Everything for micro final
1/982
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
983 Terms
Which two staining techniques employ a mordant?
Gram stain and acid-fast stain
Gram stain and capsule stain
Simple stain and acid-fast stain
Capsule stain and flagella stain
Gram stain and flagella stain
5
Which of the following uses glucose for carbon and energy?
chemoautotroph
chemoheterotroph
photoautotroph
photoheterotroph
2
Which of the following statements about gram-negative cell walls is FALSE?
They are sensitive to penicillin.
They are toxic to humans.
They have an extra outer layer composed of lipoproteins, lipopolysaccharides, and phospholipids.
They protect the cell in a hypotonic environment.
Their Gram reaction is due to the outer membrane.
1
In non-cyclic photophosphorylation, excited electrons ultimately ________.
combine with hydrogen ions and NADP+ to produce NADPH
flow through ATP synthase
generate light within the spectrum of green wavelengths
are used to form water
return to chlorophyll
1
The functions of the glycocalyx in bacteria include all of the following except:
Biofilm formation
Binary fission
Increased virulence
Protection against dehydration
Source of nutrition
2
Which of the following pairs is mismatched?
safranin – acid dye
carbolfuchsin – basic dye
alcohol-acetone - decolorizer
iodine – mordant
crystal violet – basic dye
1

