Data Representation
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
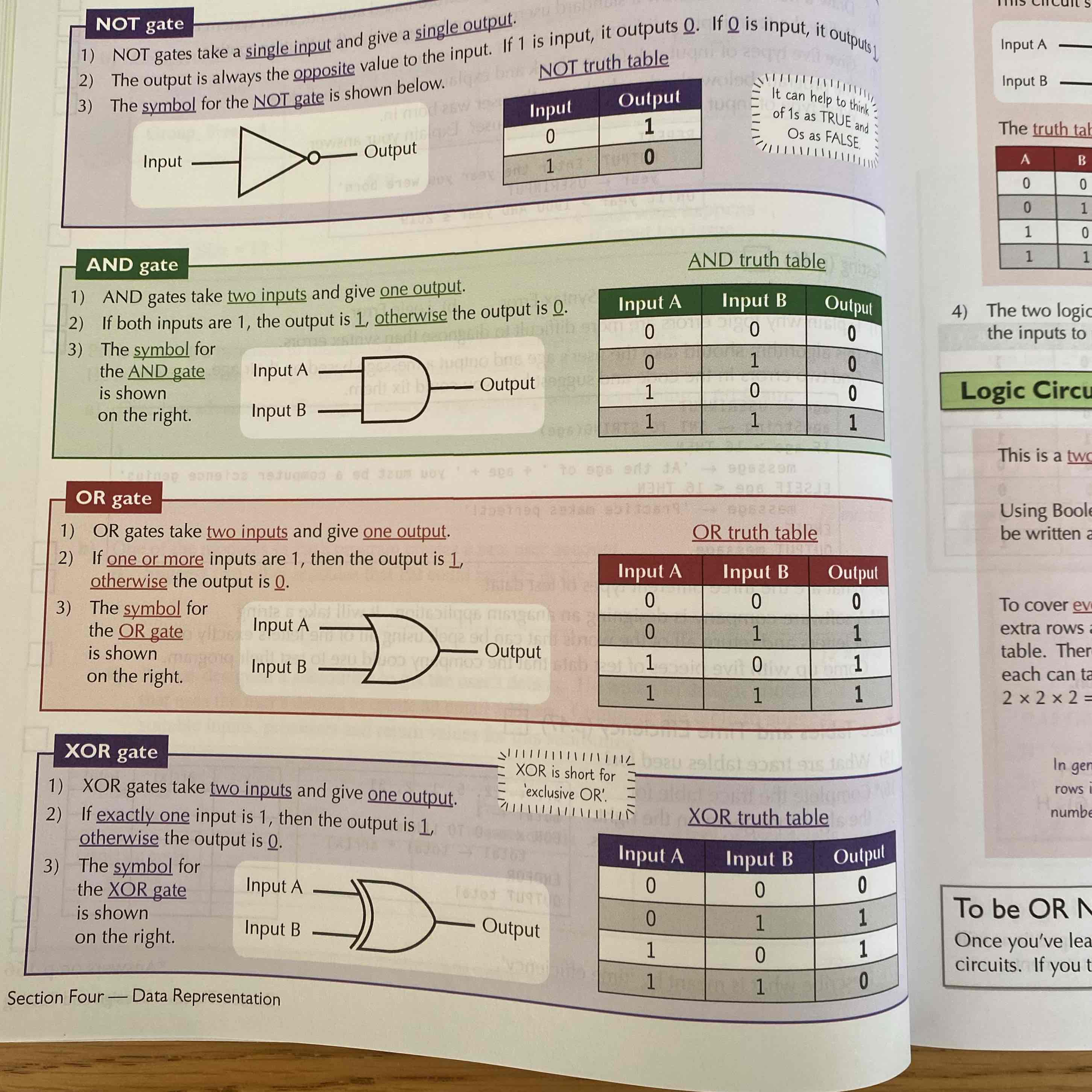
What are the 4 logic gates?
And
Or
Not
XOR
What does each gate look like and what is there truth table?
See Image:
What are the units for data?
Bit(b) - One binary Digit
Nibble - 4 Bits
Byte(B) - 8 Bits
Kilobyte(kB) - 1000 Bytes
Megabyte(MB) - 1000 Kilobytes
Gigabyte(GB) - 1000 Megabytes
Terabyte(TB) - 1000 Gigabytes
What is binary?
