(E1PX1)Basic Chemistry Review for Lecture Exam 1
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
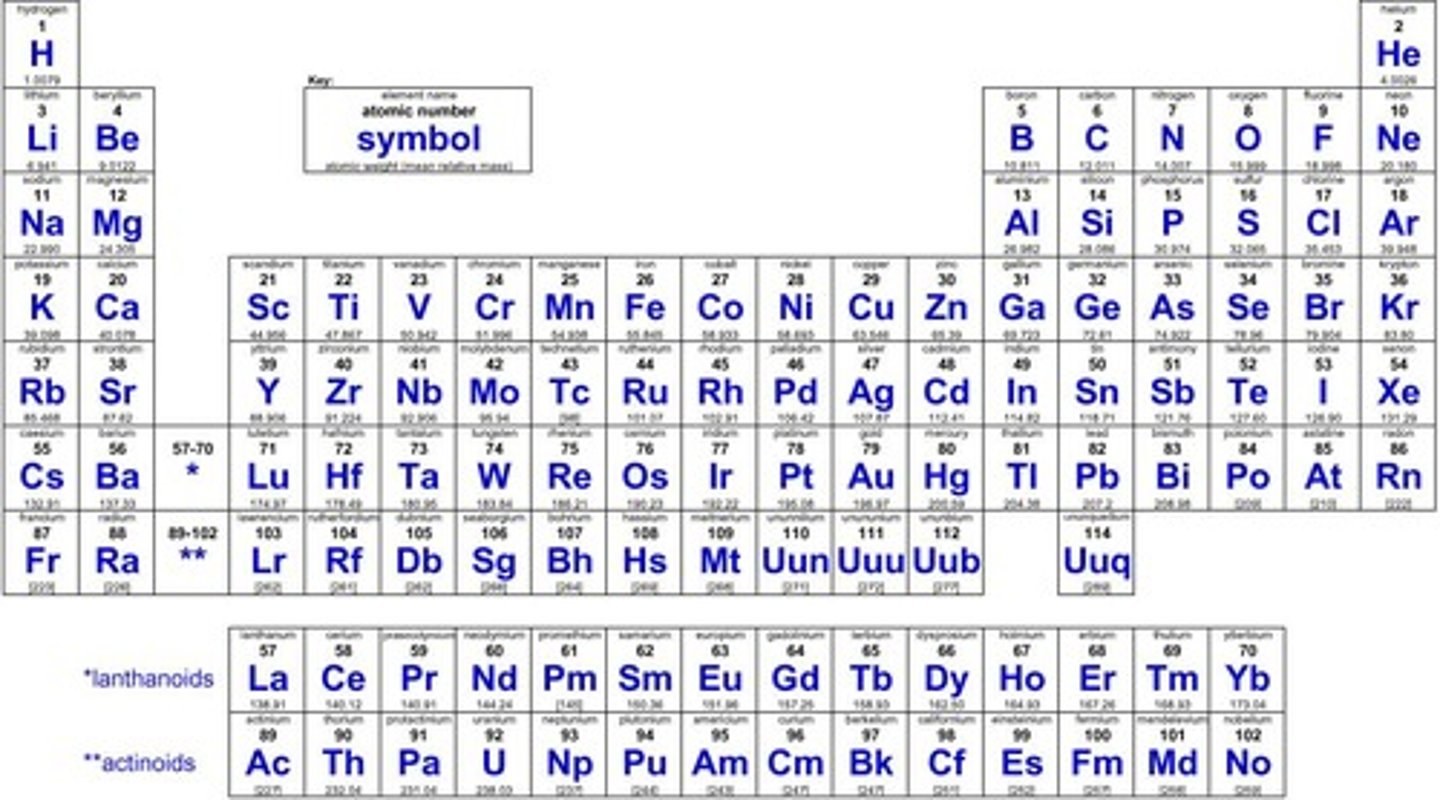
Element
Substance made of one type of atom.
