AP Environmental Science Unit 2
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
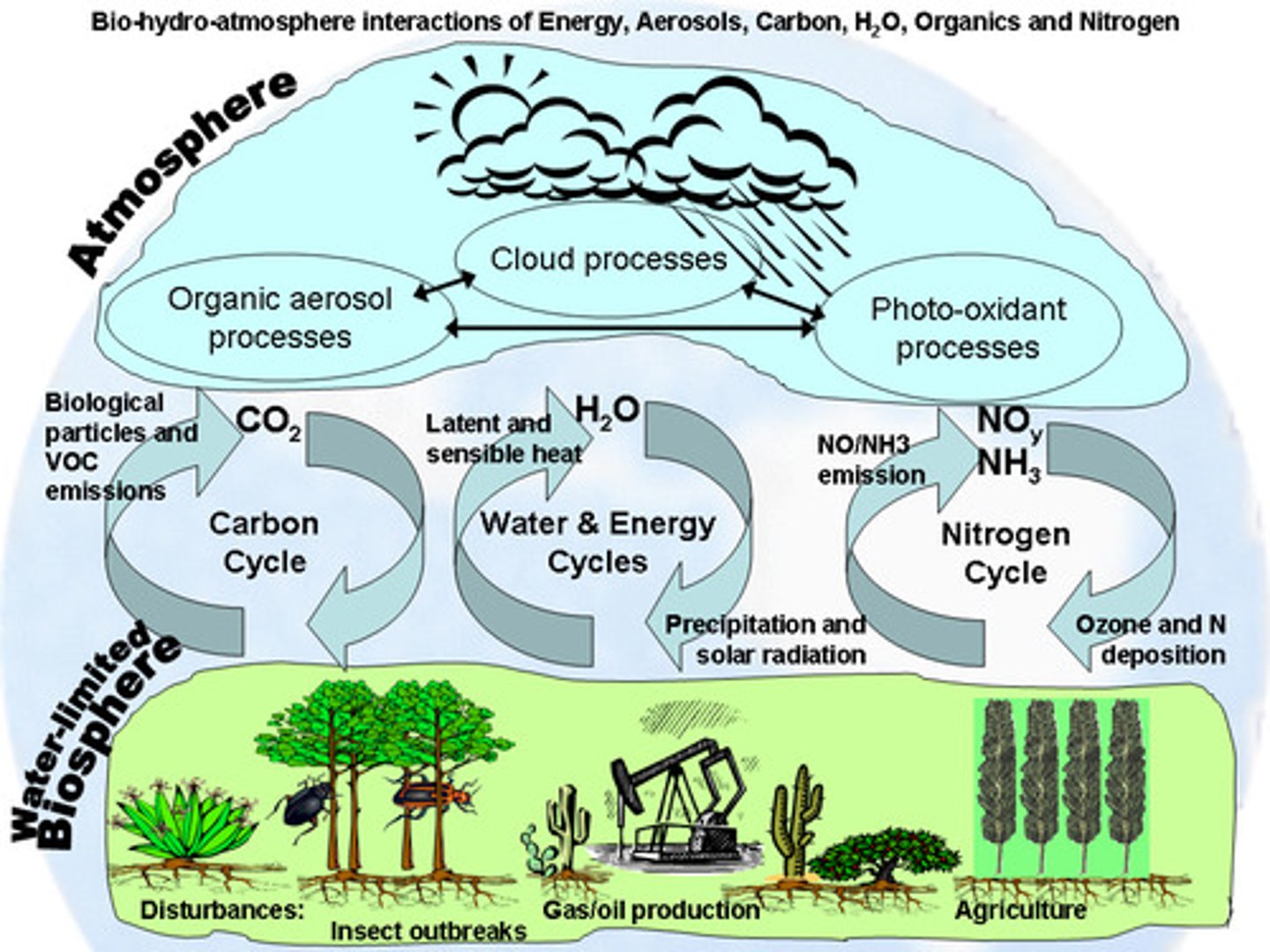
Biosphere (bio = life)
The region of our planet where life resides, the combination of all ecosystems on Earth
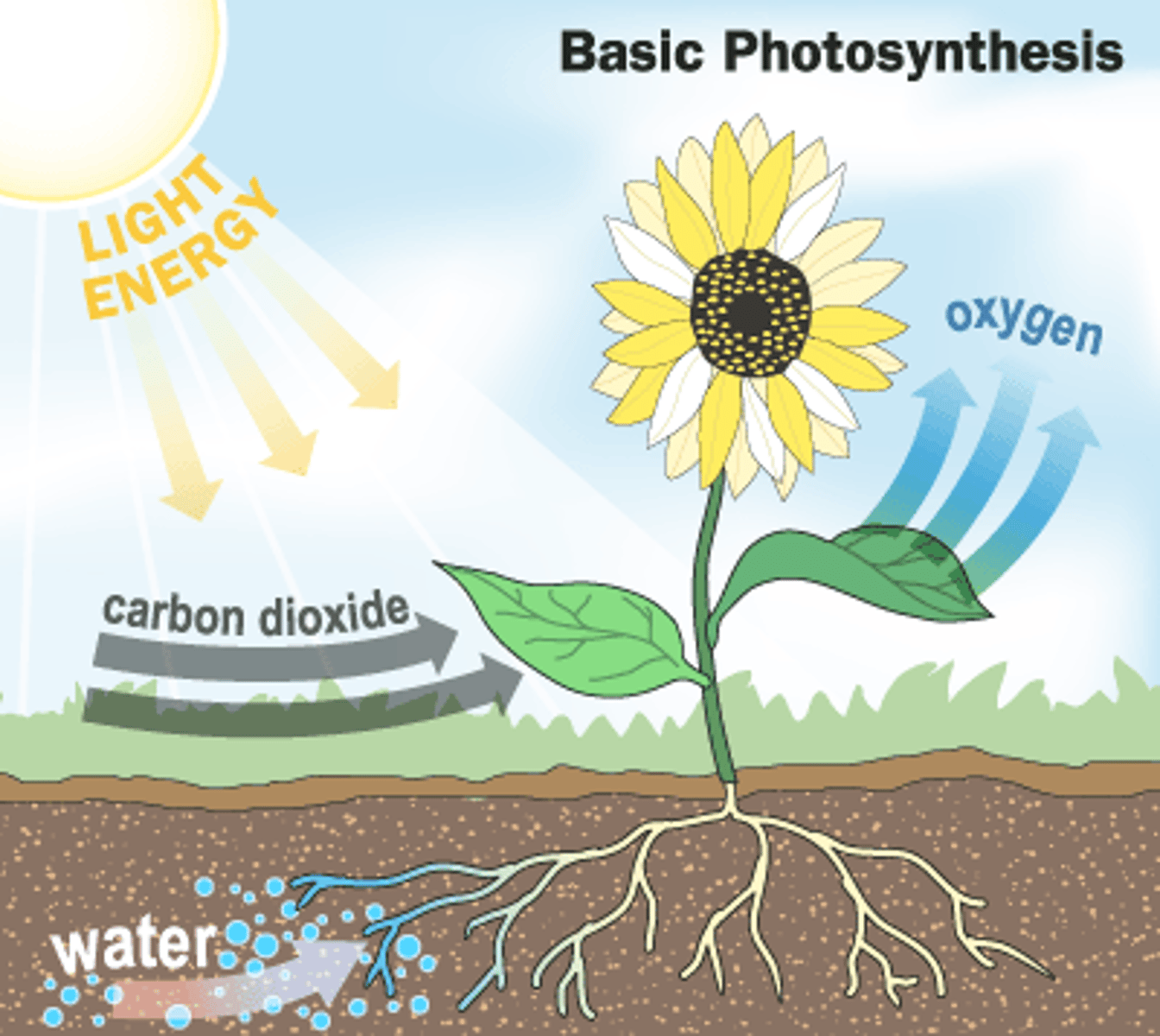
Producer
An organism that uses the energy of the Sun to produce usable forms of energy (also known as autotroph)

Photosynthesis
The process by which producers use solar energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose
Cellular respiration
The process by which cells unlock the energy of chemical compounds
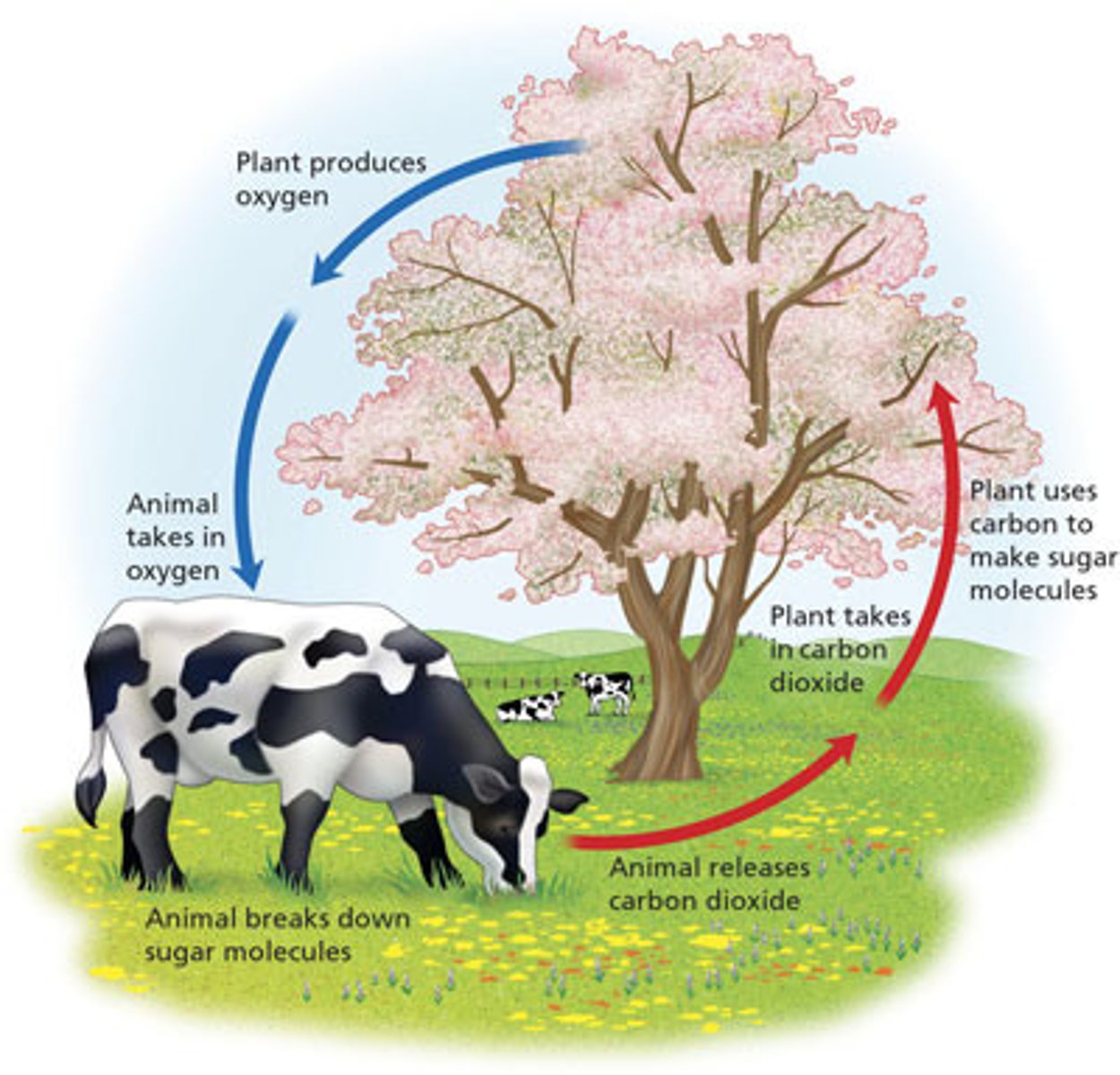
Aerobic respiration
The process by which cells convert glucose and oxygen into energy, carbon dioxide, and water