In the figure, where is ATP produced?
a
b
c
d
e
5
Which of the following structures is not a functionally analogous pair?
Chloroplasts — thylakoids
9+2 flagella — bacterial flagella
Cilia — pili
Mitochondria — prokaryotic plasma membrane
Nucleus — nucleoid region
3
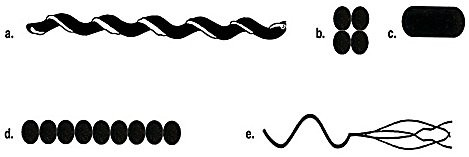
Which drawing in the figure is streptococci?
a
b
c
d
e
4
Cyanobacteria are a type of
chemoautotroph.
chemoheterotroph.
photoautotroph.
photoheterotroph.
3
Which of the following statements is incorrect about prokaryotic cells?
They typically have a circular chromosome.
They reproduce by binary fission.
They lack membrane-enclosed organelles.
They lack a plasma membrane.
Their DNA is not enclosed within a membrane.
4
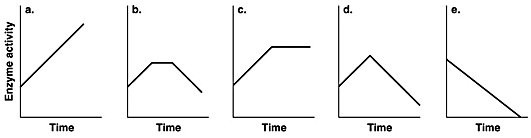
Which of the graphs in the figure best illustrates the activity of an enzyme that is saturated with substrate?
a
b
c
d
e
3
Which of the following statements regarding metabolism is not possible?
Anabolic reactions are degradative.
Heat may be released in both anabolic and catabolic reactions.
ATP is formed in catabolic reactions.
ADP is formed in anabolic reactions.
1
Microorganisms that catabolize sugars into ethanol and CO2 gas would most likely be categorized as ________.
anaerobic respirers
alcohol fermenters
aerobic respirers
heterolactic fermenters
homolactic fermenters
2
A ________ can be used to view the internal structures of cells in its native state?
fluorescence microscope
phase-contrast microscope
electron microscope
compound light microscope
scanning acoustic microscope
2
________ allows a cell transport of substances from a lower to a higher concentration area.
Simple diffusion
Active transport
Facilitated diffusion
Extracellular enzymes
Aquaporins
2
Which of the following is NOT found or observed to occur in both mitochondria and prokaryotes?
cell wall
ATP-generating mechanism
70S ribosomes
binary fission
circular chromosome
1
Which microscope takes advantage of differences in the refractive indexes of cell structures?
darkfield microscope
phase-contrast microscope
electron microscope
fluorescence microscope
compound light microscope
2
A virus measures 100 nm in length. What is its length in μm?
1 μm
10 μm
0.1 μm
0.01 μm
0.001 μm
3
An enzyme, citrate synthase, in the Krebs cycle is inhibited by ATP. This is an example of all the following except:
Feedback inhibition
Allosteric inhibition
Noncompetitive inhibition
Competitive inhibition
4
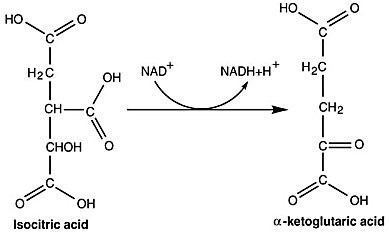
Which compound is being reduced in the reaction shown in the figure?
NADH
isocitric acid and α-ketoglutaric acid
α-ketoglutaric acid and NAD+
NADH and isocitric acid
NAD+
5
Which statements correspond to amphibolic pathways?
1. Anabolic and catabolic reactions are joined through common intermediate.
2. They are shared metabolic pathways.
