Hip FA
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Where is a common area of pain referral from the hip
knee
what type of joint is the hip
ball and socket
how many degrees of freedom are there in the hip
3
flex/ext
ab/adduction
ir/er
what does the head of femur articulate with
acetabulum
how many trabecular patterns are there in the hip
3
what does the arcuate bundle do
resist bending or shear of the head and neck of femur
what does the trochanteric bundle do
resist tensile forces from muscles acting on the great trochanter
what does the vertical bundle do
resist compression through head of femur
when people have pain at the hip, what do they usually do with their hands
they make a "c" and cup the sides of the hips to show where referred pain is going
when the knee is flexed, what is the ROM of hip flexion
120 degrees
when the legs are abducted 30-40 degrees, what is the ROM of hip flexion
150 degrees
when the knee is extended, what is the ROM of hip extension
20 degrees
when the hip is abducted, what is the ROM
45 degrees
when the hip is adducted, what is the ROM
30 degrees
when the hip is externally rotated, what is the ROM
45 degrees
when the hip is internally rotated, what is the ROM
30 degrees
when assessing ROM, what are some things to consider
pelvic tilt
kyphosis
lordosis
size of pt
when you are walking up the stairs, how much flexion is your hip in
40-67 degrees
when you are walking down the stairs, how much flexion is your hip in
36 degrees
when tying ones shoe and your legs are crossed, what is the ROM for flexion and external rotation
110 degrees flexion
33 degrees ER
what is the position of reference
line connecting the two ASISs is perpendicular to a line from the ASIS to the patella and parallel to the frontal plane
what is the resting/open packed position for hips
30 hip flexion
30 hip abduction
20 hip ER
what is the close packed position for the hips
full extension
internal rotation
abduction
what is the capsular pattern for the hip
internal rotation
flexion
abduction
slight loss of extension
