ECTOPIC PREGNANCY
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
ectopic pregnancy
pregnancy occurs when a fertilized
egg implants outside the uterine cavity, most
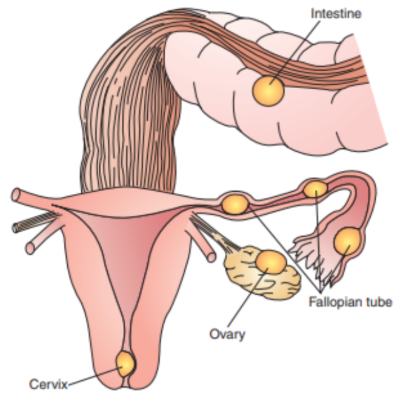
commonly in the fallopian tube (in approximately 95% of such pregnancies). 80% occur in the ampullar portion, 12% occur in the isthmus, and 8% are interstitial or fimbrial. Less frequent sit include the ovary, abdominal cavity, or cervix. It is a life-threatening condition requiring immediate medical attention.
Risk/Predisposing Factors
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PI
Infections such as chlamydia or gonorrhea
that cause scarring in the fallopian tubes.
- Previous Ectopic Pregnancy History of
ectopic pregnancies increases the likelihood
of recurrence.
- Tubal Surgery or Damage Any surgery or
trauma to the fallopian tubes can interfere
with the egg’s travel to the uterus.
- Intrauterine Device (IUD) While rare,
pregnancies occurring with an IUD in place
have a higher chance of being ectopic.
- Infertility Treatments Assisted reproductive
technologies like in vitro fertilization (IVF)
- Maternal Age Women over 35 years old are
at increased risk.
- Smoking Alters tubal motility and reduces
ciliary function in the fallopian tubes.
- Endometriosis Can lead to scarring and
adhesions that hinder proper egg
implantation.
Clinical Manifestations/ Signs &
Symptoms
Pain
Vaginal spotting or bleeding
Hemoperitoneum (Internal bleeding)
Dizziness, headache, weakness, fainting or syncope
Tender Mass
Pain
● Abdominal pain (localized or generalized)
May be confused with strong stomach pain,
it may also feel like a strong cramp.
● Shoulder Pain This is caused by free blood
tracking up the abdominal cavity and
irritating the diaphragm, and is an ominous
sign.
● Pain while urinating or having a bowel
movement.
Vaginal spotting or bleeding
Usually mild. An ectopic pregnancy is usually a failing pregnancy and falling levels of progesterone from the corpus luteum on the ovary case withdrawal bleeding.
Hemoperitoneum (Internal bleeding)
Severe internal bleeding from the affected tube can lead hemodynamic instability.
Dizziness, headache, weakness, fainting or
syncope
Resulting from internal bleeding and
hypovolemia
Tender Mass
On pelvic examination, an adnexal
mass may be felt.
Prevention
1. Prevent and Treat STIs Early diagnosis and
management of sexually transmitted
infections reduce the risk of PID
2. Stop Smoking Smoking cessation can
improve reproductive health
3. Careful Monitoring Post-Tubal Surgery
Women with previous tubal surgeries should
have close monitoring during early
pregnancy.
4. Family Planning Proper use of
contraceptives and avoidance of unintended
pregnancies in high-risk individuals
Diagnostic Tests
1. Transvaginal Ultrasound (TVS) The gold
standard for confirming the location of t
pregnancy
2. Serum Beta-hCG Abnormally low or
plateauing hCG levels suggest an abnormal
pregnancy
3. Complete Blood Count (CBC) To assess
for anemia or signs of internal bleeding
4. Culdocentesis Rarely used; checks for
blood in the peritoneal cavity
5. Laparoscopy Diagnostic and therapeutic;
allows visualization and management of
ectopic pregnancy.
Medication Management
Methotrexate
- Used for the treatment of
unruptured tubal pregnancy and for
persistent disease after
salpingostomy.
- A chemotherapeutic agent that
inhibits cell division in the
developing pregnancy. Best for
early, unruptured ectopic
pregnancies.
- Antineoplastic, Antimetabolite - used to
terminate pregnancy.
- Leucovorin - used with folic acid
antagonists, such as methotrexate.
- Vasopressors - used for their alpha and
betal properties and for stimulating
vasoconstriction in peripheral circulation.
- Vasopressin (Pitressin)- has vasopressor
and antidiuretic (ADH) activity. In linear
salpingostomy, the involved tube is
identified and freed from surroundi
structures.
Surgical Management
- Salpingostomy: Removal of the ectopic
pregnancy while preserving the fallopian
tube.
- Salpingectomy: Removal of the entire
fallopian tube, usually in cases of rupture or
severe damage.
- Laparoscopy: Minimally invasive approach
for diagnosis and treatment.
- Laparotomy: Open surgery, reserved for
unstable patients or extensive damage.
assessment
- Monitor for signs of rupture (severe pain,
hypotension, tachycardia, shoulder pain).
- Assess for vaginal bleeding and
hemodynamic stability.
- Check serum beta-hCG levels and
ultrasound reports.
interventions
1. Preoperative Care:
- Explain the procedure to the patient and
obtain informed consent.
- Administer fluids and blood products
needed.
- Monitor vital signs and signs of shock.
2. Postoperative Care
- Monitor for complications such as infection,
bleeding, or thromboembolism.
- Provide pain management.
- Educate about wound care and signs of
infection.
3. Psychological Support
- Offer counseling to address emotion
distress and grief.
- Provide resources for support groups or
therapy.
4. Patient Education
- Teach about the importance of follow-up
care, including beta-hCG monitoring.
- Discuss future pregnancy planning and risk
reduction strategies.
- Emphasize adherence to prescribed
medications and lifestyle modification