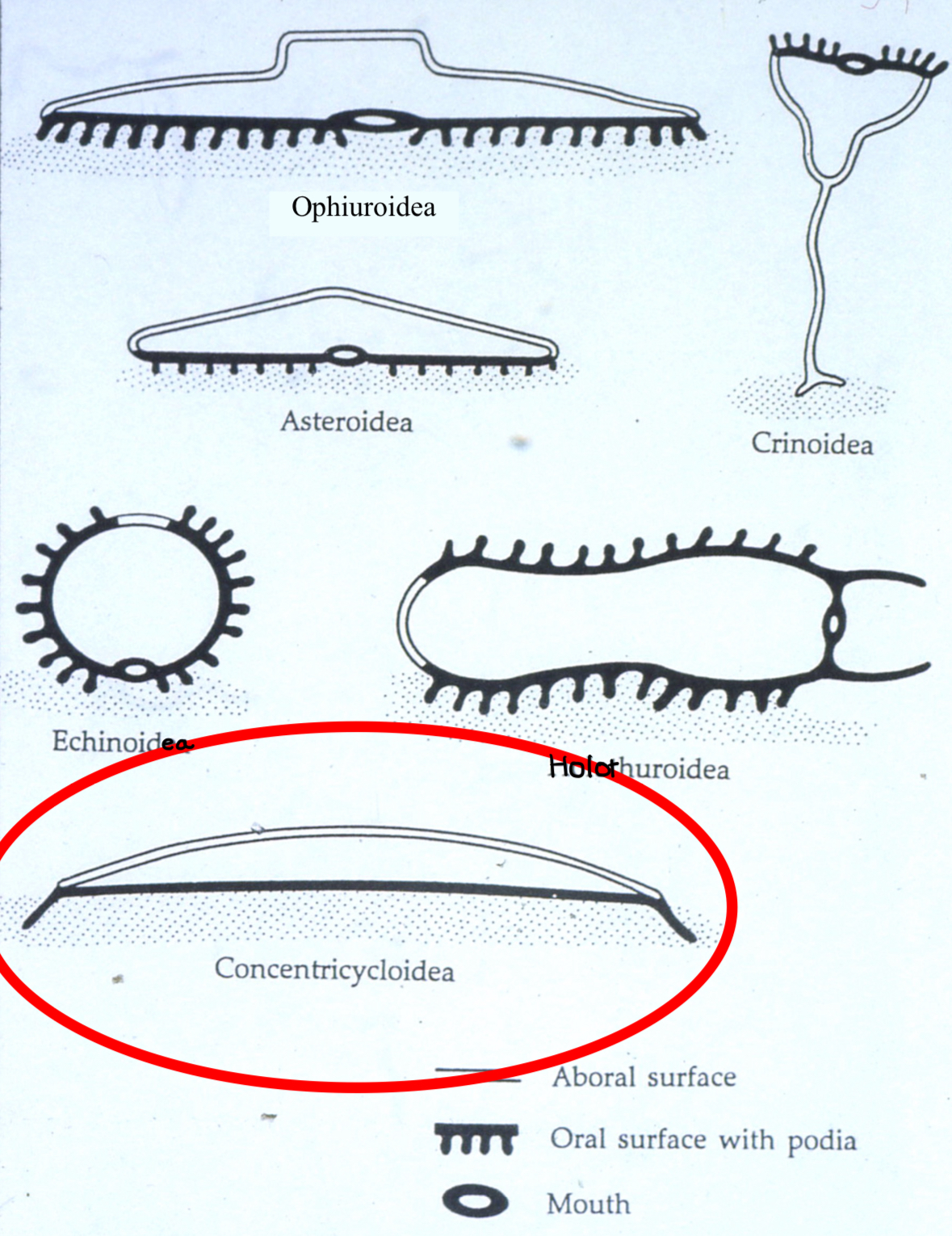
P: Echinodermata C: Ophiuroidea SO: Euryalida C: Asteroidea O: Valvatida C: Crinoidea C: Echinoidea C: Holothuroidea
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
P. Echinodermata E-chin-oder-mata
- all marine, NO parasitics
- dominated deep sea floors
- pentamerous radial symmetry
- deuterostome (anus then mouth, nerve cord dorsal)
- bilateral as larva, secondarily radial as adult
- internal skeleton of calcareous OSSICLES
- oral surface usually against substrate
- no excretory organs
P. Echinodermata General Features
-Water vascular system: coelomate, fluid filled channels, pore (madreporite) connect to external surface
-Function: movement, respiration, sensory
-Tube Feet: hydraulic extension, muscular retraction
- Mutable connective tissue: catch collagen, stiffening of spines (stiff gel to flexible sol in second)
- Endoskeleton: plates or ossiccles, single calcite crystals (CaCO3, Mg rich, no/little organic matrix) riddle with pores
-Pedicellaria: defense, anti-fouling
- spacious coelom w/ complex partitions
- 3 network of nerve ring, radiating nerves, poor sensory system, control connective tissue