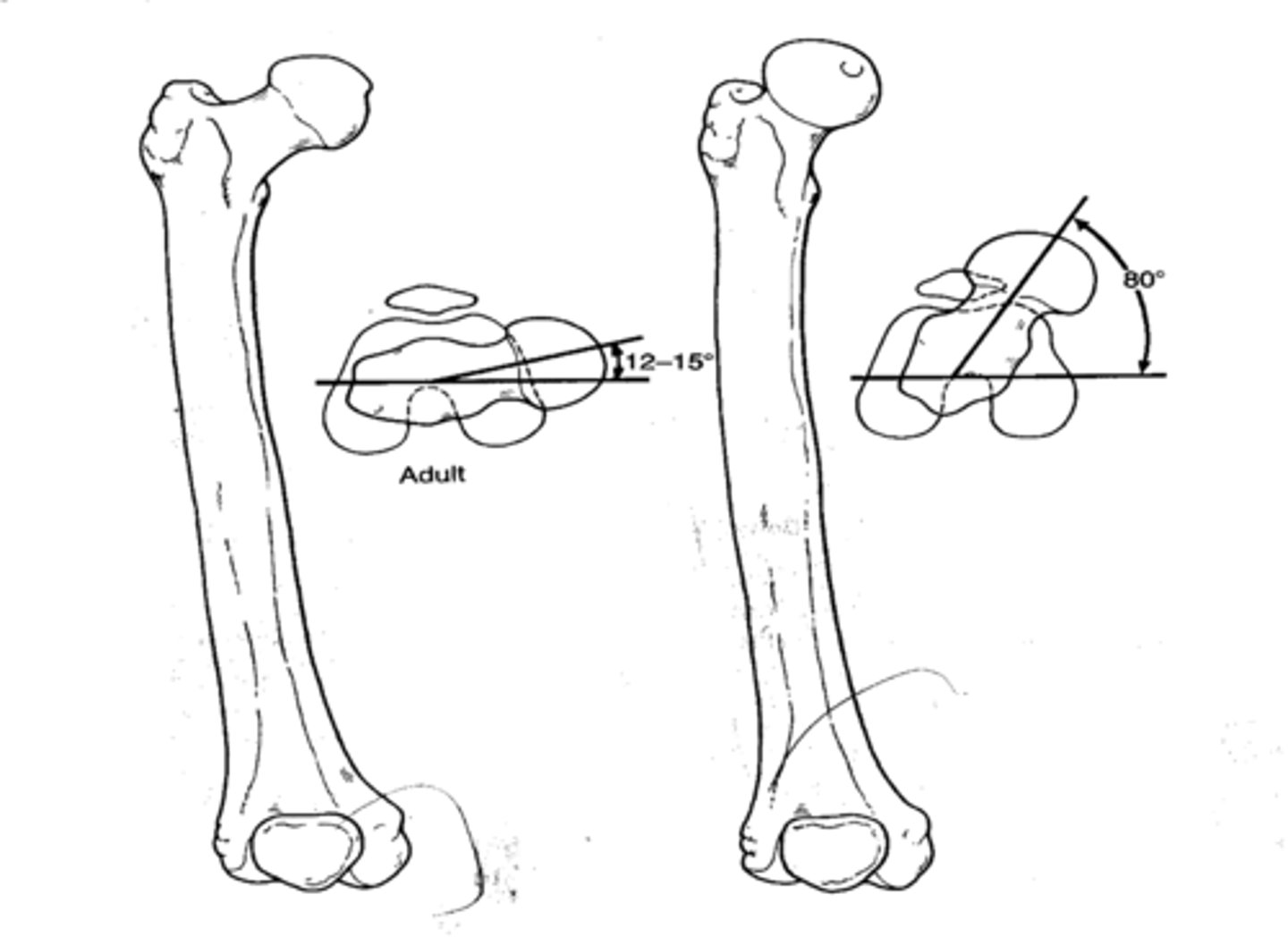
true or false: the angle of inclination is typically bigger in men
true
what is the normal angle of inclination
125 degrees
what is coxa valga
angle of inclination greater than 150 degrees
what is coxa vara
angle of inclination less than 120 degrees
what influences the collum angle
ROM
speed of motion
strength of bony structure
shearing forces on the femoral head and neck
what is the angle of torsion
angle between the axis of the femoral condyles and the axis of the head/neck of the femur in the transverse plane
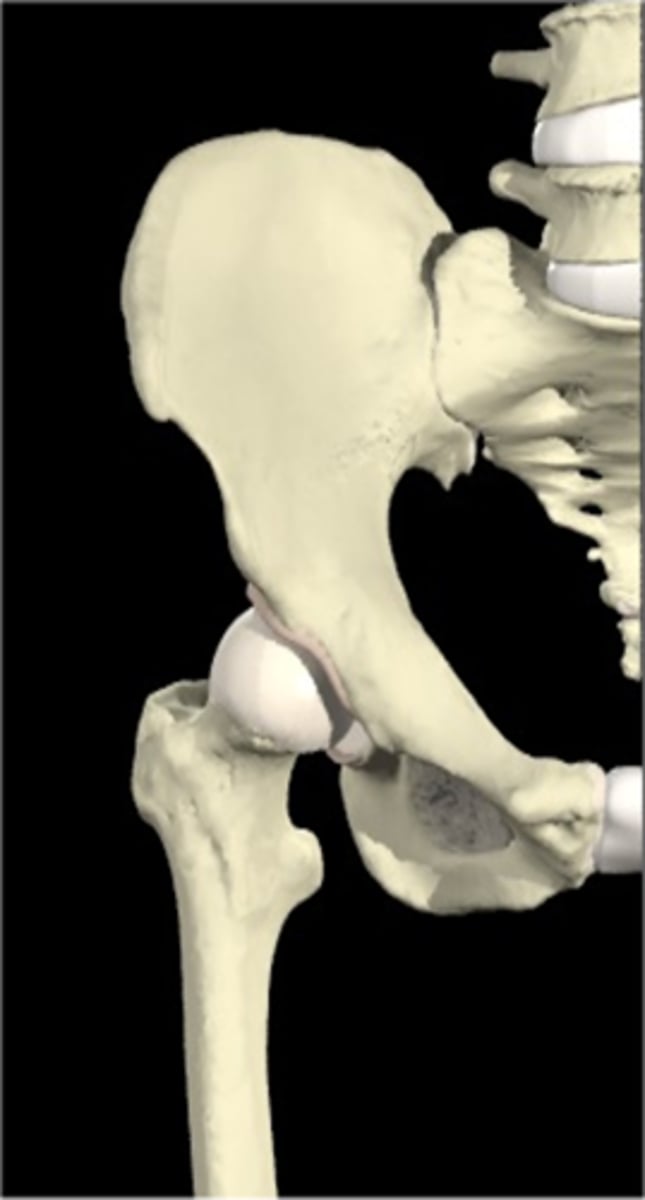
how does the acetabulum face
lateral
anterior
inferior
how does the femoral head face