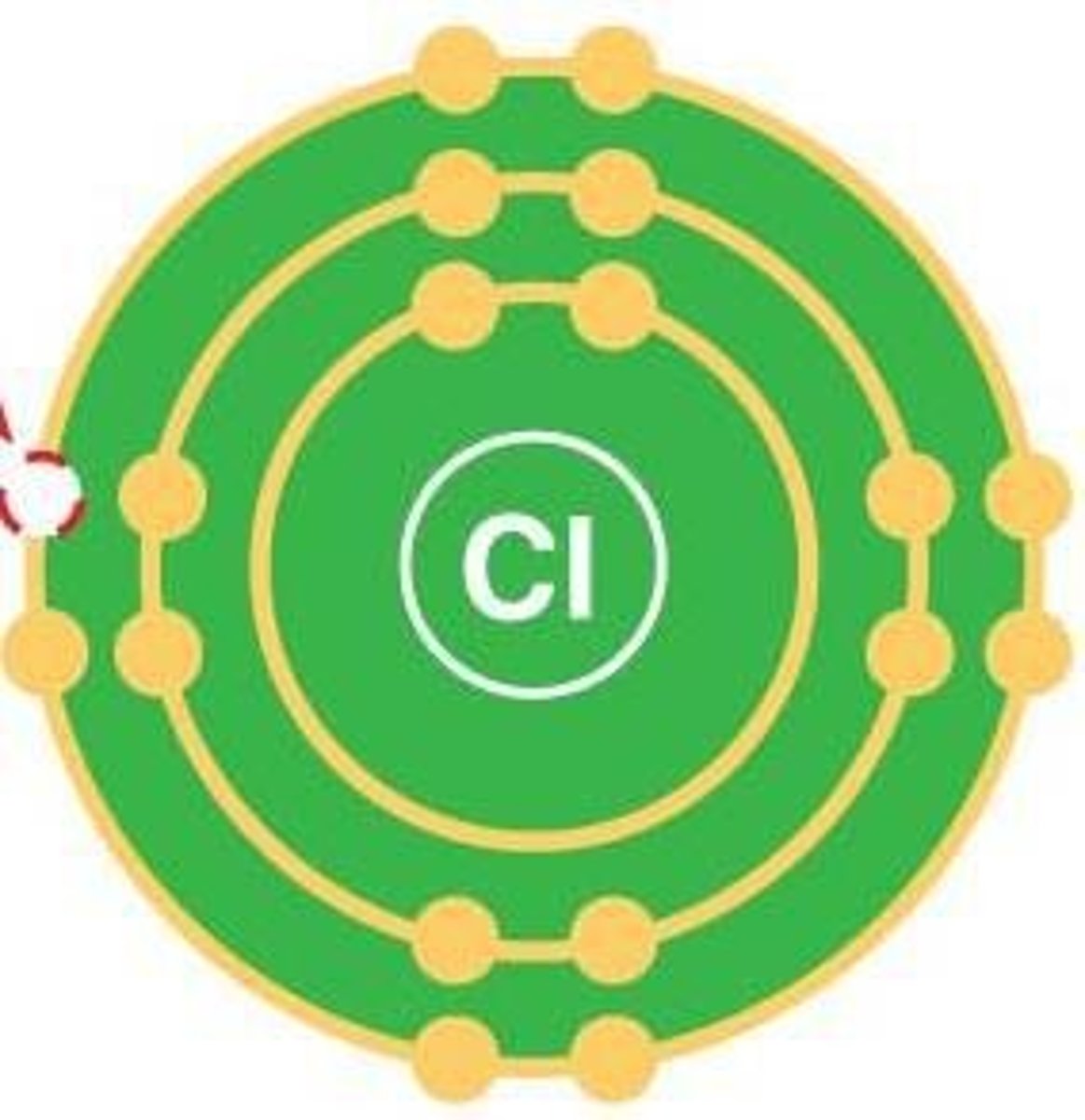
Atom
Smallest unit of an element.
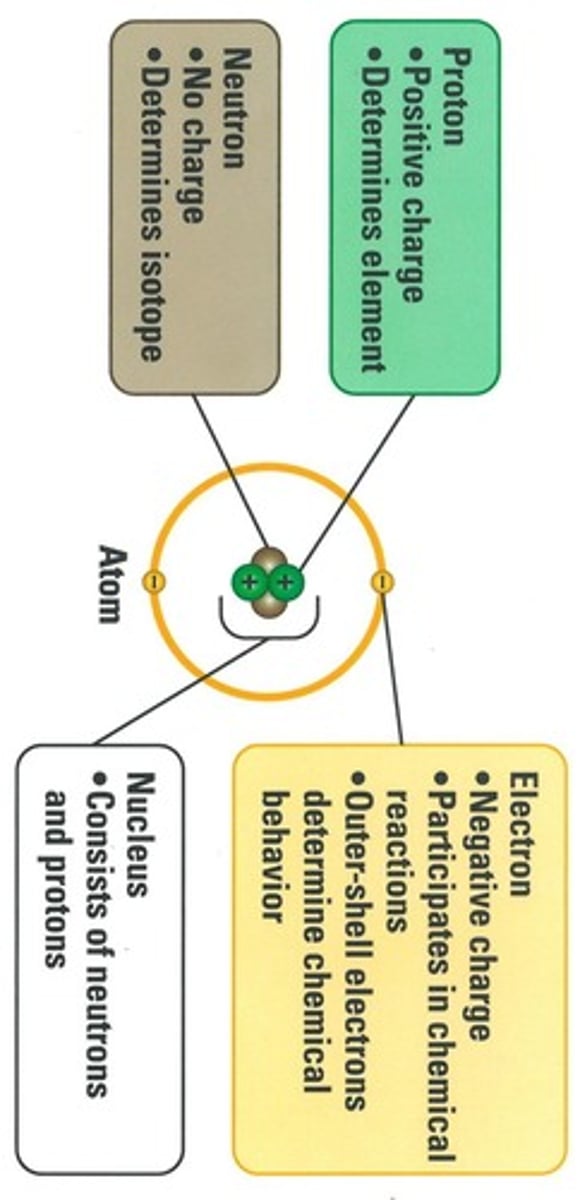
Proton
Positive charge, 1 mass unit, in nucleus.
