measurement and research applications
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
non-scientific method: method of tenacity
belief perserverence
ideas that survive because they’ve been around for a long time
non-scientific: method of intuition
just vibe
non-scientific: method of authority
ask an expert
non-scientific: rational method
use logic
non-scientific: method of empiricism
observation
what does science do?
be as objective as possible, error detection mechanisms
what is the scientific method process?
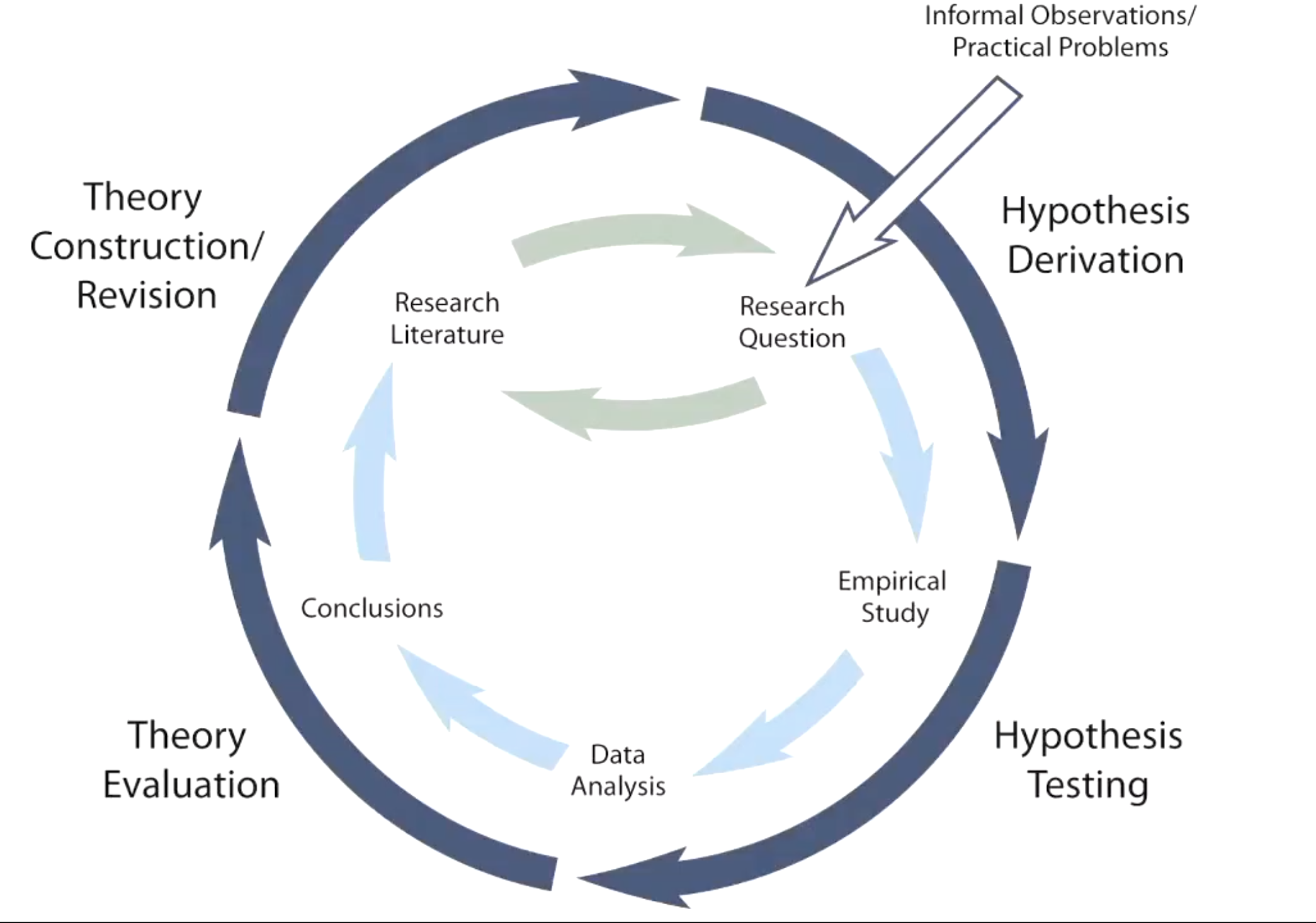
what is the hypothetico-deductive model?
just the scientific method
what are the four things hypotheses must be?
