Human Phys chapter 3
1/145
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
146 Terms
macroscopic structure
structural elements that may be viewed with the naked eye
tendon
Connects muscle to bone
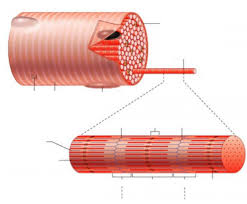
myofibril
tightly packed filament bundles found within skeletal muscle fibers
muscle cell
long and slender and contains fibers that aid in contracting and relaxing
muscle fiber
a single muscle cell
fascicle
bundle of muscle fibers
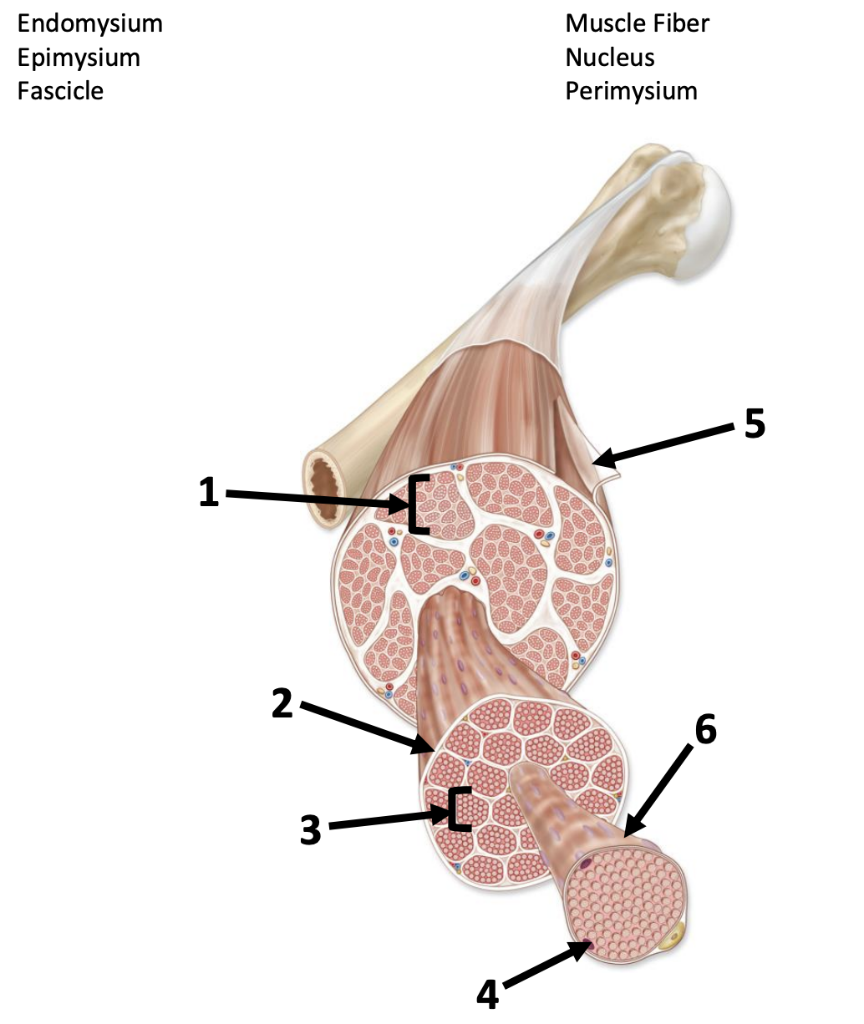
endomysium (3) (gaps)
Connective tissue surrounding a muscle fiber
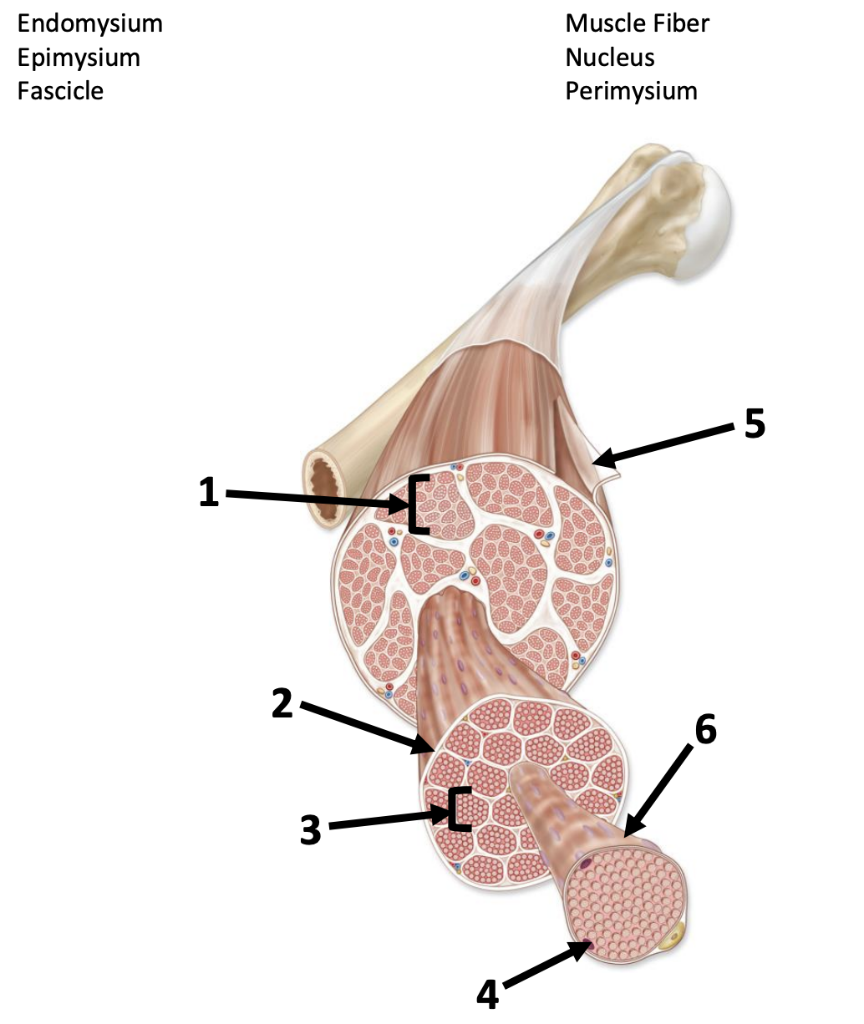
perimysium (1) (gaps)
Connective tissue surrounding a fascicle
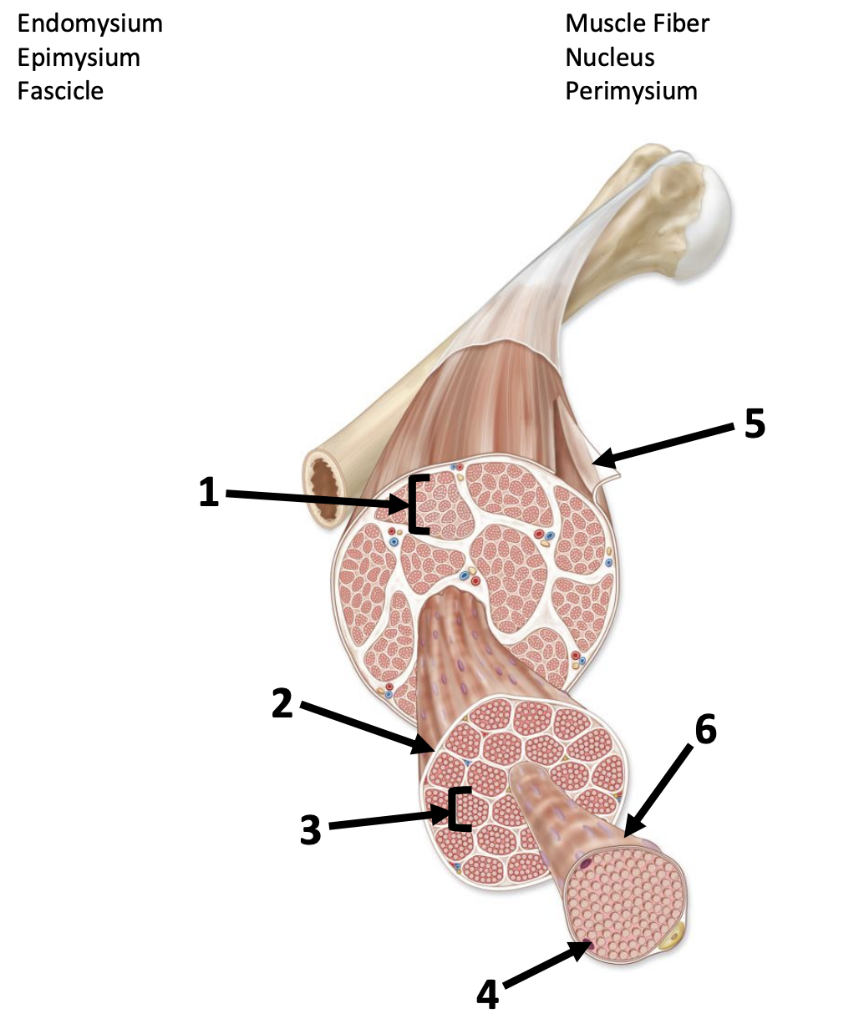
epimysium (5)
surrounds entire muscle
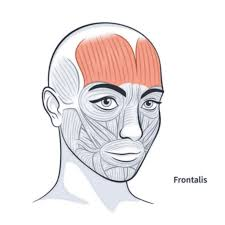
frontalis
raises eyebrows, wrinkles forehead
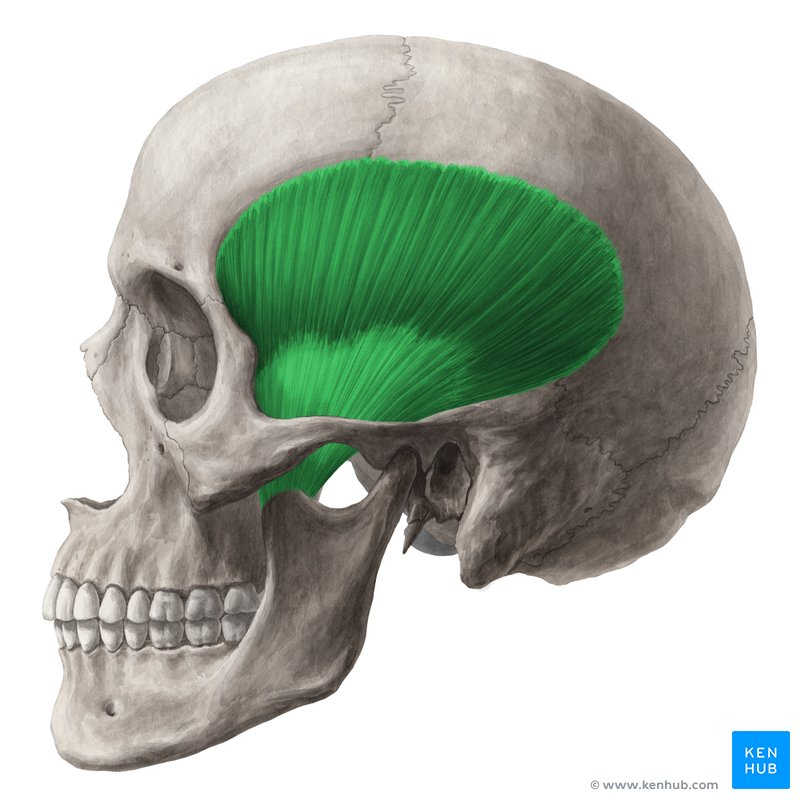
temporalis
elevates and retracts mandible
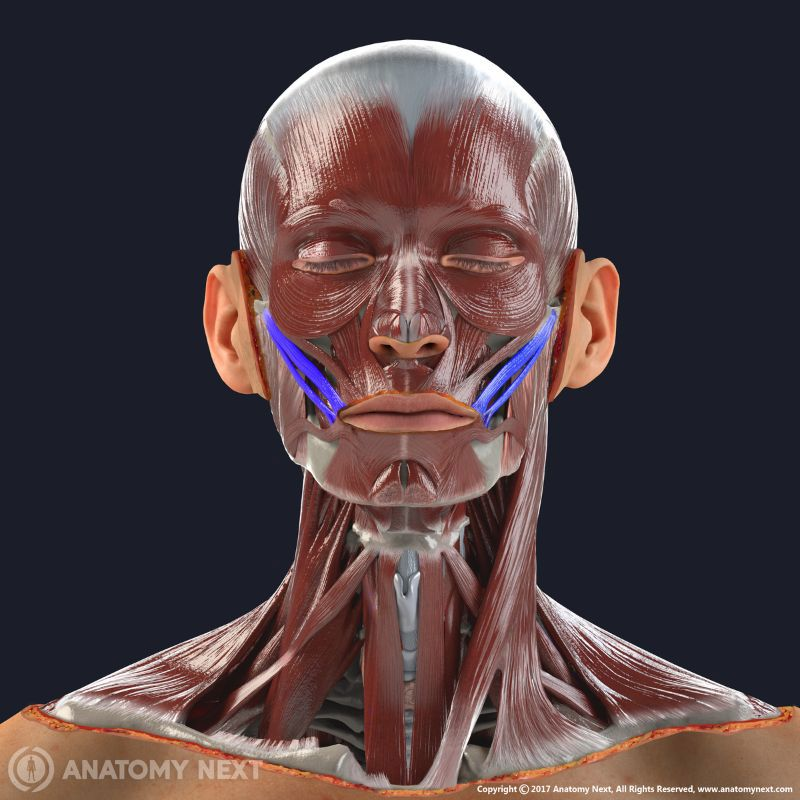
zygomaticus
smiling muscle
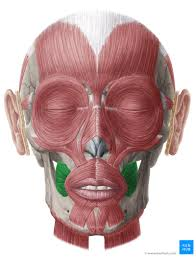
buccinator
Used to suck in your cheeks
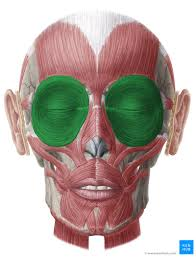