Neutron
No charge, 1 mass unit, in nucleus.
Electron
Negative charge, negligible mass, orbits nucleus.
Atomic number
Number of protons in an element.
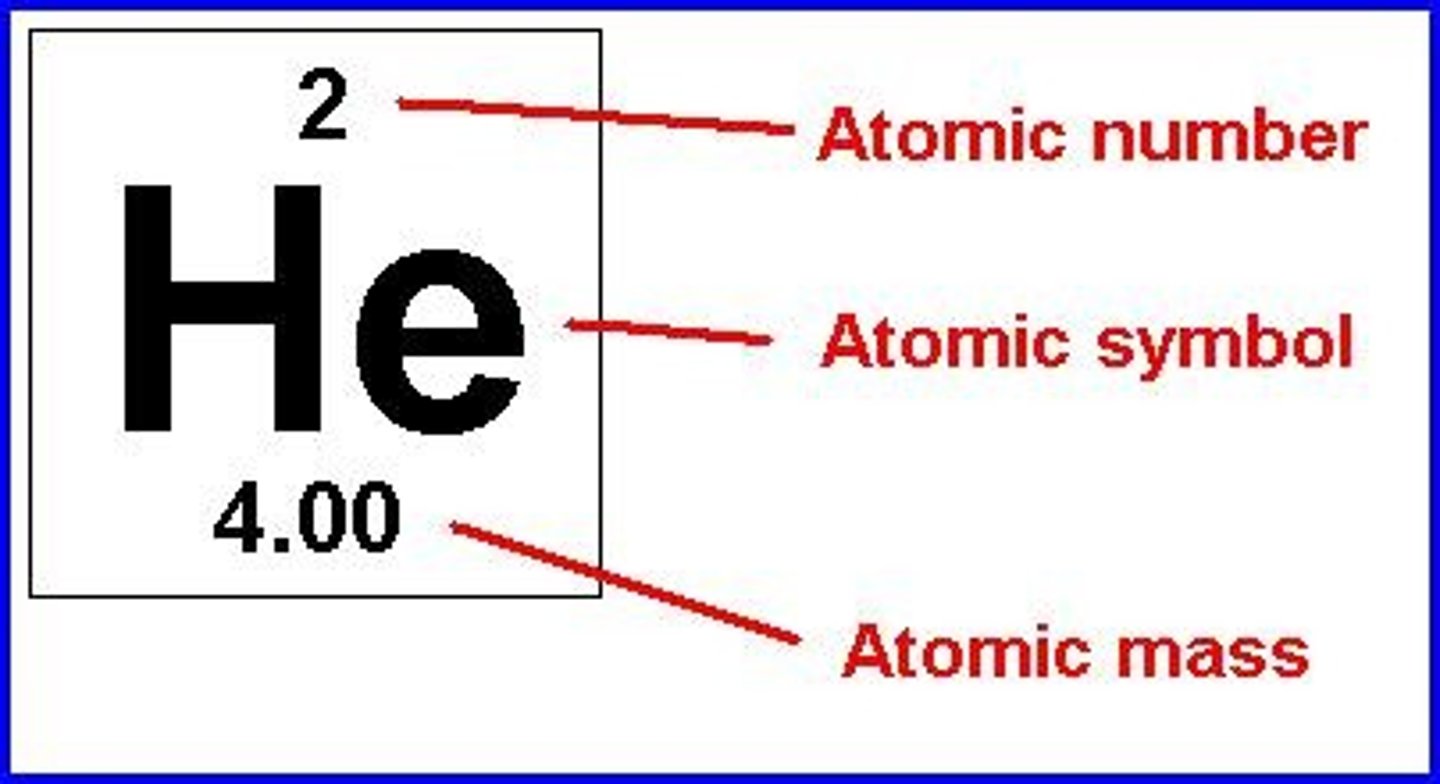
Atomic mass
Total mass of protons and neutrons.

Ion
Charged atom due to electron loss or gain.