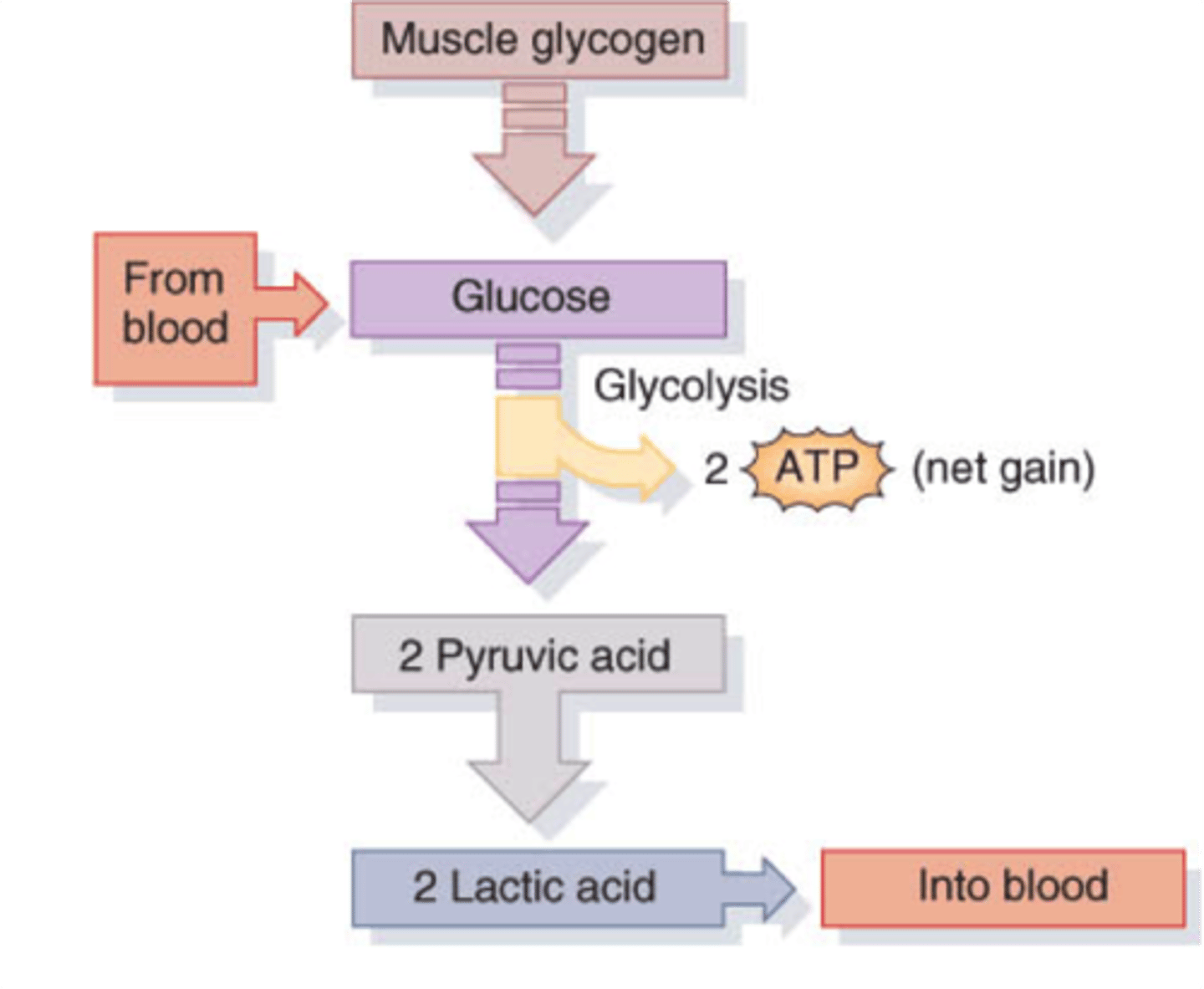
Anaerobic respiration (tell me how im s'posed to breath w no air)
The process by which cells convert glucose into energy in the absence of oxygen
Consumer (eats plants)
An organism that is incapable of photosynthesis and must obtain its energy by consuming other organisms (also known as heterotroph)

Herbivore (free the herb)
A consumer that eats producers (also known as Primary consumer)

Carnivore
A consumer that eats other consumers

Secondary consumer
A carnivore that eats primary consumers

Tertiary consumer
A carnivore that eats secondary consumers

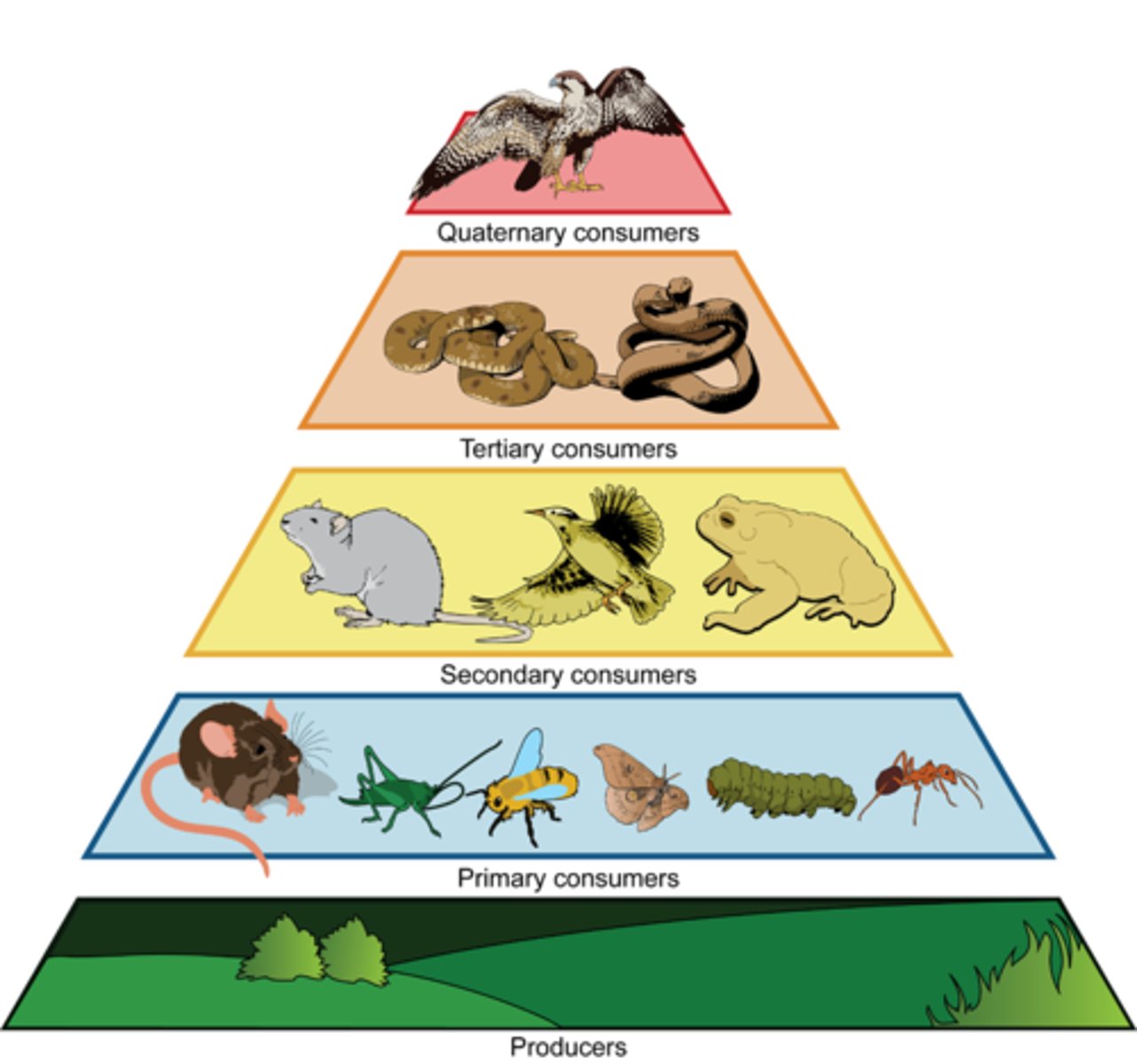
Trophic levels (trophy at top)