Logical
must come from previous theory
Testable
stated in such a way that the variables are measurable
Refutable/falsifiable
stated in such a way that it can be proven false
Positive
stated so it is directional /non-directional
LTRFP (let trisha rest for petes sake)
main issue in current psychology study particpants?
Sample bias: psychology students (WEIRD)
what is the experimental method attemping to do?
attempting to draw causality
what is a confounding variable?
extraneous variable that may effect the DV
what are the two sources of measurement error?
random error
systematic error
what is random error, and what type does it increase the chances of?
measurement error caused randomly
increases the chance of type 2 error (false negative)
what is systematic error and what type does it increase the chances of?
measurement error that are consistenly different from the true value in nature
increases the chance of type I error (false positive)
low precision reflects _____ error, while low accuracy reflects _____ error
random, systematic
what is a contruct?
a mental attribute that is not directly observable, but is inferred from observed behaviours
when a raw score is compared to a standard, what is a criterion referenced test?
judging it against the criteria (aka needed 8 out of 20 to pass)
when a raw score is compared to a standard, what is a norm referenced test?
judging your score relative to other people that have taken the test
derived score?
raw score thats been transformed
what is percentile score?
number of people who fall below a particular raw score
what is linear z/standard score?
how far away your score is (in SD) from the mean
can r for reliability be less than zero?
if it is, look at your data something has gone wrong
what is rxx?
correlation between scores on two administrations of the same test
if you administered an infinte amount of tests to a 6yo, what does the mean of the distribution represent, and what is the std dev of that disribution called?
true score
standard error of measurement
for any random individual (i), we can express the observed score (x) as?
made up of the true score (t) with contribution from random measurement error (e)
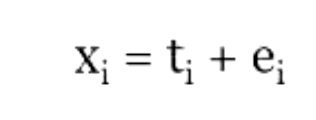
reliability (rxx) is defined as?
a ratio of two variances
variance of true scores divided by the variance of raw scores
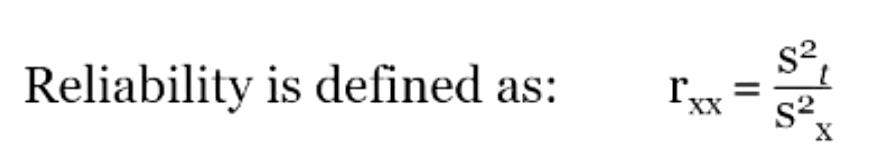
error variance is described as?
1 - rxx
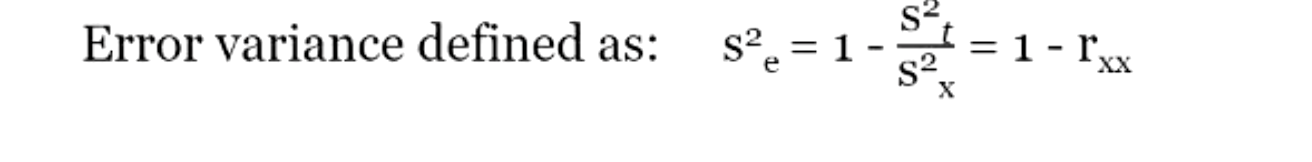
test-retest reliability?
same test is given to same group of people on two occasions
what is error variance attributed to in test-retest reliability?
time-sampling
what are alternative forms of reliability?
two versions of test contructed in the same way, but with different items
what is content sampling?
differences in item content when 2nd test is immediate or delayed
split-half reliability?
single test is administed, test is split into two equal halves
error variance in split-half reliability due to?
content sampling
how are cronbachs alpha and split-half reliability related?
cronbach alpha value is equal to the mean of all possible split-half correlation coefficients
error variance in cronbach’s alpha is attributable to?
content sampling
heterogeniety of the domain sampled
kuder-richardson?
basically cronbach’s alpha for dichotomously scored items (e.g correct / incorrect)
inter-rater reliability?
two raters provide scores for an individual on a test
error variance attributable to what in inter-rater reliability?
differences between raters
what does standard error of difference look at? What is its logo(?))
whether a difference between two scores is actually significant.
