Body Systems
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
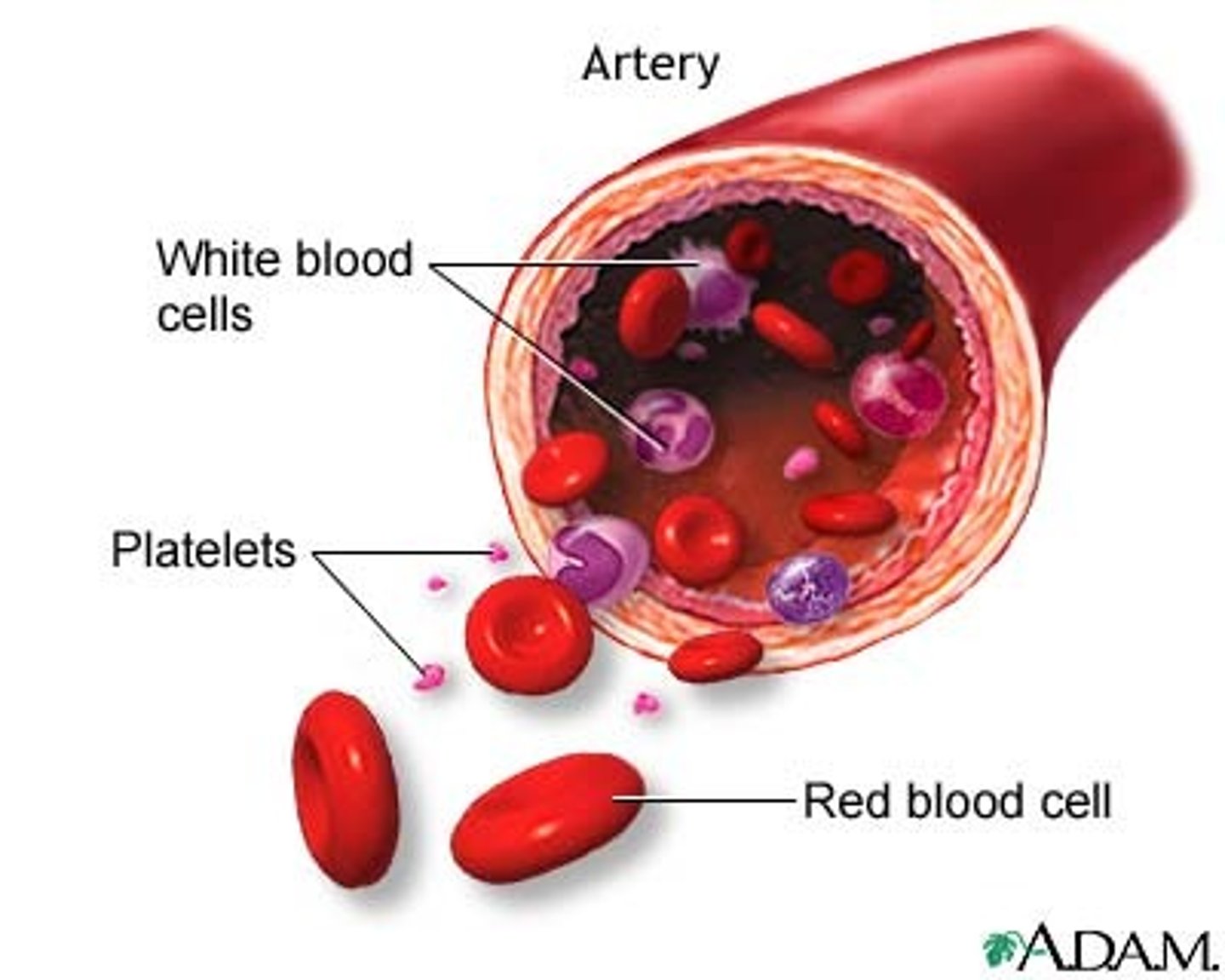
White Blood Cells
Defend against disease
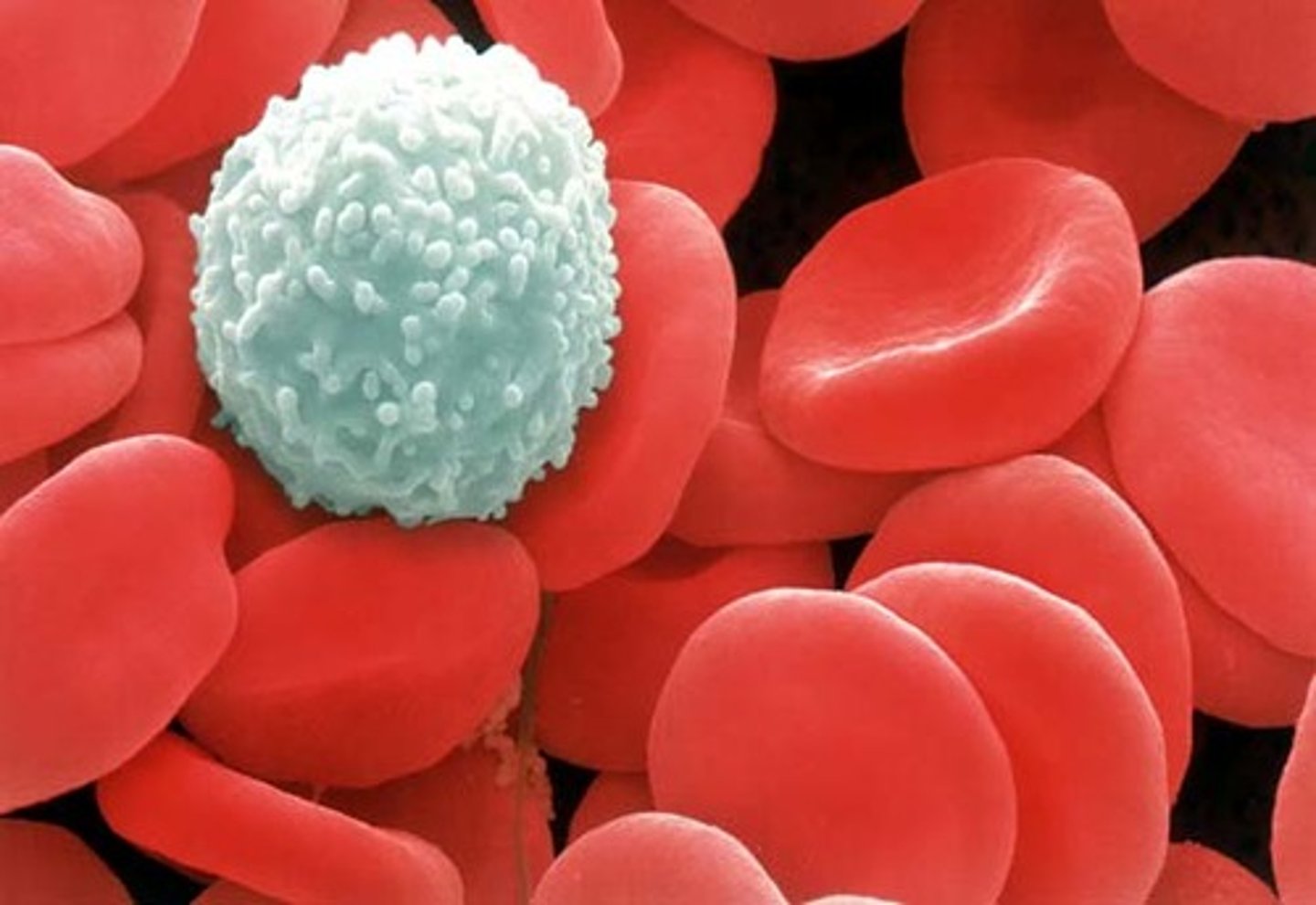