The language computers run on (1s and 0s).
How do you add binary numbers?
By putting them in line in a column and adding the corresponding numbers together. If there is a:
0+0 - Write 0 under
1+0 - 0+1 - Write 1 under
1+1 - Carry the 1 over to the next column.
You do the same for 3 binary numbers:
0+0+0 - Write 0 under
0+1+0 - Write 1 under
1+1+0 - Carry the 1 over
1+1+1 - Write 1 under and carry a second 1 over
How do you multiply and divide in binary?
For multiplying you would shift the whole binary number over tot he left:
If it is *8 then move over 3 as 2³ = 8
If it is *4 then move over 2 as 2² = 4
For dividing you do the same but shift the number to the right, and all numbers on the end that are destroyed are remainders and aren’t counted.
What is hexadecimal?
Another number system used in programming that can represent numbers and letters:
0-9 = 0-9
10-15 = A-F
This means that 3E =
0011 1110
What is ASCII?
ASCII is a 7-but character set used to represent characters in english. This is similar to hexadecimal.
How can images be written in binary?
It can be written in bitmap where each square is a pixel. Colour can also be take in where 1-but colour depth would have 0-black 1-white. With a higher colour depth more colours can be used.
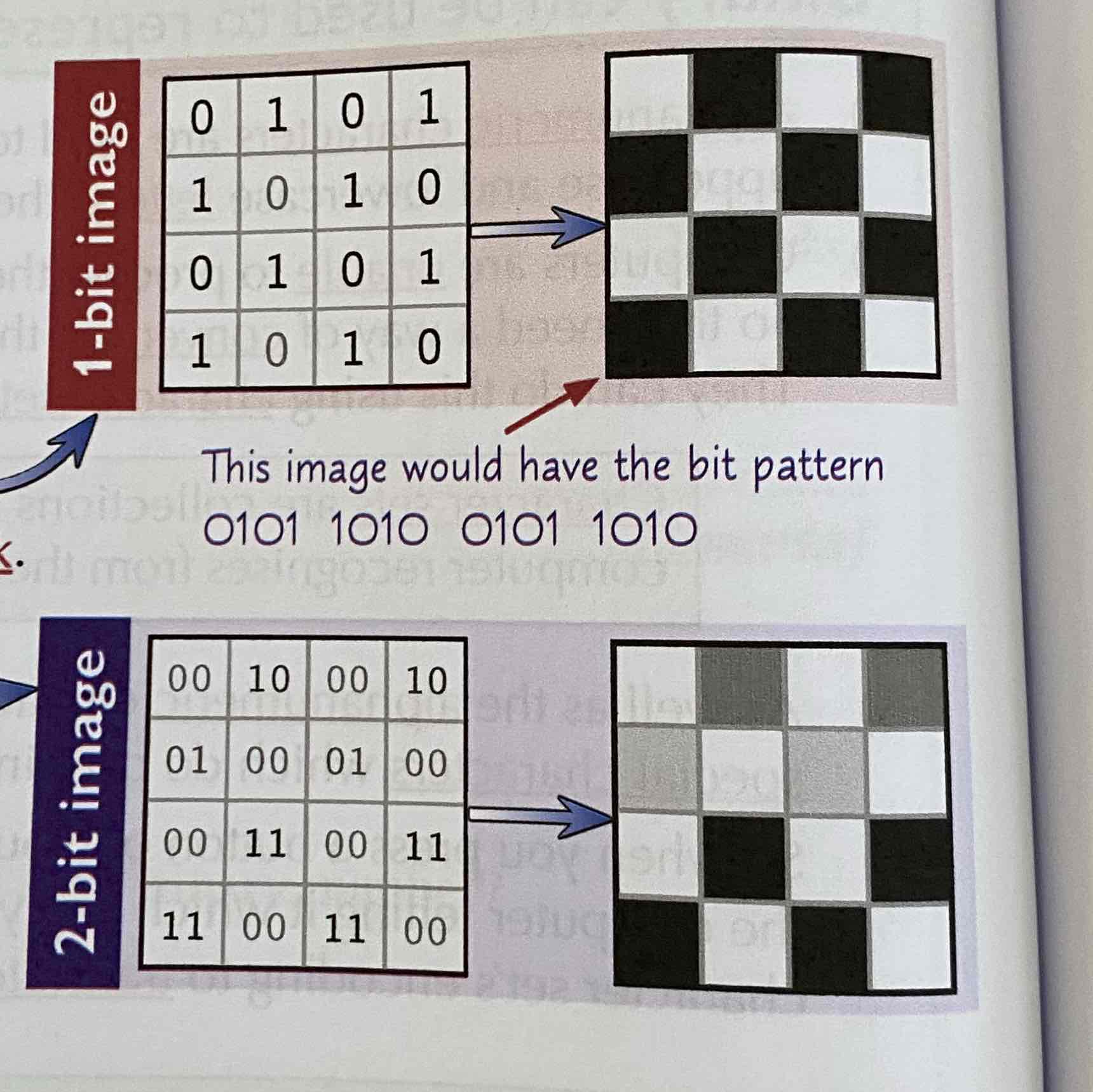
How is file size calculated?