3. Feedback inhibition can help regulate rates of reactions.
4. Both types of reactions are necessary but do not occur simultaneously.
2, 3, 4
2, 4
1, 2, 3, 4
1, 2, 3
1 only
4
Which of the following statements about anaerobic cellular respiration is not true?
It yields lower amounts of ATP when compared to aerobic respiration.
The complete Krebs cycle is utilized.
It generates ATP.
It involves the reduction of an organic final electron acceptor.
It requires cytochromes.
4
Which of the following is the best definition of oxidative phosphorylation?
ATP is directly transferred from a substrate to ADP.
Electrons are passed through a series of carriers to O2.
A proton gradient allows hydrogen ions to flow back into the cells through transmembrane protein channels, releasing energy that is used to generate ATP.
Electrons are passed through a series of carriers to an organic compound.
3
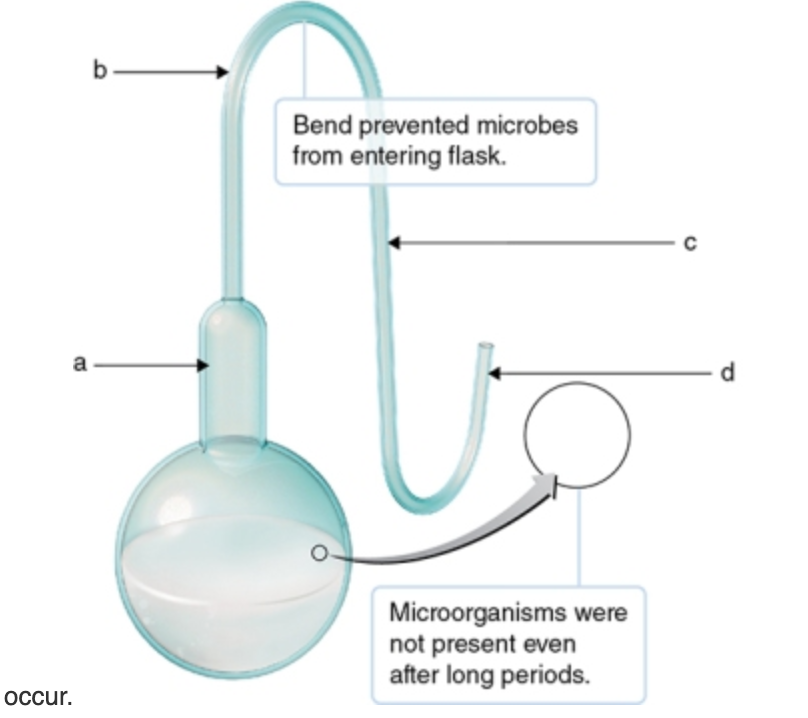
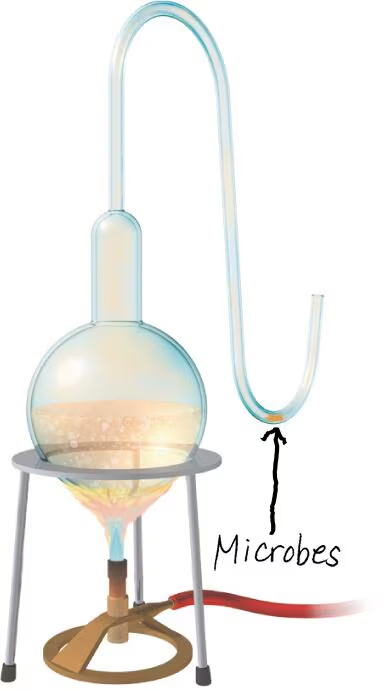
1) Predict which scenarios would most likely produce growth/airborne microbial contamination of sterile beef broth if Pasteur's S-shaped neck flask were cut.
a: break near flask.
b: break before the first curve.
c: beak between the first and second curve in the S-shaped neck.
d: break after the second curve in the S-shaped flask.
a,b
2) Which of the following statements are TRUE?
1. Electron carriers are located at ribosomes.
2. ATP is a common intermediate between catabolic and anabolic pathways.
3. ATP is used for long-term storage of energy and so is often found in storage granules.
4. Anaerobic organism can generate ATP via respiration.
5. ATP can be generated by the flow of protons across protein channels.
2, 4, 5
3) What is defining about fermentation?
the partial oxidation of glucose with organic molecules serving as electron acceptors
4) What organism type has a carbon source of CO2 with inorganic molecules as energy source?
chemoautotroph
5) Which of the following is NOT a functionally analogous pair?
Select one:
a. 9+2 flagella - bacterial flagella
b. mitochondria - prokaryotic plasma membrane
c. nucleus -nucleiod region
d. chloroplasts - thylakoids
e. cilia - pili
e
Chapter 1 VT
Which is NOT an emerging pathogen as described in your text.
Emerging infectious diseases (EIDs) are diseases that are new or changing and are either increasing in incidence or have the potential to increase in the near future
list of emerging infectious diseases:
Covid
Monkeypox
Zika virus
Influenza
Antibiotic resistant infections
Ebola
Marburg virus
Pretty sure the answer on the exam when this question came up was polio (cuz everyone’s been vaccinated)
Chapter 3 VT
What happens to Gram + and Gram - cells if you forget to do the mordant step during a Gram staining?
Both gram + and - cells will become colorless from decolorizer —> inaccurate gram staining results
Chapter 4 VT