The successive levels of organisms consuming one another; Most energy/biomass found at producer level and decreases while going up pyramid
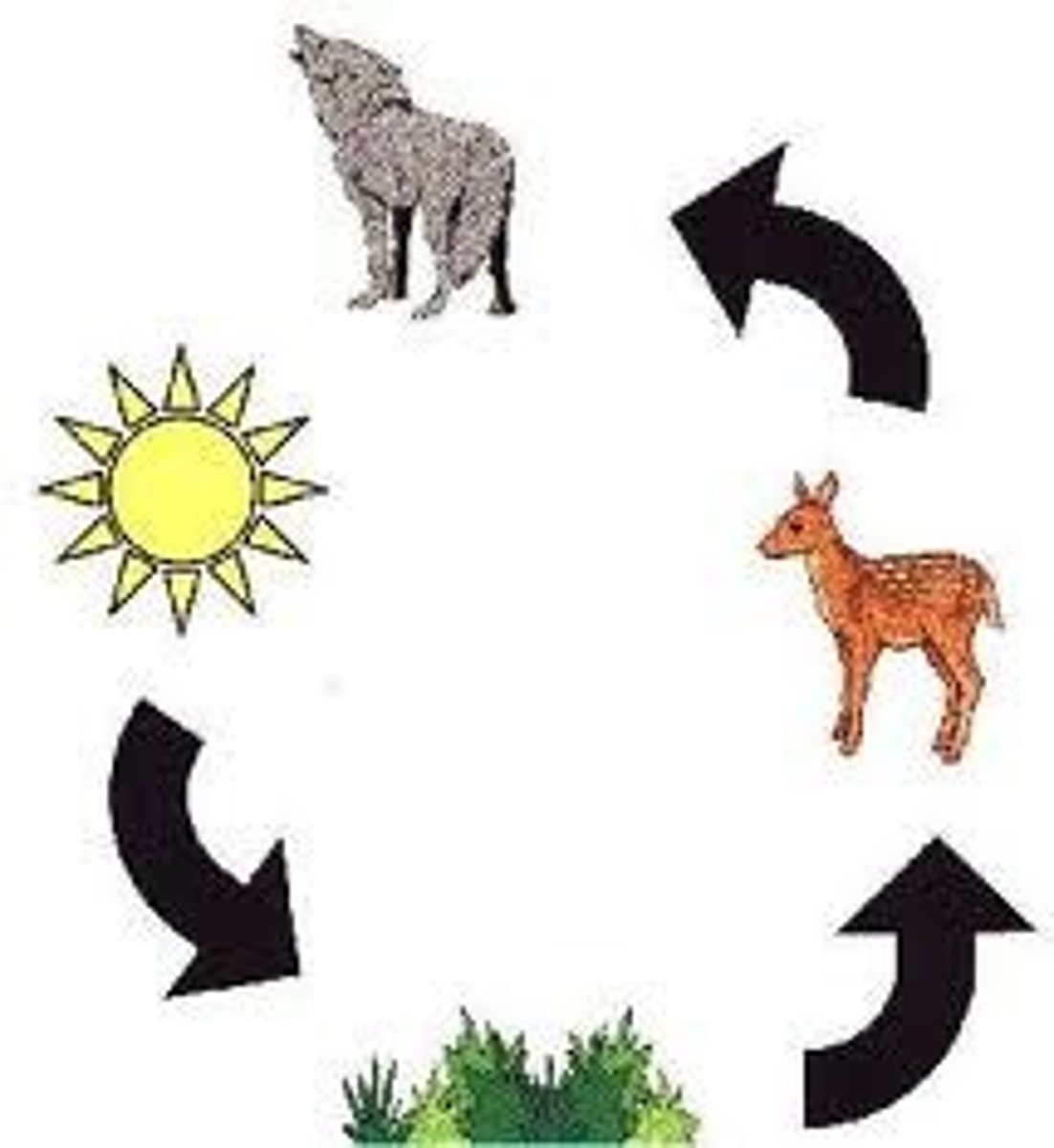
Food chain
The sequence of consumption from producers through tertiary consumers
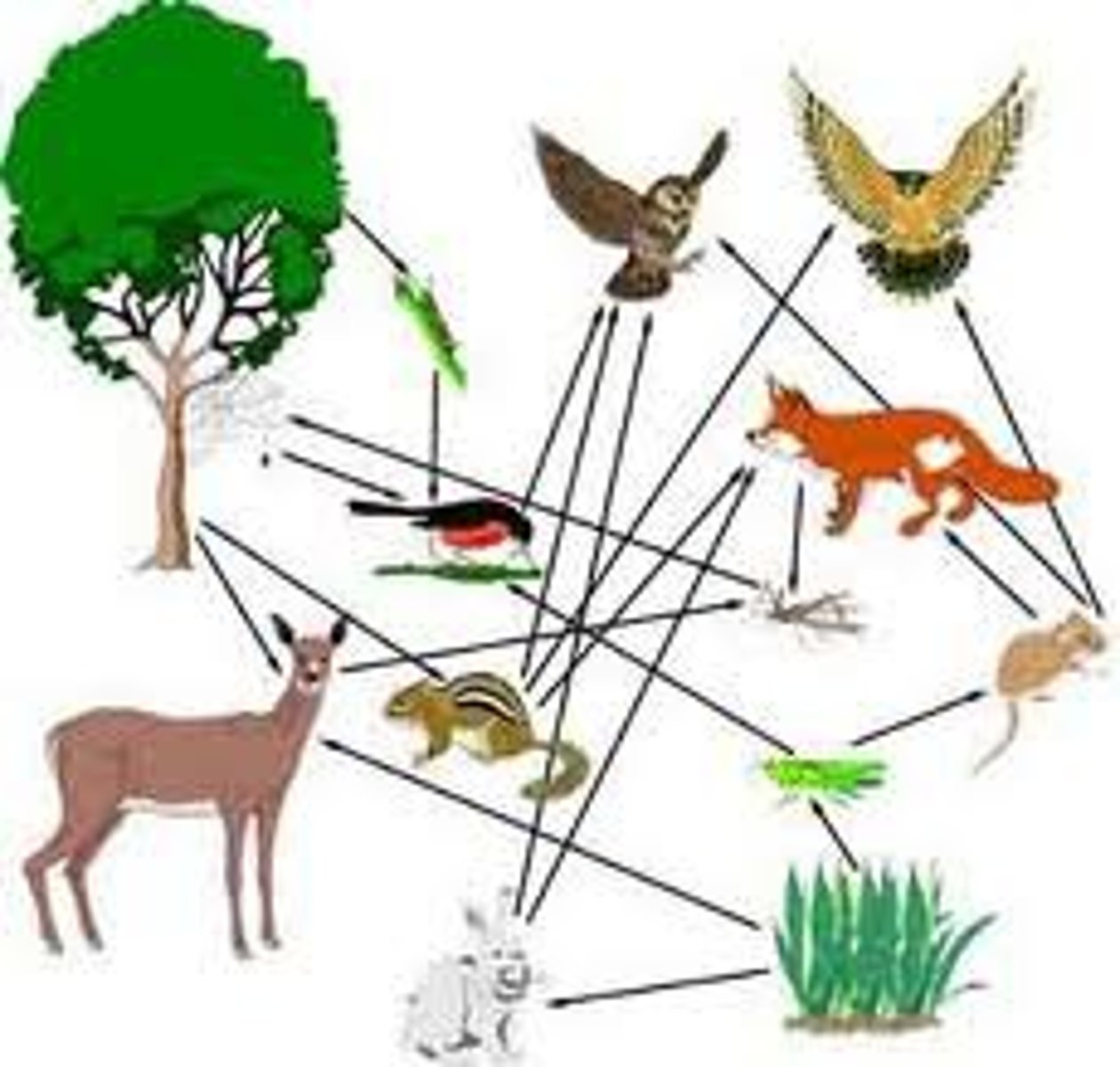
Food web
A complex model of how energy and matter move between trophic levels
Scavenger (savageeee)
An organism that consumes dead animals

Detritivore (DEad Tissues)
An organism that specializes in breaking down dead tissues and waste products into smaller particles

Decomposer
The fungi and bacteria that complete the breakdown process by converting organic matter into small elements and molecules that can be recycled back into the ecosystem.