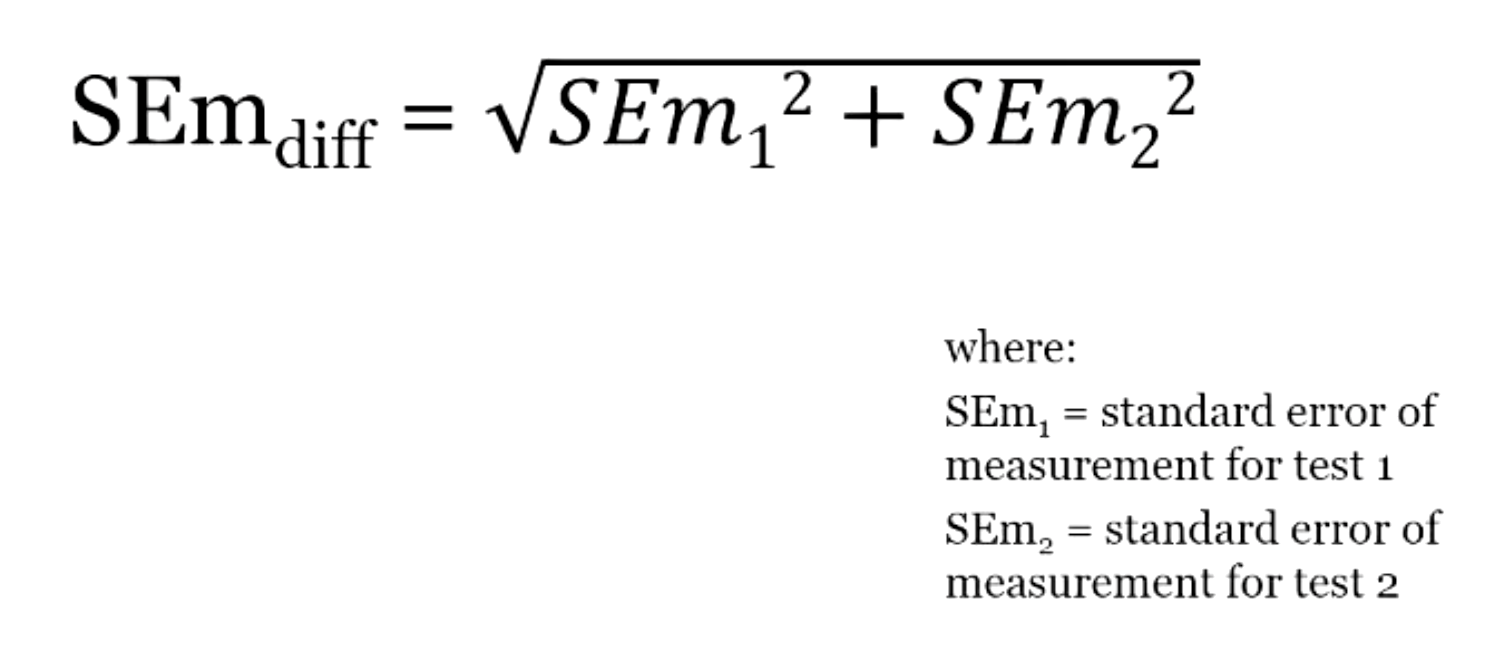
we can only calculate standard error of difference when?
the standard deviation for them is the same
what if the standerd error of difference doesn’t have the same standard deviation?
normalise the scores so they have the same std dev
when calculating the critical difference between score, once you get the SEmdiff, what do you do?
what is the interpretation of this?
at a 0.05 probability, times SEmdiff by 1.96
the interpretation of this is that the difference between the two scores to be significant would have to be ABOVE this number
what is face validity?
the test appears to be testing what it set out to test
what is content validity?
test covers a representative sample of the domain being measured
what is criterion related validity? (rxy)
test scores ‘predict’ performance on another broadly accepted measure
what is construct related validity (rxy)?
test scores reflect individual differences in a psychological construct
what are the two types of criterion-related validity and explain them.
concurrent validity
measures tests and criterion variables at the same time
predictive validity
test question then criterion variable
good level of criterion-related validity?
0.2 - 0.5
what is standard error of estimate (SEest)?
expected error in prediction of a persons score on a crietrion variable given their test score
if rxy = 1, SEest = ?
if rxy = 0, SEest = ?