File Size = Image size (Pixel Width*Length) * Colour depth
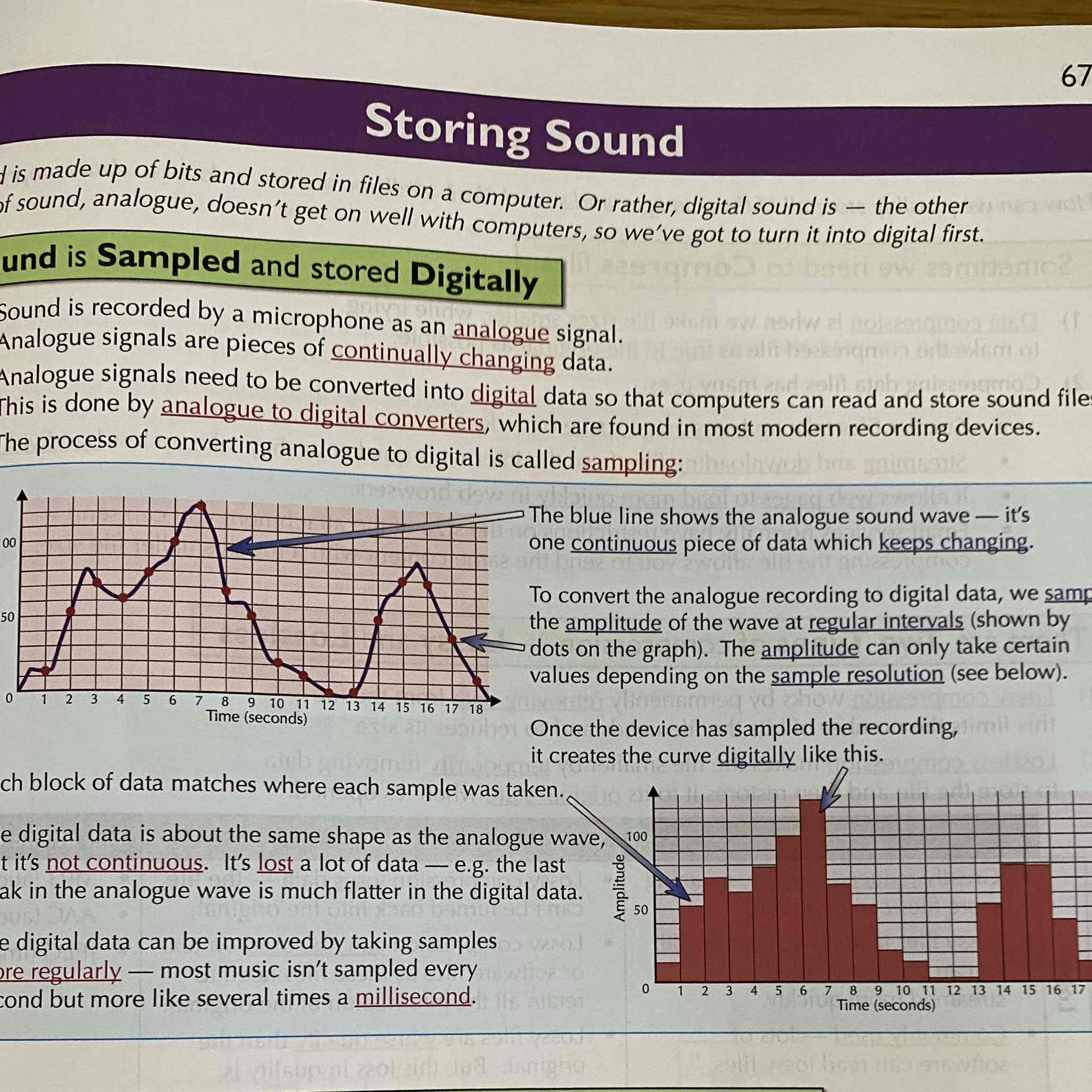
What is sound sampling?