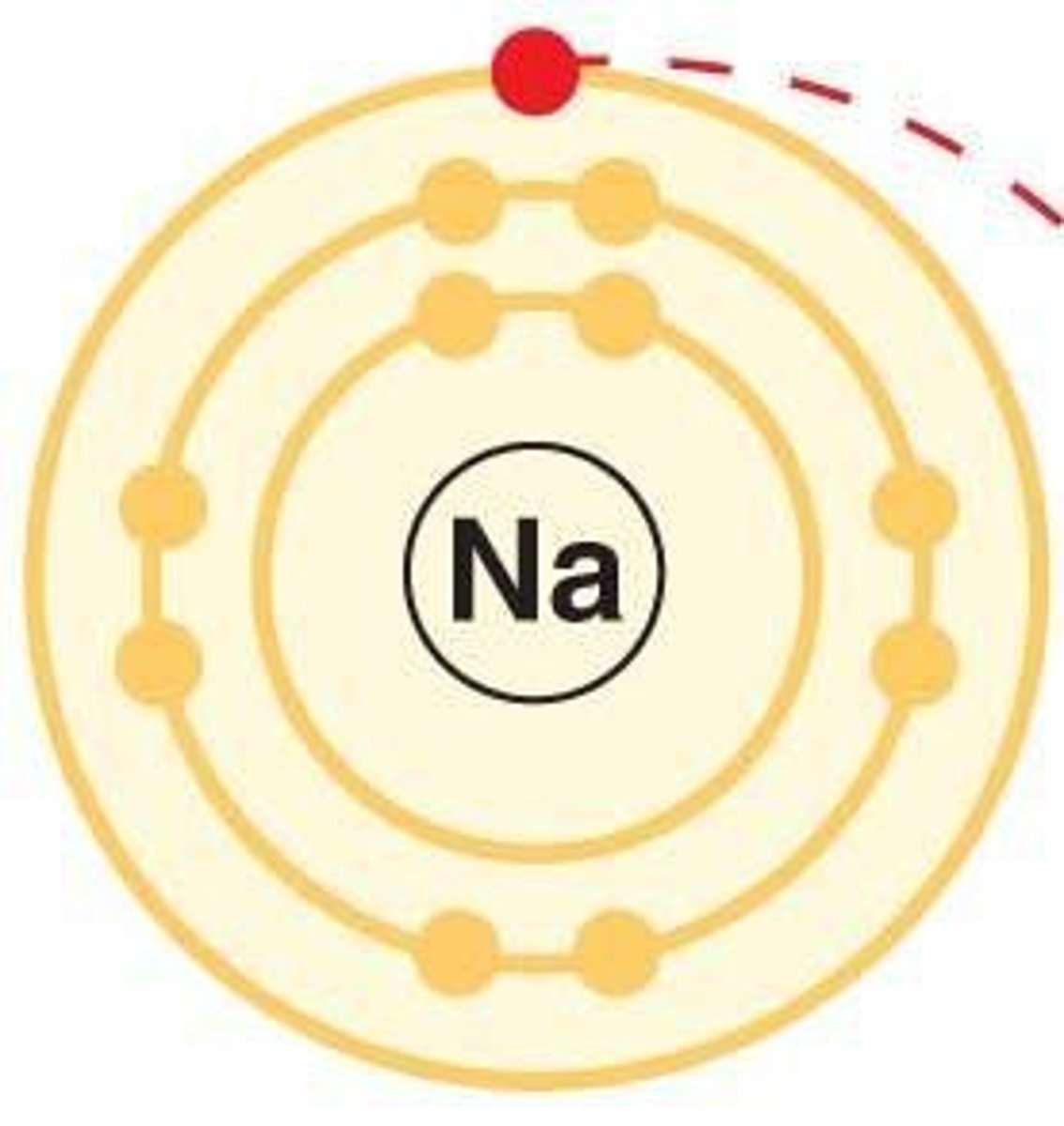
Anion
Negatively charged ion (gains electrons).
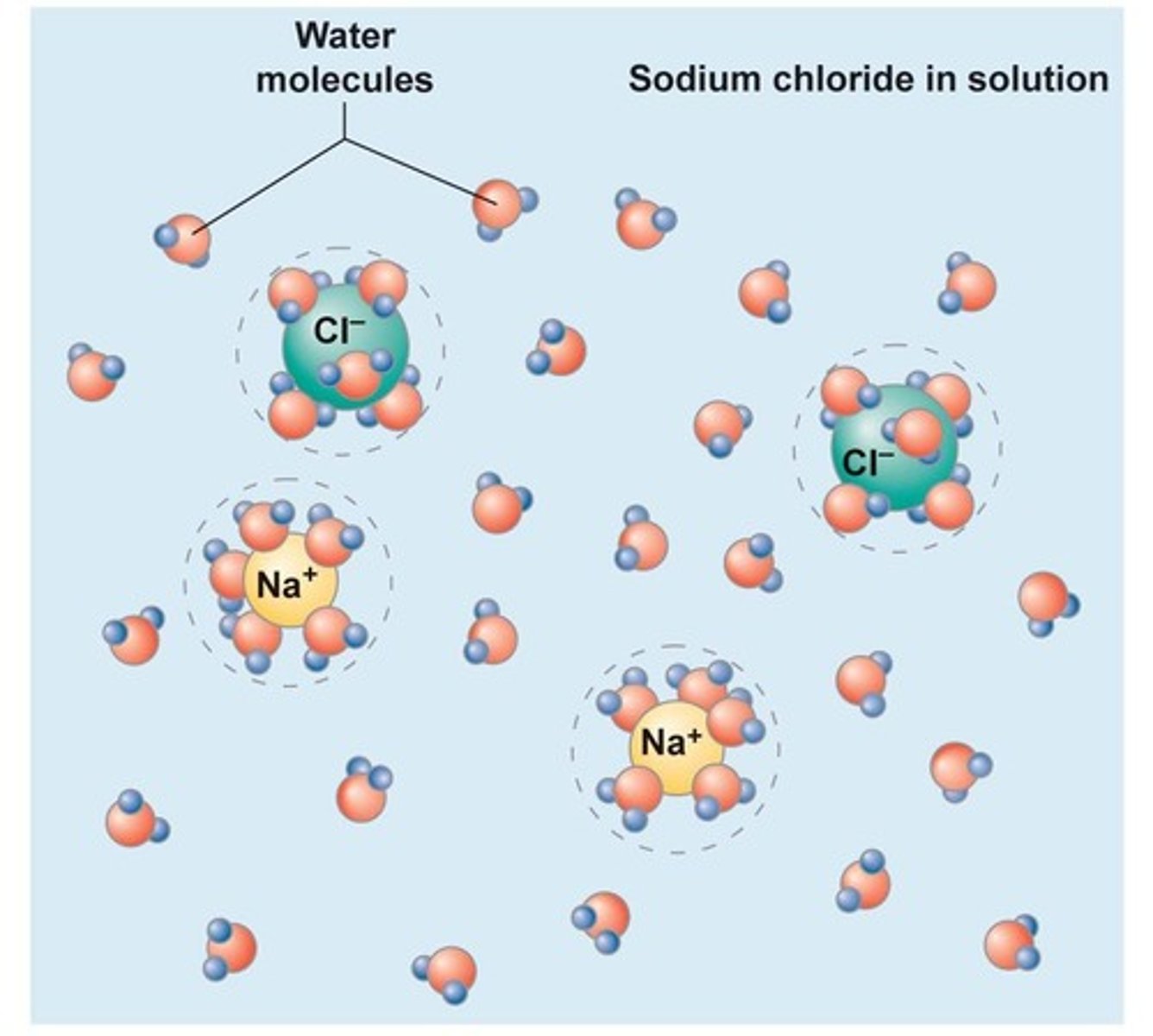
Cation
Positively charged ion (loses electrons).
Isotope
Atoms of the same element with different neutrons.
