CH 19: testing considerations, patient history, mechanisms of disease, and physical examination
1/219
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
220 Terms
Whose responsibility is it to make the determination that a diagnostic study is medically necessary?
Ordering physician
List the 4 integrations of outside data that the sonographer should take note of prior to non-invasive cerebrovascular testing.
Obtain a good history
Document relevant physical exam findings
Identification of risk factors
Knowledge of some differential diagnoses
What environment should the sonographer maintain prior to non-invasive cerebrovascular testing?
Warm
List the 2 interpretations and reportings that the sonographer should take note of prior to non-invasive cerebrovascular testing.
All final reports must be standardized
Accurately reflect the contents and interpretation of the noninvasive study
List the 4 testing considerations for non-invasive cerebrovascular testing.
Appropriate indications
Integration of outside data
Environment
Interpretation and reporting
List the 4 risk factors that will contribute to cerebrovascular diseases.
Smoking
Diabetes mellitus
Hypertension
Hyperlipidemia
What is the abbreviation for hyperlipidemia?
HLD
Hyperlipidemia is the medical term for what?
High cholesterol
Which pathology learned in this lecture is considered a warning sign of a stroke?
Transient ischemic attack
Name the pathology:
“A fleeting neurologic dysfunction without lasting effects”
Transient ischemia attack
What does ‘TIA’ stand for?
Transient ischemic attack
What is transient ischemic attack?
Fleeting neurologic dysfunction without lasting effects
How long do symptoms last for a transient ischemic attack? (2)
Anywhere from a few minutes to a few hours
Never more than 24 hours
List the 3 symptoms of transient ischemic attack.
Sensory and/or motor dysfunction of an arm or leg
Speech impairment
Visual disturbances
Etiology of transient ischemic attack is usually…
Embolic
In which 2 structures will the source of an emboli of a transient ischemic attack be found?
Heart
Carotid artery
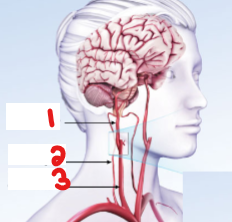
Label the crossed-out structures on this image and specify which side it is on.
Right internal carotid artery
Right vertebral artery
Right common carotid artery

If this was taken at the carotid bifurcation and there is atherosclerotic plaque seen in the internal carotid artery, how will that affect the internal carotid artery?
Reduces blood flow in the internal carotid artery
List the 3 symptoms of reversible ischemic neurologic deficit (RIND).
Sensory and/or motor dysfunction of an arm or leg
Speech impairment
Visual disturbances
What does ‘RIND’ stand for?
Reversible ischemic neurologic deficit
Between these 2 pathologies:
Transient ischemic attack
Reversible ischemic neurologic deficit
Which will have symptoms that last longer?
Reversible ischemic neurologic deficit
How long will it take for the deficit to resolve with reversible ischemic neurologic deficit?
Longer than 24 hours
Is there complete recovery with reversible ischemic neurologic deficit?
Yes
What does ‘VBI’ stand for?
Vertebrobasilar insufficiency
What does ‘CVA’ stand for?
Cerebrovascular accident
What is another term for stroke?
Cerebrovascular attack
What is another term for cerebrovascular attack?
Stroke
What kind of symptoms does a vertebrobasilar insufficiency present?
Fleeting symptoms
How long will symptoms last for vertebrobasilar insufficiency/VBI?
A few seconds or minutes
What kind of deficits will a cerebrovascular accident/stroke produce?
Permanent neurologic deficit
Name the pathology:
“Causes fleeting symptoms often lasting only seconds or minutes”
Vertebrobasilar insufficiency
Name the pathology:
“Produces permanent neurologic deficits”
Cerebrovascular accident/Stroke
Which vessels supply blood to the brain’s cerebral hemispheres?
Anterior
Posterior
Anterior
List the 4 anterior vessels that feed the brain’s cerebral hemispheres.
Internal carotid artery
Anterior cerebral artery
Middle cerebral artery
Anterior communicating artery
Which hemisphere of the brain controls the right side of the body?
Left
Which hemisphere of the brain controls the left side of the body?
Right
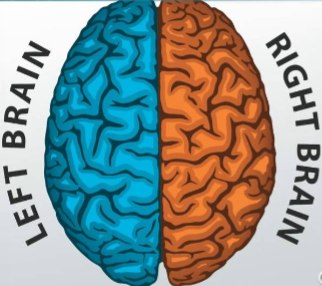
The left hemisphere controls which side of the body?
Right
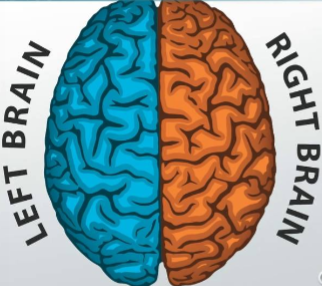
The right hemisphere controls which side of the body?
Left
A left hemispheric stroke results in neurologic deficits to the _______ side of the face and body.
Right
A right hemispheric stroke results in neurologic deficits to the _______ side of the face and body.
Left
In this lecture, what does the term ‘lateralizing’ refer to?
Indicating which side or hemisphere of the brain has been affected
Name the term:
“Indicating which side or hemisphere of the brain has been affected”
Lateralizing
In this lecture, what does the term ‘non-lateralizing’ refer to?
Non-specific to the right or left side of the brain
Name the term:
“Non-specific to the right or left side of the brain”
Non-lateralizing
List 2 examples of pathologies with non-lateralizing symptoms.
Ataxia
Vertigo
Non-lateralizing symptoms are usually associated with problems in which 2 structures?
