Module 9 Prelab 3: Urease Test & Friends
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
media being inoculated for SIM
agar deep tube
what does the SIM test detect?
characteristics of enteric bacteria
sulfide reduction (H2S)
indole production
motility
positive result for sulfide reduction into hydrogen sulfide
black agar
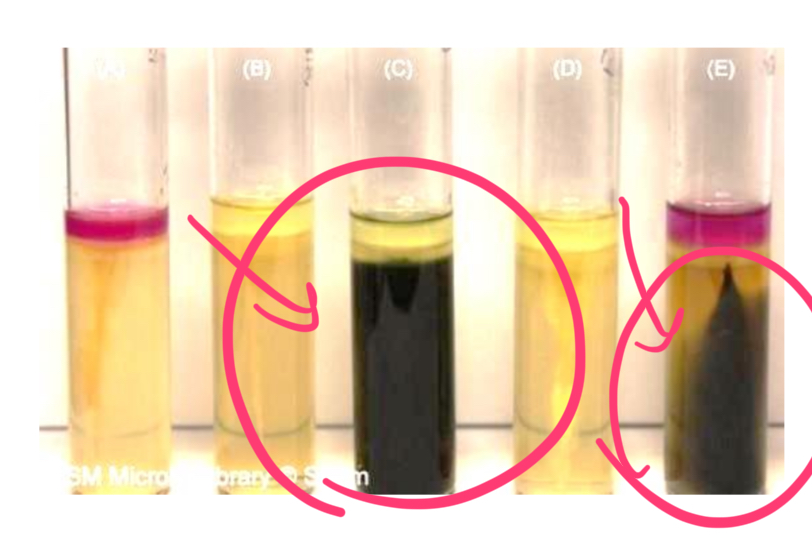
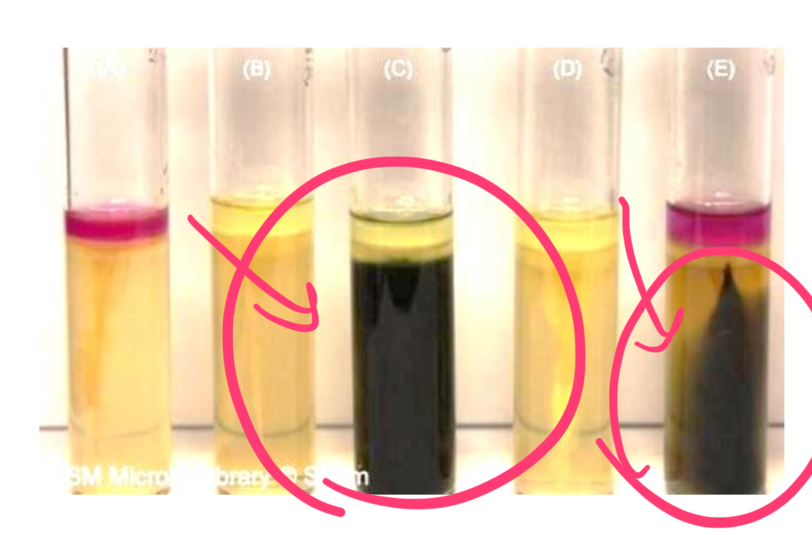
what is this positive for?
sulfide reduction into hydrogen sulfide
what is added to test indole production for SIM test?
kovac’s reagent
positive result for indole production?
pink

positive result for motility in SIM test?
you’ll see fuzzy, spread-out growth away from the stab line
negative result for motility in SIM test?
growth in a straight line along the stab line
media being inoculated for MRVP
liquid broth
what does MRVP test for?
what kind of waste products a bacteria makes after fermenting glucose
how to set up MRVP test
then split the incubated broth into two tubes for two different tests
add methyl red indicator
what does the methyl red test look for?