- no excretory system
- SOME have circulatory system (haemal system in sea cukes)
- Gut in coiled tube (NOT in starfish or brittlestar)
- Radial gonads (NOT sea cukes, crinoids)
- Separate sexes, little dimorphism
- Broadcast spawners, some brood
- 3 pairs of coelomic spaces: form coelom, water vascular system, haemal system
- some autonomy and regeneration
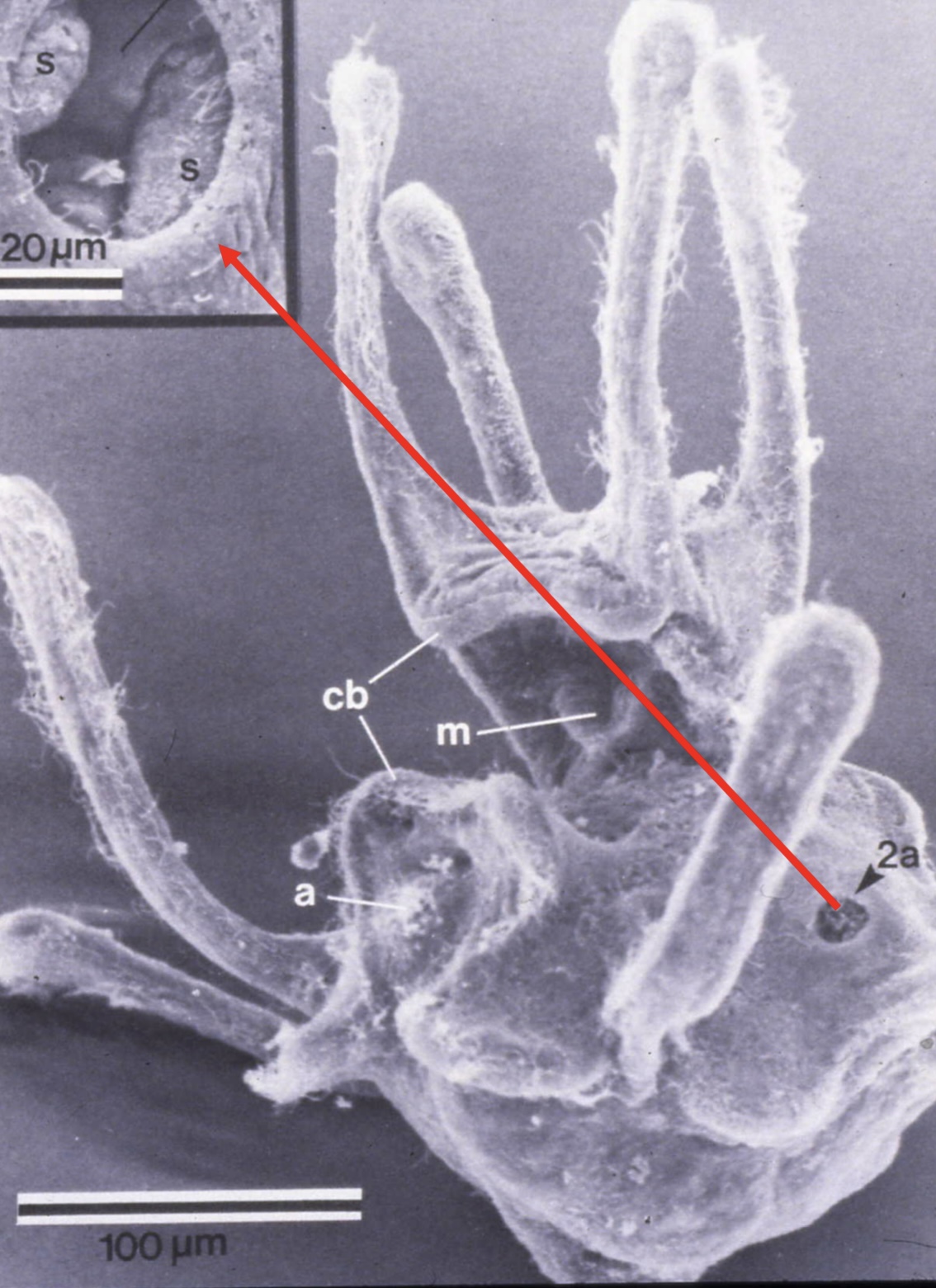
C. Echinoidea Larva
Sand dollar larva
- has vestibule which allows juvenile sand dollar form
M= mouth
A= anus
Cb= ciliary bands
2a= vestibule
S= vestibule with adult sand dollar
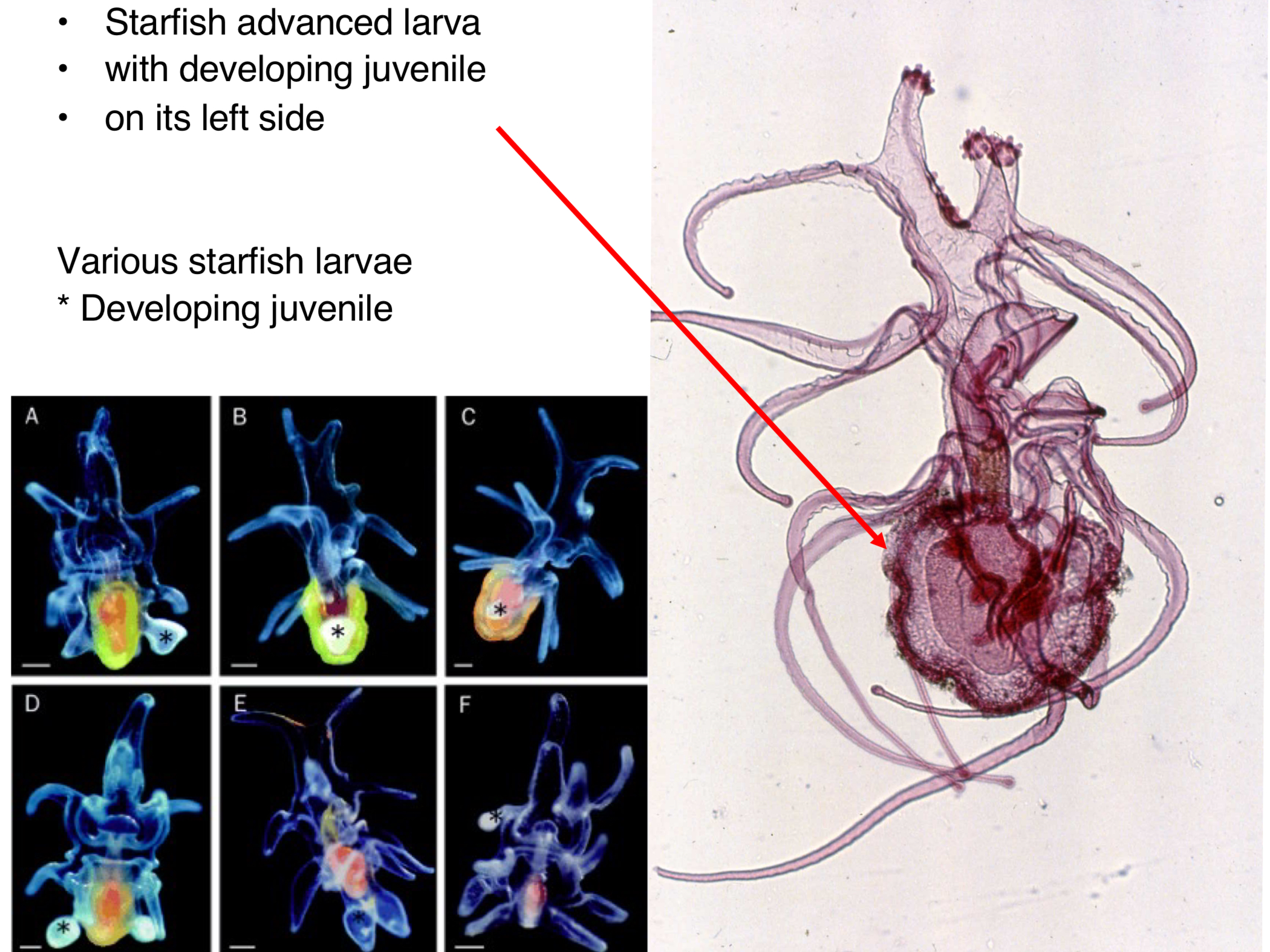
C. Asteroidea Larva
Starfish advanced larva with developing juvenile on left side
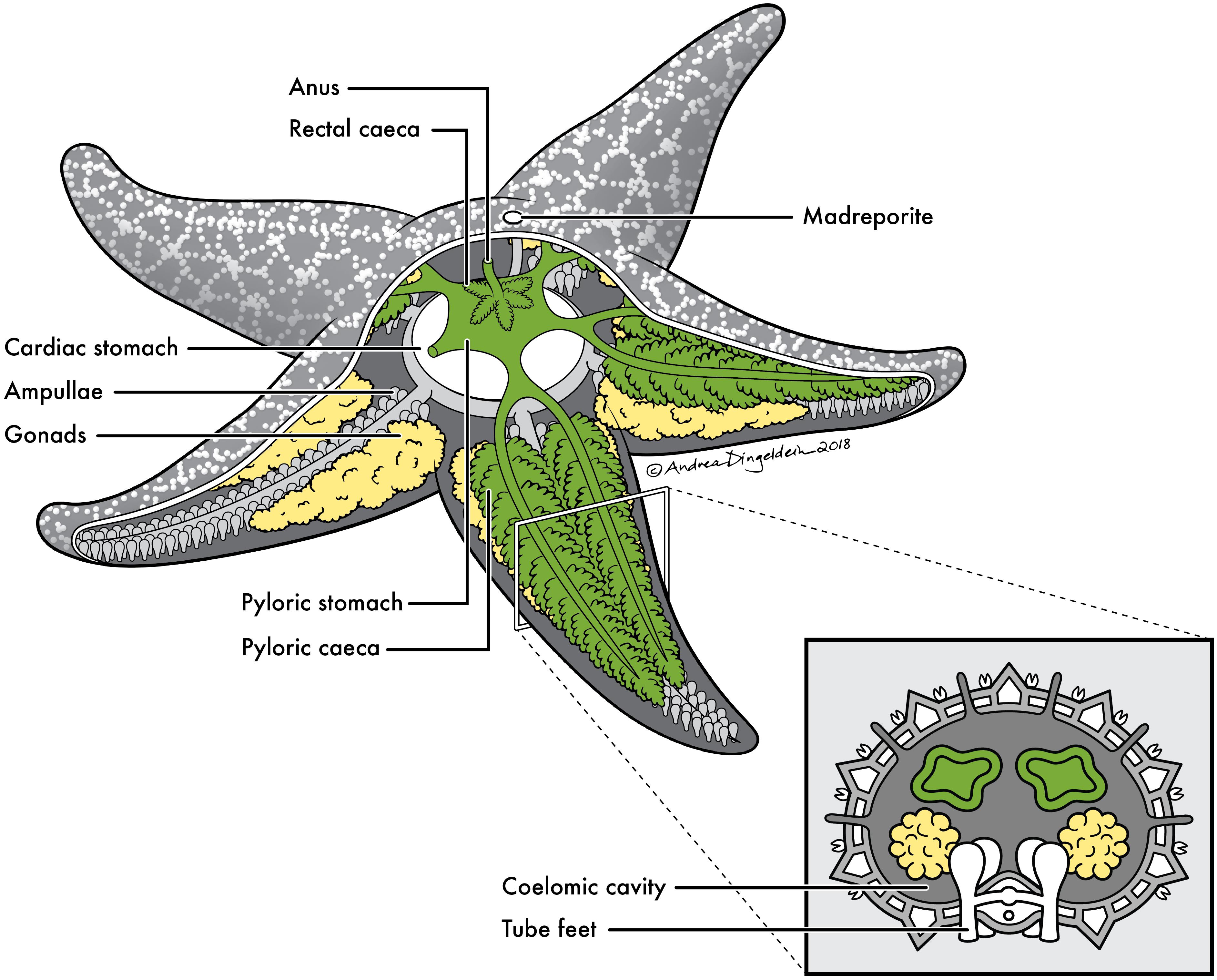
C. Asteroidea Astero-idea
= Starfish and sea daisies
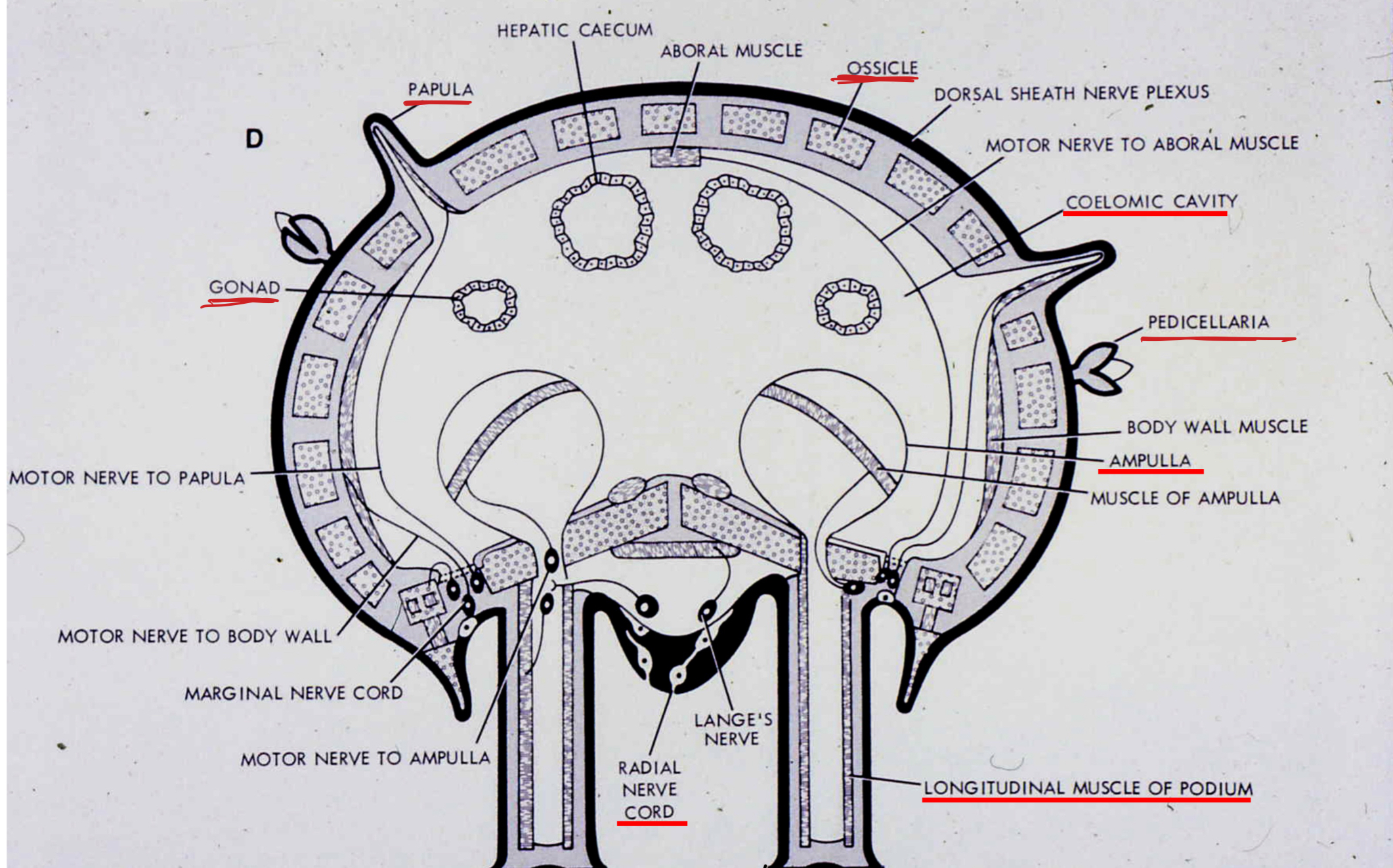
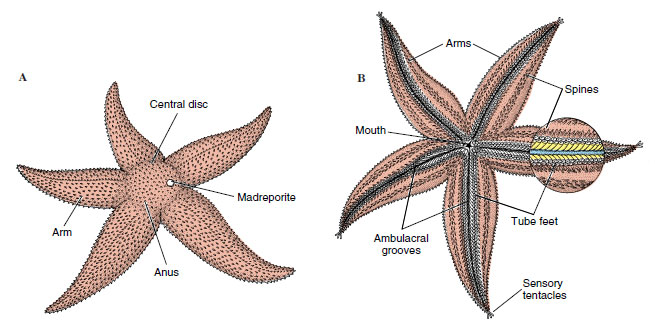
- flattened, 5 or more arms from poor defined central disc
- ambulacra on oral surface
- tube feet with internal Ampullae (small muscular sac that help extend tube feet) for locomotion (movement)
- papulae - specialized respiratory organs
- gonads radial
- endoskeleton of separate ossicles and spines
