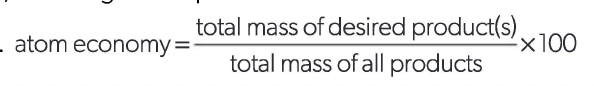S1 .4 - Quantitative chemistry
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
Avogadro constant
number of 12 C atoms in exactly 12.00g of 12C, = 6.02 x 1023
ideal gas
All collisions between particles (in constant, random motion) are perfectly elastic
no intermolecular forces between the particles
particles have negligible volume
The temperature of the gas is proportional to the average kinetic energy of its particles, and the pressure is due to collisions of the particles with the vessel walls.
real gas
Some attractive forces between the particles and the particles themselves do occupy some space
can condense into liquid
will behave ideally in high temperatures and low pressures
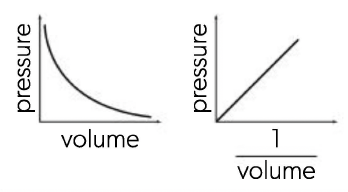
Boyle's Law
P∝1/V , At constant temperature: as the volume decreases the concentration of the particles increases, resulting in more collisions with the container walls. The increase in pressure is inversely proportional to the decrease in volume, i.e. doubling the pressure halves the volume
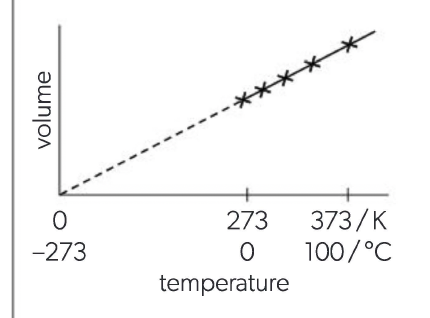
Charles's Law
V∝T, At constant pressure: at higher temperatures, the particles have a greater average velocity so individual particles collide with the container walls with greater force. To keep the pressure constant there must be fewer collisions per unit area so the volume of the gas must increase. The increase in volume is directly proportional to the absolute temperature, i.e. doubling the absolute temperature doubles the volume.
Gay-Lussac's Law
P∝T, At constant volume: increasing the temperature increases the average kinetic energy, so the force with which the particles collide with the container walls increases. Hence pressure increases and is directly proportional to the absolute temperature, i.e. doubling the absolute temperature doubles the pressure.
Avogadro's law (molar volume of gases)
Avogadro's law states that equal volumes of different gases at the same temperature and pressure contain the same number of moles.
One mole of any gas will occupy the same volume at the same temperature and pressure. at STP: 22.7 × 10-2m3
atom economy
a measure of the amount of starting materials that become useful products