orbicularis oculi
Closes eyelids; used in blinking, winking, and squinting
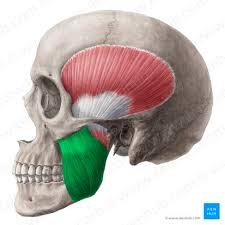
masseter
elevates mandible
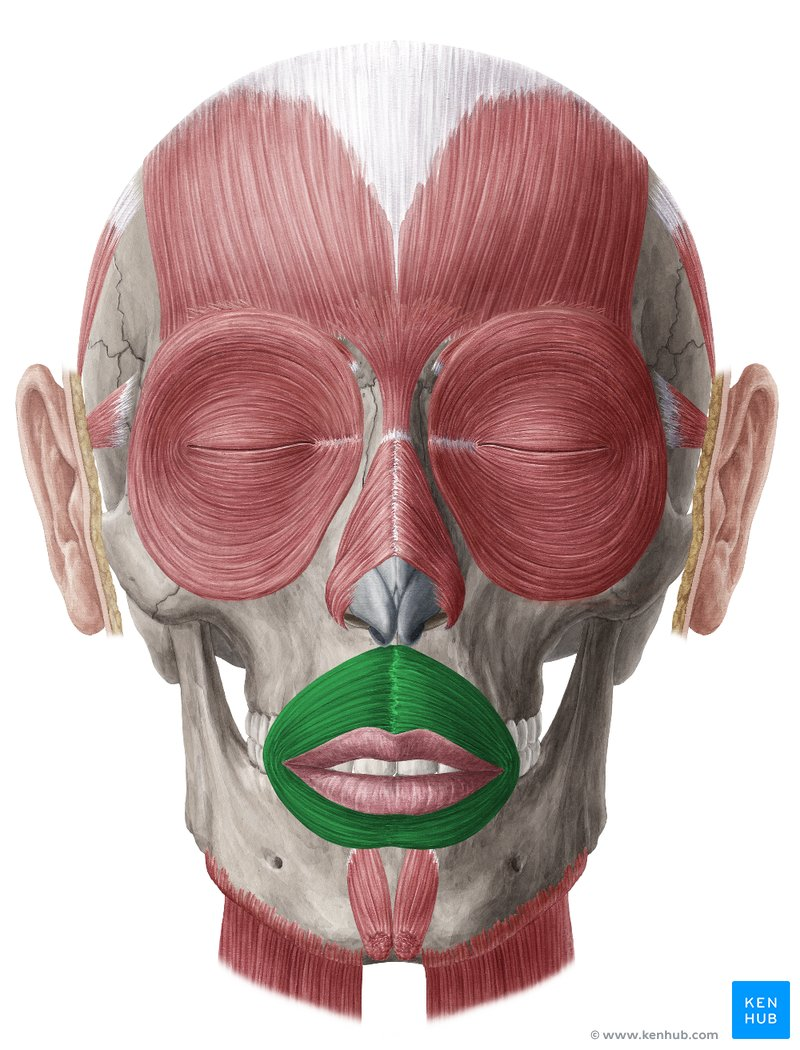
orbicularis oris
closes and protrudes lips
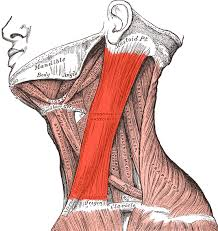
sternocleidomastoid
Contraction of one side: laterally flexes neck, rotates head to opposite side; Contraction of both sides together: flexes neck
platysma
Draws down the lower lip and angles of the mouth; tenses skin of the neck; helps depress mandible
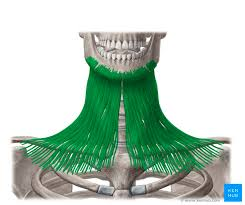
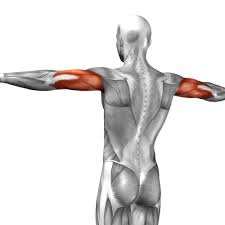
trapezius
Elevates, depresses, retracts, and rotates the scapula; rotates the arm
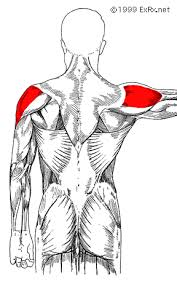
deltoid
shoulder
latissimus dorsi
extends and adducts humerus
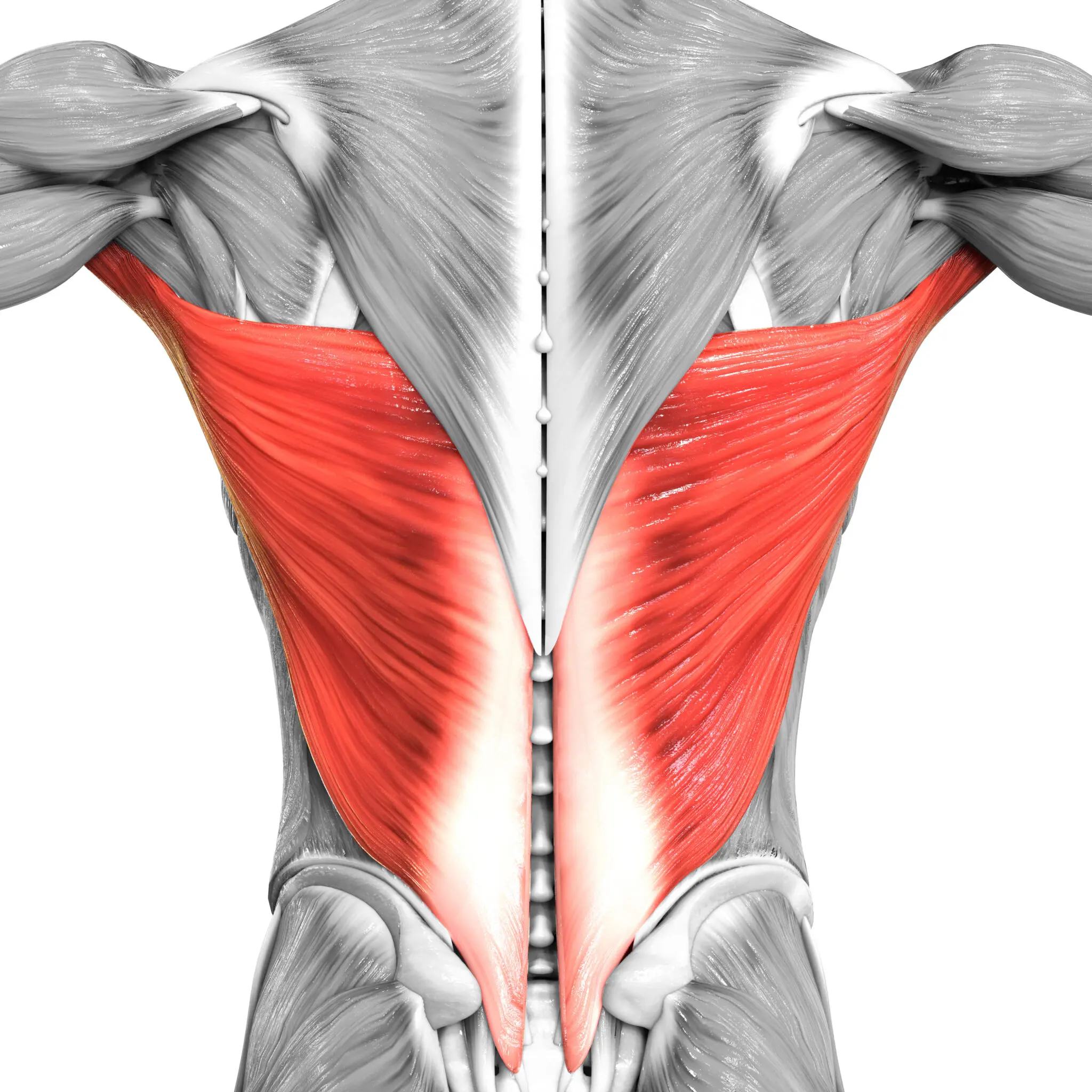
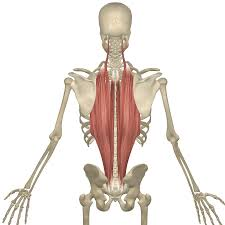
erector spinae
prime mover of back extension
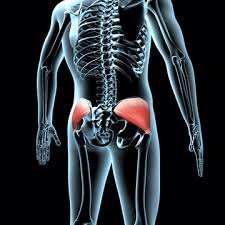
gluteus medius
abducts and medially rotates thigh
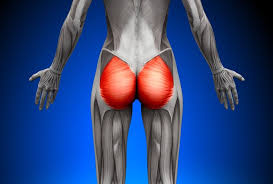
gluteus maximus
extends thigh at hip joint
hamstring group