In bacteria, photosynthetic pigments are found in...
chromatophores
Chapter 5 VT
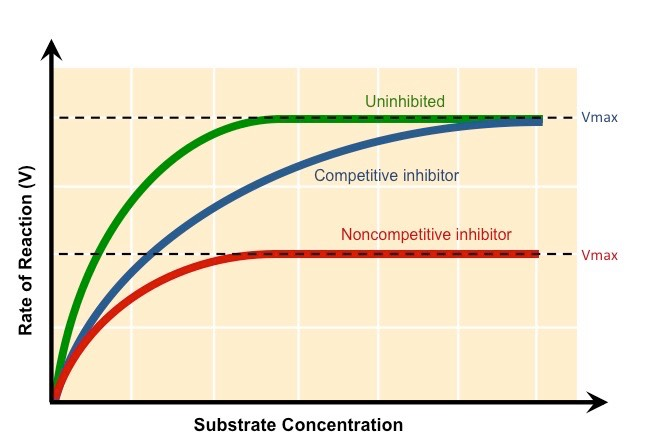
Be able to explain a graph that shows the normal reaction rate of an enzyme and the reaction rate when a competitive inhibitor is present.
if it’s an irreversible competitive inhibitor, the reaction rate would decrease significantly and flatline compared to the uninhibited enzyme’s reaction rate (similar to red line)
if it’s a reversible competitive inhibitor, the reaction rate would initially decrease compared to the uninhibited enzyme’s reaction rate but eventually equalize with increasing substrate concentration (similar to blue line)
Knowledge and Comprehension
How did the idea of spontaneous generation come about?
People saw
flies coming out of manure
maggots coming out of dead animals,
microorganisms appearing in liquids after 1-2 days
—> so they believed living organisms arose from nonliving matter
Briefly state the role microorganisms play in each of the following:
biological control of pests
1. Certain microorganisms cause diseases in insects. Microorganisms that kill insects can be effective biological control agents because they are specific for the pest and do not persist in the environment.
Briefly state the role microorganisms play in each of the following:
recycling of elements
Carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and phosphorus are required for all living organisms. Microorganisms convert these elements into forms that are useful for other organisms. Many bacteria decompose material and release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, which plants use. Some bacteria can take nitrogen from the atmosphere and convert it into a form that plants and other microorganisms can use.
Briefly state the role microorganisms play in each of the following:
normal microbiota
Normal microbiota are microorganisms that are found in and on the human body. They do not usually cause disease and can be beneficial.
Briefly state the role microorganisms play in each of the following:
sewage treatment
Organic matter in sewage is decomposed by bacteria into carbon dioxide, nitrates, phosphates, sulfate, and other inorganic compounds in a wastewater treatment plant.
Briefly state the role microorganisms play in each of the following:
human insulin production
Recombinant DNA techniques have resulted in insertion of the gene for insulin production into bacteria. These bacteria can produce human insulin inexpensively.
Briefly state the role microorganisms play in each of the following:
vaccine production
Microorganisms can be used as vaccines. Some microbes can be genetically modified to produce components of vaccines.
Briefly state the role microorganisms play in each of the following:
biofilms
Biofilms are aggregated bacteria adhering to each other and to a solid surface.