GPP (Gross Primary Productivity)
The total amount of solar energy that producers in an ecosystem capture via photosynthesis over a given amount of time
NPP (Net Primary Productivity)
The energy captured by produces in an ecosystem minus the energy producers respire
Biomass
The total mass of all living matter in a specific area
Standing crop
The amount of biomass present in an ecosystem at a particular time
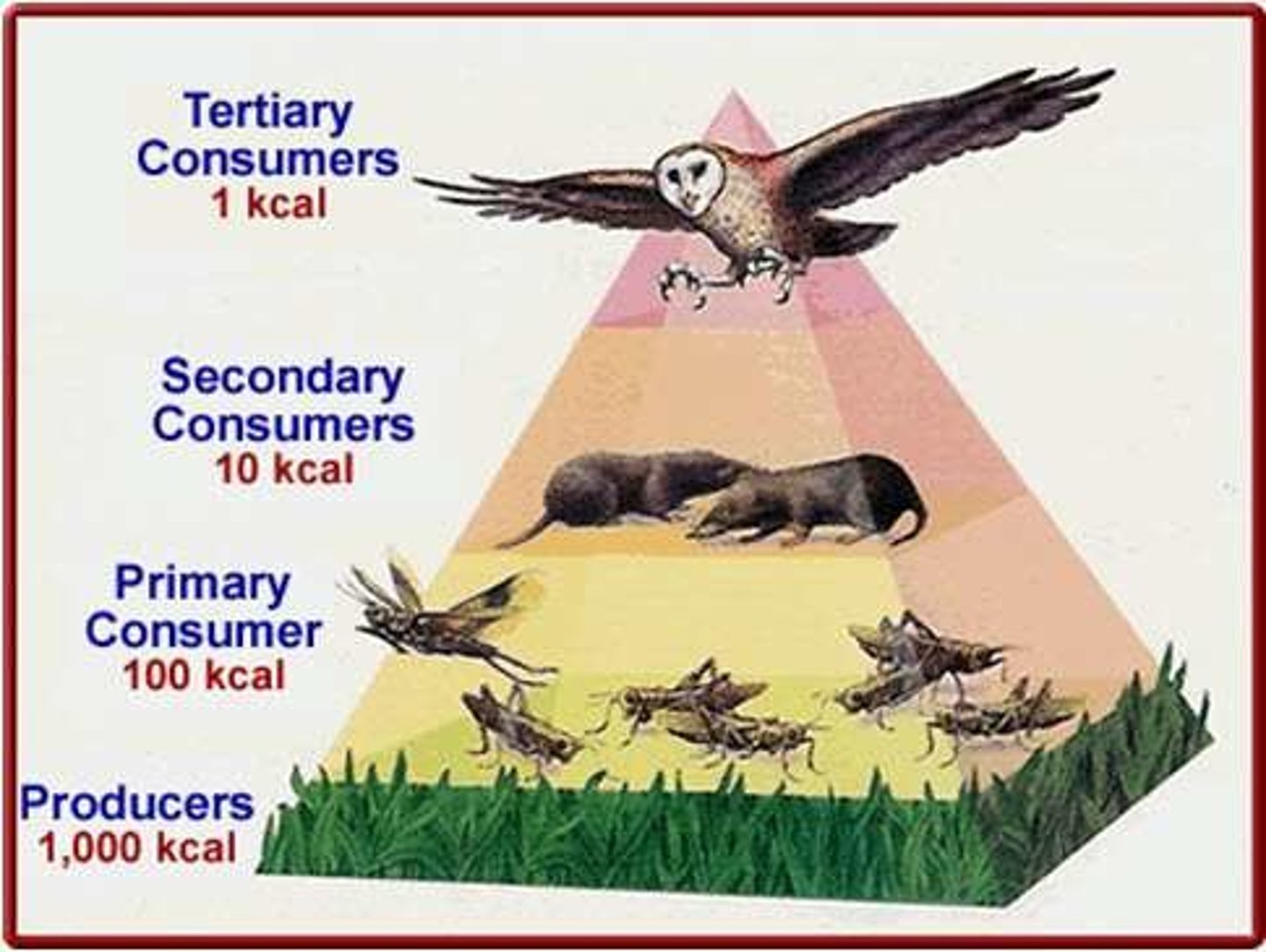
Ecological efficiency
The proportion of consumed energy that can be passed from one trophic level to another; generally organisms can only convert 10% of food into chemical energy (this is why trophic levels rarely exceed 5 or 6)
Trophic pyramid
A representation of the distribution of biomass, numbers, or energy among trophic levels
Biogeochemical cycle
The movements of matter within and between ecosystems
Carbon cycle
The movement of carbon around the atmosphere
Macronutrient
One of six key elements that organisms need in relatively large amounts: nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and sulfur.