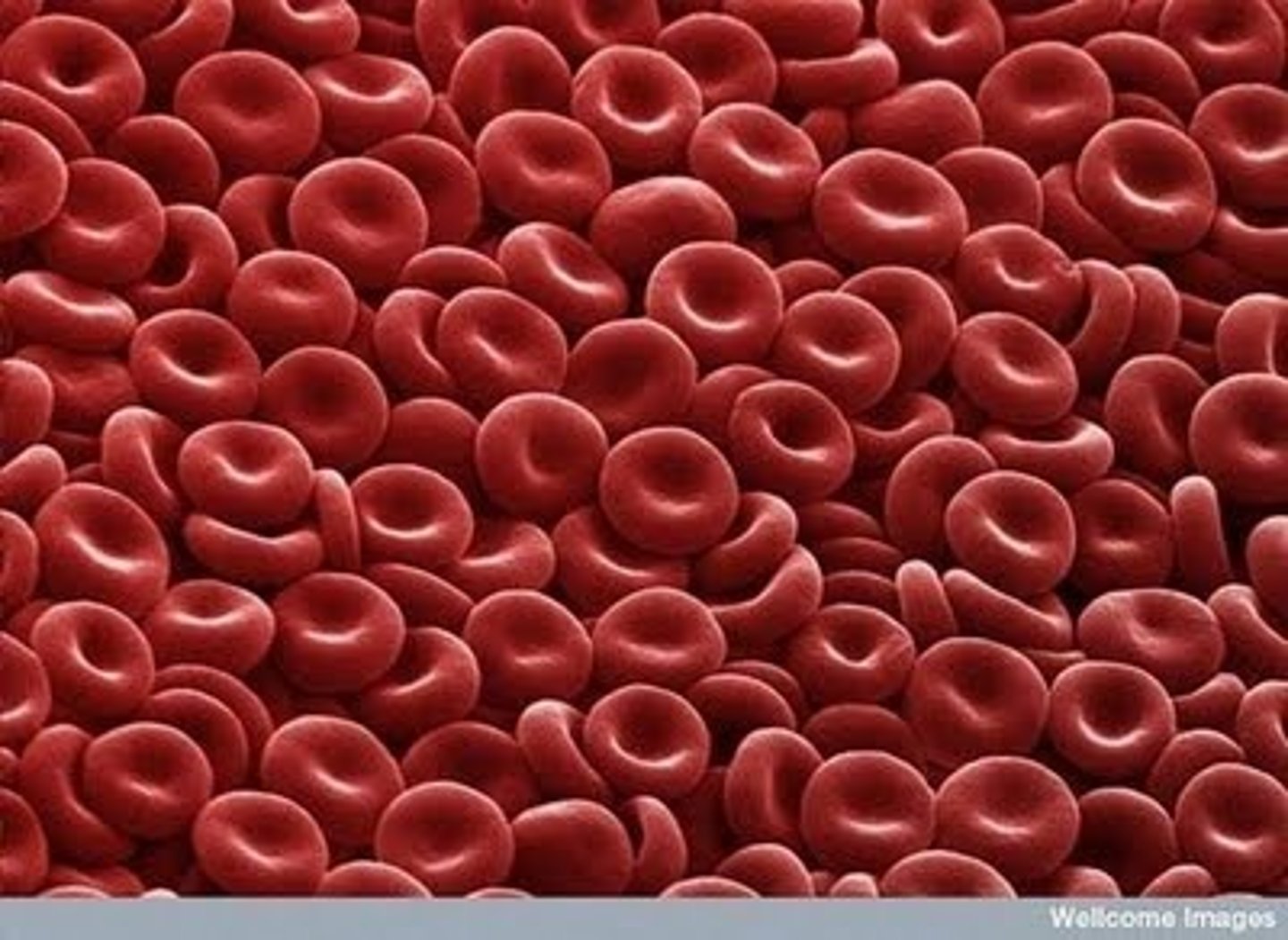
red blood cells
Carry oxygen to all body cells
Plasma
90% water plus dissolved proteins, glucose, mineral