Meiosis & Genetic Diversity Quiz
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
review notes, lab slideshow, RF worksheet, helpful videos
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
asexual reproduction
produces genetically identical cells from a single parent
examples of asexual reproduction
binary fission in bacteria, mitosis, budding
sexual reproduction
production of genetically different cells; leads to genetic diversity in offspring
examples of sexual reproduction
meiosis
meiosis
produces genetically different haploid gamete cells; undergoes two rounds of division
when does interphase occur?
before meiosis I
prophase I
chromosomes condense, synapsis occurs, crossing over occurs
synapsis
when homologous chromosomes pair up, forming a tetrad
crossing over
when parts of the p/q arm of non-sister chromatids swap at the chiasmata; creates recombinants/non-recombinants
when does crossing over occur?
during prophase I only
chiasmata
physical connection point between non-sister chromatids
non-recombinant chromosomes
offspring with the same phenotype as one of the parental chromosomes, aka parental types
recombinant chromosomes
offspring with different phenotypes from the parent chromosomes
metaphase I
independent assortment occurs as homologous pairs align at the metaphase plate
independent assortment
homologous pairs randomly line up in the middle, increasing genetic variation
anaphase I
spindle fibers shorten to pull homologous chromosomes apart to opposite poles of the celll
telophase I/cytokinesis
daughter nuclei form around each set of chromosomes and two haploid cells form
prophase II
chromosomes condense again
metaphase II
chromosomes align at the metaphase plate
anaphase II
spindle fibers shorten to pull sister chromatids apart
telophase II/cytokinesis
daughter nuclei form and cells split
result of meiosis
four genetically different haploid cells
law of independent assortment
alleles will separate independently into gamete cells if they are unlinked
how to calculate the number of ways homologous chromosomes can arrange themselves during metaphase
2n
recombination frequency
determines if two genes are linked and how tightly linked they are
linked genes
genes that are located close to each other on a chromosome; oftentimes inherited together
linkage map
genetic map that shows the order of genes and the distances between each gene; help determine how likely crossing over will occur
unit used to measure distance between genes?
map units/centimorgans (cM)
conversion between cM and recombination frequency
1 cM = 1% RF
what does a 50% RF mean?
genes are very far apart on the chromosome/on different chromosomes; genes will independently assort
what does a RF of <50% mean?
linked genes; lower chance of recombination/independent assortment
what does a lower recombination frequency mean
the genes are more likely to be linked
what does a higher recombination frequency mean
the genes are more likely to be unlinked
if the RF of two genes is 20%, what percentage of gametes would be recombinant types? parental types?
20% recombinant, 80% parental types
how to calculate recombination frequency
(number of recombinants / total offspring) x 100
chromosomal mutations
nondisjunction, duplication, inversion, deletion, insertion, translocation
nondisjunction
chromosomes fail to separate properly during cell division; results in aneuploid cells; creates a zygote with a trisomy or monosomy
aneuploid cells
cells with an abnormal amount of chromosomes
trisomy
3 copies of the chromosome
monosomy
1 copy of the chromosome
duplication
an extra copy of part or the whole chromosome is created, lengthening the chromosome
insertion
part of a chromosome is removed and inserted into another, shortening one chromosome and lengthening the other
translocation
pieces of two chromosomes swap
deletion
part of a chromosome is removed, shortening it
inversion
a piece of the chromosome is flipped
karyotype
diagram to show an individual’s chromosomes; shows their chromosome abnormalities, biological gender, and species
autosome
non sex chromosomes; pairs 1-22 in humans
sex chromosomes
biological gender; pair 23 in humans
binary fission
how prokaryotes divide; don’t need microtubules because they don’t have them and they only have one chromosome; produces two identical daughter cells
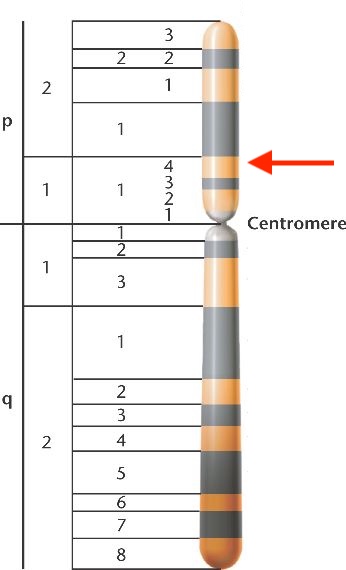
name this (this is chromosome X)
Xp11.4