Into which field of microbiology would the following scientists best fit?
A
a. 1, 3

Into which field of microbiology would the following scientists best fit?
B
b. 8

Into which field of microbiology would the following scientists best fit?
C
c. 1, 4, 5

Into which field of microbiology would the following scientists best fit?
D
d. 2

Into which field of microbiology would the following scientists best fit?
E
e. 5

Into which field of microbiology would the following scientists best fit?
F
f. 3

Into which field of microbiology would the following scientists best fit?
G
g. 6

Into which field of microbiology would the following scientists best fit?
H
h. 7

Match the microorganisms in column A to their descriptions in column B.
A
a. 7

Match the microorganisms in column A to their descriptions in column B.
B
b. 4

Match the microorganisms in column A to their descriptions in column B.
C
c. 3

Match the microorganisms in column A to their descriptions in column B.
D
d. 2

Match the microorganisms in column A to their descriptions in column B.
E
e. 6

Match the microorganisms in column A to their descriptions in column B.
F
f. 5

Match the microorganisms in column A to their descriptions in column B.
G
g. 1

Match the people in column A to their contribution toward the advancement of microbiology, in column B.
A
a. 11

Match the people in column A to their contribution toward the advancement of microbiology, in column B.
B
b. 14

Match the people in column A to their contribution toward the advancement of microbiology, in column B.
C
c. 15

Match the people in column A to their contribution toward the advancement of microbiology, in column B.
D
d. 17

Match the people in column A to their contribution toward the advancement of microbiology, in column B.
E
e. 3

Match the people in column A to their contribution toward the advancement of microbiology, in column B.
F
f. 9

Match the people in column A to their contribution toward the advancement of microbiology, in column B.
G
g. 10

Match the people in column A to their contribution toward the advancement of microbiology, in column B.
H
h. 2

Match the people in column A to their contribution toward the advancement of microbiology, in column B.
I
i. 1

Match the people in column A to their contribution toward the advancement of microbiology, in column B.
J
j. 12

Match the people in column A to their contribution toward the advancement of microbiology, in column B.
K
k. 18