located at the back of the upper leg, consists of three separate muscles: biceps femoris, semitendinosus, semimembranosus
biceps femoris
extends thigh and flexes leg
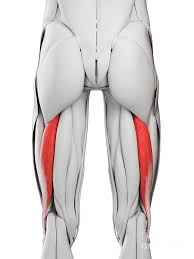
semitendinosus
Flexes leg at the knee and extends thigh at the hip; belongs to the hamstring group
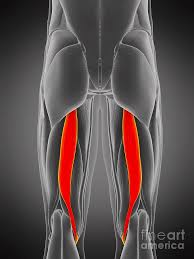
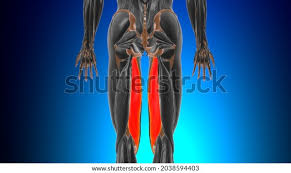
semimembranosus
Flexes leg at the knee and extends thigh at the hip; belongs to the hamstring group
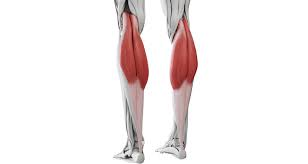
gastrocnemius
plantar flexes foot
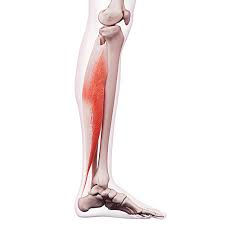
soleus
plantar flexion
biceps brachii
flexes forearm
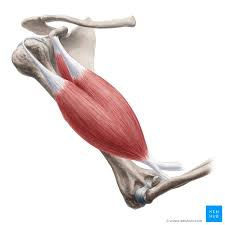
brachialis
flexes forearm
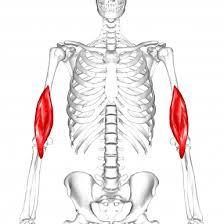
triceps brachii
extends forearm
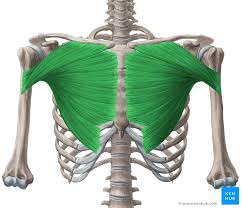
pectoralis major
Adducts and flexes humerus, chest muscle
transversus abdominis
compresses abdomen
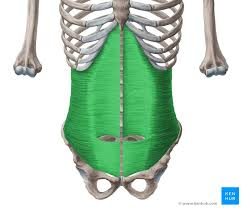
internal oblique
tenses abdominal wall and compresses abdominal contents
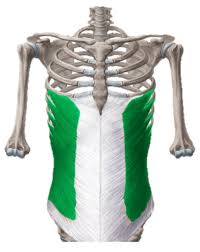
external oblique
Compresses abdomen; laterally flexes and rotates vertebral column