ions, hormones, & carbon dioxide.
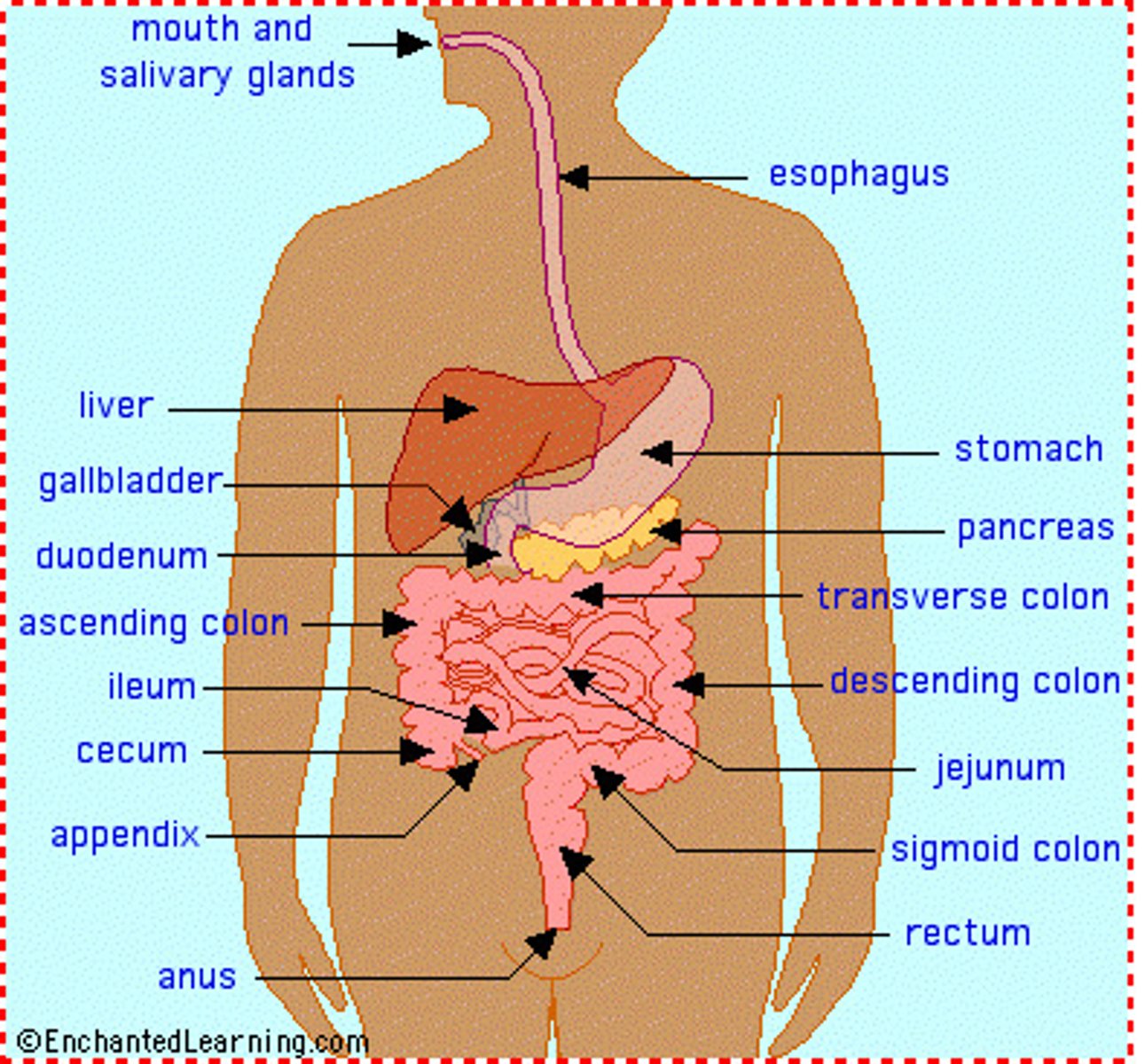
digestive system
Breaks down food into smaller molecules. Absorbs these nutrients into the body.