Sound is recorded as an analogue signal but can be converted to digital in a process called sampling.
How does sampling work?
You sample the amplitude at regular intervals and plot it on a graph. Then it should create a curve digitally as shown in the image.
What is sample rate or sample frequency?
How many samples you take in a second. It is measured in Hertz (Hz) or Kilohertz (kHz).
What is sample resolution and how can it help calculate file size?
Sample resolution is the number of bits available for each sample.
File Size=Sample Rate*Sample Resolution *Length
What are two types if compression?
Lossy
Lossless
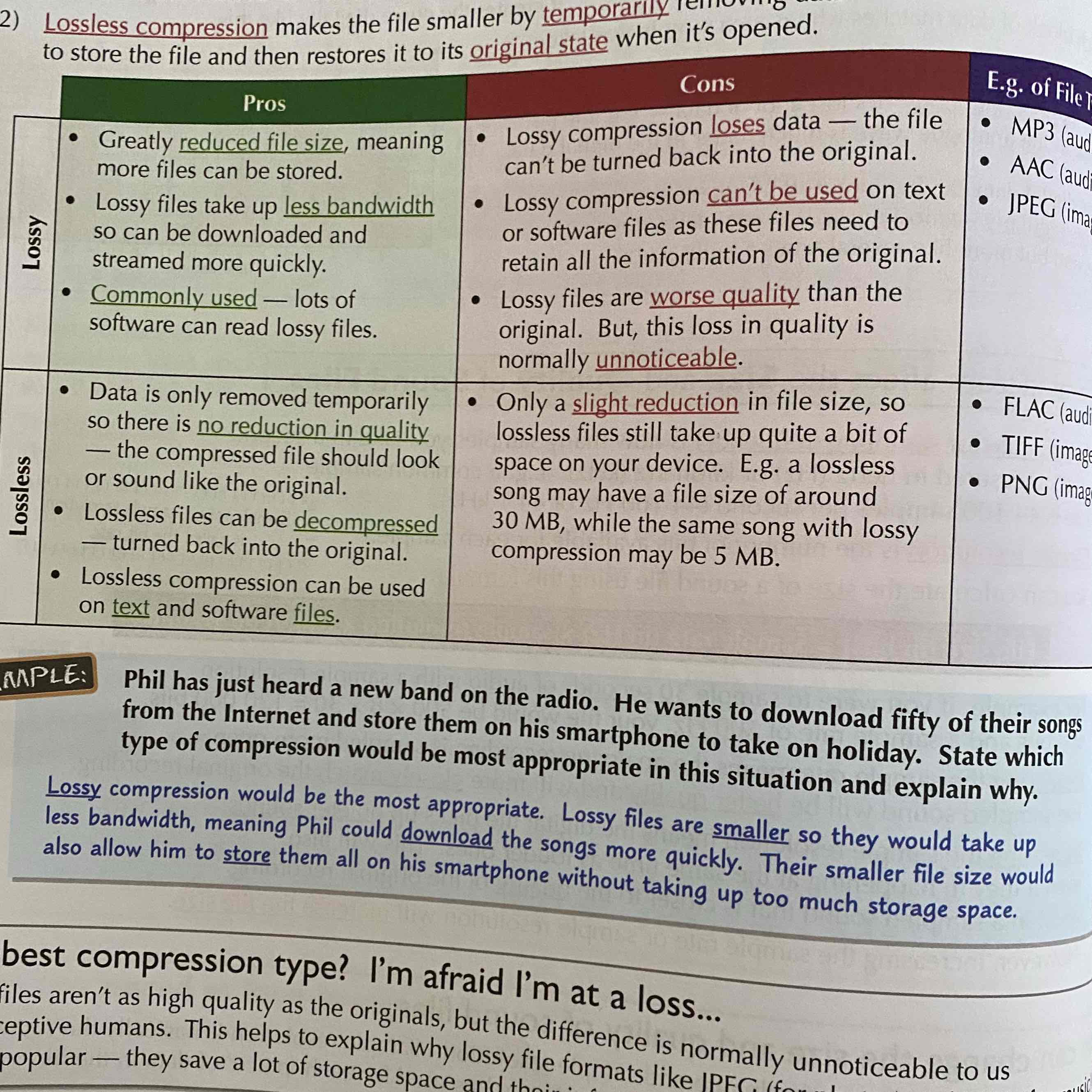
What are advantages and disadvantages of Lossy and Lossless compression?