- gut sac-likes, digestive glands in arms
- Pedicellaria (protection and eating) on aboral side
- Ambulacral grooves: open, ridge of tube feet & radial canal
P. Echinodermata Body Plans
Asteroidea: starfish
Concentricycloidea: sea daisies
Echinoidea: sea urchines, sand dollars
Crinoidea: sea lilies, feather star
Holothuroidea: sea cucumbers
Ophiuroidea: brittle star, basket star
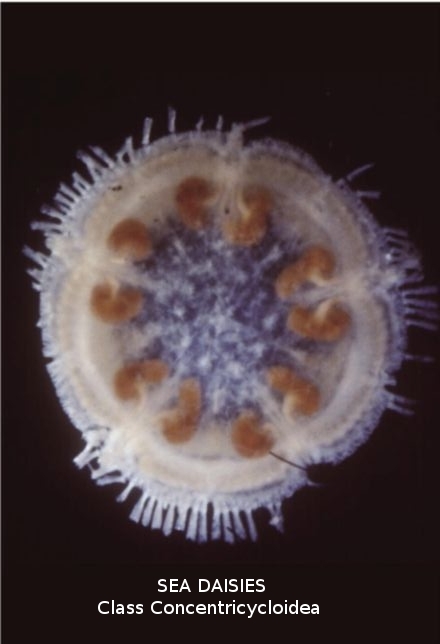
C. Asteroidea Concentricycloidea Astero-idea Concen-tri-cyclo-idea
= Sea Daisies
- deep sea, on sunken wood
- no pentamerous, double ring canal
- no gut in 2 of 3 species, oral membrane for absorption of dissolved organic matter
- brood eggs, direct development, weird sperm
C. Asteroidea O. Valvatida Sp. Patiria Miniata Valva-tida
Species. Pati-ria Mini-ata
Bat Star
- tube feet eith suckers
- has anus
Japan Starfish Invasion
Asterias Amurensis: overpopulated
- need biological control = Orchitophrya parastic castrator of male starfish
- survive in scallop culture raft
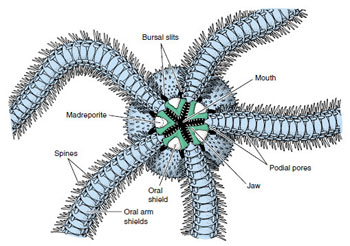
C. Ophiuroidea Ophi-uro-idea
= brittle stars, basket stars
- dominate deep sea soft bottom