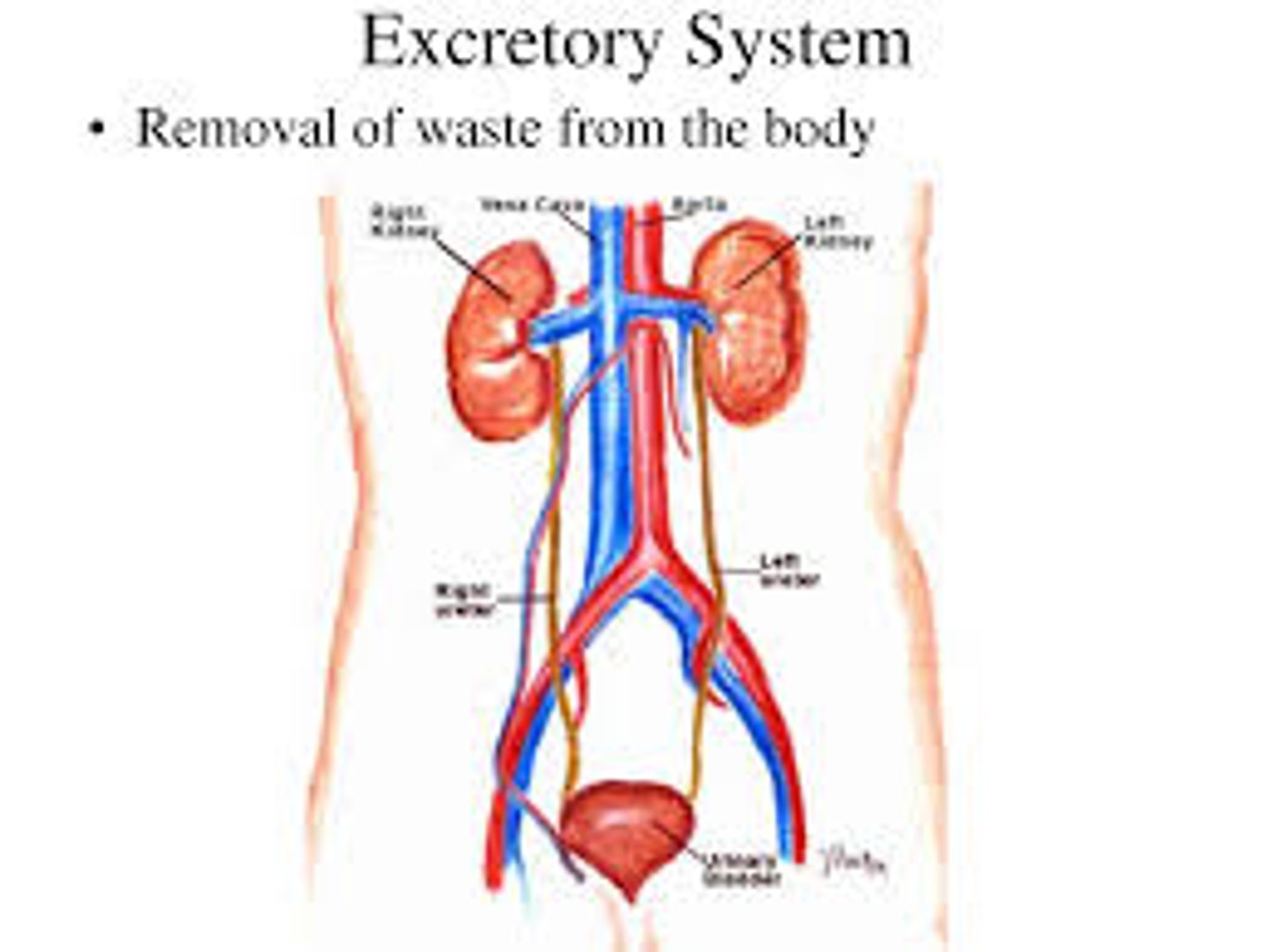
urinary system
the system that removes waste from your body and controls water balance
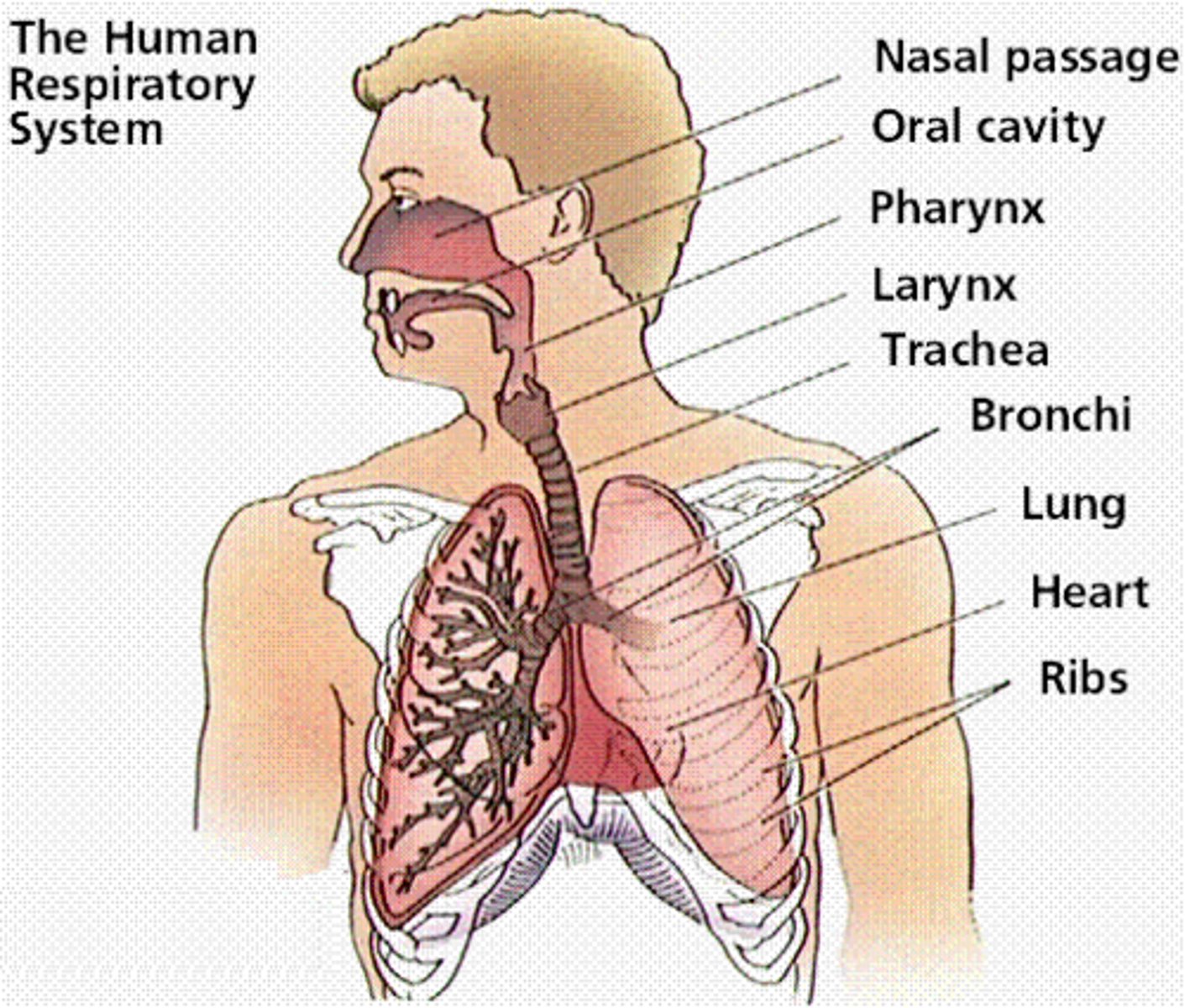
respiratory system
A system of organs, functioning in the process of gas exchange between the body and the environment, consisting especially of the nose, nasal passages, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs.