See Image:
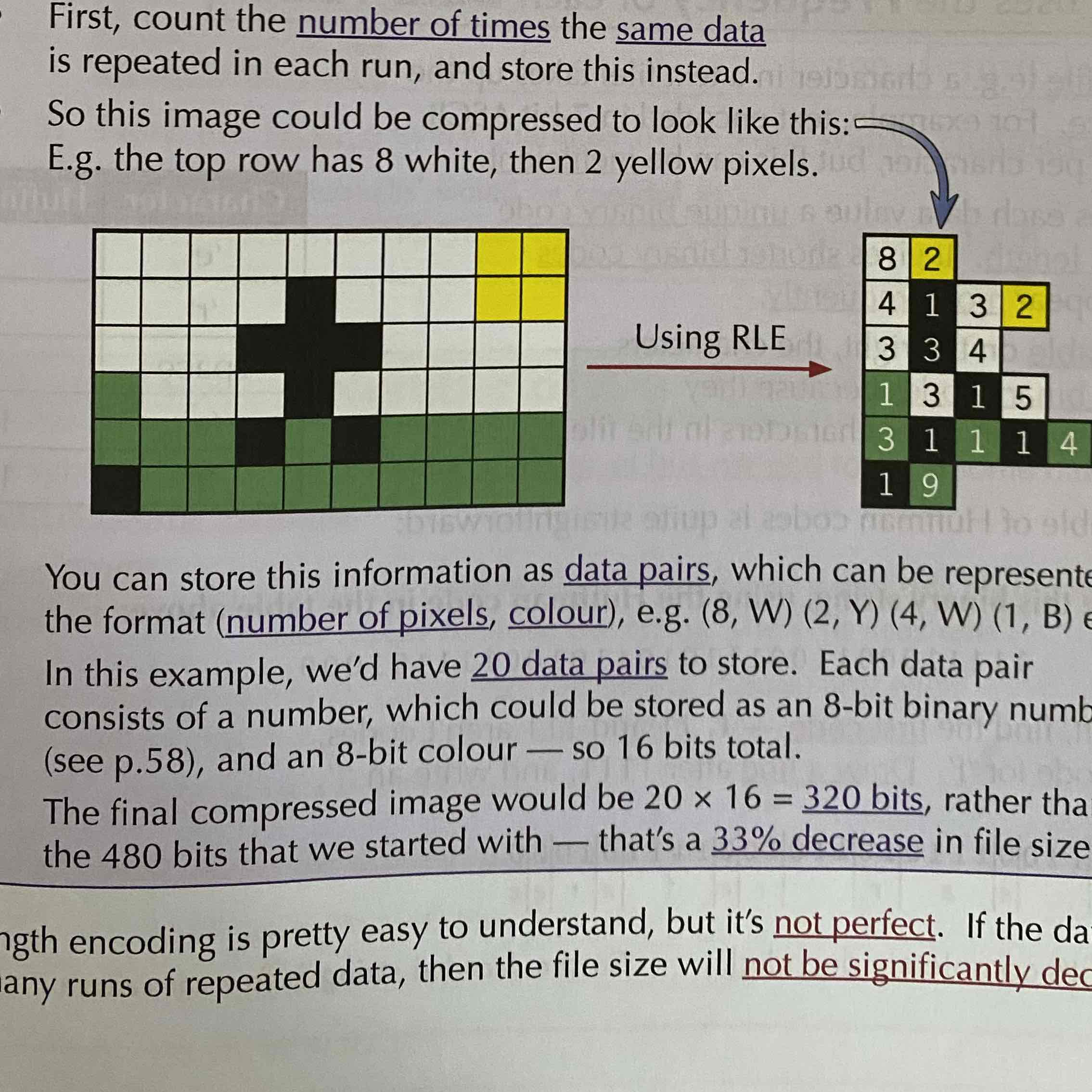
What is Run-Length Encoding?