0, Sy
what is decision theory?
explores how to determine the appropriate tests and criterion cut-off score
what are the two types of construct validity?
divergent validity
convergent validity
what is convergent validity?
performance on your test correlates with peformance on another test, that you would expect it to correlate with → rxy positive
what is divergent/discriminate validity?
do your test scores correlate with stuff they shouldn’t correlate with → rxy near zero
what types of validity do clark and watson think is necessary for test development and what is their definition?
substanstive validity (basically content validity)
structural validity
item selection (how similar they are)
what does cronbach’s alpha measure?
internal consistency
what does a factor analysis do?
tells you how much different stuff you are measuring in a construct
what is item response theory used for?
to determine good structural validity
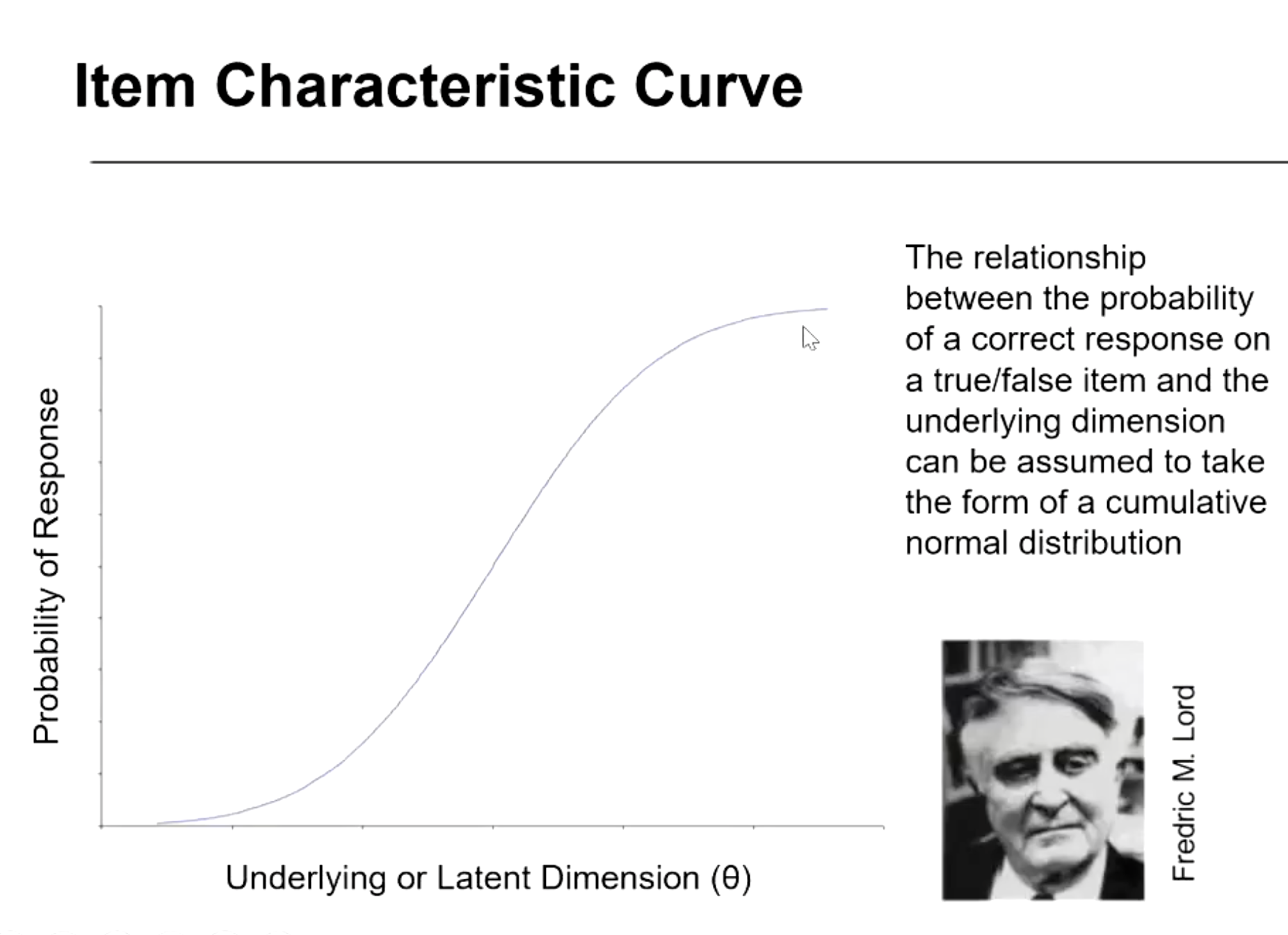
what relationship does item response theory focus on?
relationship between individual items and the latent dimension ‘O’
item characteristic curve graph?
what is internal validity?
the extent to which the study establishes a causal relationship between the IV and the DV
what is extraneous variable?
any variable other than IV and DV that could potentially effect DV
what is confounding variable?
any variable other than IV and DV that DOES actually effect DV