- worst osmoregulator among P. echinoderms (as whole, not good osmoregulators)
- well-defined flat central disc
- long, slender arms
- no ambulacral grooves (nonsuctorial tube feet come out of groove but still have tube feet)
- radial canals inside arms
- madreporite on oral surface
- gut blind sac (no anus)
- gonads released into bursal slits (a pair each arm)
- central nervous system control arms, most active echinoderms
- GREAT autonomy and regeneration (throw arm off)
- NO pedicellariae (protection and eating), NO papullae (water vascular system)
- UNBRANCHED arms, movement in S shape, fast waving arms, move only laterally (VERTEBRAL ossicles - like door hinge only up and down, brittle star left and right)
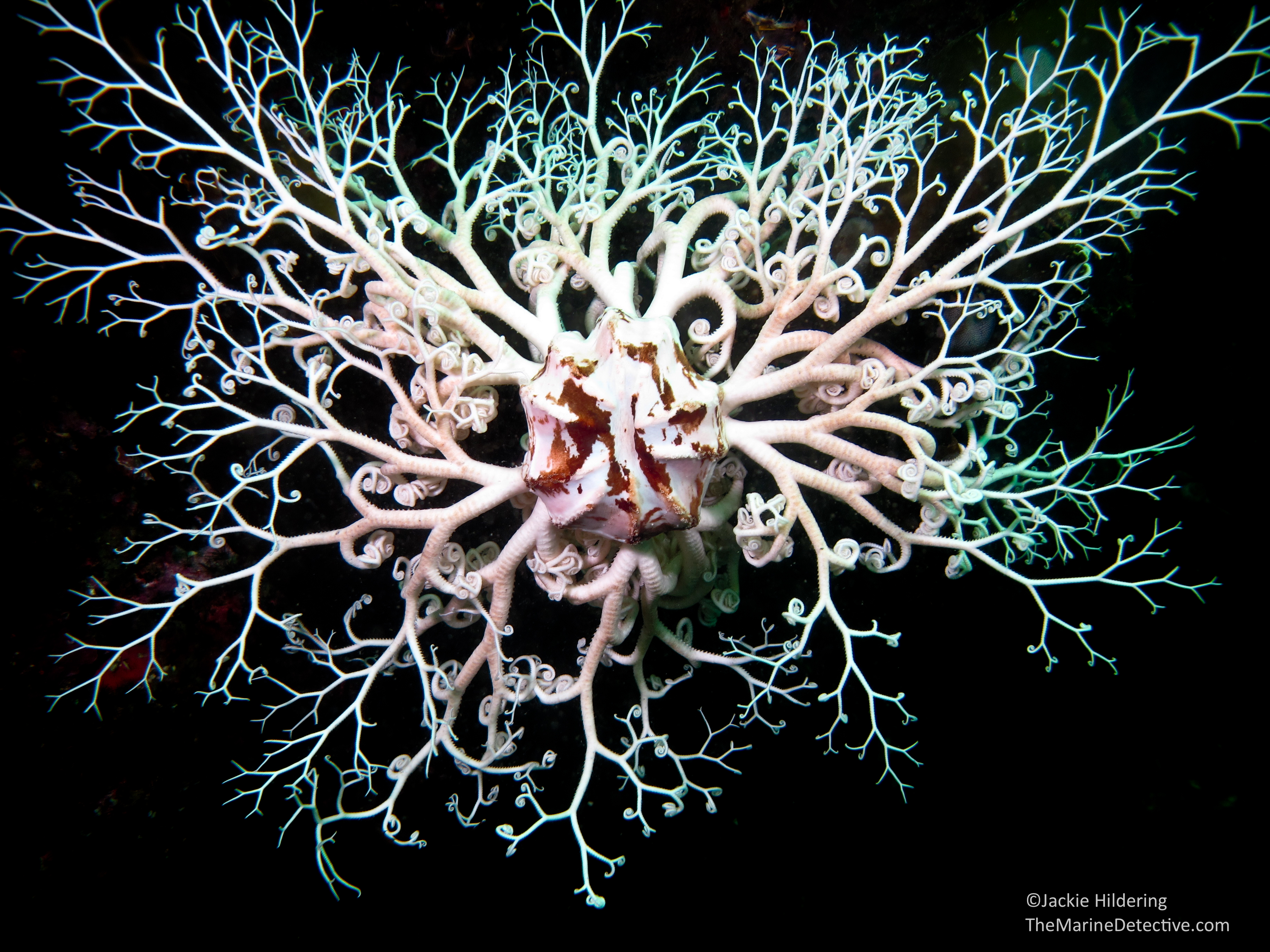
C. Ophiuroidea SO: Euryalina Ophi-uro-idea Eur-ya-lina
= Basket Stars
- branched and curly arms, move in all directions
- vertebral ossicles- universal joints, can switch from left and right to up and down
- mutable connective tissues lock arms to allow filter feeding and keep arms from raging currents

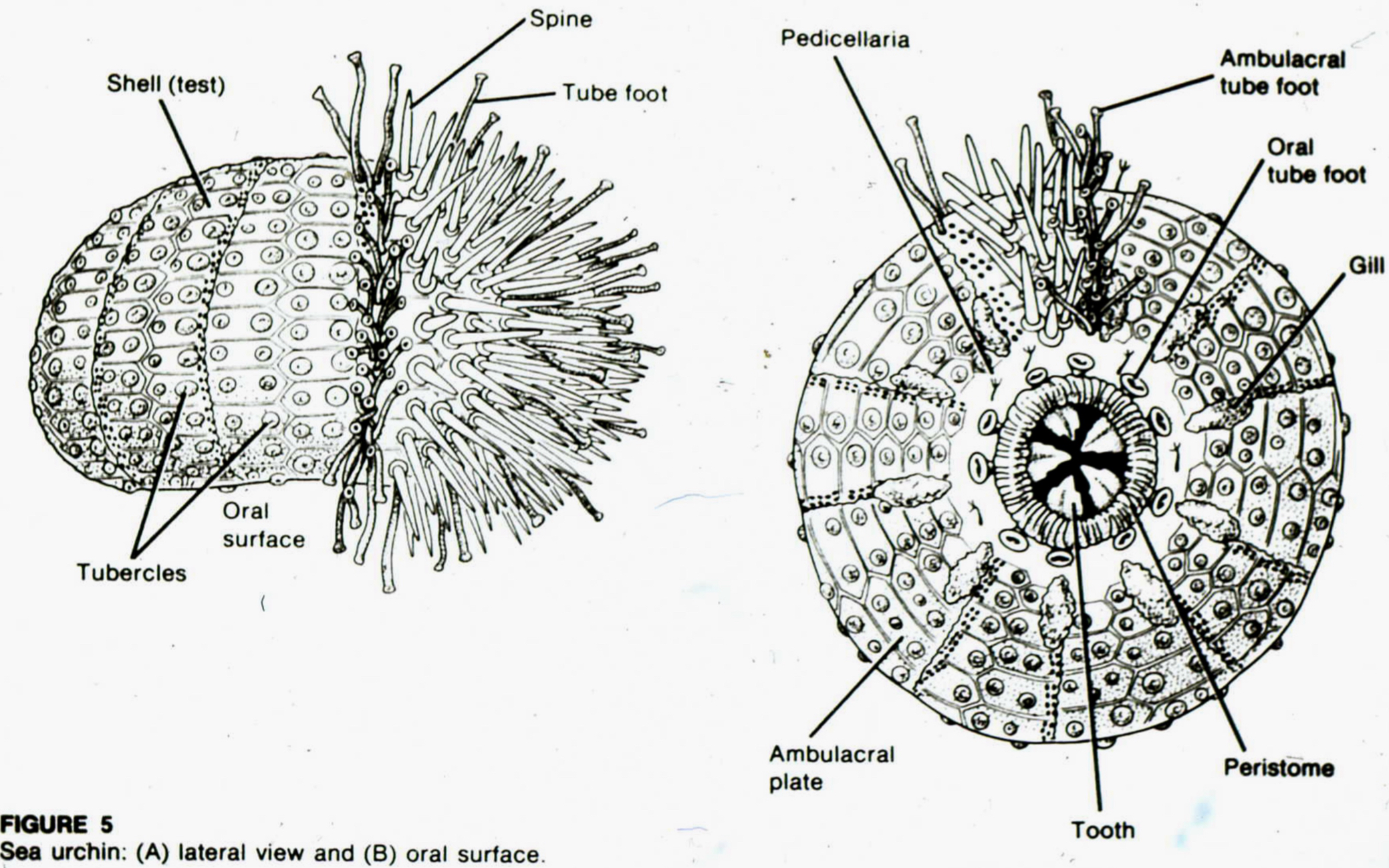
C. Echinoidea E-chin-o-idea
= Sea urchins, sand dollar, heart urchins
