e) Adaptations of plants to the availability of water in their environment
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Name some xerophytes
Cacti
Marram grass
Name a hydrophyte
Water lilies
Xerophyte adaptations to reduce water loss:
Rolled leaves
Hairy leaves
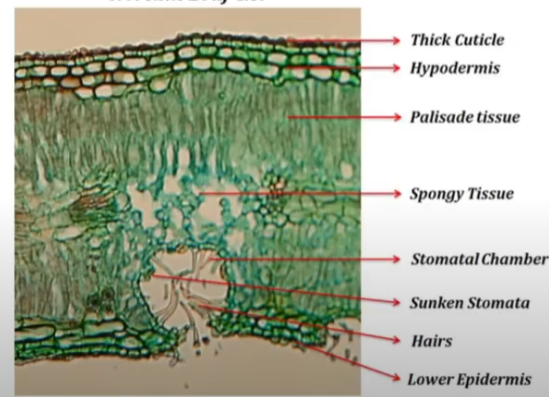
Sunken stomata
Needle like leaves
Dense spongy mesophyll layer
Less stomata
Thick waxy cuticle
Long deep root systems
Xerophyte adaptations - Rolled leaves
Reduces surface area for evaporation
Traps a layer of water vapour, creating a higher water potential outside the stomata, reducing the water vapour potential gradient, reducing evaporation of water from the leaves
Xerophyte adaptations -Hairy leaves
Traps a layer of water vapour, creating a higher water potential outside the stomata, reducing the water vapour potential gradient, reducing evaporation of water from the leaves
Xerophyte adaptations -Sunken stomata
Traps a layer of water vapour (it isn’t taken away by the wind as easily), creating a higher water potential outside the stomata, reducing the water vapour potential gradient, reducing evaporation of water from the leaves
Xerophyte adaptations -Needle like leaves
Reduces the surface area of the leaf, therefore less evaporation of water vapour

Xerophyte adaptations -Dense spongy mesophyll layer
Smaller surface area for evaporation
Xerophyte adaptations -Less stomata
Less stomata which are closed in the day
Most of the stomata will be found on the lower surfaces of the leaves to reduce evaporation
Xerophyte adaptations -Thick waxy cuticle
Waterproof, prevents water leaving through evaporation
Xerophyte adaptations -Long deep root systems
Long deep roots to take up water
There are also a high solution concentration in root hair cells to draw more water in via osmosis
Hydrophyte adaptations
Aerenchyma
Large leaves
Pneumatophore
Lots of stomata
Thin waxy cuticle
Short root system
Hydrophyte adaptations - Aerenchyma
Allows buoyancy
Hydrophyte adaptations - Large leaves
Allows large surface area for leaves to increase the rate of photosynthesis
Hydrophyte adaptations - Pneumatophores
Roots that grow out of the water to aid with gas exchange
Increases the rate of photosynthesi

Hydrophyte adaptations - Lots of stomata
Open most of the time
Found on the upper surfaces of the leaves to increase gas exchange
Hydrophyte adaptations - Thin waxy cuticle
No need for a thick waxy cuticle as water loss doesn’t need to be prevented
Hydrophyte adaptations - Short root system
Prevents damage by currents
The plants can meet its requirements for water because it lives in water.