RLE is a form of lossless compression. It’s a consecutive run of repeating data.
As well as pictures it can also be used to compress bit patterns:
000110111001
30 11 10 31 20 11
302110312011
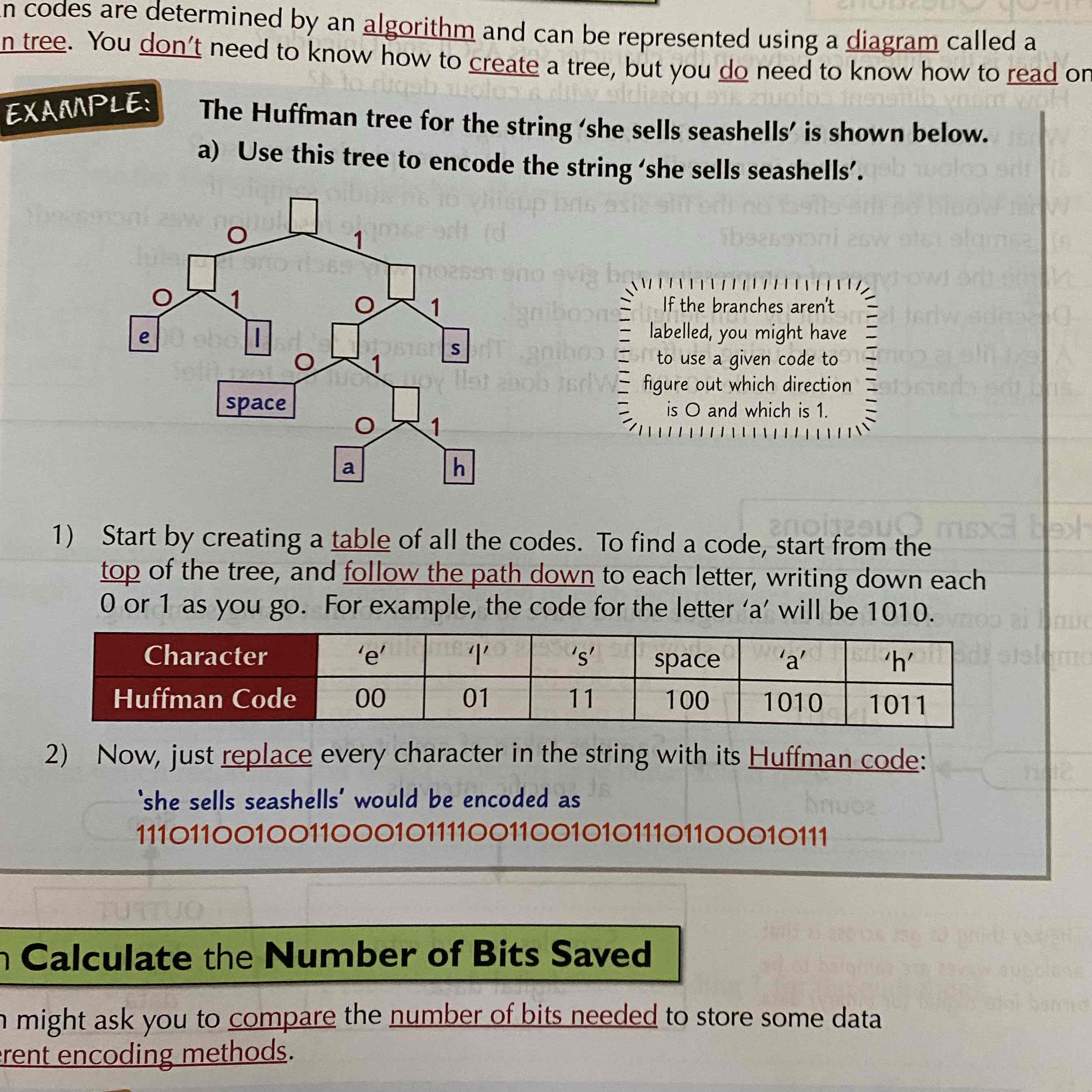
What are Huffman trees?
They are determined by an algorithm and displayed as a tree to represent Huffman codes.