Physics: Particle Model of Matter
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What is the diagram for solids and how are the particles described?
Particles are very close together
arranged in a regular pattern
Vibrate but don’t move place
Very high density, as particles are closely packed and high mass for volume
What is the diagram for liquids and how are the particles described?
Particles close together
Not in a regular pattern
Particles can move around each other
High density as particles are close together and high mass for volume
What is the diagram for gases and how are the particles described?
Particles very fast apart
Not arranged in any pattern
Moving very rapidly
Very low density because particles are far apart and low mass for volume
What is density? How is it measured?
Mass for given volume
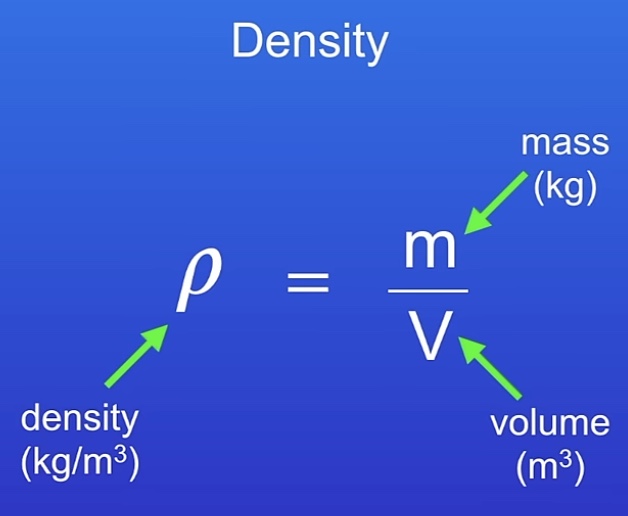
How to determine density for regular solids?
Measure mass with scales (kg)
Measure length of each side (HxWxL) for volume
Mass / volume (Kg/m3)
How can you determine the density of an irregular solid?
Find mass using scales
Use eureka can to measure amount of water displaced with measuring cylinder which is equal to volume of object
Mass / volume (kg/m3)
What is internal energy?
The energy stored in a system by the particles
Total of: Kinetic energy & potential energy (intermolecular forces and chemical bonds)
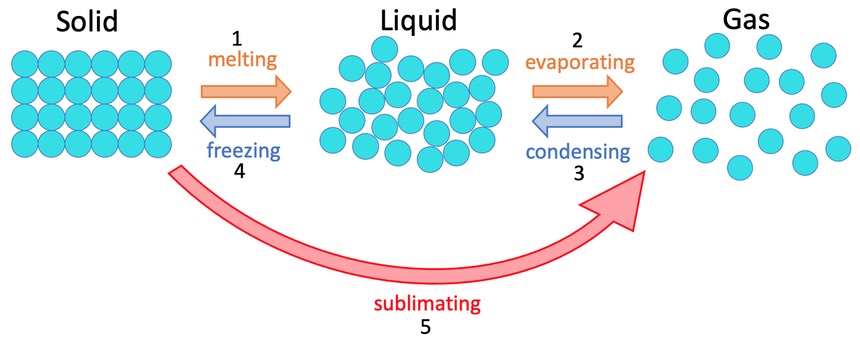
What happens when a material when it changes state?
When solid is heated, the internal energy increases and turns into liquid vice versa
Mass is always conserves (not adding or removing particles)
This physical change can be reversed
Deposition
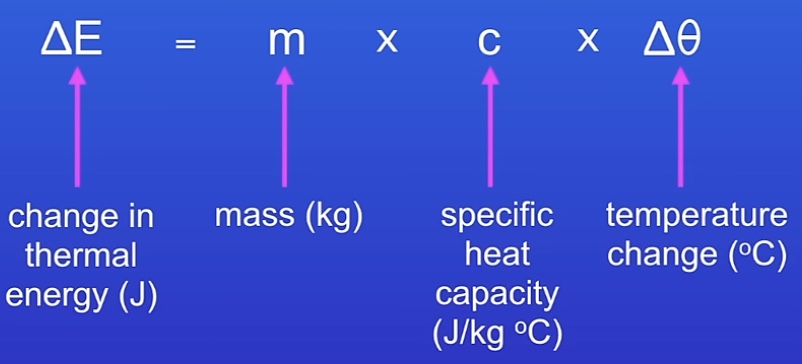
What is specific heat capacity?