- few are predators of sea lilies
- most abundant in shallow water
- large oral surface, small aboral part on top
- Test: internal shell w/ water canals
- spines made from Tubercles, used for burrowing in soft rock/coral, defense
- Pedicellariae (defensive) supported within internal Ossicles
- Tube feet used for movement, food collection, waste removal, respiration
- Aristotle Latern: jaw like feeding
- Echinoplutes: planktonic larvae w/ bilateral symmetry
- Turbellarian in gut (parasitic)
- Gonads release gametes through genital pore on aboral plate, develop alternate with test growth
- broadcast spawning
- no autonomy, poor regeneration
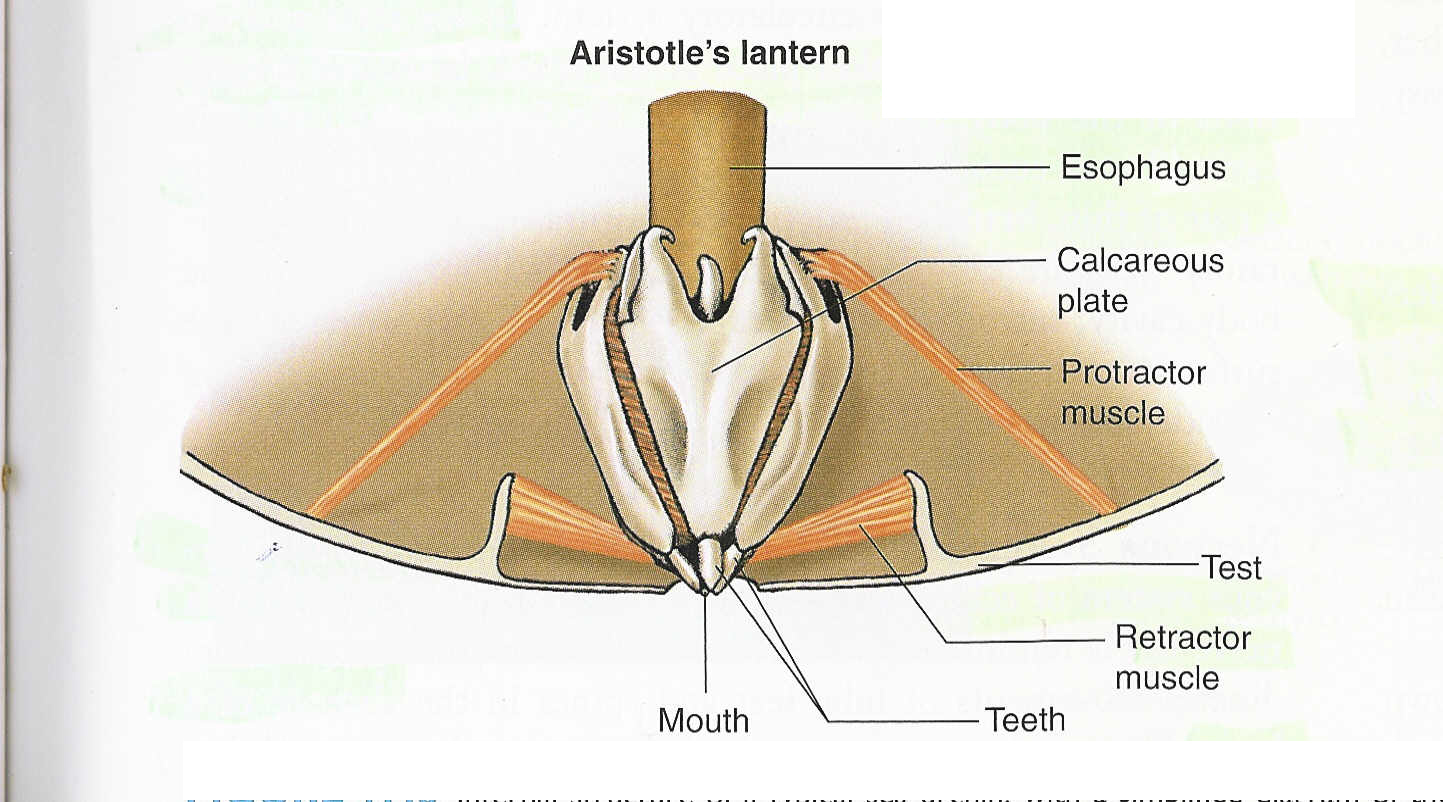
C. Echinoidea Aristotle Lantern
-Chisel teeth: slice and grind algae
-40 skeletal support pieces
- Teeth secreted from internal sacs 1mm/wk
- Teeth VERY hard
C. Echinoidea Regularia
Sea urchins
- radially symmetry
- grazers
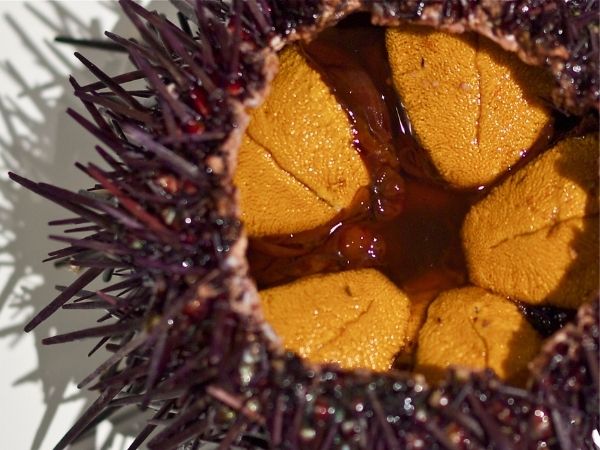

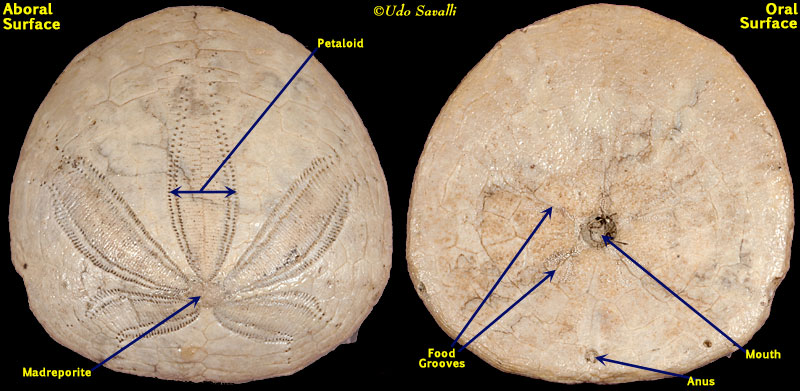
C. Echinoidea Irregularia
Sand dollars, heart urchins, sea biscuits
- secondarily bilaterally symmetrical
- burrow, filter, or deposit feeder
- feed with ciliary currents and tube feet
