Oceanography
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Wave height
top of crest to bottom of adjacent trough

Frequency
the number of complete wavelengths that pass a point in a given time; speed x wavelength
Wavelength
The distance between two corresponding parts of a wave
Water depth
calculates speed of waves
Tsunami speed equation
Normal conditions
Winds move water from eastern part to the western Pacific Ocean; driven west
El Nino
Warm water driven east by strong counter currents
Surface
Driven by wind and global patterns
Deep
Density and temp. differences in the ocean
Important for marine ecosystems
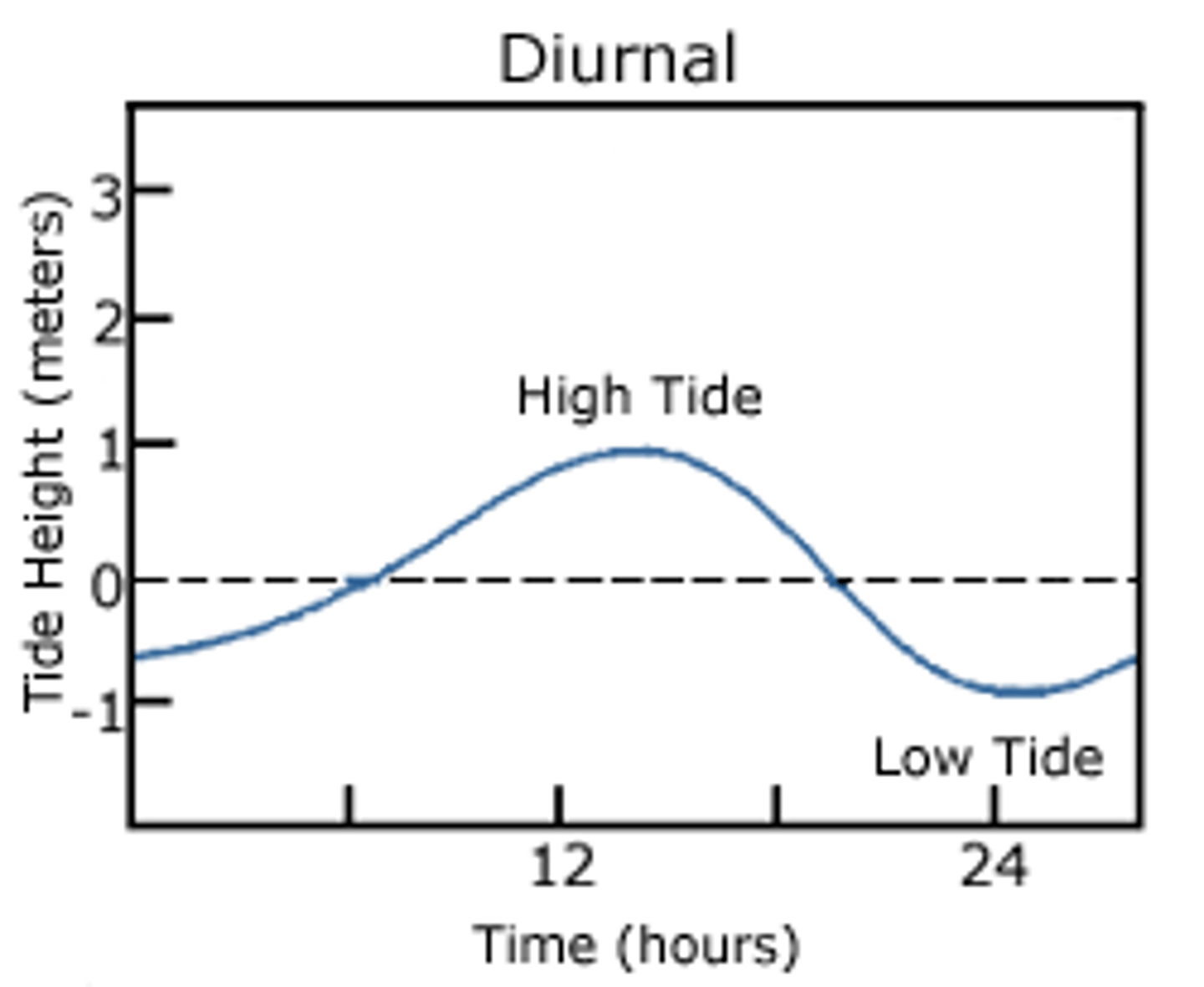
Diurnal
occur once daily
semidiurnal
occur twice daily and also equal height

Mixed semi-diurnal
occur twice and unequal height

High tide
The lower of 2 high tides
Higher High Tide
The higher of 2 high tides
Low tide
Higher of 2 low tides
Lower low tide
Lower of 2 low tides
Neap Tides
First and third quarter; Smallest tide ranges
Spring Tides
Full and New Moon; Highest tide ranges
Stages of the moon do not tell us whether itd be higher or lower tide;
Which tell us what the tidal range would be
Estuary
Partially enclosed coastal water body freshwater + salt water
Where rives meet the sea
Despositional
Prevents pollution
Mud flats
silt mud brought in by sea and ocean
Salt Marsh
Near spits
Absorbs majority of water hitting the coast line
Mangrove Forest
Tropics/subtropics
Acts as a barrier between tides and coast lines
roots being exposed during low tides
Depositional
Erosional
Fossil fuel being burned increases the amount of carbon dioxide that is trapped in the atmosphere,
increases the temperature
74 mph
To become a hurricane
130
Under 5 cateagory hurricane
Twilight
3% down in the ocean
90% of animals use Bioluminescence Chemicals
Midnight
Species are energy deficient
harder to take a swim than walk in space
Abyssal Plain
Grey mud and rocks
Manganese nodules
400C jets
Hadal Zone
Underworld of the sea
Long narrow trenches