 are produced
Interpret a TSI test with an a blackening of butt
hydrogen sulfide produced
Interpret a TSI test with an alkaline slant and butt (red)
none of the 3 sugars fermented
Interpret a motility test for motile bacteria
bacteria spread out from the stab line, making the whole medium turbid/cloudy
Interpret a motility test for nonmotile bacteria
bacteria only grow along stab line where needle was inserted, rest of medium stays clear
Why is it essential to have pure cultures for biochemical tests?
Contamination can cause different results that do not reflect the bacteria being tested, which can result in inaccurate results.
How are conditions different between the slant and butt areas of some of the tests?
The slant is an aerobic medium
Butt is an anaerobic medium
What are the advantages of Enterotube II?
It contains many media chambers, so it can test for multiple suspected pathogens at once.
1 inoculation = 15 test results in a single day (18-24 hrs)
Describe two methods for creating an anaerobic environment to culture anaerobic bacteria
1. Fluid thioglycollate broth: a reducing medium of sodium thioglycolate that reacts with oxygen to keep free oxygen low.
Redox potential » high oxygen at top of tube, absence of oxygen at bottom of tube. Organisms will only grow where their oxygen requirements are met in the broth, allowing distinction
2. GasPak jar: inoculated agar plates sealed in the jar. Sachet containing chemicals that binds free oxygen is placed in the jar making it anaerobic
Identify and describe 3 features of clinical anaerobic infections
endogenous » part of our indigenous microbiota
non-transmissible » most (not all) are not contagious from human to human
polymicrobic » mixed infection with other anaerobic species/facultative anaerobes
slow growth and fastidious in nature