Match the people in column A to their contribution toward the advancement of microbiology, in column B.
L
l. 4

Match the people in column A to their contribution toward the advancement of microbiology, in column B.
M
m. 7

Match the people in column A to their contribution toward the advancement of microbiology, in column B.
N
n. 5

Match the people in column A to their contribution toward the advancement of microbiology, in column B.
O
o. 6

Match the people in column A to their contribution toward the advancement of microbiology, in column B.
P
p. 8

Match the people in column A to their contribution toward the advancement of microbiology, in column B.
Q
q. 13

Match the people in column A to their contribution toward the advancement of microbiology, in column B.
R
r. 16
It is possible to purchase the following microorganisms in a retail store. Provide a reason for buying each.
a. Bacillus thuringiensis
b. Saccharomyces
a. sold as a biological insecticide
b. the yeast sold for making bread, wine, and beer
NAME IT What type of microorganism has a peptidoglycan cell wall, has DNA that is not contained in a nucleus, and has flagella?
Bacterium

DRAW IT Show where airborne microbes ended up in Pasteur’s experiment.
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a scientific name?
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Tubercle bacillus
1
Which of the following is not a characteristic of bacteria?
are prokaryotic
have peptidoglycan cell walls
have the same shape
grow by binary fission
have the ability to move
3
Which of the following is the most important element of Koch’s germ theory of disease? The animal shows disease symptoms when
the animal has been in contact with a sick animal.
the animal has a lowered resistance.
a microorganism is observed in the animal.
a microorganism is inoculated into the animal.
microorganisms can be cultured from the animal.
4
Recombinant DNA is
DNA in bacteria.
the study of how genes work.
the DNA resulting when genes of two different organisms are mixed.
the use of bacteria in the production of foods.
the production of proteins by genes.
3
Which of the following statements is the best definition of biogenesis?
Nonliving matter gives rise to living organisms.
Living cells can only arise from preexisting cells.
A vital force is necessary for life.
Air is necessary for living organisms.
Microorganisms can be generated from nonliving matter.
2
Which of the following is a beneficial activity of microorganisms?
Some microorganisms are used as food for humans.
Some microorganisms use carbon dioxide.
Some microorganisms provide nitrogen for plant growth.
Some microorganisms are used in sewage treatment processes.
all of the above
5
It has been said that bacteria are essential for the existence of life on Earth. Which of the following is the essential function performed by bacteria?
control insect populations
directly provide food for humans
decompose organic material and recycle elements
cause disease
produce human hormones such as insulin
3
Which of the following is an example of bioremediation?
application of oil-degrading bacteria to an oil spill
application of bacteria to a crop to prevent frost damage
fixation of gaseous nitrogen into usable nitrogen
production by bacteria of a human protein such as interferon
all of the above
1
Spallanzani’s conclusion about spontaneous generation was challenged because Antoine Lavoisier had just shown that oxygen was the vital component of air. Which of the following statements is true?
All life requires air.
Only disease-causing organisms require air.
Some microbes do not require air.
Pasteur kept air out of his biogenesis experiments.
Lavoisier was mistaken.
3
Which of the following statements about E. coli is false?
E. coli was the first disease-causing bacterium identified by Koch.
E. coli is part of the normal microbiome of humans.
E. coli is beneficial in human intestines.
E. coli gets nutrients from intestinal contents.
None of the above; all the statements are true.
1
Analysis
How did the theory of biogenesis lead the way for the germ theory of disease?
People had originally thought that diseases were punishment for someone's crimes because they believed that living things could just spontaneously pop up. Pasteur showed that the living cells can only come from another living cell. This made the germ theory of disease possible because diseases do come from microorganisms.
1876, Robert Koch found first proof that bacteria cause disease through his discovery of anthrax organism in affected individuals
Even though the germ theory of disease was not demonstrated until 1876, why did Semmelweis (1840) and Lister (1867) argue for the use of aseptic techniques?
Both Semmelweis and Lister observed healthier or more positive results from their patients by using aseptic techniques. These techniques prevent contamination from unwanted micro-organisms which are now became the standard practices in laboratory and many medical procedures.
The genus name of a bacterium is “erwinia,” and the specific epithet is “amylovora.” Write the scientific name of this organism correctly. Using this name as an example, explain how scientific names are chosen.
The scientific name of this organism is Erwinia amylovora. First name is the genus name and can be thought of like our family name. Second name is the specific epithet can be thought of like your personal name. Scientific names can describe an organism, honor a scientist, or identify the habitat of a species.
Find at least three supermarket products made by microorganisms. (Hint: The label will state the scientific name of the organism or include the word culture, fermented, or brewed.)
1. Cheese; live cultures in ingredients list, lactic acid bacteria
2. Alcoholic beverages like beer and wine; yeasts used to ferment the sugars from grapes or barley
3. Insect/bug killers; bacillus thuringiensis which is a bacterium that produces insecticidal proteins that destroy the lining of insects
yogurt
bread
In the 1960s, many physicians and the public believed that infectious diseases were retreating and would be fully conquered. Discuss why this didn’t happen. Is it possible?
Infectious diseases were/are not fully conquered due to mutation that bacterias goes through. Bacteria become resistant to antibiotics available, making it very hard to completely eradicate diseases. Some disease got really close to become eradicated, such as Polio and Measles but this hasn't been possible due to some people not being vaccinated.
Exception: Small Pox is the only diseases that has been completely eradicated, thanks to vaccination
Clinical Applications and Evaluations
The prevalence of arthritis in the United States is 1 in 10,000 children. However, 1 in 10 children in Lyme, Connecticut, developed arthritis between June and September 1973. Allen Steere, a rheumatologist at Yale University, investigated the cases in Lyme and found that 25% of the patients remembered having a skin rash during their arthritic episode and that the disease was treatable with penicillin. Steere concluded that this was a new infectious disease and did not have an environmental, genetic, or immunologic cause.
a. What was the factor that caused Steere to reach his conclusion?
b. What is the disease?
c. Why was the disease more prevalent between June and September?
A. the factor that caused Steere to reach his conclusion was that the disease was treated with penicillin, if it was arthritis it couldn't have been cured with penicillin
b. the disease was lyme disease (a bacterial infection caused by borrelia) that if untreated can lead to joint pains and stiffness
c. it is was more prevalent between June and September because the insect or tick that transmits that disease is more prevalent in those months. the time period favorable to young ticks, they feed on animals and increase the rate the disease spreads
In 1864, Lister observed that patients typically recovered completely from simple fractures but that compound fractures, in which parts of the broken bone pierce the skin, had “disastrous consequences.” He knew that the application of phenol (carbolic acid) to fields in the town of Carlisle prevented cattle disease. Lister treated compound fractures with phenol, and his patients recovered without complications.
How was Lister influenced by Pasteur’s work?
Why was Koch’s work still needed?
Joseph Lister was influenced by Louis Pasteur's germ theory. Pasteur demonstrated that microorganisms cause disease and rotting, but they could be killed through various means such as chemical solutions. This inspired Lister to experiment with chemical solutions and develop antiseptic methods in surgery since he believed these germs were the cause of infections.
Robert Koch's expanded and clarified the germ theory. Koch's methods to isolate and grow bacteria in a laboratory setting established definitive links between specific organisms and diseases, and his guidelines, known as Koch's postulates, are still used to identify the causative agents of infectious diseases.
Discuss whether antibacterial soaps and detergents should be used in the home.
it is better NOT to use antibacterial soaps at home
it is best to use normal soap and wash hands well for 20 seconds
it is important to keep the normal microbiota in the skin which protects against harmful pathogens
antibacterial soap will kill the "good" bacteria along with harmful pathogens
Knowledge and Comprehension