medial
anterior
superior
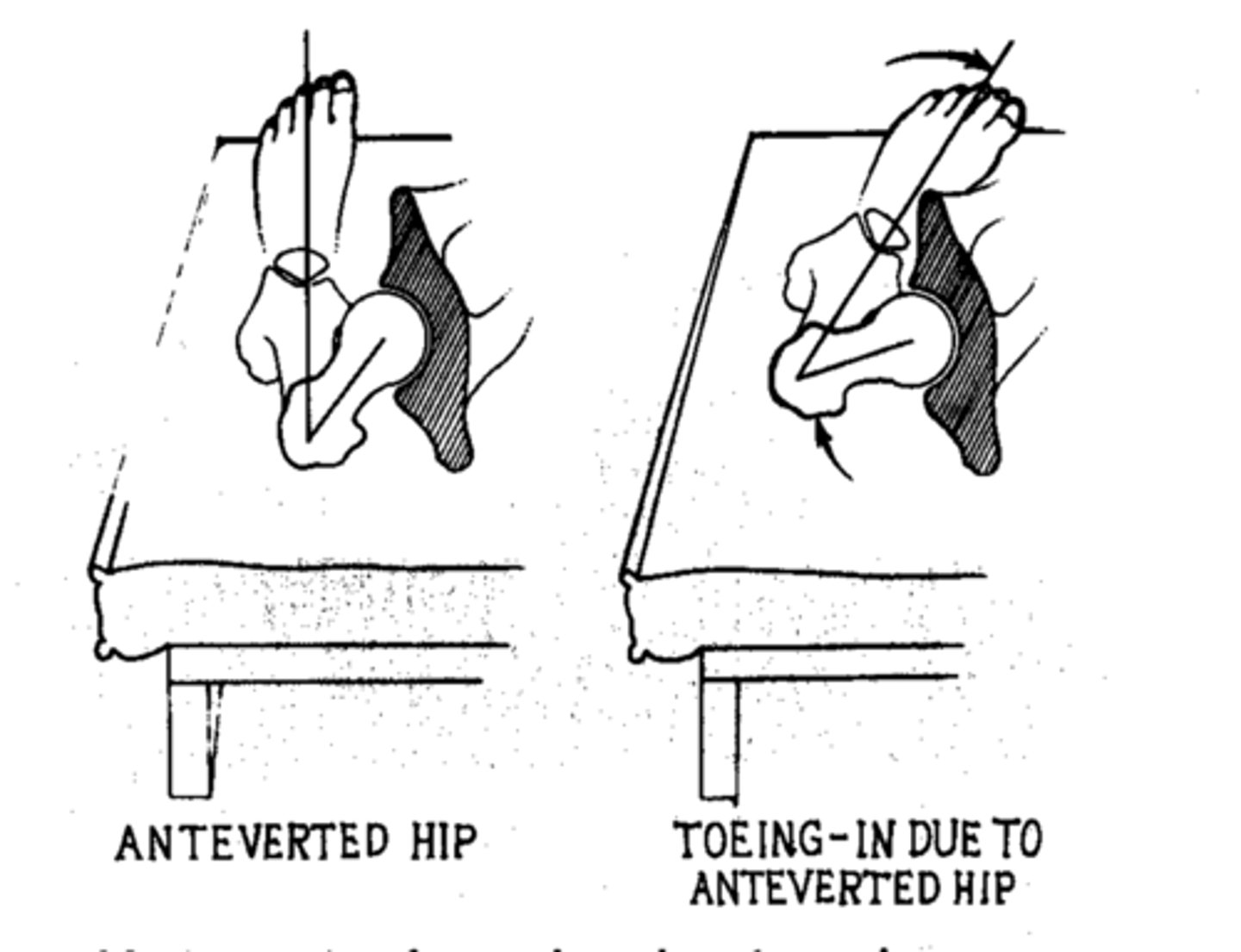
what is anteversion
angle of torsion is greater than 15 degrees
lacks ER
toe-in gait
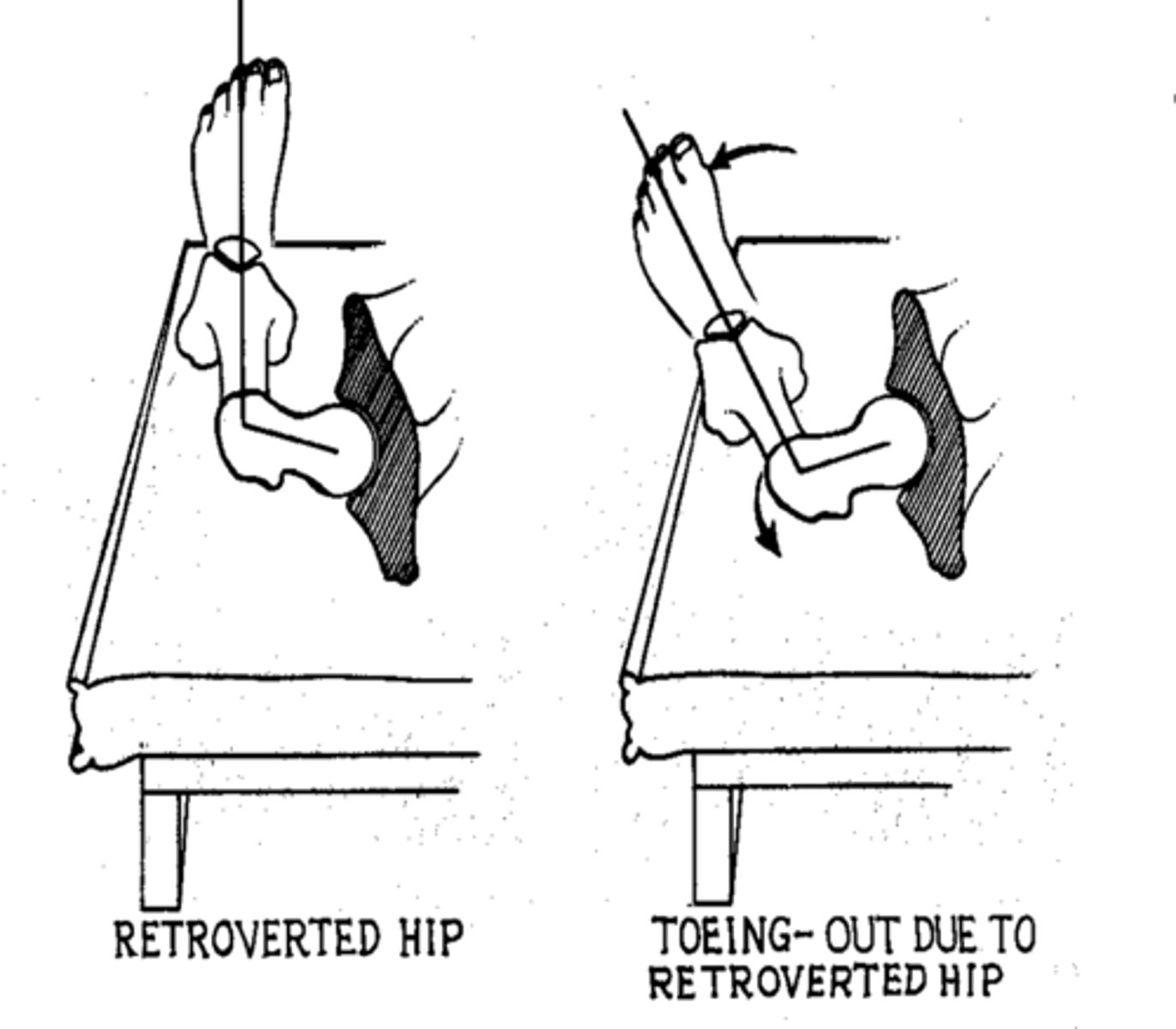
what is retroversion
angle of torsion is less than 8 degrees
lacks IR
toe-out gait
what is the labrum composed of
type I collagen, little cartilage
true or false: the labrum creates a negative intra articular pressure
true
what are some functions of the labrum
lubricates and cushions joint
improves load distribution
true or false: there is about 25 mm of articular cartilage which is attached to the neck of the femur
false; about 9 mm
true or false: the hip has the most cartilage than any joint in the body