Brain stem
Posterior circulation
Problems with posterior circulation will be associated with what pathology?
Vertebral basilar insufficiency
List 2 pathologies that can result from an ICA lesion.
Significant stenosis
Occlusion
List the 5 neurologic deficits that may be associated with an ICA lesion.
Unilateral paresis
Unilateral paresthesia or anesthesia
Aphasia
Amaurosis fugax
Homonymous hemianopia
Name the neurologic deficit:
“Weakness or slight paralysis on one side of the body”
Unilateral paresis
Name the neurologic deficit:
“Tingling, numbness, or lack of feeling on one side of the body”
Unilateral paresthesia or anesthesia
Name the neurologic deficit:
“Inability to speak”
Aphasia
Name the neurologic deficit:
“Temporary partial or total blindness, usually of only one eye”
Amaurosis fugax
Name the neurologic deficit:
“The loss of vision in one half of the visual field of both eyes”
Homonymous hemianopia
Define ‘unilateral paresis.’
Weakness or slight paralysis on one side of the body
Define ‘unilateral paresthesia/anesthesia.’
Tingling, numbness, or lack of feeling on one side of the body
Define ‘aphasia.’
Inability to speak
Define ‘amaurosis fugax.’
Temporary partial or total blindness, usually of only one eye
Define ‘homonymous hemianopia.’
The loss of vision in one half of the visual field of both eyes
If a patient suffers from right arm paresis, which ICA would be affected with disease?
Left
If a patient suffers from left arm paresis, which ICA would be affected with disease?
Right
How is the visual loss with ‘amaurosis fugax’ described by patients?
“A shade coming down over the eye”
Which neurologic deficit is associated with this finding:
“A shade coming down over the eye”
Amaurosis fugax
Which artery is associated with vision and arises from the ICA?
Opthalmic artery
The ophthalmic artery arises from what artery?
ICA
Where could the origin of an embolic process be that would cause temporary vision loss?
Ipsilateral internal carotid artery
If the patient is experiencing vision loss in the right eye, which ICA would be affected by disease?
Right
If the patient is experiencing vision loss in the left eye, which ICA would be affected by disease?
Left
Why would the right ICA be the source of temporary vision loss in the right eye?
Because the ophthalmic artery branches off the ICA
Homonymous hemianopia is not always related to what kind of lesions?
ICA lesions
Between these 2 options, which vision pathology most closely matches this description:
Temporary partial or total blindness, usually of only one eye
Amaurosis fugax
Homonymous hemianopia
Amaurosis fugax
Between these 2 options, which vision pathology most closely matches this description:
The loss of vision in one half of the visual field of both eyes
Amaurosis fugax
Homonymous hemianopia
Homonymous hemianopia

Which neurologic deficit pathology is associated with this image?
Amaurosis fugax
What does dysphasia refer to?
Impaired speech
Severe hemiparesis/hemiplegia from an MCA lesion is most commonly seen in which structure option?
Face/Arm
Leg
Face/Arm
Less severe hemiparesis/hemiplegia from an MCA lesion is most commonly seen in which structure option?
Face/Arm
Leg
Leg
List the 3 symptoms seen with an MCA lesion.
Aphasia/Dysphasia
Severe facial and arm hemiparesis/hemiplegia
Behavioral abnormalities
List the 3 symptoms seen with an ACA lesion.
Severe leg hemiparesis
Incontinence
Loss of coordination
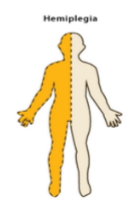
Define ‘hemiplegia.’
Paralysis affecting one side of the body including arm, leg, and trunk
List the 4 posterior vessels that supply blood to the brain stem, cerebellum, and occipital lobes.
Vertebral artery
Basilar artery
Posterior cerebral artery
Posterior communicating arteries
Which vessels supply blood to the brainstem, cerebellum, and occipital lobes?
Anterior
Posterior
Posterior
List the 5 symptoms of a vertebrobasilar lesion.
Vertigo
Ataxia
Bilateral blurry vision or diplopia
Bilateral paresthesia
Drop attack
Define ‘vertigo.’
Difficulty maintaining equilibrium
Name the symptom of vertebrobasilar lesion:
“Difficulty maintaining equilibrium”
Vertigo
Define ‘ataxia.’
Muscular incoordination
Name the symptom of vertebrobasilar lesion:
“Muscular incoordination”
Ataxia
Define ‘diplopia.’
Double vision/seeing double
Name the symptom of vertebrobasilar lesion:
“Double vision/seeing double”
Diplopia
Define ‘paresthesia.’
The sensation of prickling or tingling of the skin (Loss of sensation)
Name the symptom of vertebrobasilar lesion:
“The sensation of prickling or tingling of the skin (Loss of sensation)”
Paresthesia
Define ‘drop attack.’
Falling to the ground without a loss of consciousness
Name the symptom of vertebrobasilar lesion:
“Falling to the ground without a loss of consciousness”
Drop attack
List the 2 symptoms commonly seen with a PCA lesion.
Dyslexia
Coma
What does it mean for a symptom to be ‘nonlocalizing’?
Not associated with a specific area, just generalized symptoms
List the 5 non-localizing symptoms learned in this lecture.
Dizziness
Syncope
Difficulty with speech
Headache
Confusion
Define ‘syncope.’
A transient loss of consciousness
How is an ‘auscultation’ performed?
By a doctor listening with a stethoscope
Normal flow patterns are evident when listening through a…
Stethoscope
What kind of abnormal sounds can be heard on auscultation with a stethoscope?
These abnormal sounds are a result of what?
Bruits
Turbulent flow
Bruits are associated with what pathology?
Hemodynamically significant lesion