Nitrogen Cycle
The movement of nitrogen around the biosphere
Limiting nutrient
A nutrient required for the growth of an organism but available in a lower quantity than other nutrients
Nitrogen fixation (fixed to be ammonia)
A process by which some organisms can convert nitrogen gas molecules directly into ammonia
Denitrification
The conversion of nitrate in a series of steps into the gases nitrous oxide and, eventually, nitrogen gas, which is emitted into the atmosphere
Leaching
The transportation of dissolved molecules through the soil via groundwater
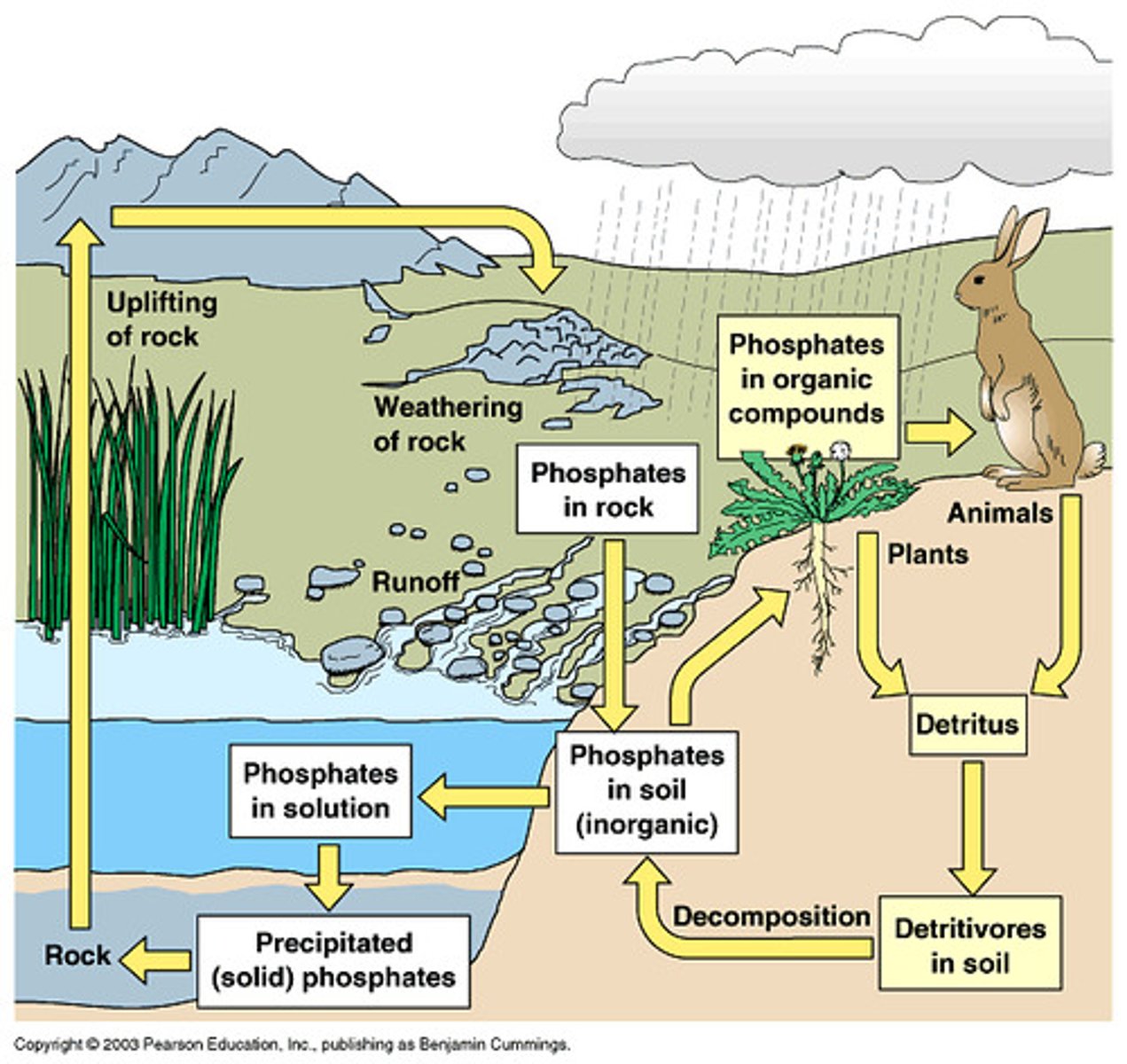
Phosphorus cycle
The movement of phosphorus around the biosphere; after ________ is mined/weathered/used as fertilizer, it goes into soil or water -> then, used by producers into the food web; in water makes new phosphate rocks
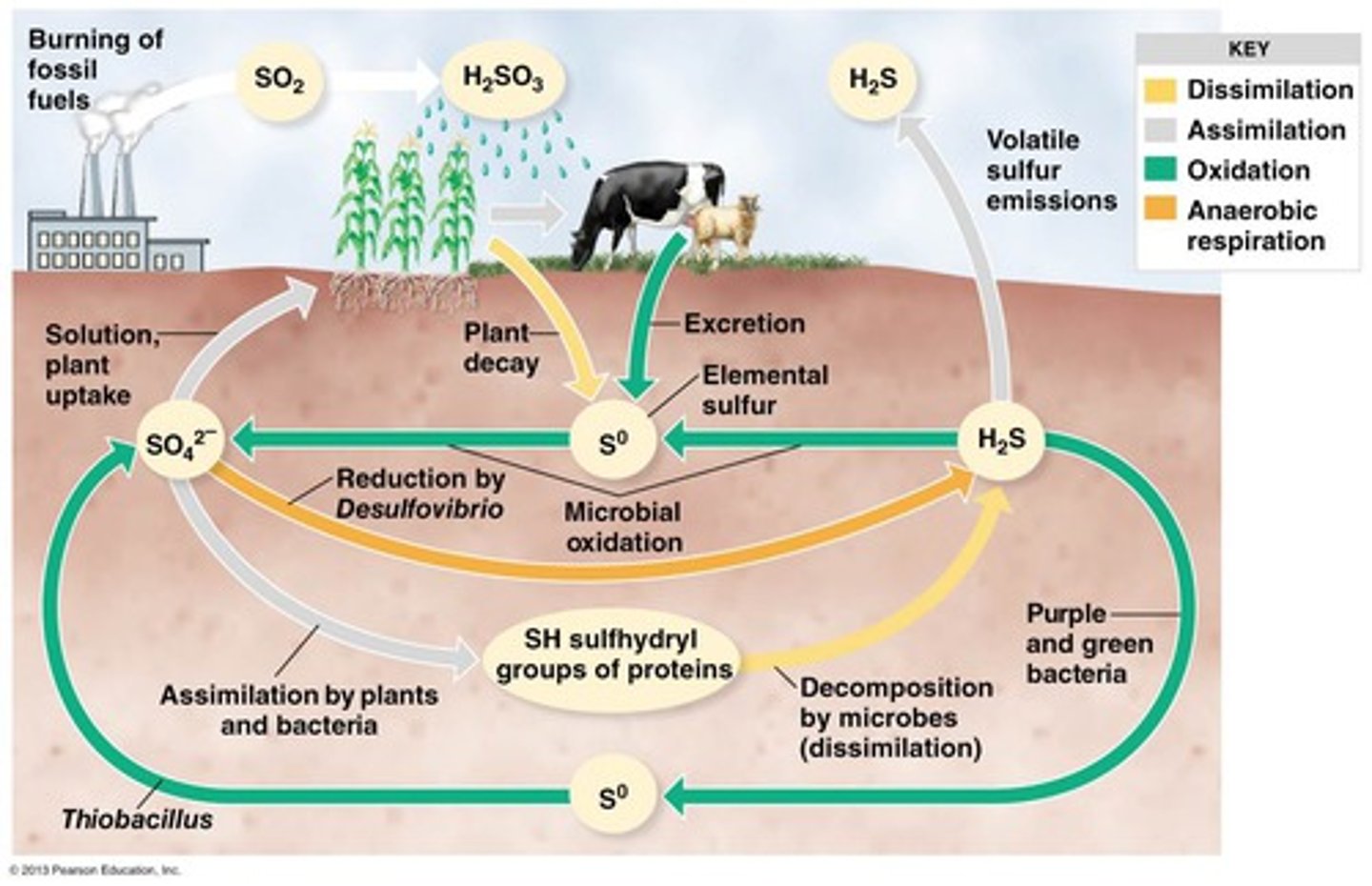
Sulfur cycle
The movement of sulfur around the biosphere
Disturbance
An event, caused by physical , chemical, or biological agents, resulting in changes in population size or community composition

Resistance