acid waste from glucose fermentation (like lactic or acetic acid)
appearance of positive methyl red (MR) test
the broth turns red
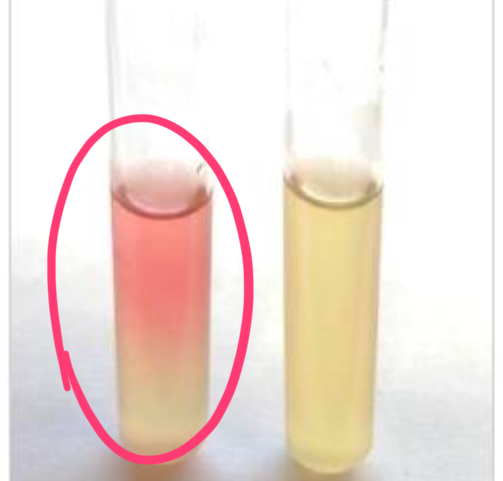

appearance of negative methyl red (MR) test
broth stays yellow/orange (no change)
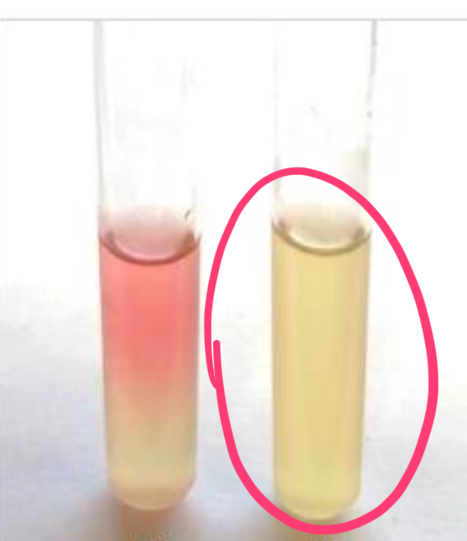

how does e. coli test for the MR test?
positive
makes a lot of acid from glucose
how does K. aerogenes test for the MR test?
negative
makes neutral products instead of strong acids
what does the voges proskauer (VP) test look for?