Half-life
Time for half of a radioactive isotope to decay.
Chemical reactivity
How an atom interacts with other atoms.
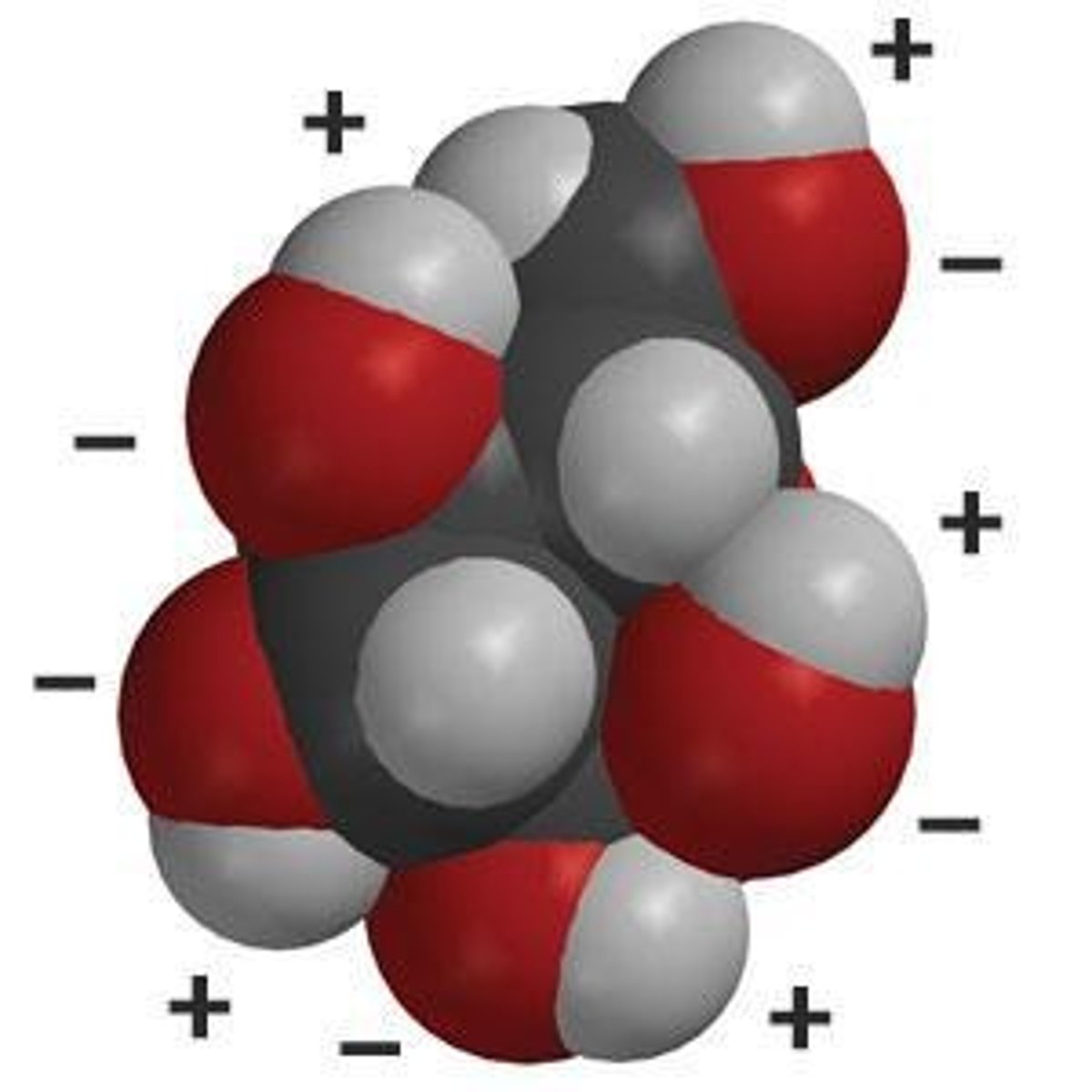
Hydrophilic
Water-loving, polar substances that dissolve in water.
