SCIENCE STUDY GUIDE
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:05 AM on 4/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
1
New cards
Chemical Property
When a substance change into another substance but the process isn’t reversible (Flamibility, Change in color, Change in smell, Solid Formation, Gas Production).
2
New cards
Physical Property
When a substance change into another substance but the process is reversible (Color, Density, Smell, Form changes, Melting point)
3
New cards
Solid
Definite shape, definite volume, particles can’t move but packed together.
4
New cards
Liquid
shape of container, definite volume, closely packed particles but can move past each other.
5
New cards
Gas
Shape of container, volume of container, molecules move freely in container.
6
New cards
Amorphous Solid
Amorphous solid is particles that aren't arranged in a normal pattern.
7
New cards
Crystalline Solid
Crystalline solid is particles in a certain PATTERN
8
New cards
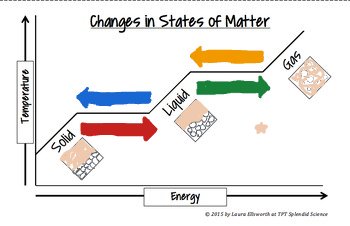
The red arrow means_______
Melting process
9
New cards
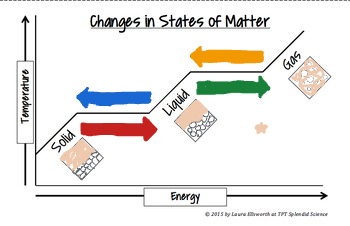
The blue arrow means_______
Freezing process
10
New cards
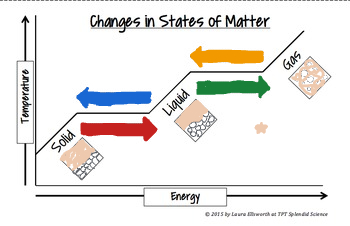
The green arrow means_______
Evaporation (Phase change)
11
New cards
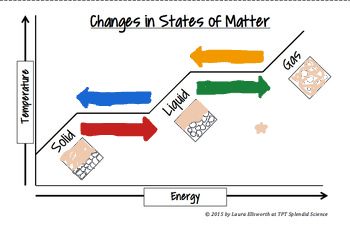
The yellow arrow means_______
Condensation
12
New cards
In an exothermic reaction, heat is being _____
released
13
New cards
In an endothermic reaction, heat is being_____
absorbed (taken in)
14
New cards
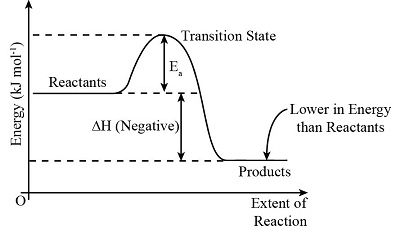
This is an ______ graph
exothermic
15
New cards
A word that means to start a reaction is_____
Activation Energy
16
New cards
What can be used to lower the activation energy of a reaction?
Catalyst
17
New cards
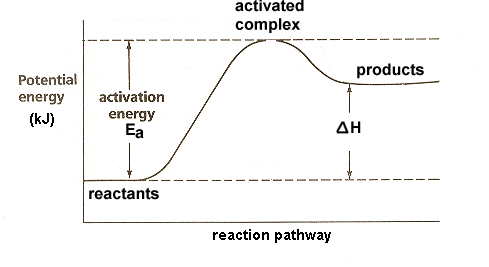
This is a ______ graph
Endothermic reaction
18
New cards
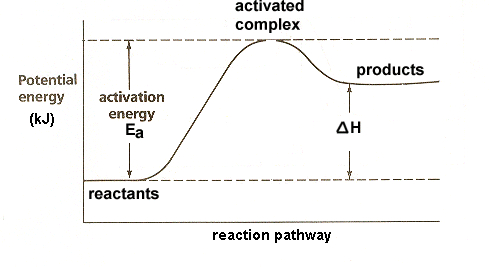
In an endothermic reaction change in H is always
Positive
19
New cards
Sodium Cloride dissolving in water is an endo process, which means the temperature ______
decreases
20
New cards
__***Photosynthesis***__ is an __***endothermic***__ reaction because_______
reactants combine chemically to produce new substances
21
New cards
__***Cellular respiration***__ is an __***exothermic***__ reaction because_____
when carbon reacts to oxygen, it produces carbon dioxide.