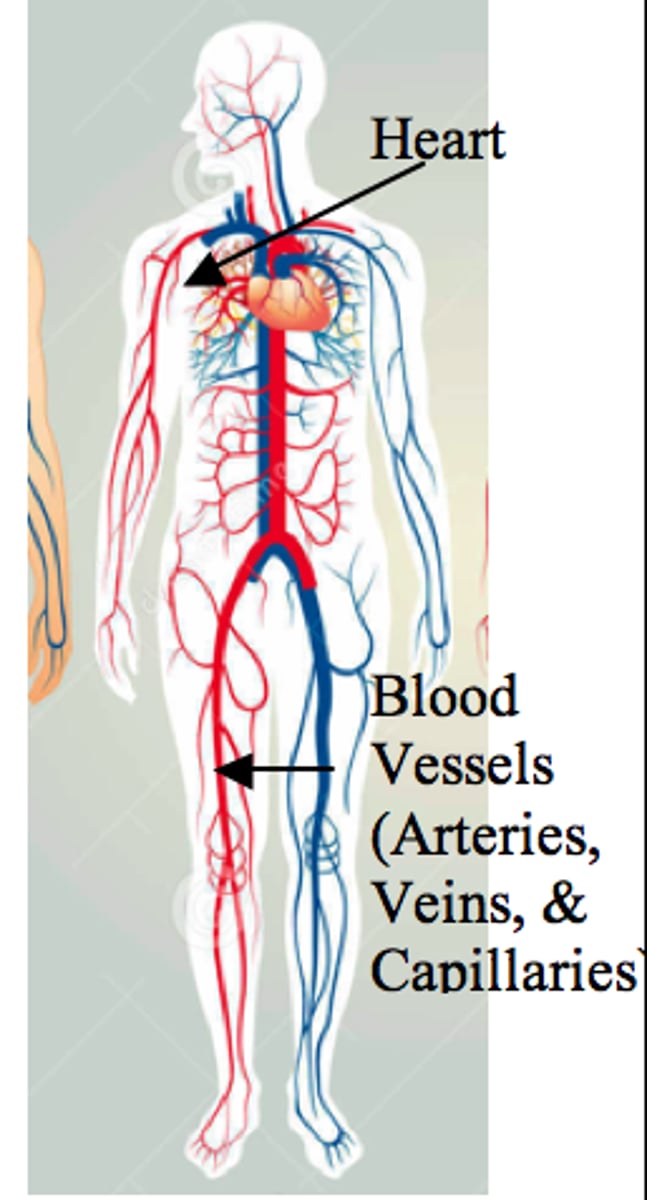
circulatory system
(aka cardiovascular system) This system works as the transportation highway for the body. It consists of the heart, blood, and blood vessels. It transports substances