Hydrophobic
Water-fearing, nonpolar substances that do not dissolve.
Cohesion
Attraction between molecules of the same substance.
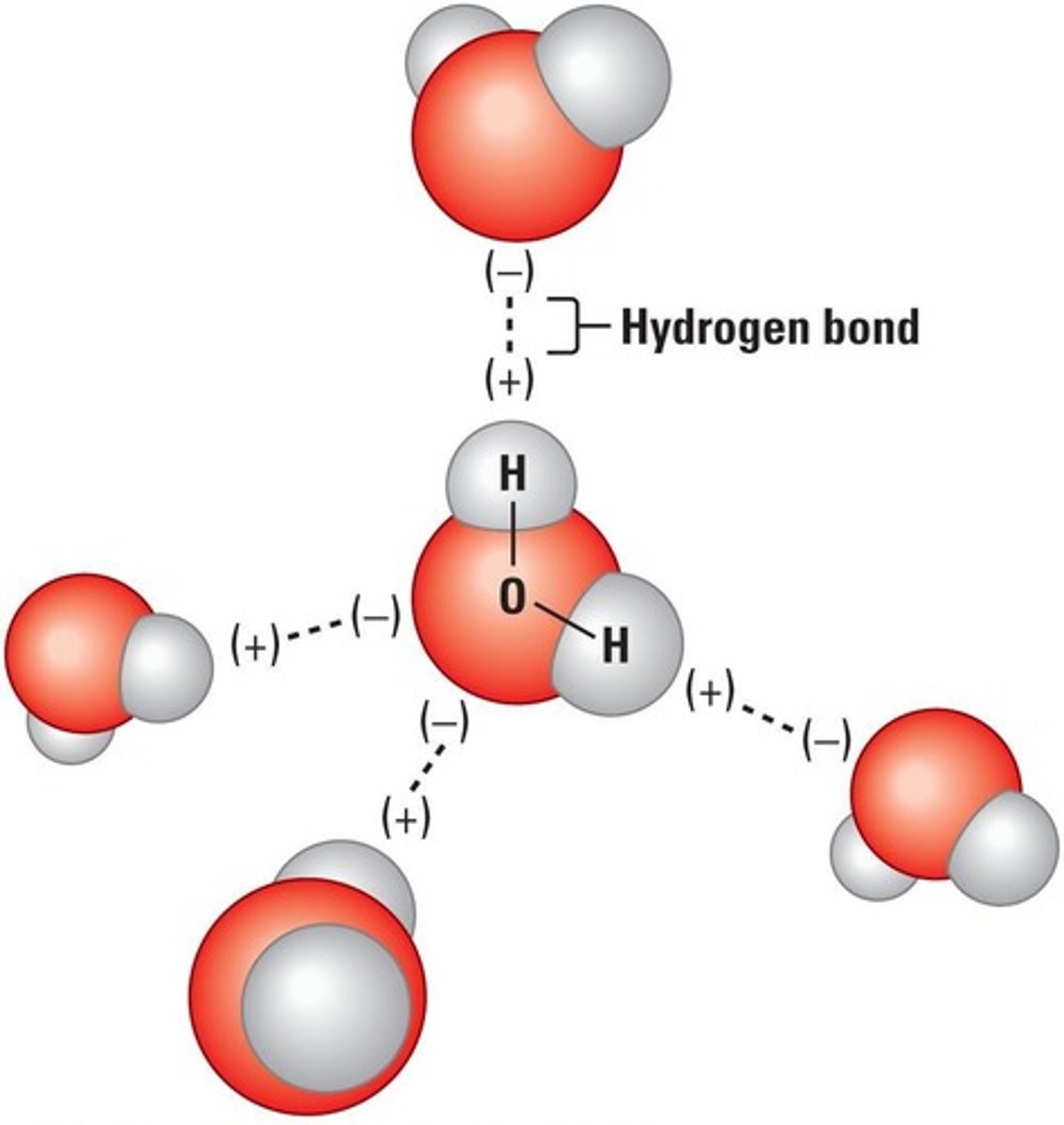
Adhesion
Attraction between molecules of different substances.
Heat capacity
Energy needed to raise temperature of 1 g by 1°C.

Boiling point
Temperature at which a liquid turns to vapor.