A measure of how much a disturbance can affect flows of energy and matter in an ecosystem
Resilience
The rate at which an ecosystem returns to its original state after a disturbance
Restoration ecology
The study and implementation of restoring damaged ecosystems

Intermediate disturbance hypothesis
The hypothesis that ecosystems experiencing intermediate levels of disturbance are more diverse than those with high or low disturbance levels
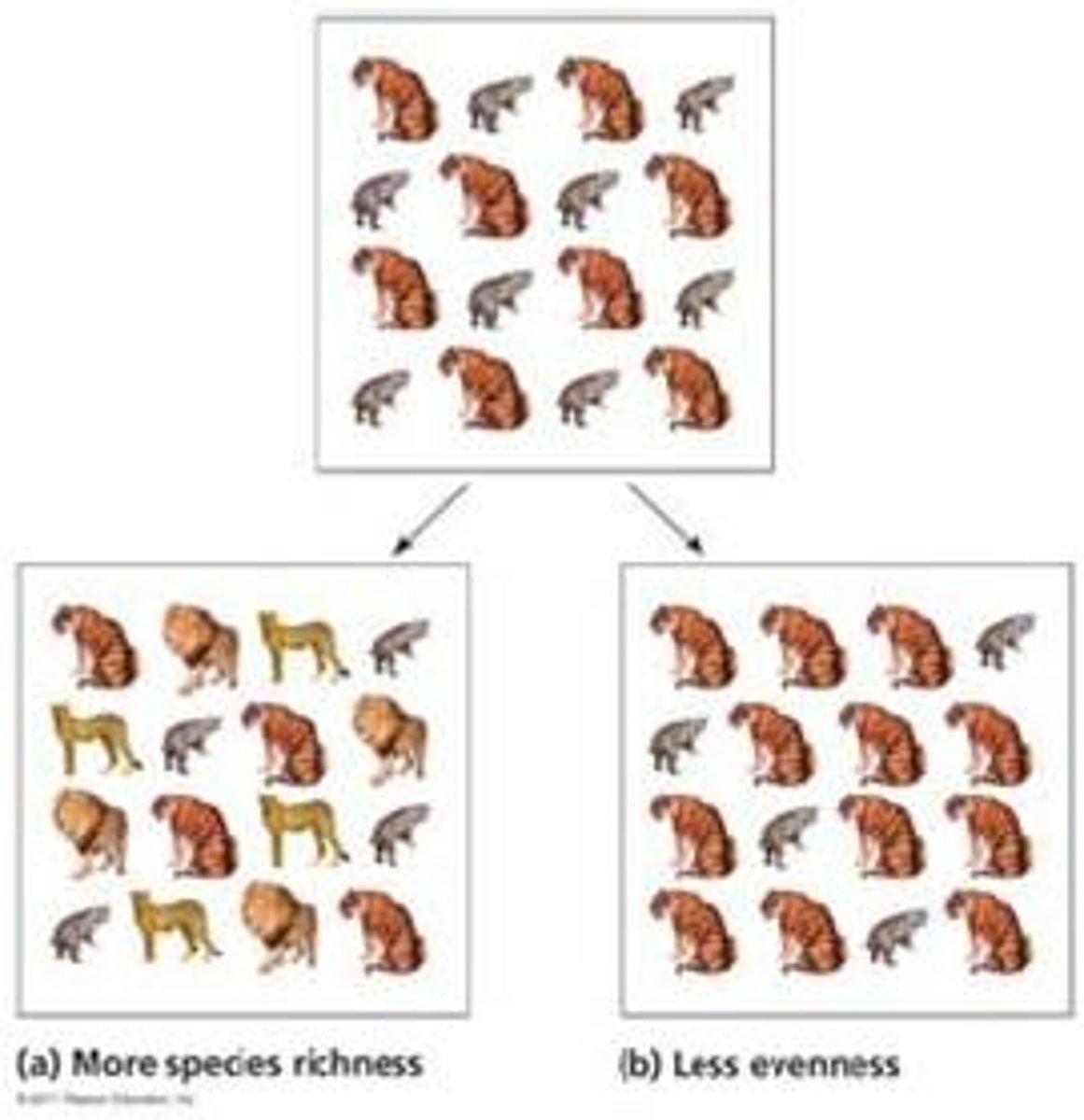
species richness
The number of species in a given area

species evenness
the relative proportion of different species in a given area
Evolution
change in the genetic composition of a population over time
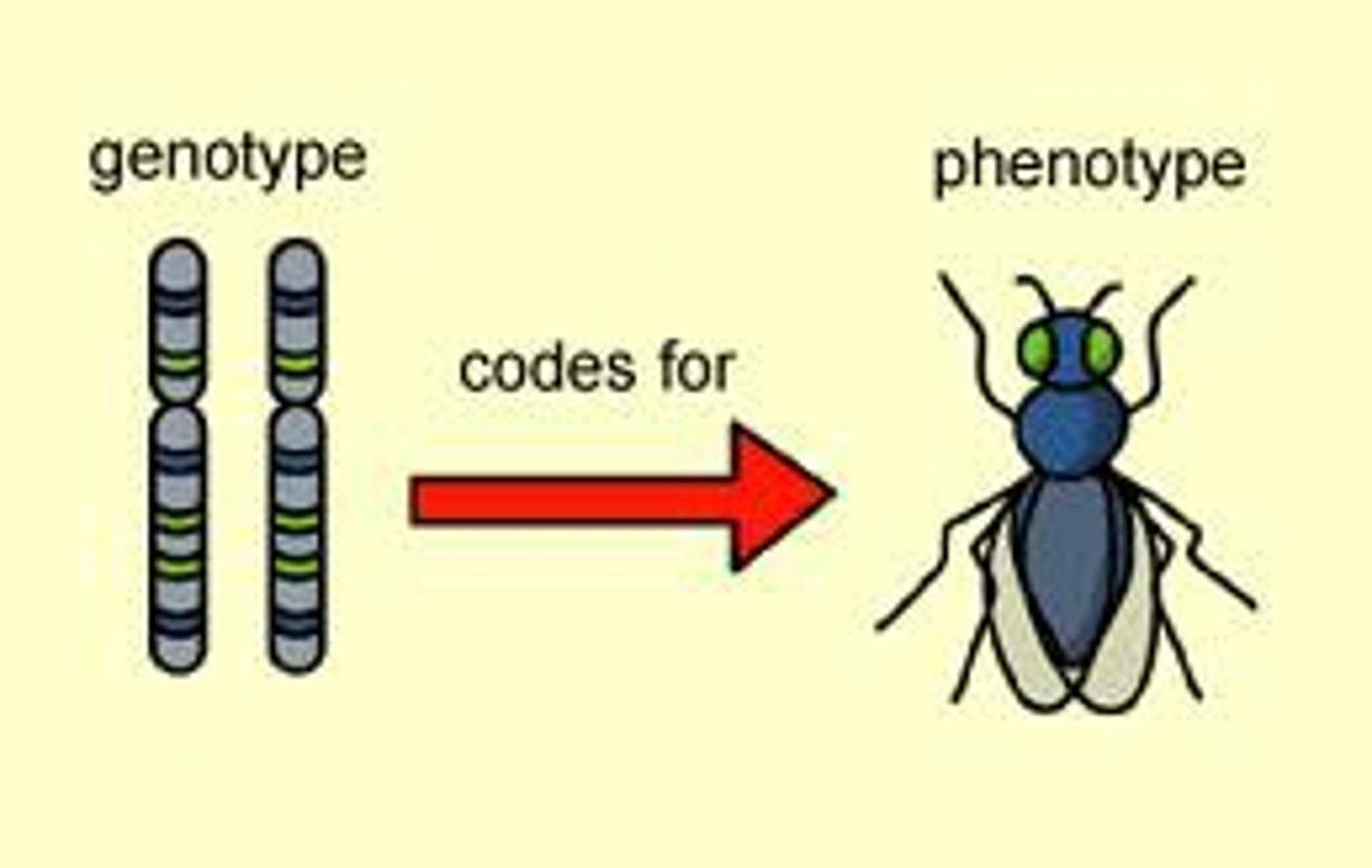
Genotype
genetic makeup of an organism
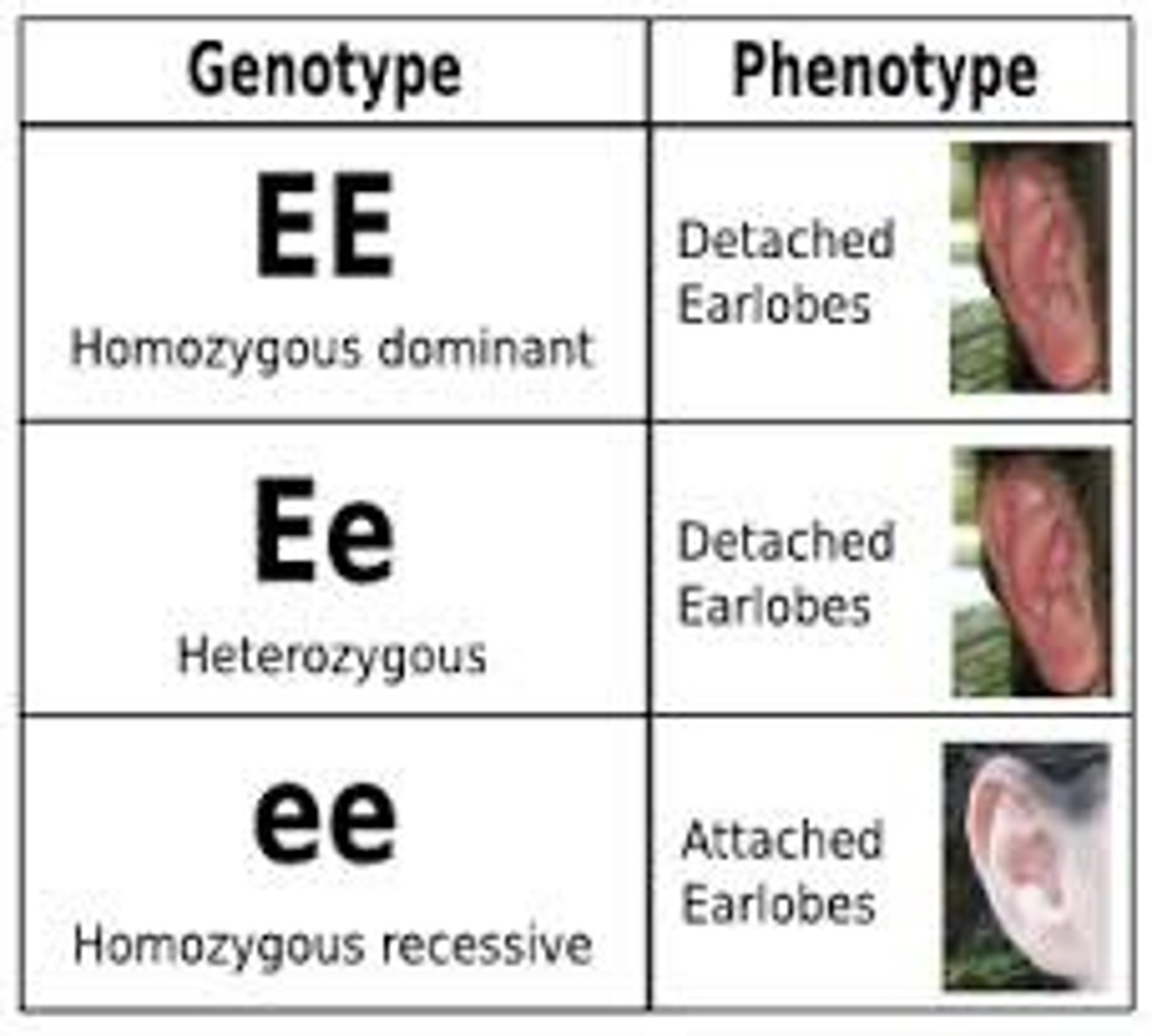
Phenotype
a set of traits expressed by an individual
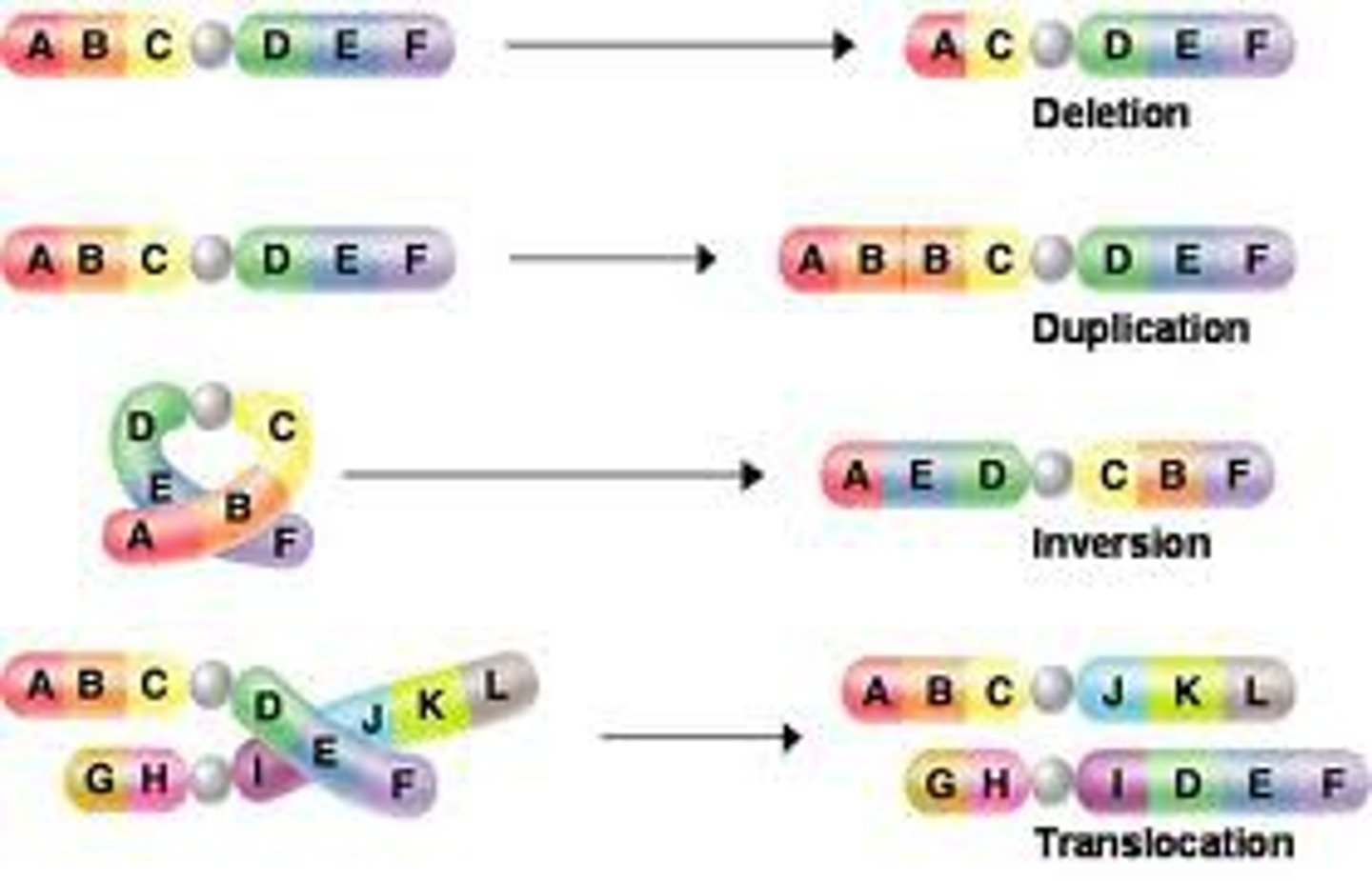
Mutation
a random error in gene replication that leads to a change
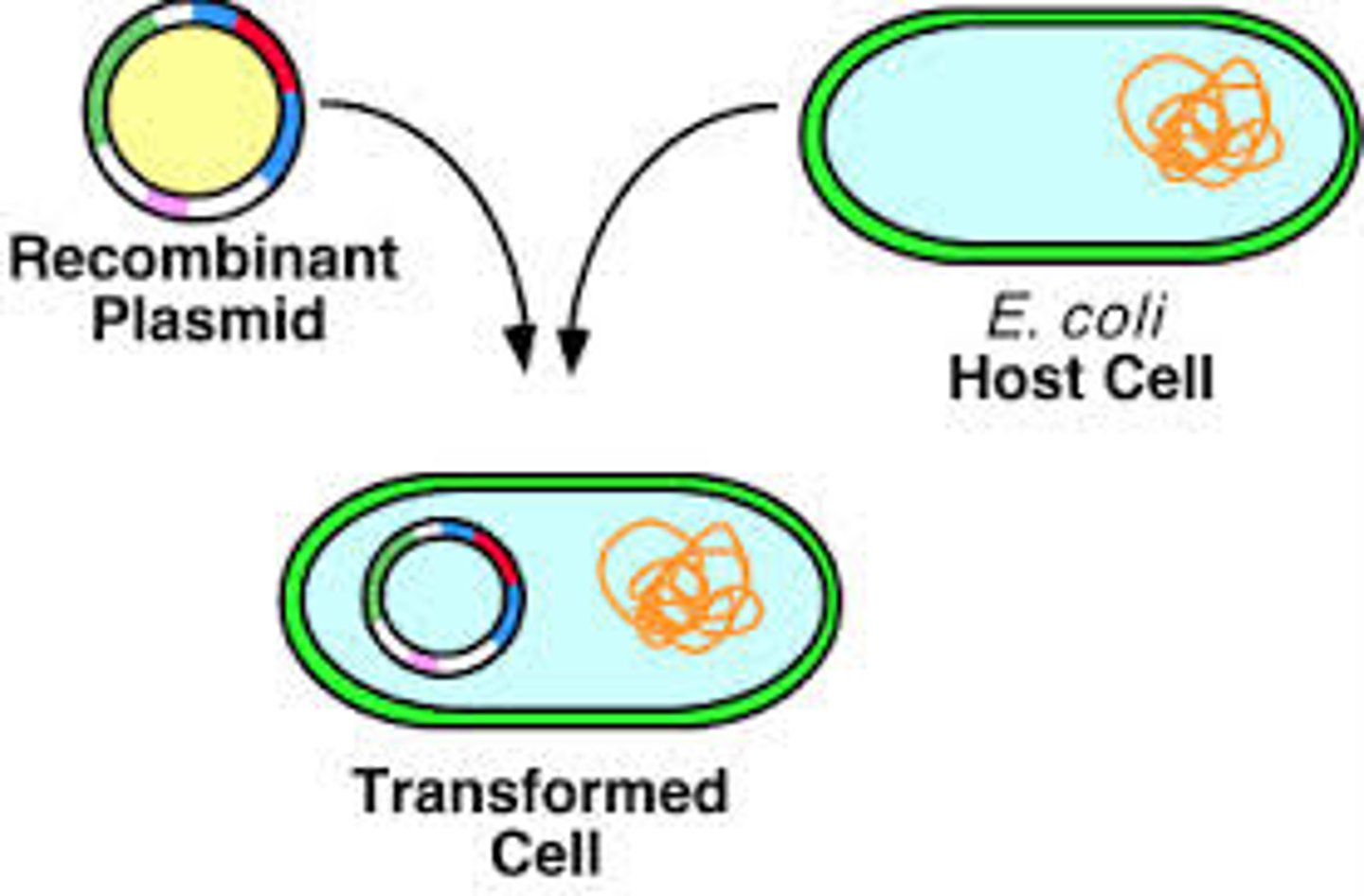
recombination