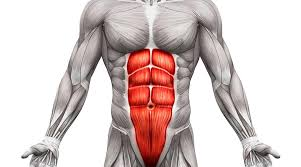
rectus abdominis
flexes vertebral column
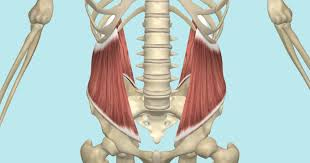
iliopsoas
flexes hip
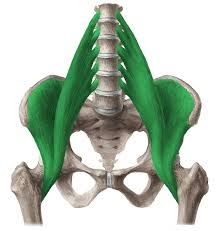
adductor muscles
adduct and medially rotate thigh
quadriceps group
rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, vastus intermedius
rectus femoris
extends leg and flexes thigh
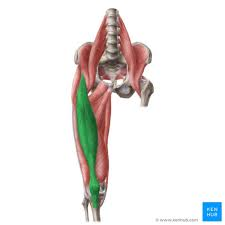
vastus lateralis
extends leg at knee
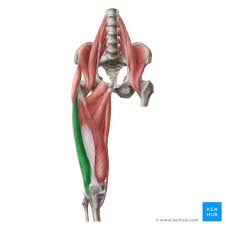
vastus medialis
extends knee
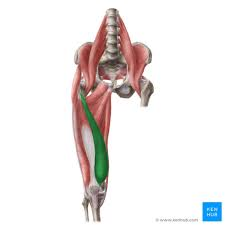
tibialis anterior
dorsiflexion and inversion of foot
flexion
bending a joint
extension
Straightening of a joint
hyperextension
Excessive straightening of a body part
abduction
Movement away from the midline of the body
adduction
Movement toward the midline of the body
circumduction
circular movement of a limb at the far end
rotation
circular movement around an axis such as the shoulder joint
dorsiflexion
bending of the foot or the toes upward
plantar flexion
bending of the sole of the foot by curling the toes toward the ground