true
what part of the femur is not covered by cartilage
the fovea
what is another name for the illiofemoral ligament
Y ligament
what is the job of the Y ligament
to check IR and extension; movements in the sagittal plane
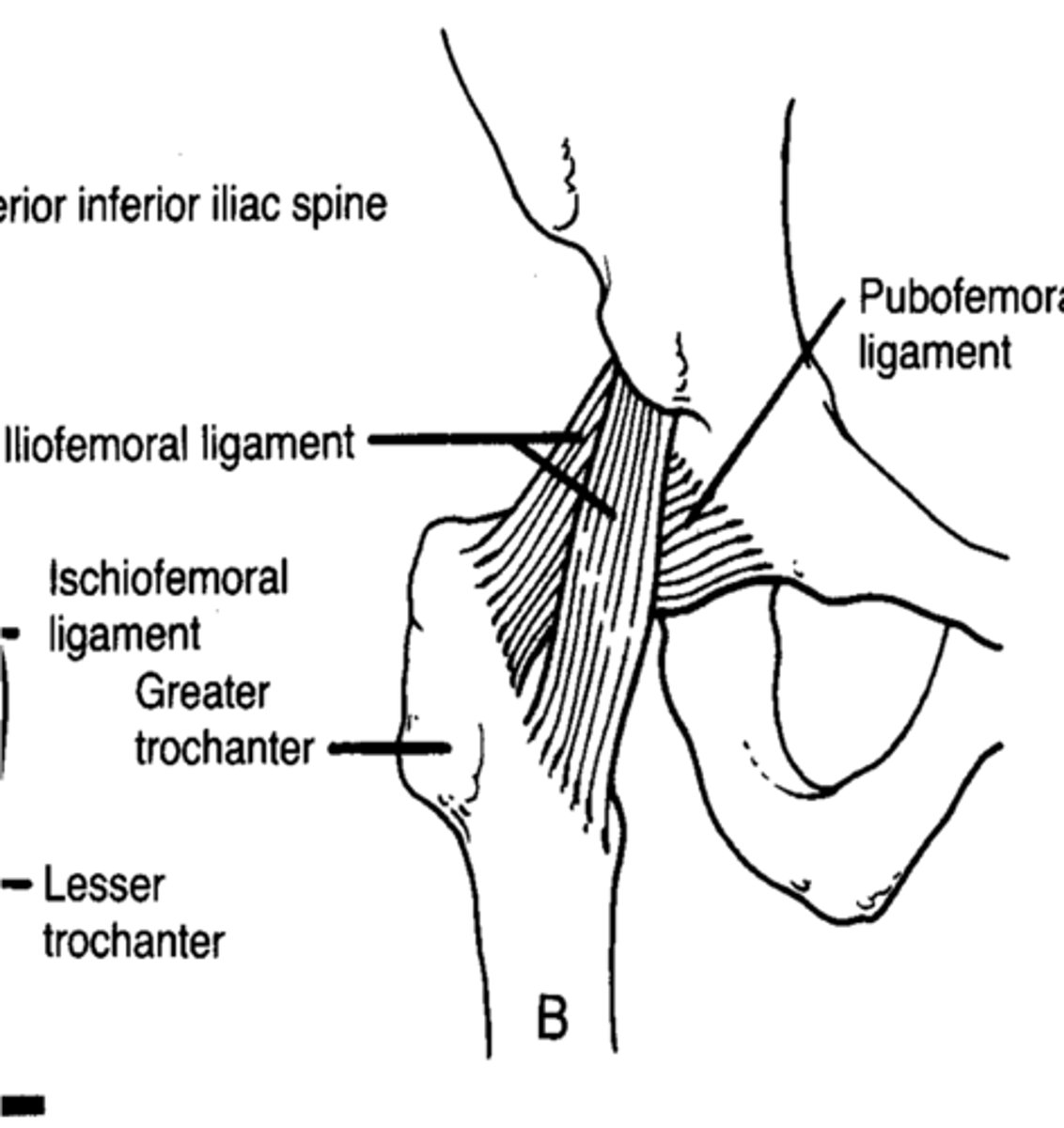
what is the job of the pubofemoral ligament
checks abduction and IR; movements in the frontal plane
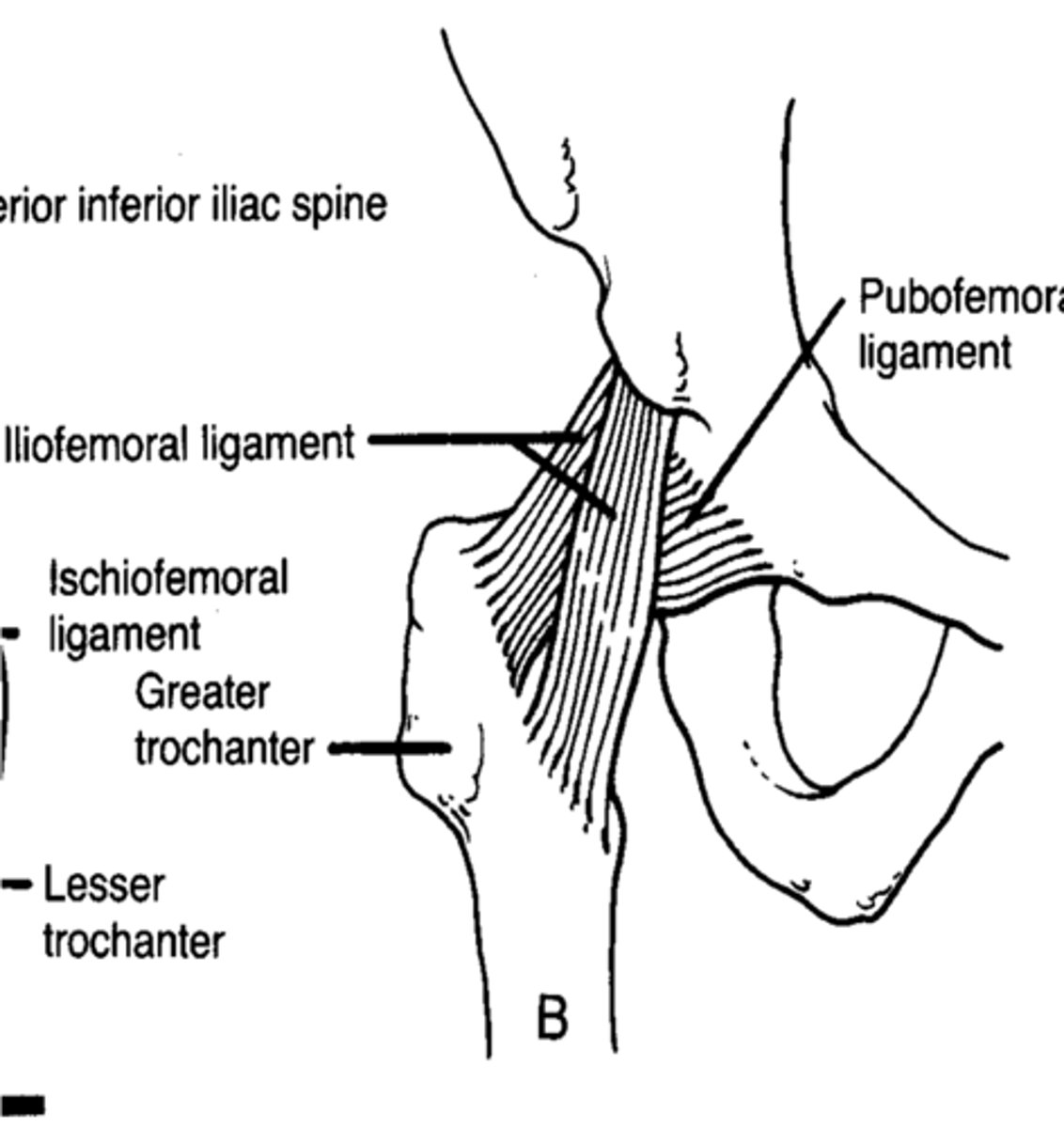
in the hip, what ligament is posterior
ishiofemoral ligament
what is the job of the ishiofemoral ligament
checks extension and IR
where does the ligament teres attach to
acetabular notch and fovea
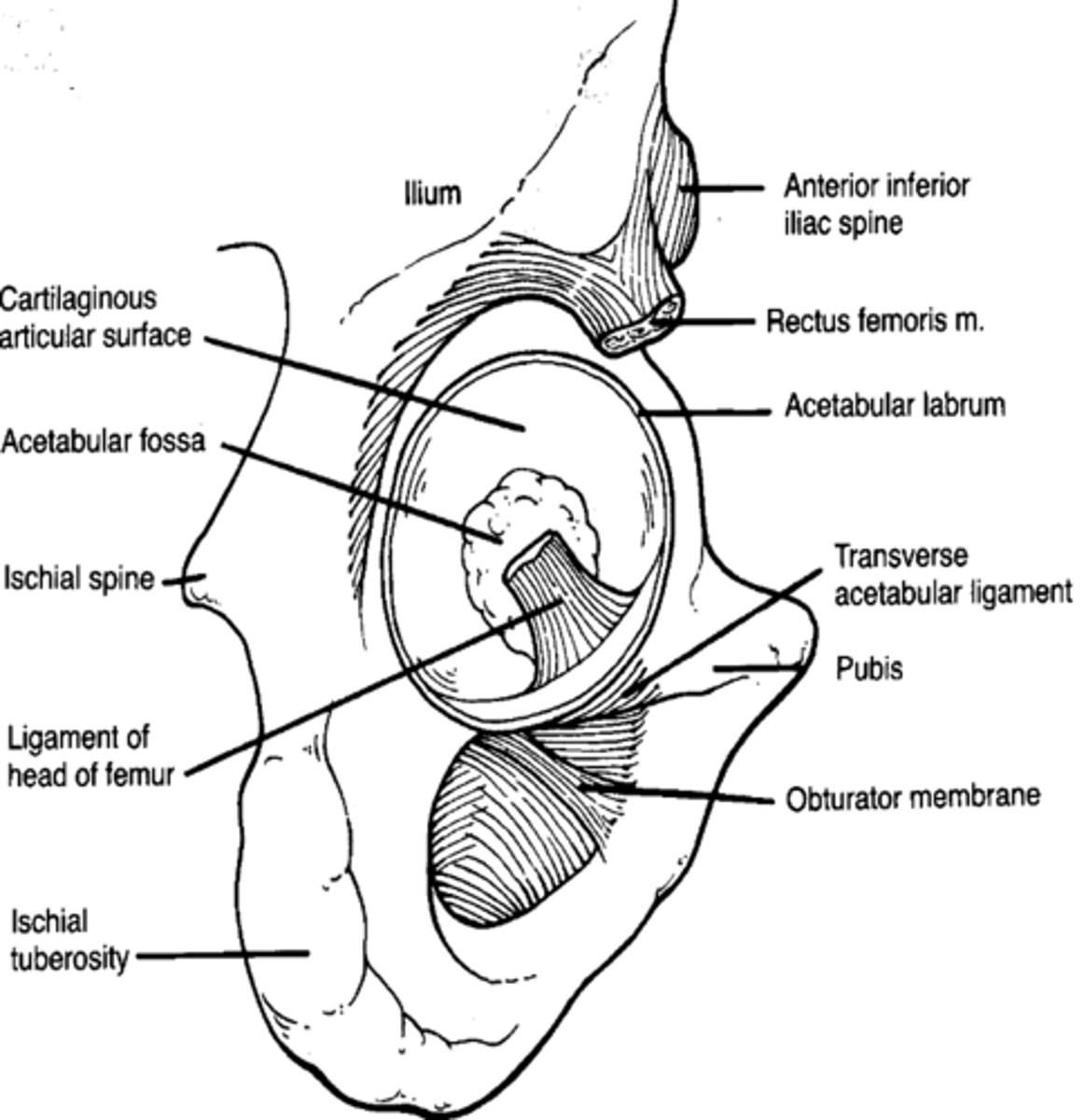
ligamentum teres is taut in what movement