C. Echinoidea Calcification
Sea Urchins
- test composed of fused plates, each separate ossicles
- new CaCO3 laid down from outside of plate aborally
- new calcification occurs on outer surface, growth lines seen on inner surface of plate
- Fast growth: ossicles open and spacious
- Slow growth: ossicles less space, close together
- highly regulated, don’t vary in shape
- plates can be resorbed as mouth is enlarged/ animal grows
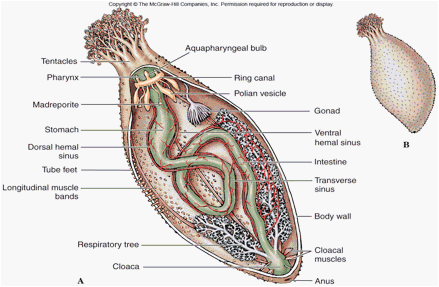
C. Holothuroidea Holo-th-uro-idea
= sea cucumbers
- elongated oral and aboral
- Test leathery, tough, embedded ossicles
- internal madreporite
- Buccal tentacles (around mouth) for feeding, modified tube feet w/ extension of water vascular system
- mucus traps food particles, tentacles sweep food to mouth
- single gonad, genital oiral at oral end
- broadcaster spawners
- Respiratory tree connect to hind gut (pump water in and out), cuverian tubules at base of tree (shoot sticky tubules, defensive, shot out of cloaca)
- Ambulacral grooves- closed
- Evisceration: defensive mechanism, internal organs ejected through cloace often w/ release toxins (Holotheurin)
- Haemal system: closed circulatory system