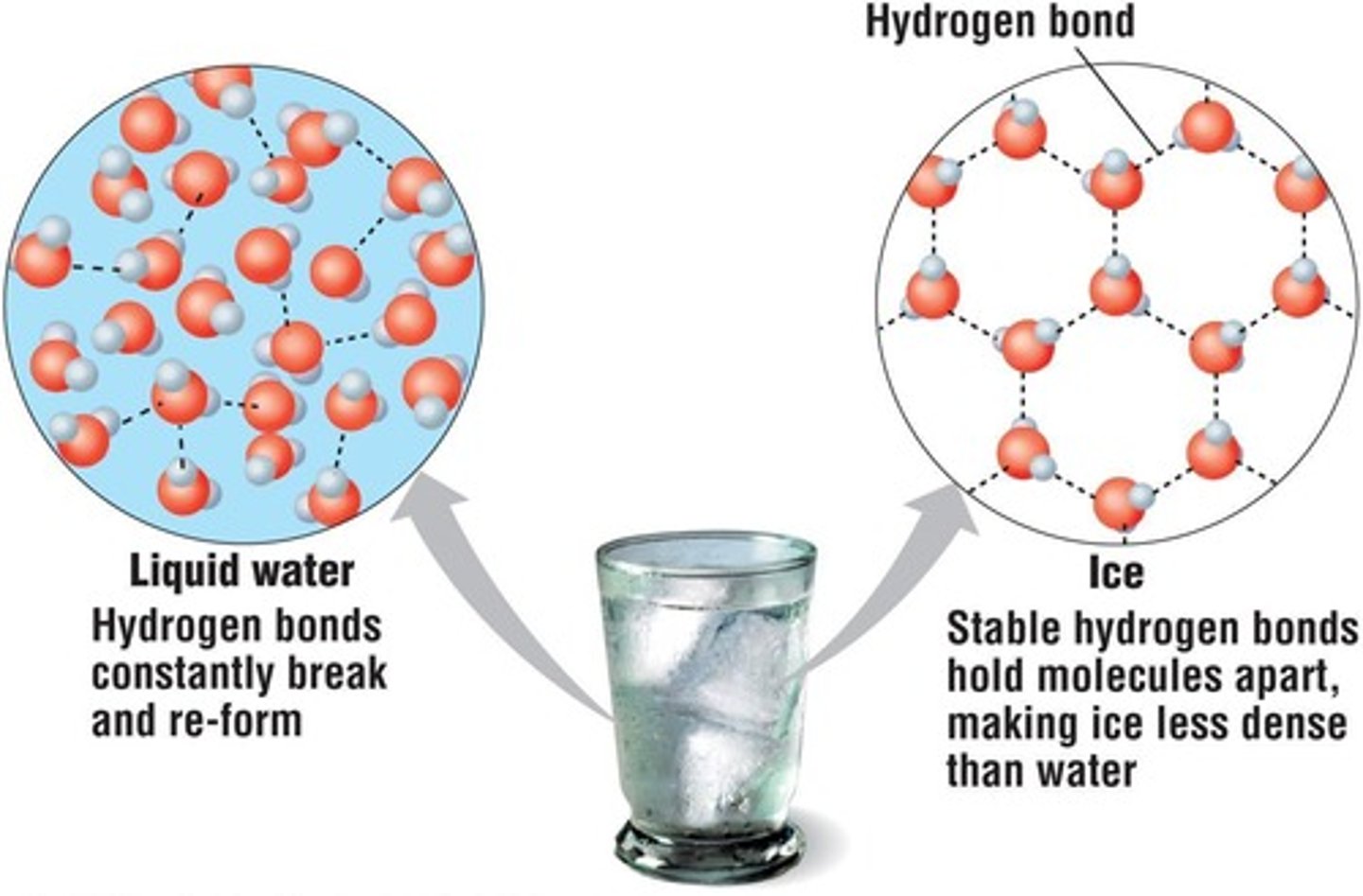
pH
Measure of hydrogen ion concentration in a solution.

Acid
Substance that donates protons (H+).

Base
Substance that accepts protons (H+).
Solvent
Liquid that dissolves solutes to form a solution.
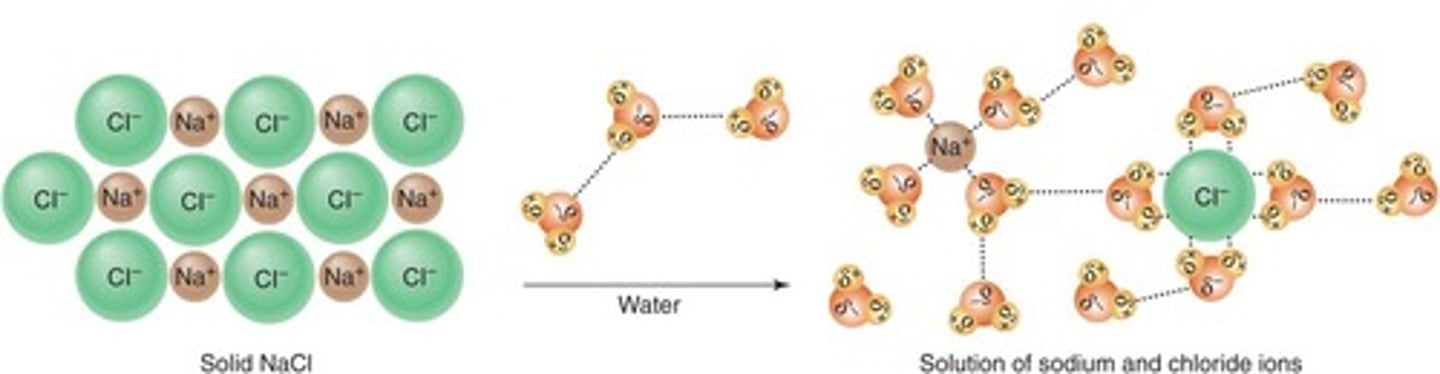
Solute
Substance dissolved in a solvent.