adduction of the hip
what ligament provides vascular supply to the head of the femur
ligamentum teres
what ligament helps the obturator artery to pass through
transverse ligament
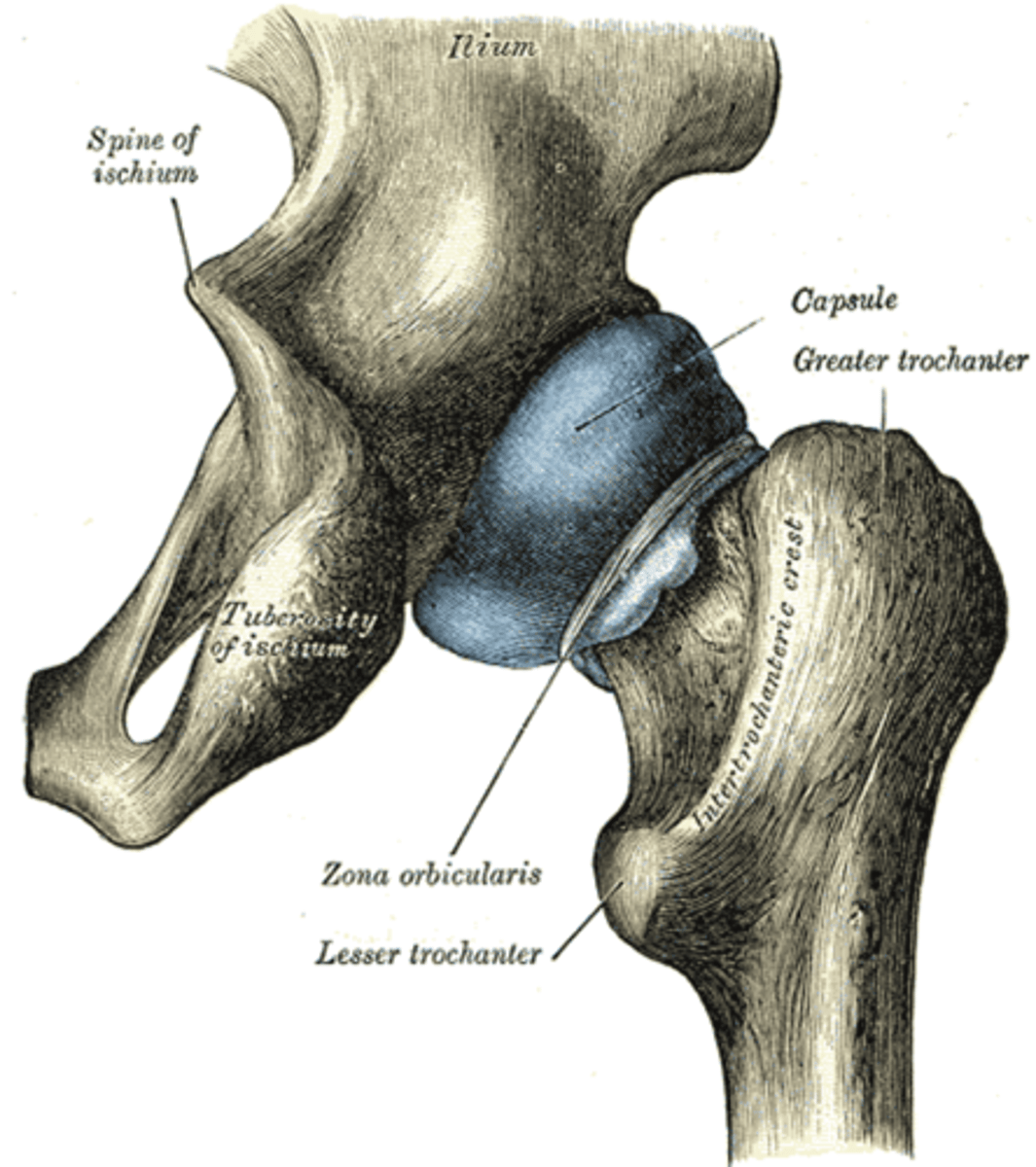
what does the zona obicularis resist
hip distraction
how is the zona obicularis formed by
the circular fibers of the hip capsule
what 3 muscles make up the pes anserine
semitendenosis
gracilis
sartorius
what is trendelenberg sign
indicates weakness of gluteus medius
causes opposite side to drop
common before hip replacements
what is a common injury in long distance rummers, downhill skiers, jumping sports, etc. due to repetitive stress from friction of the ITB as it slides over the femoral condyle
iliotibial band friction syndrome
what are the major synergistic muscles of hip flexion
psoas major
iliacus
TFL
sartorius
rectus femoris
gluteus medius
gluteus minimus
what are the major synergistic muscles of hip extension
gluteus maximus
biceps femoris
semitendinosus
semimembranosus
when extended, do the hamstrings assist
true
what is a synergistic muscle for abduction
gluteus max/med/min
what is a synergistic muscle for adduction
adductor magnus/longus/brevis
what is piriformis syndrome
entrapment of the sciatic n. by the ms. as it passes through the sciatic notch
what is piriformis syndrome caused by
overuse
trauma
females