Structure and Properties
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Structure of thermoplastics (e.g polyethene)
- COVALENT BONDING between atoms/within molecules
- SECONDARY BONDING( E.G. VAN DE WAALS, H BONDING, DIPOLE-DIPOLE BONDING) between molecules -> provide strength to material
Structure of thermosets (e.g. epoxy resin)
- COVALENT BONDING between atom/ within molecule
- HIGH NUMBER OF COVALENT CROSSLINKS between polymer chain
Properties due to crosslinks
presence of crosslinks-> no plastic deformation
increase in no. of crosslinks->
decrease in elastic deformation
increase stiffness
increase hardness
increase strength
increase brittleness
Structure of elastomer (e.g. rubber(polyisoprene))
- COVALENT BONDING between atoms/within molecules
- LOW NUMBER OF CROSSLINKS between long polymer chain
Structure of ceramics
- IONIC OR COVALENT BONDING between metallic and non-metallic element throughout whole structure
Properties of ionic bonded ceramics vs covalent bonded ceramics
theoretically:
ionic: non directional->undergo plastic deformation and slip and low stiffness
covalent: directional-> cannot slip and high stiffnesspractically:
ionic: high stiffness and brittle
covalent: high stifffness and brittle
Definition of hardness
compression strength
- for non-brittle materials
- dimensions of indentation
Name of hardness test
Vichers Hardness Test
Definition of stiffness
resisting elastic deformation
- determined by elastic strain of Youngs Modulus/ elastic modulus
Definition of strength
stress to break/fail material
- stress (Pa)
Definition of tensile strength AKA ultimate tensile strength (UTS)
tensile stress to fracture/fail/neck material
Definition of compressive strength
YIELD STRENGTH(metal &plastic): stress to undergo plastic deformation
(yield stress<UTS stress)
FRACTURE STRESS(ceramics due to no slip): compressive stress to fracture material
Definition of ductility
degree of plastic deformation before fracture
- strain (%)
Definition of toughness
work required to fracture material
- brittle vs tough
Tough material for plastically deformable materials
- slip occurs before fracture
- slip absorbs energy
- make defect tip blunt
- local stress decrease
Tough material for non-plastically deformable materials
low number of defects+not sharp long or deep
- acts as stress concentrations
-> local stress near defect>>global stress - local bond break
-low apparent stress
Definition of fatigue stress
resist failure under cyclic stress
- occur below UTS or yield stress
- affected by amplitude of alternating stress
Definition of corrosion resistance
rate of reaction with environment
Definition of abrasion resistance
avoidance of wear between sliding contact components
Definition of necking
decrease in cross-sectional area at failure point
conservation in volume
-> becomes longer and thinner
Result of necking
global load required to deform decreases
Proof strength
experimental proven stress value at 0.1% or 0.2% strain
Theoretical relationship of fracture stress and stiffness for non brittle material
δ=0.1E
Definition of viscoelasticity
time-dependent elastic behaviour
Definition of strain-rate sensitive
speed of strain affecting stiffness
Definition of isotropic
same properties in all direction
Can ionic bonds shear?
- non-directional bond
- has to slip twice to maintain low energy change distribution
(one slip will have repulsion between like ions) - bonds dont break
Can covalent bond shear
- highly directional bond, thus cannot slip
Factor affecting strength of thermoplastics
strength dependent on:
- weak intermolecular forces between covalently bonded molecules
types of intermolecular bonding
Van der Waals
H bonds
Secondary bonding(dipolar interaction)
Definition of dipole-dipole interaction
a positive portion of a polar molecule is attracted to the negative portion of another polar molecule
weak intermolecular bond
Definition of a Van der Waals bond
- molecules form temporary dipoles
- form weak intermolecular bonds
Can metallic bonds shear?
- non-directional
- easily slip
Structure of amorphous solid
- short range order over few molecular dimensions
- disordered arrangement of molecules (supercooled liquid)
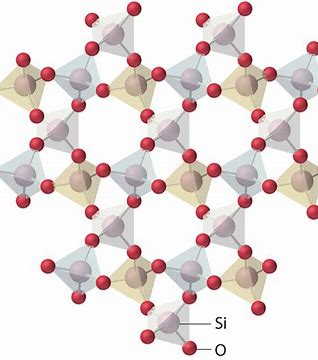
Structure of crystalline solid
- long range order throughout solid
- ordered arrangement of molecules
Difference in MP of amorphous and crystalline solids
Crystalline: defined MP
Amorphous: undefined MP, soften slowly-> different amount of thermal energy needed to overcome different interactions
Formation of amorphous structure
cool liquid rapidly
- easier to do with molecules, due to more complex structures
-> metal is unlikely amorphous
Types of material that is amorphous
Metal: assumed always crystalline
Ceramics: most are crystalline
Polymer:
Thermopolymer: amorphous by default
-> can change degree of crystallinity by processing
thermosets & elastomer: amorphous
-> crosslinks prevents ordering
Process of creating amorphous metal
rotating copper disc process
Process of increasing degree of crystallinity for thermopolymer
- strain polymer until before final failure
- large strain aligned the molecule
Change in properties from amorphous thermopolymer and crystalline thermopolymer
- density increase
- stiffness increase
- yield strength increase
- UTS stress increase
- toughness decrease
- ductility decrease
Definition of glass transition temperature
Temperature where a hard/glassy amorphous solid turns molten