22
New cards
What happens to the temperature and the molecules of an __endothermic__ reaction?
More energy is being taken in. Temperature gets warmer while molecules move faster
23
New cards
What happens to the temperature and the molecules of an __endothermic__ reaction?
Less energy is being used to release. Temperature gets colder while molecules move slower
24
New cards
when ice melts, it is called an _____ reaction. Explain.
endothermic, ice gets heat up by warm air, water gets colder, and heat goes to cold areas.
25
New cards
Conduction
direct heat contact (hot to cold through direct touch)
26
New cards
Convection
Transfer of heat by movents/cycle (when boiling water, heat from the bottom rises to the top, colder water from the top sinks)
27
New cards
Radiation
Transfer of heat/energy by electromagnetic waves (heat/energy is being transfer by air)
28
New cards
A reaction that causes temperature of the surroundings to decrease is
Endothermic
29
New cards
Opposite of evaporation is
condensation
30
New cards
Example of mechanical energy is
after the car takes in \**chemical energy*\* (gas), it is drivable (mechanical energy)
31
New cards
Example of electromagnetic energy is
Microwave
32
New cards
Example of thermal energy is
Water boils or melting ice cream
33
New cards
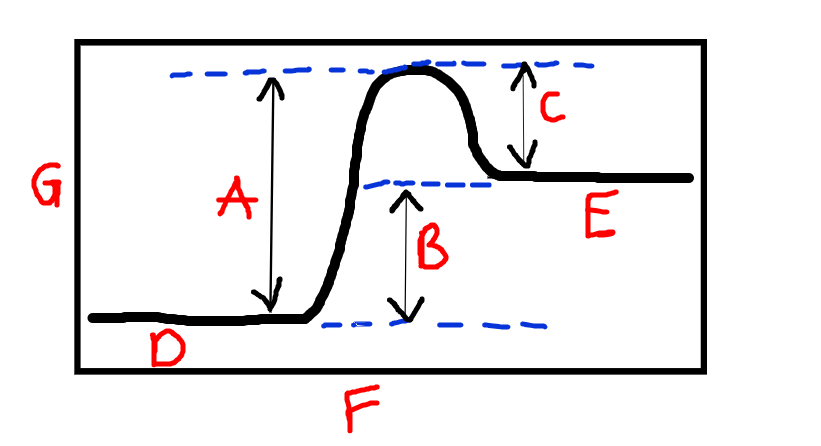
Label F and G
F is reaction progress. G is Chemical energy
34
New cards
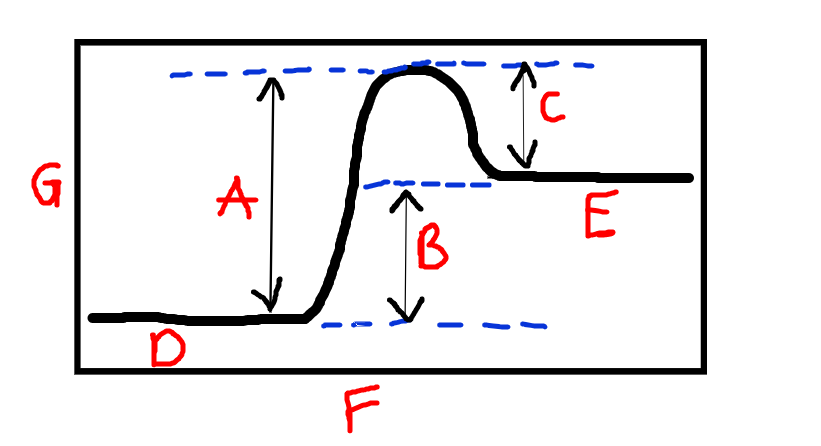
Label A
Activation energy
35
New cards
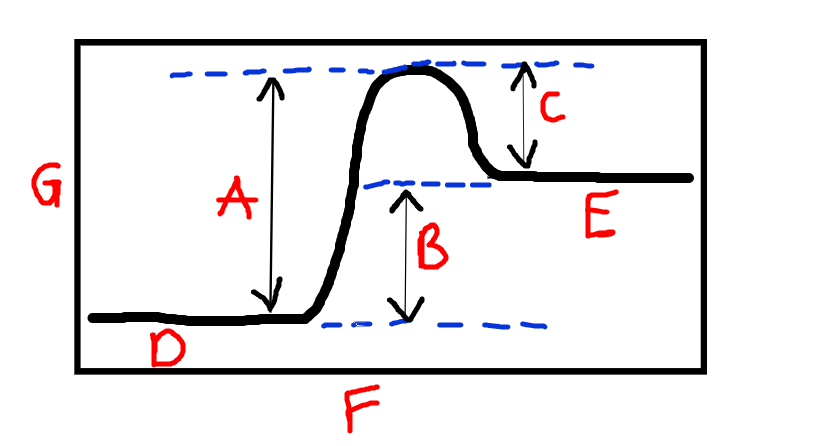
Label B
Energy absorbed
36
New cards
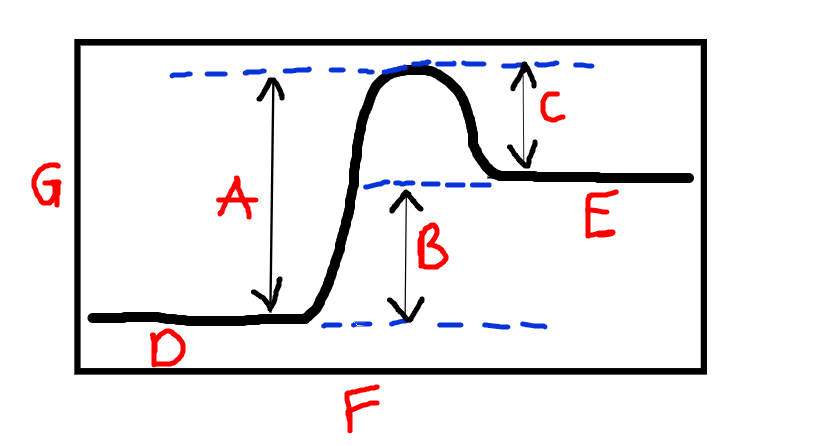
Label C
Energy released
37
New cards
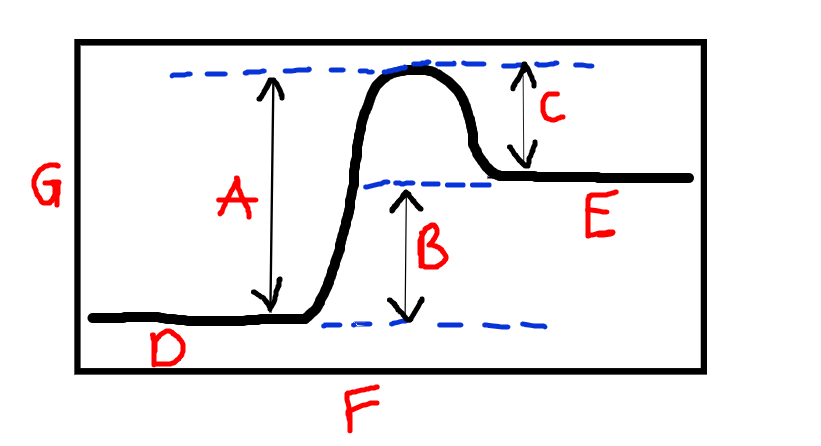
Label D and R
D=reactants, E=Products
38
New cards
This equation “__*Reactants→Products + Energy (heat)”*__ represents ______ reaction
Exothermic
39
New cards
This equation “__*Reactants + Energy (heat) → Products”*__ represents ______ reaction
Endothermic
40
New cards
What causes water to condense?
Heat that surrounds it