inversion
Turning the sole of the foot inward
eversion
turning the sole of the foot outward
supination
movement that turns the palm up (thumb out)
pronation
turning the palm downward (thumb in)
opposition
Movement of the thumb to touch the fingertips
origin
part of the muscle that does not move
insertion
part of the muscle that moves
applied force
a force that is applied to an object by a person or another object
prime mover
The muscle that acts as the initial and main source of motive power.
synergist
muscle that aids a prime mover in a movement and helps prevent rotation
antagonist
muscle that opposes or reverses a prime mover
fixator
muscle that prevents movement of bone
skeletal muscle
A muscle that is attached to the bones of the skeleton and provides the force that moves the bones.
nuclei
clusters of neuron cell bodies in CNS
dendrites
Branchlike parts of a neuron that are specialized to receive information.
axon
the extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons or to muscles or glands
axonal terminals
the end of the axon branches, contain hundreds of tiny vesicles that contain neurotransmitters.
neuromuscular junction
point of contact between a motor neuron and a skeletal muscle cell
synaptic cleft
gap between muscle cell and axonal terminal
neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons
electrical signal
an electric current that carries information
brain
The mass of nerve tissue that is the main control center of the nervous system
action potential
a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon
spinal cord
Nerves that run up and down the length of the back and transmit most messages between the body and brain
motor neuron
a neuron that sends an impulse to a muscle or gland, causing the muscle or gland to react
sliding filament theory
theory that actin filaments slide toward each other during muscle contraction, while the myosin filaments are still
calcium ions
Serves as the actual "trigger" for muscle contraction by removing the inhibition of the troponin molecules
myosin binding site
where myosin head attaches during contraction
ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work
motor units
one neuron and all muscle cells it touches
muscle twitches
a single rapid contraction of a muscle followed by relaxation
phosphorylation by creatine phosphate
super fast, doesn’t need oxygen, only lasts 6-8 seconds
anaerobic fermentation
1 glucose=2ATP, produces lactic acid, lasts 40 seconds, 2.5 times faster than A.R., no oxygen required
Yields little ATP and toxic lactic acid, a major factor in muscle fatigue
aerobic respiration
1 glucose=26 ATP, slowest method, requries oxygen
muscle fatigue
Inability of muscle to maintain its strength of contraction or tension; may be related to insufficient oxygen, depletion of glycogen, and/or lactic acid buildup
oxygen debt
temporary lack of oxygen in the muscle due to exertion
heat generation
Muscle contractions produce heat
Helps maintain normal body temperature
endurance exercises
strain the oxygen loading/unloading systems and the aerobic mechanism in muscle cells
resistance exercises
strain and damage the pulling apparatus in muscles
prime mover of elbow flexion
biceps brachii
synergist of elbow flexion
brachilalis
antagonist of elbow flexion
triceps brachii
prime mover of jaw closure
masseter
synergist of jaw closure
temporalisa