the genetic process by which one chromosome breaks off and attaches to another chromosome during reproductive cell division
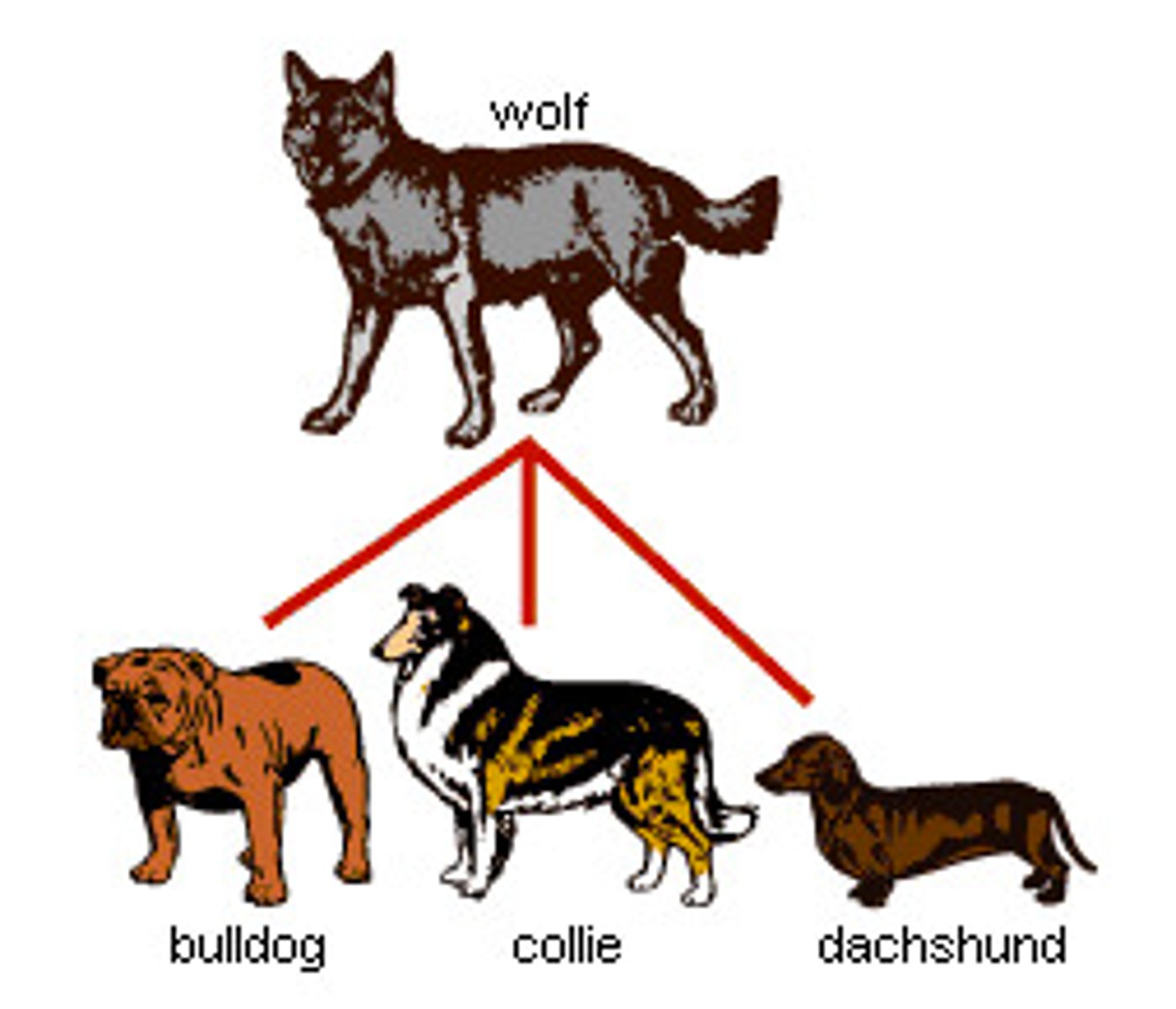
evolution by artificial selection
The process in which humans determine which individuals breed, typically with a preconceived set of traits in mind
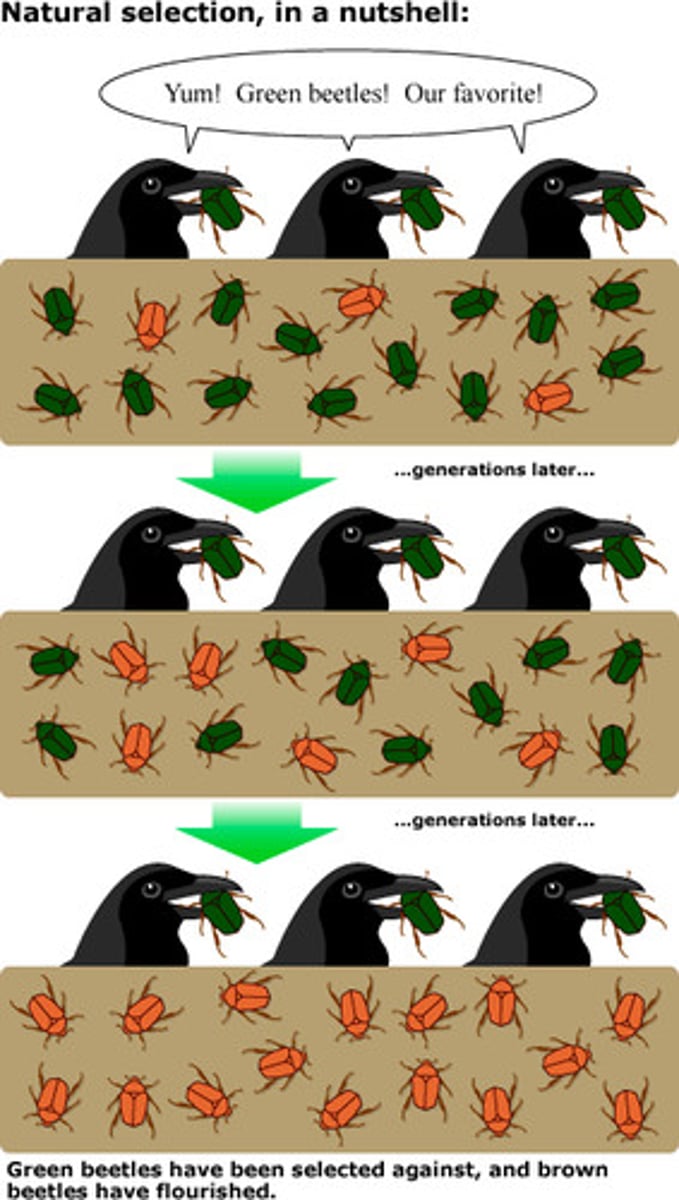
Evolution by natural selection
The process in which the environment determines which individuals survive and reproduce.
Fitness
ability to survive and reproduce

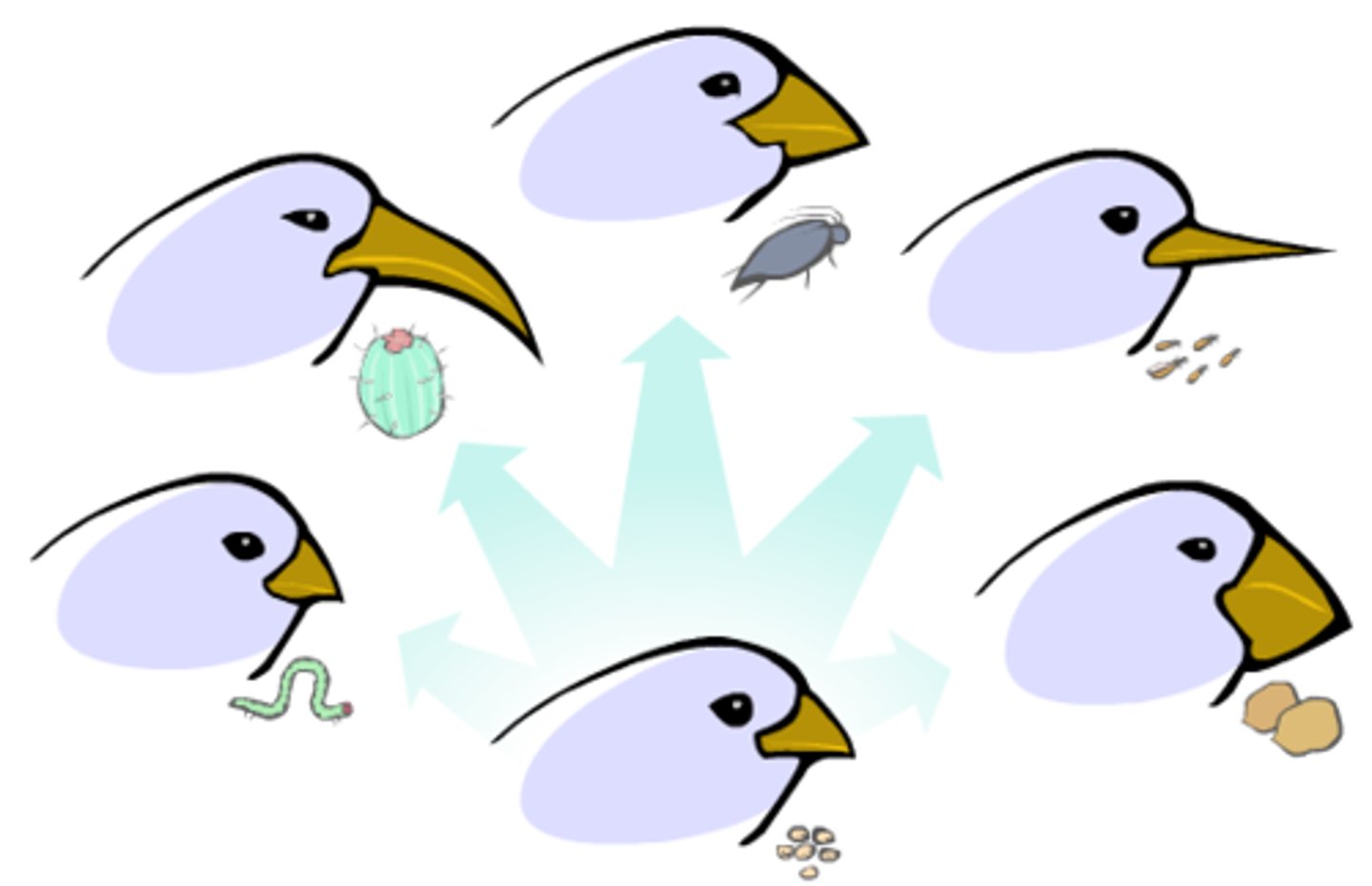
Adaptation
A characteristic that improves an individual's ability to survive and reproduce in a particular environment.
Gene Flow
movement of alleles from one population to another
genetic drift
a change in genetic composition of a population over time as a result of random mating.
bottleneck effect
a reduction in the genetic diversity of a population caused by a reduction in its size
Extinction
the diminishing of a conditioned response. DEATH
Founder Effect
change in allele frequencies as a result of the migration of a small subgroup of a population
geographic isolation
physical separation of a group of individuals from others of the same species
reproductive isolation
result of 2 populations within a species evolving separately to the point that they can no longer interbreed and produce viable offsprings.
GMO (genetically modified organism)
An organism that is created when scientists take one or more specific genes from one organism and introduce them into another organism thus creating a new version
range of tolerance
the limits to the abiotic conditions that a species can tolerate
fundamental niche
The suite of abiotic conditions under which a species can survive, grow, and reproduce
realized niche
the range of abiotic and biotic conditions under which a species actually lives
Distribution
areas of the world in which a species lives
niche generalist
a species that can live under a wide range of abiotic and biotic conditions
niche specialist
a species that is specialized to live in a specific habitat or to feed on a small group of species
mass extinction
A large extinction of species in a relatively short period of time