C. Holothuroidea F: Synatidae Syn-at-idae
= medusa worms
- lack tube feet, retractor muscles, repsiratory tree, caverian tubules
- Sp. Leptosynapta albcans

C. Crinoidea Cri-no-idea
= feather stars, sea lilies
- reef passage, feather stars are sedentary (move if disturbed), sea lilies are sessile
- 10 arms, branched w/ pinnules
- simple tube feet, no ampullae, no hydraulic extensions (respiration, waft food to mouth)
- internal madreporite
- arms held out to filter, stiffen by mutable connective tissue to hold on in strong currents
- gonadal cell line coelomic extensions in pinnules of arms (no distinct gonads)
- stalked or free swimming
- cupliked body “calyx”
- anus on oral disc next to mouth
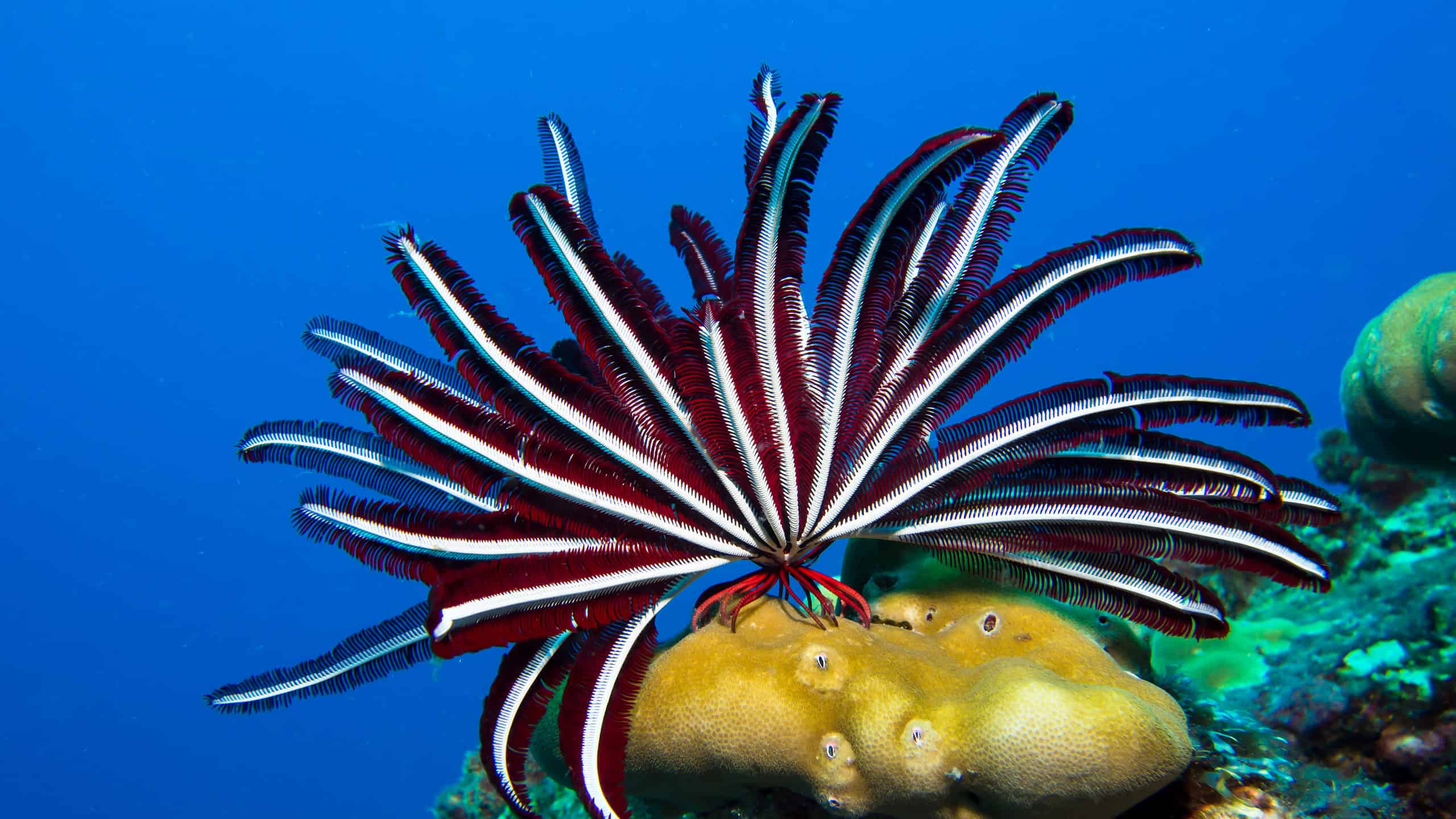

P. Echinodermata Deep Sea
- deeper you go, the more echinoderm dominate
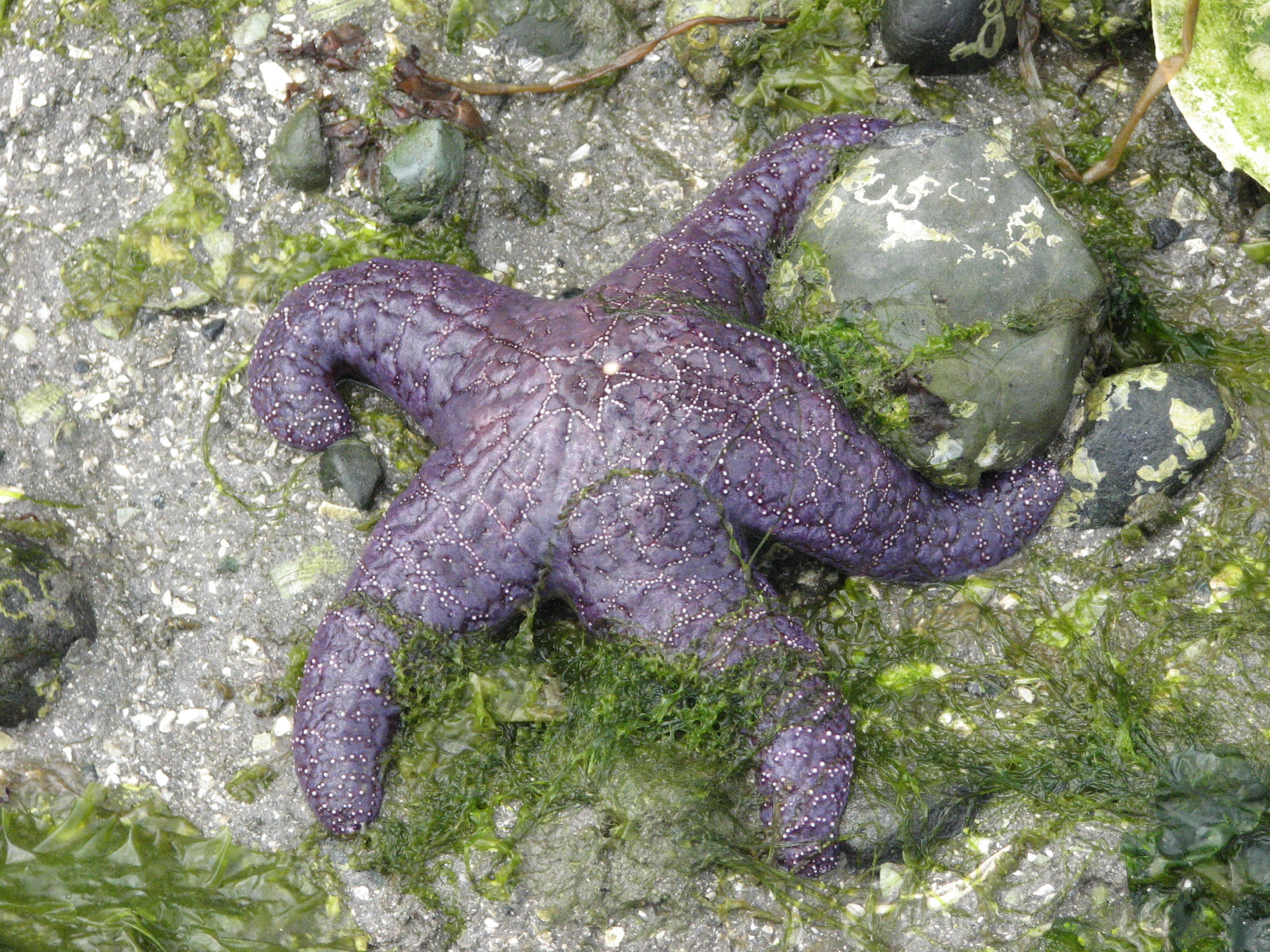
P. Echinodermata Mid-Intertidal Zone
Pisaster and Leptasterias
Pisaster (keystone species) Feeding preference
- mussels > barnacles > chitons > turban snails
- lower down the food preference, more competition
- lots of muscle, BIG and vice versa
- INTRAspecific competition: more dense pisaster pop, smaller they are