Solution
Homogeneous mixture of solute and solvent.
Chemical bond
Attraction between atoms that forms molecules.
Electron shell
Region around nucleus where electrons reside.
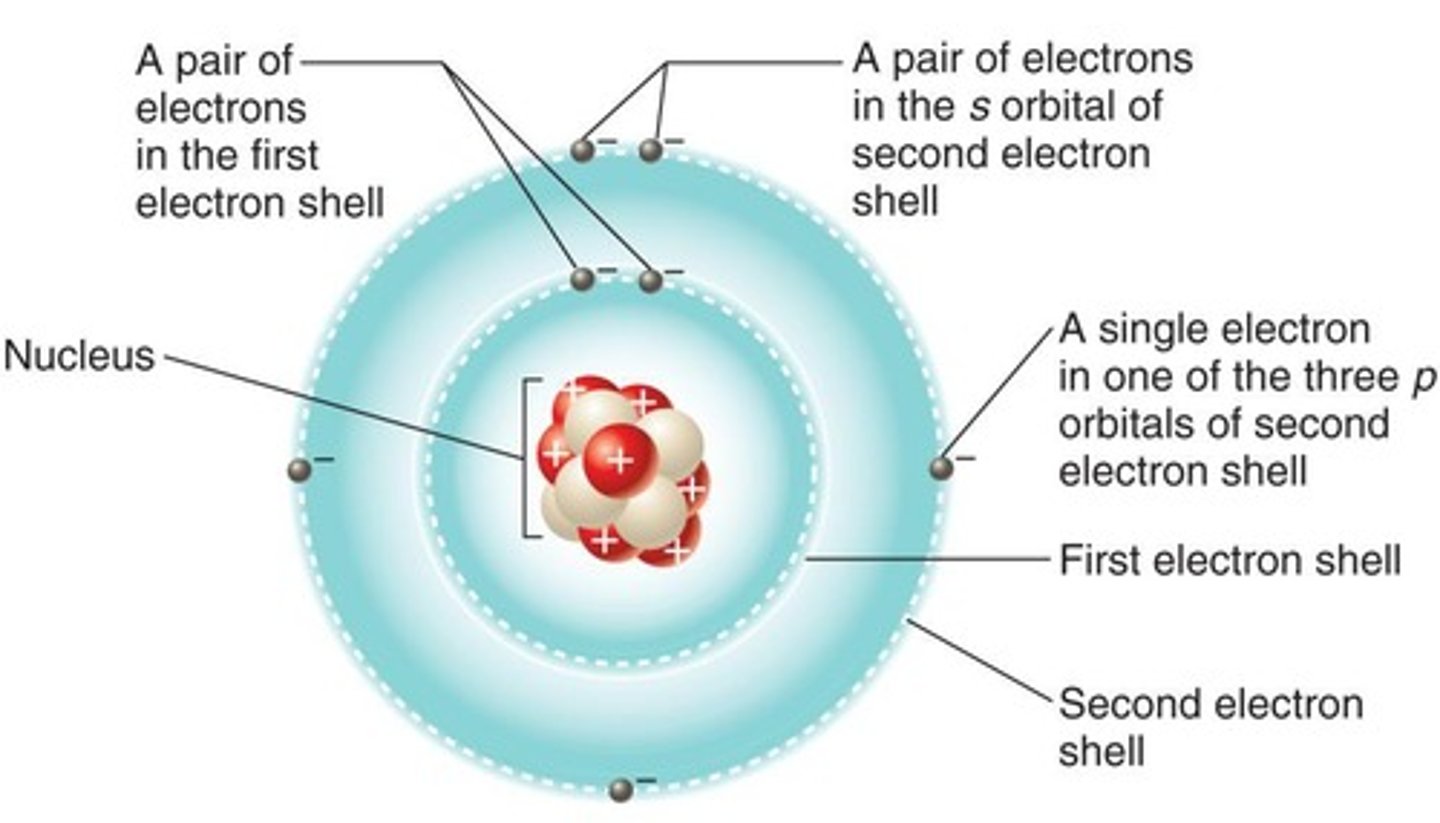
Electron configuration
Arrangement of electrons in an atom's shells.