The amount f energy required to change the temp of 1kg of a substance by 1ºc
(Equation given in exam)
Label a heating and cooling graph
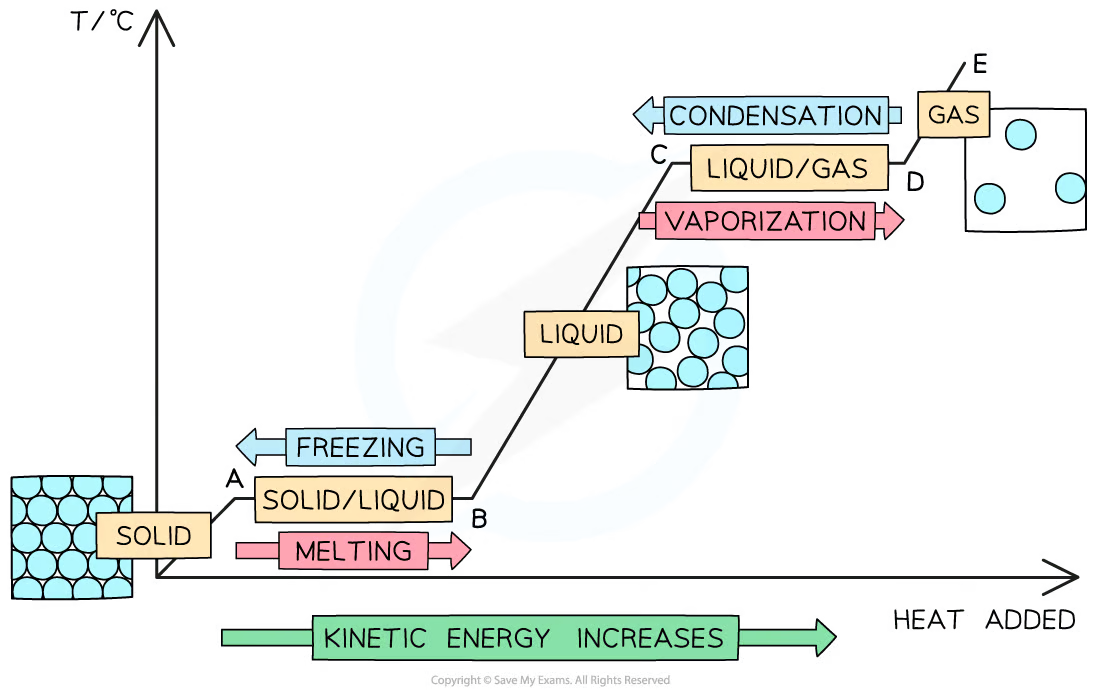
What is happening at the point between changes of state on a heating or cooling graph?
The line is horizontal because the object is changing state. The temperature rises until the energy is used to change state.
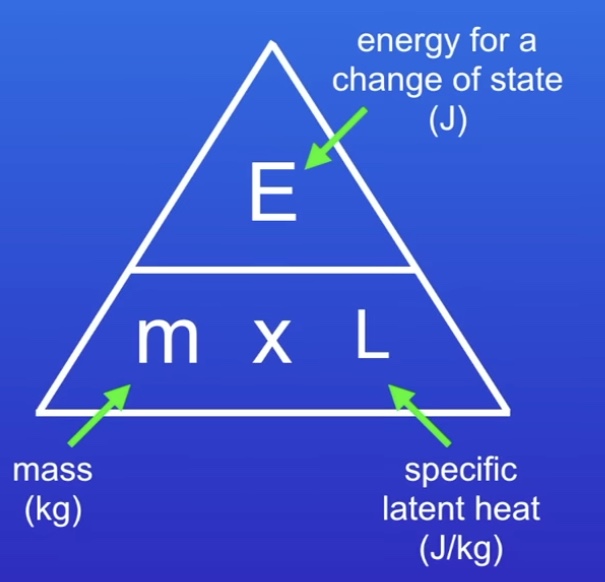
What is Specific Latent Heat?
Amount of energy required to change the state of 1 kg of the substance with no change in temperature.
The energy being transferred to the particles is being used to weaken or break the forces of attraction between the particles.
How can you calculate the energy change taking place when a substance changes state?
(Equation given in exam)
What is specific latent heat of fusion?
The energy required to change 1 kg of a substance from a solid to a liquid with no change in temperature.
What is specific latent heat of Vaporisation
The energy required to change 1 kg of a substance from a liquid to a vapour with no change in temperature.
How is the temperature of a gas related to the energy of the particles?
Particles collide with the walls of the container
This exerts pressure
The pressure can be increased by increasing the number of collisions per second or increase the energy pf each collision (Increase temp)
How does a temp change of gas change the pressure?
At low temp, particles have lower kinetic energy. Fewer collisions per second. Low energy collisions. Low pressure Vice versa
How is pressure of a gas related to its volume?
Pressure is due to particles colliding with the walls of the container.
The collisions cause a force which acts at right angles to the walls. This causes gas pressure.
Increased volume of the container reduces pressure because there is more space between the particles which reduces collisions as they have to travel further to reach the walls. (Inversely proportional)
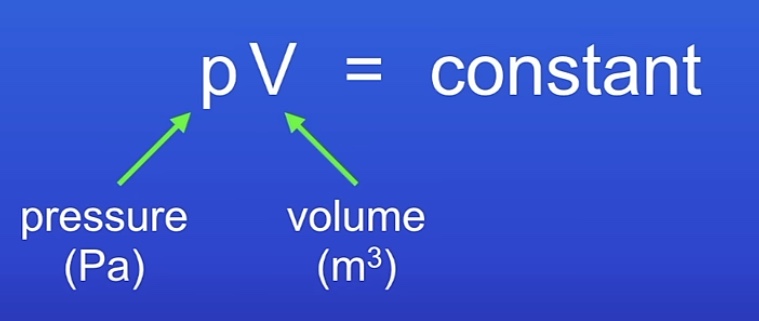
What is the effect of doing work on an enclosed gas?
Compressing the gas in an enclosed space is doing work (applying force)
This transfers energy to the gas and increases the internal energy.
The temperature is increased. E.g. bike tyre pump gets warm