neutral waste like acetoin instead of strong acids
how does E. coli test for VP?
negative
makes a lot of acid from glucose
how does K. aerogenes test for the VP test?
positive
makes neutral products instead of strong acids
media being inoculated for citrate tests
slant tube
purpose of the citrate test
to see if a bacteria can use citrate (a type of carbon) to survive and grow
what kind of agar is used in the citrate test?
Simmons citrate agar
if the bacteria can use citrate, then…
• they grow
• they make alkaline (basic) waste
• the agar turns blue = positive test
appearance of positive test for citrate
agar turns dark blue
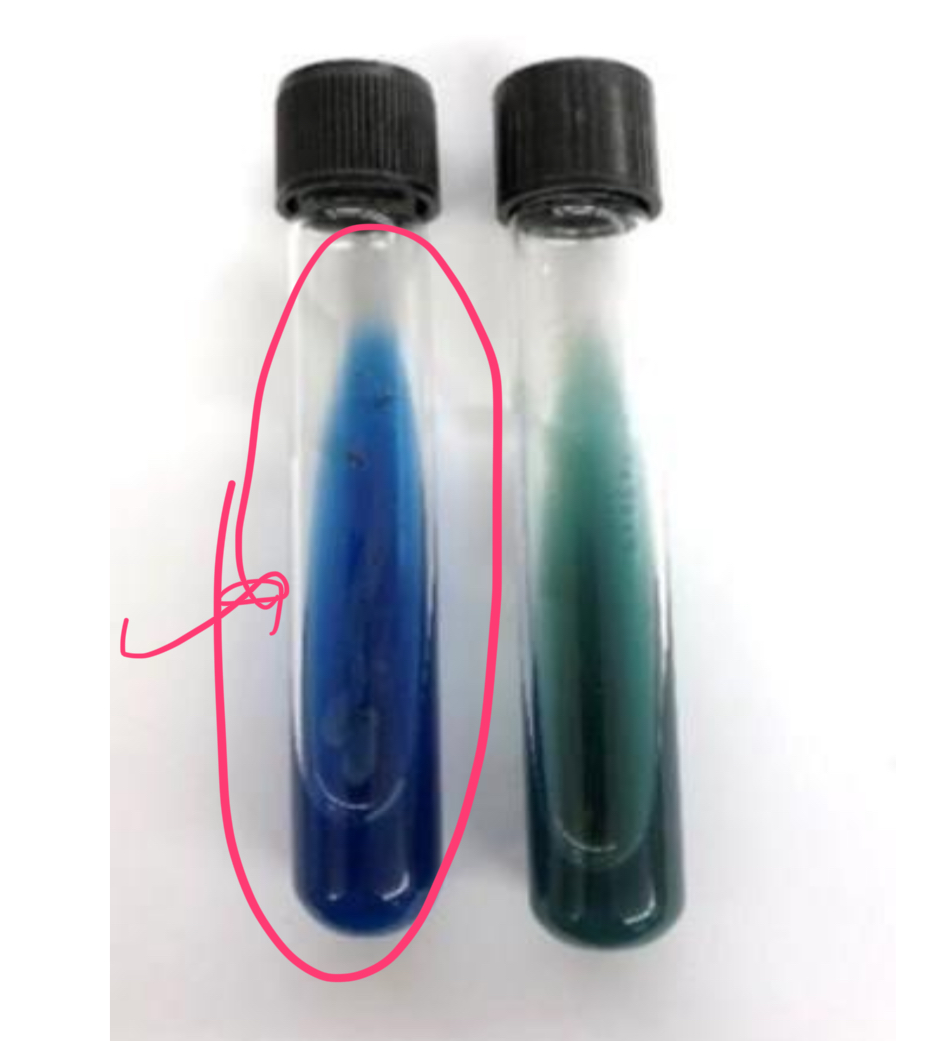

if the bacteria can NOT use citrate, then…
• they don’t grow
• agar stays green = negative test
appearance of negative test for citrate
agar stays green

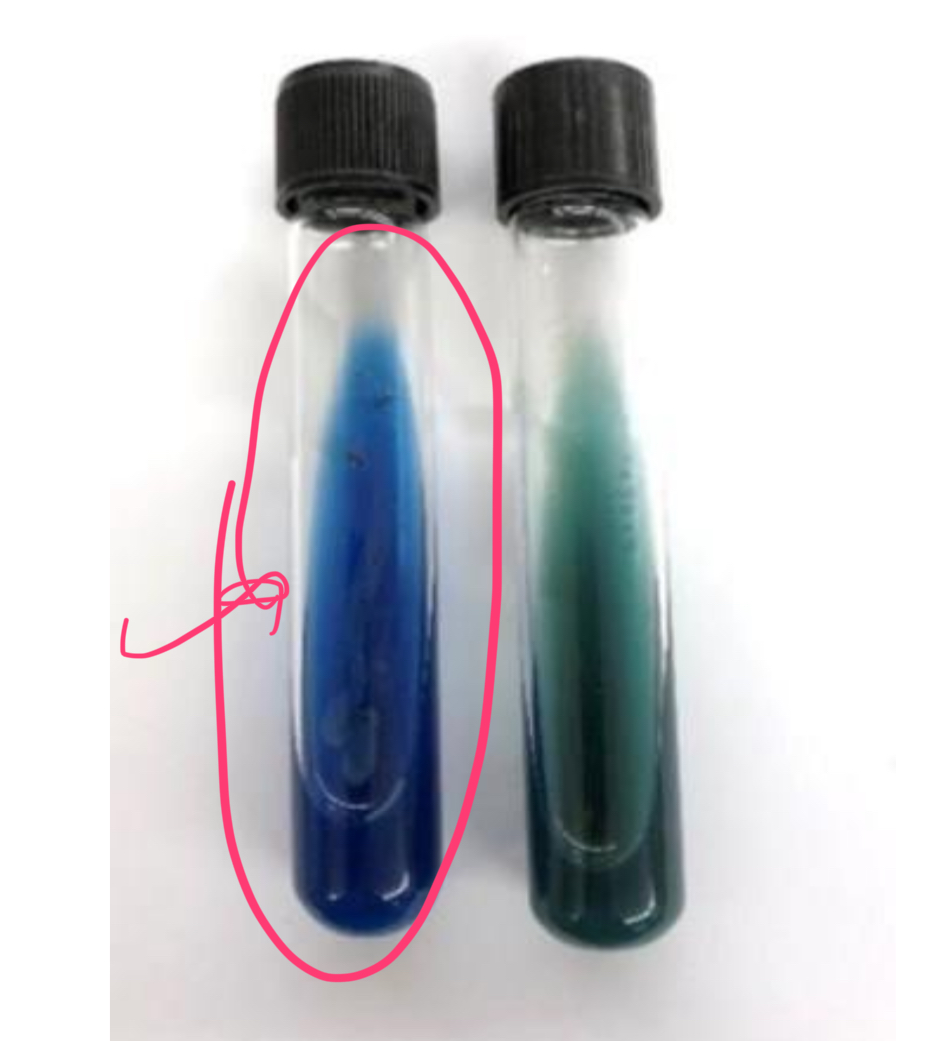
how does E. coli test in citrate test?
negative
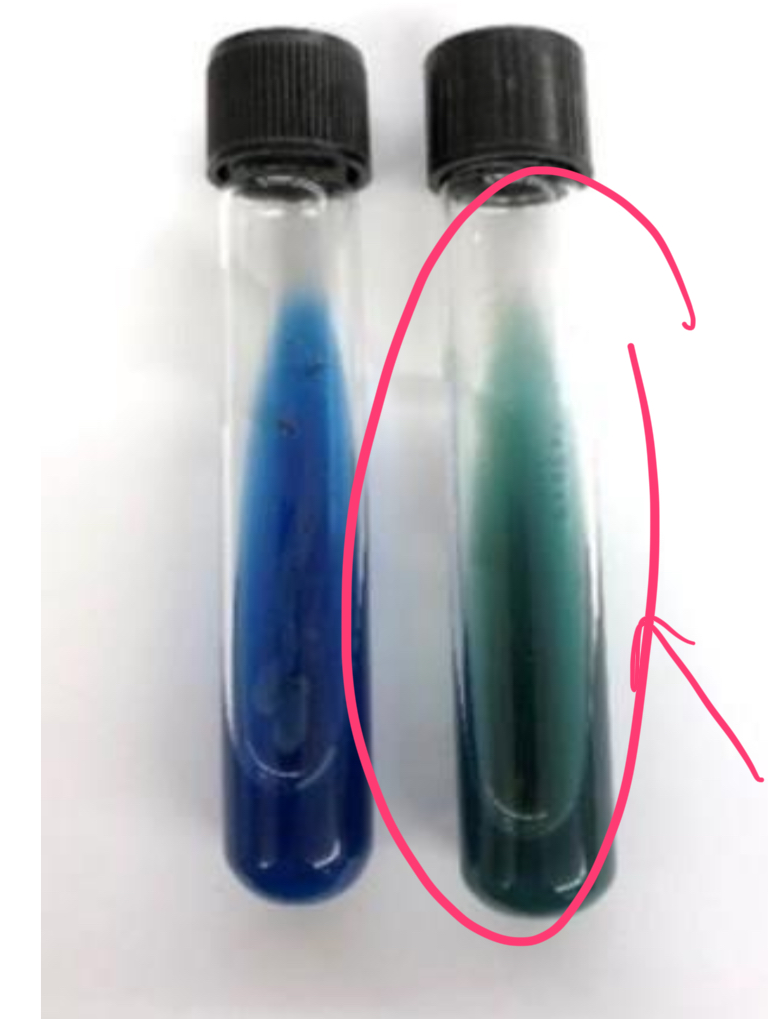

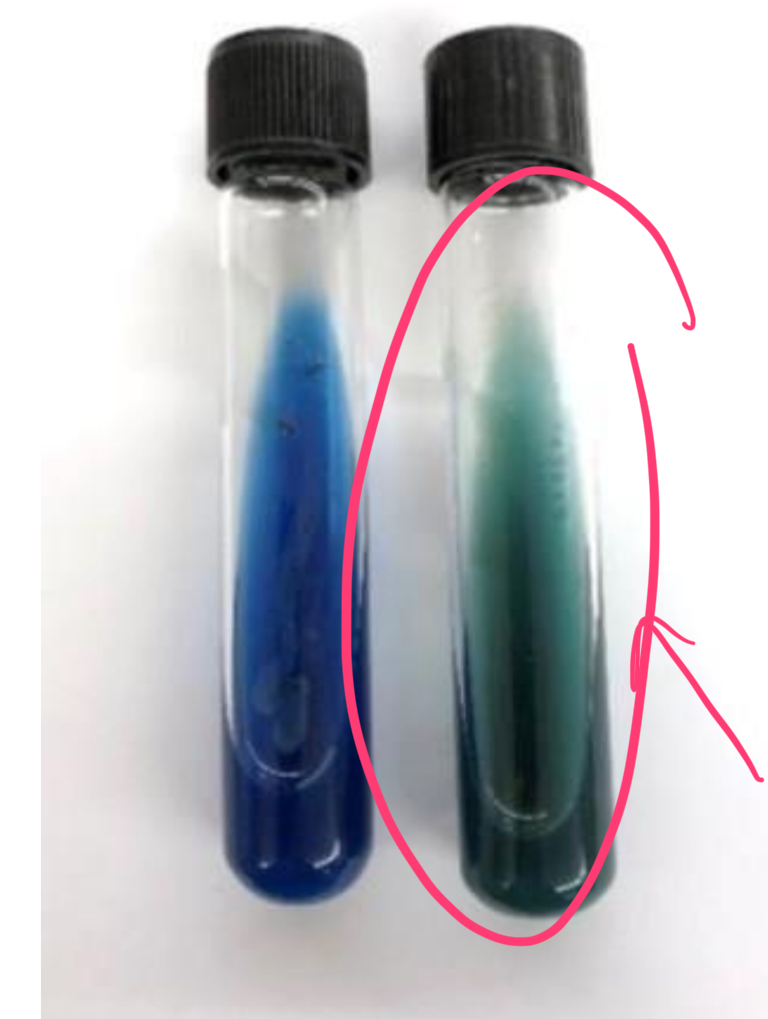
how does Proteas vulgaris test in citrate test?
positive

what is in the citrate test agar?
bromothymol blue, a pH indicator (green = neutral, blue = alkaline)
purpose of the urease test
identify bacteria that produce the enzyme urease
urease
enzyme that breaks down urea into ammonia and carbon dioxide
ammonia is basic, it raises the pH
procedure of urease test
1. Use tape to label each tube with your initials, date, and organism number.
2. Aseptically inoculate each broth tube with bacteria.
3, Place tubes in a common rack for incubation at 37C for 18-24 hours.