Leptasterias Feeding preference
- Turban snails > chitons> mussels> barnacles
INTERspecific competition of the two groups
- when one is common, the other is not
- Pisaster > Leptasterias (pinch and drive away)

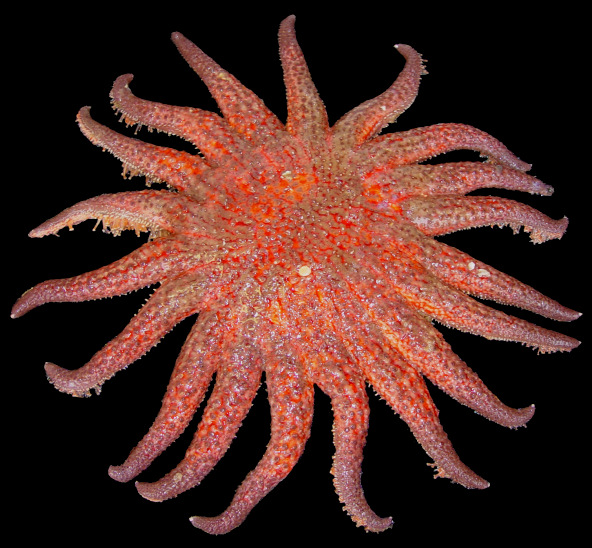
P. Echinodermata Low intertidal zone
-Sea urchins graze on algae
- Pycnopodia keystone species: main food sources is sea urchins as they have lots of arms and large stomach, eat lots
- stampedes 12/urchins a day but only eats 1/day

P. Echinodermata Pacific Coast Subtidal Zone
New England: Lobster →Sea urchins→ kelp
North Cali to Alaska: Sea otter→ Sea urchins→ Kelp
Southern Cali: Lobster, Sea star→ sea urchins→ Kelp
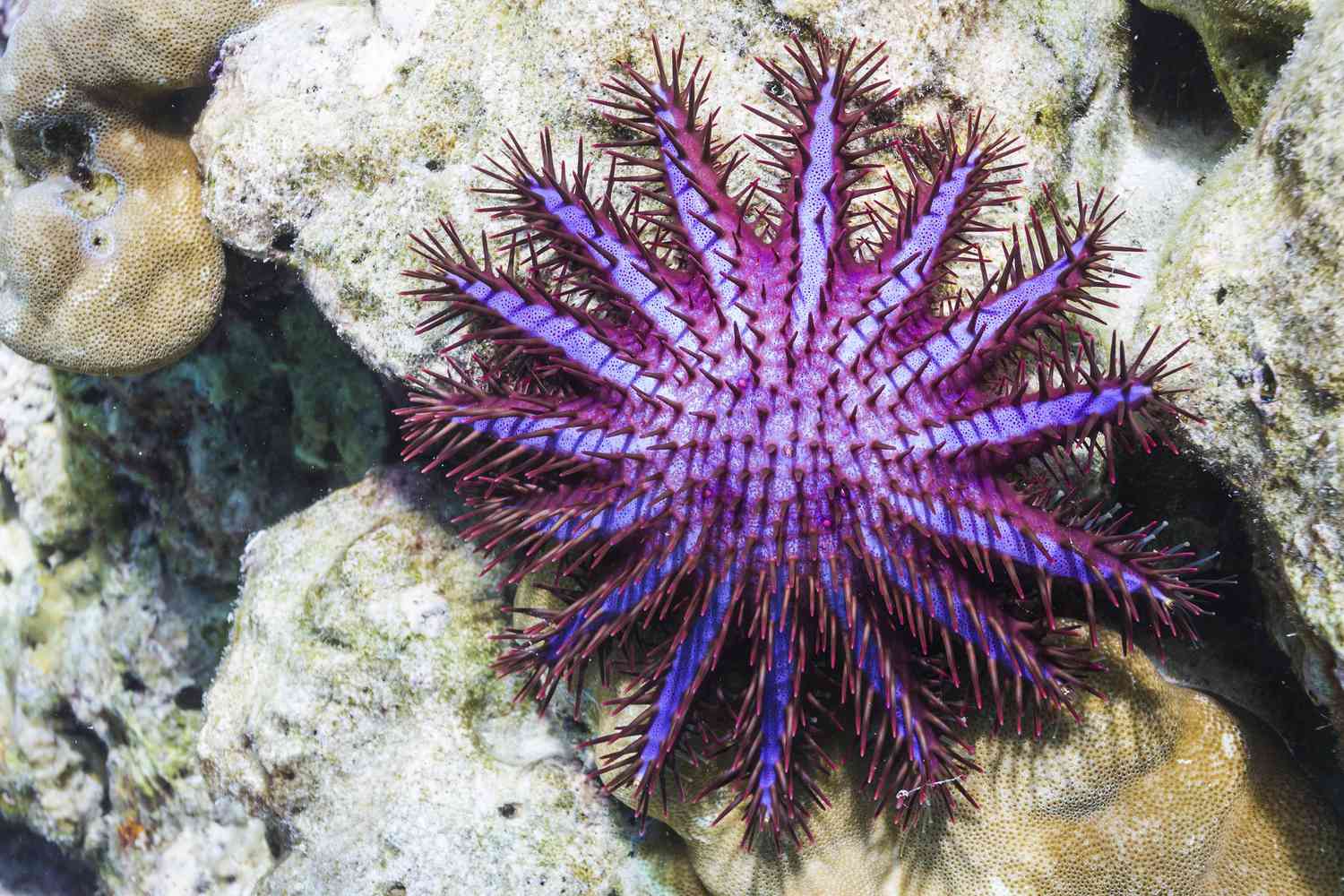
P. Echinodermata Indo-Pacific Coral Reefs
-Acanthaster outbreak destroy coral reefs, eat all coral
- Eaten area turns white and whiter
- Outbreaks occur on high islands or coast margin, few years after heavy rain

P. Echinodermata Carribbean Coral Reefs
-Acropora branching coral thicket before hurricane
- Diadema urchins: feed nocturnally, in crevice during day
-Triggerfish eats them
-Effects: graze a halo, feed on sea grasses