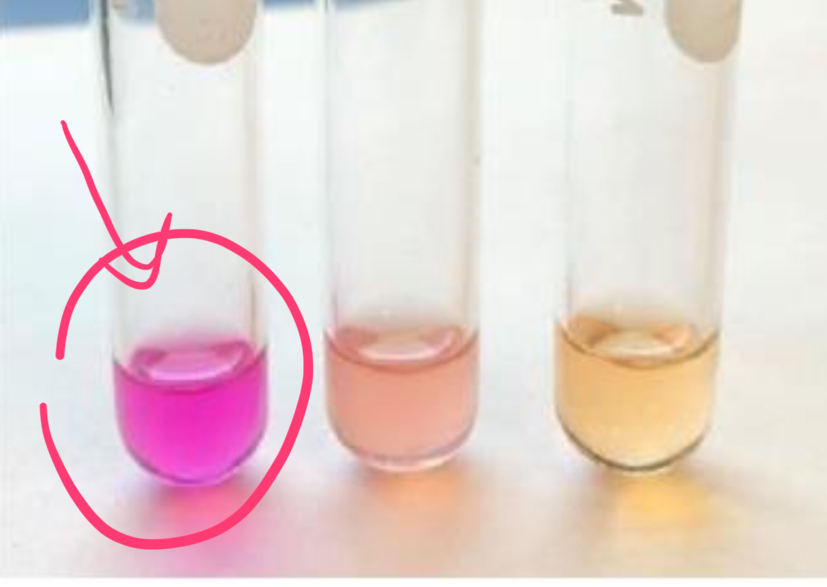

meaning of positive urease result
urease was made, ammonia was produced, pH increased
appearance of positive urease rest
bright pink
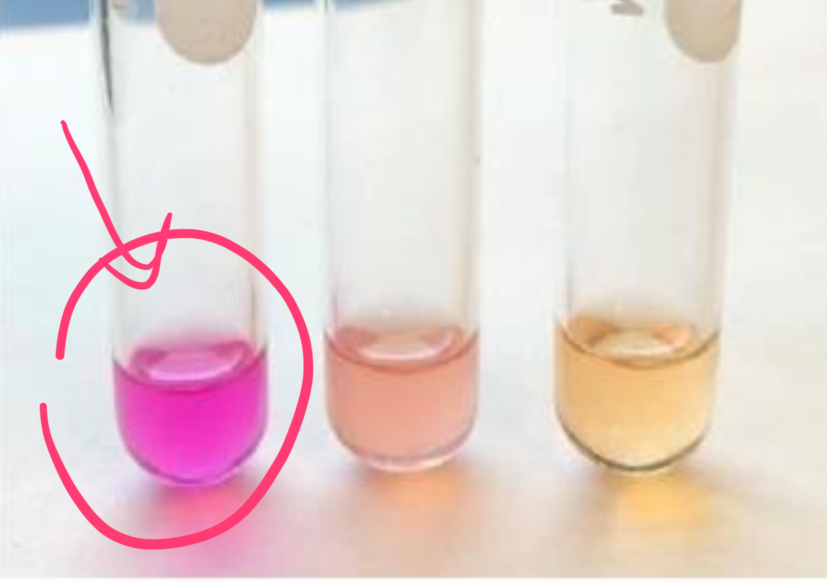


meaning of negative urease result
no urease, no ammonia, the broth stayed acidic
appearance of negative urease result
yellow/no change
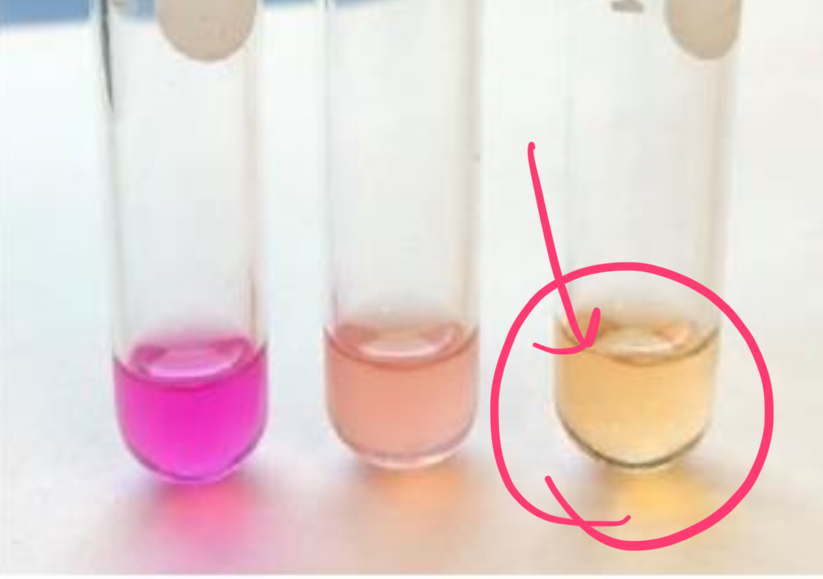

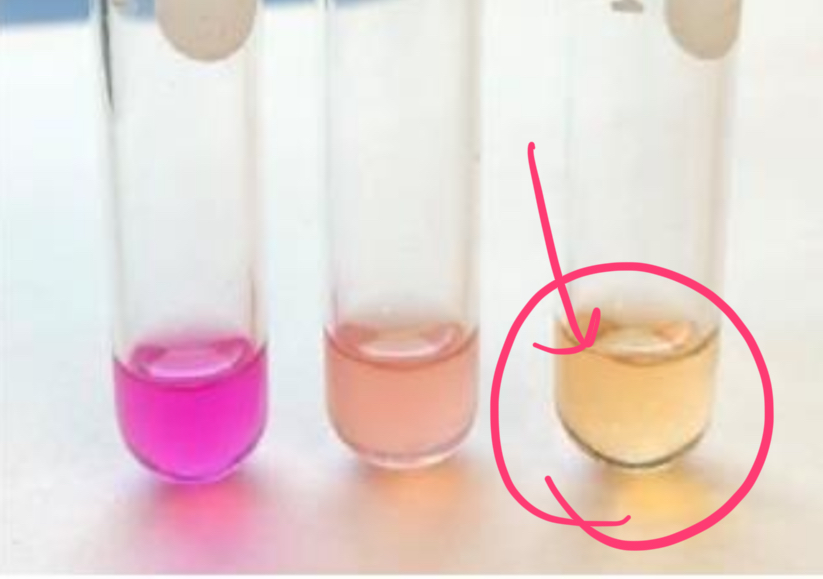
how does E. coli test in urease test?
negative
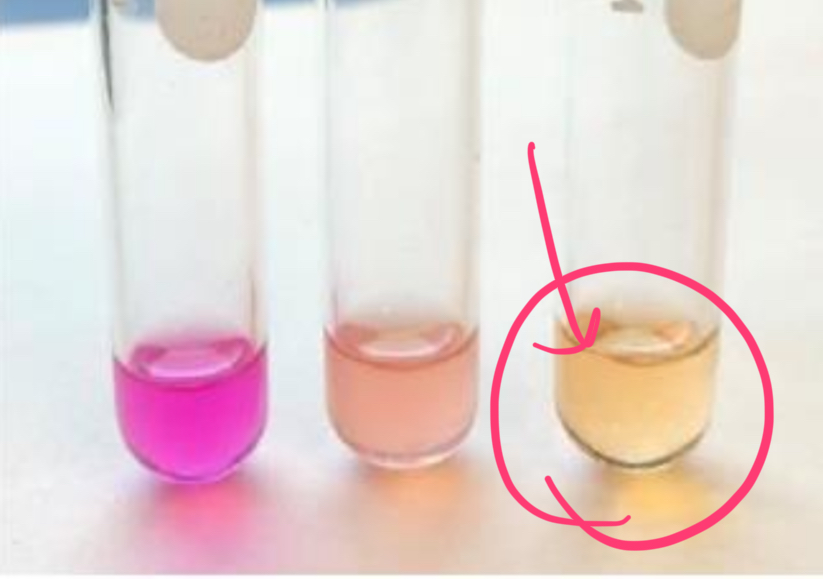

how does Proteas vulgaris test in urease test?
positive

which IMVC medium provides the most info to identify unknowing ram negative bacteria?
SIM
it uses 3 different bacteria