such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nutrients in the body.
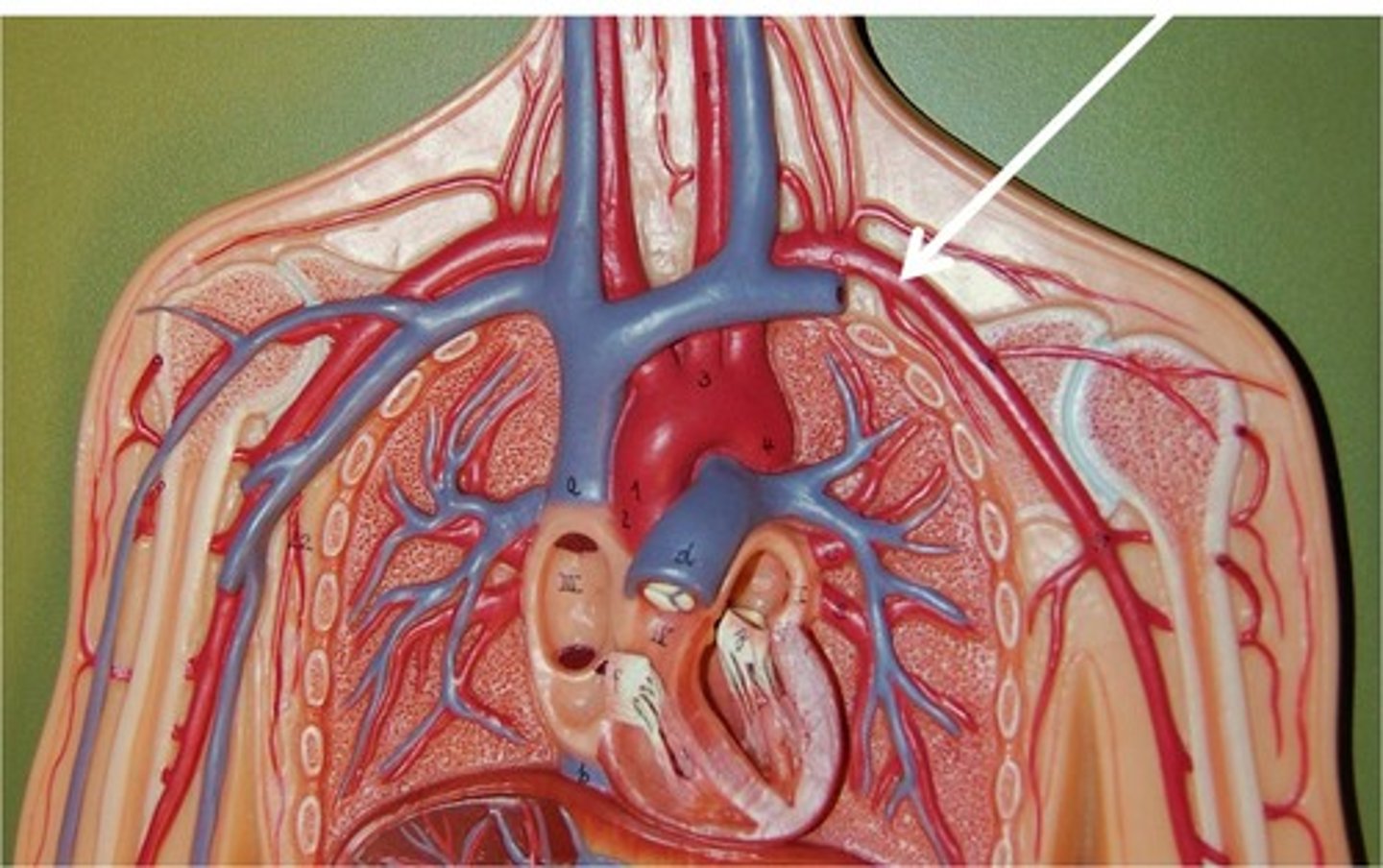
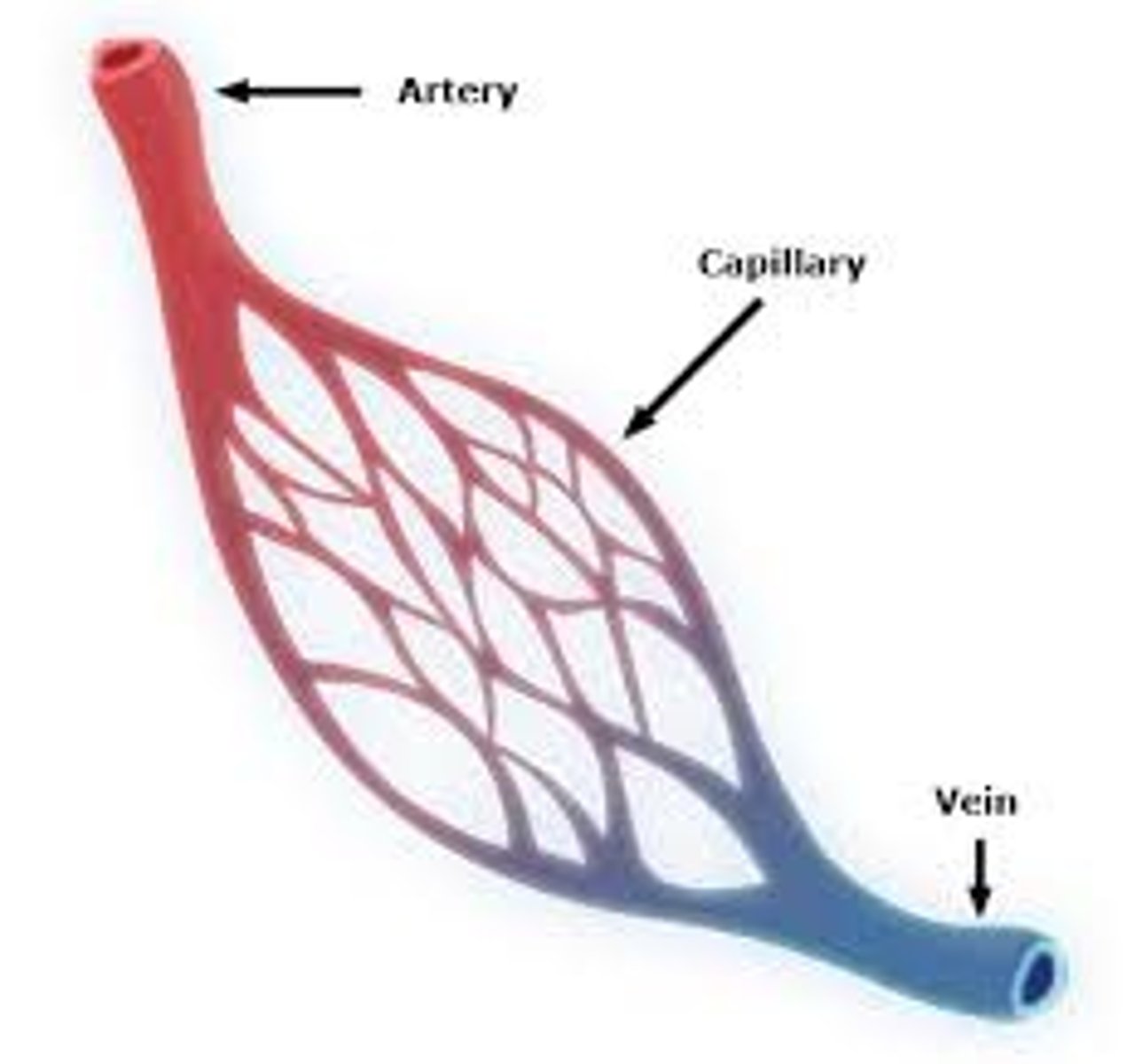
arteries
Blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart. eg aorta
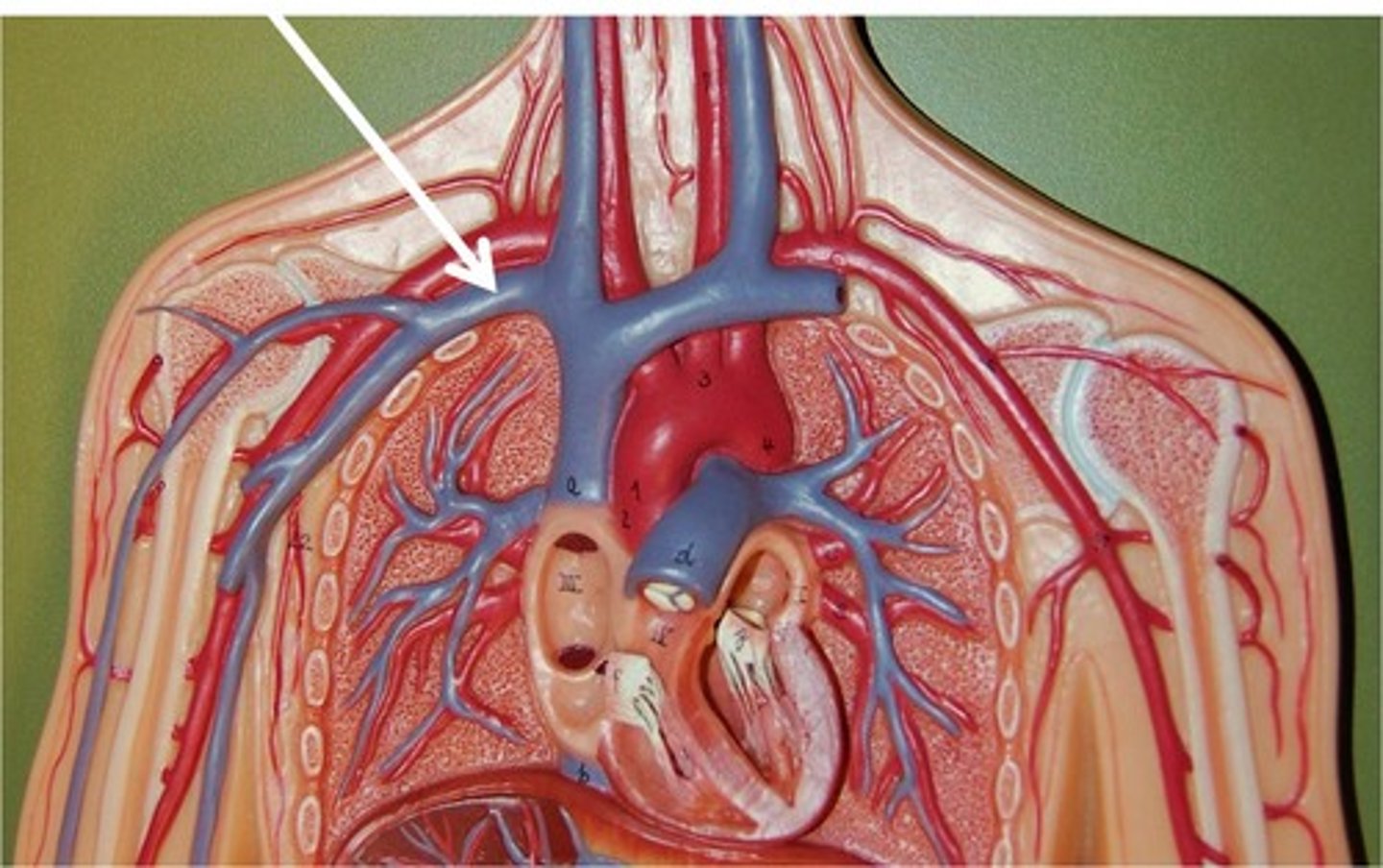
veins
Blood vessels that carry blood back to the heart. eg vena cava
blood vessels
found throughout the body and vary in size
capillaries
Microscopic vessel through which exchanges take place between the blood and cells of the body
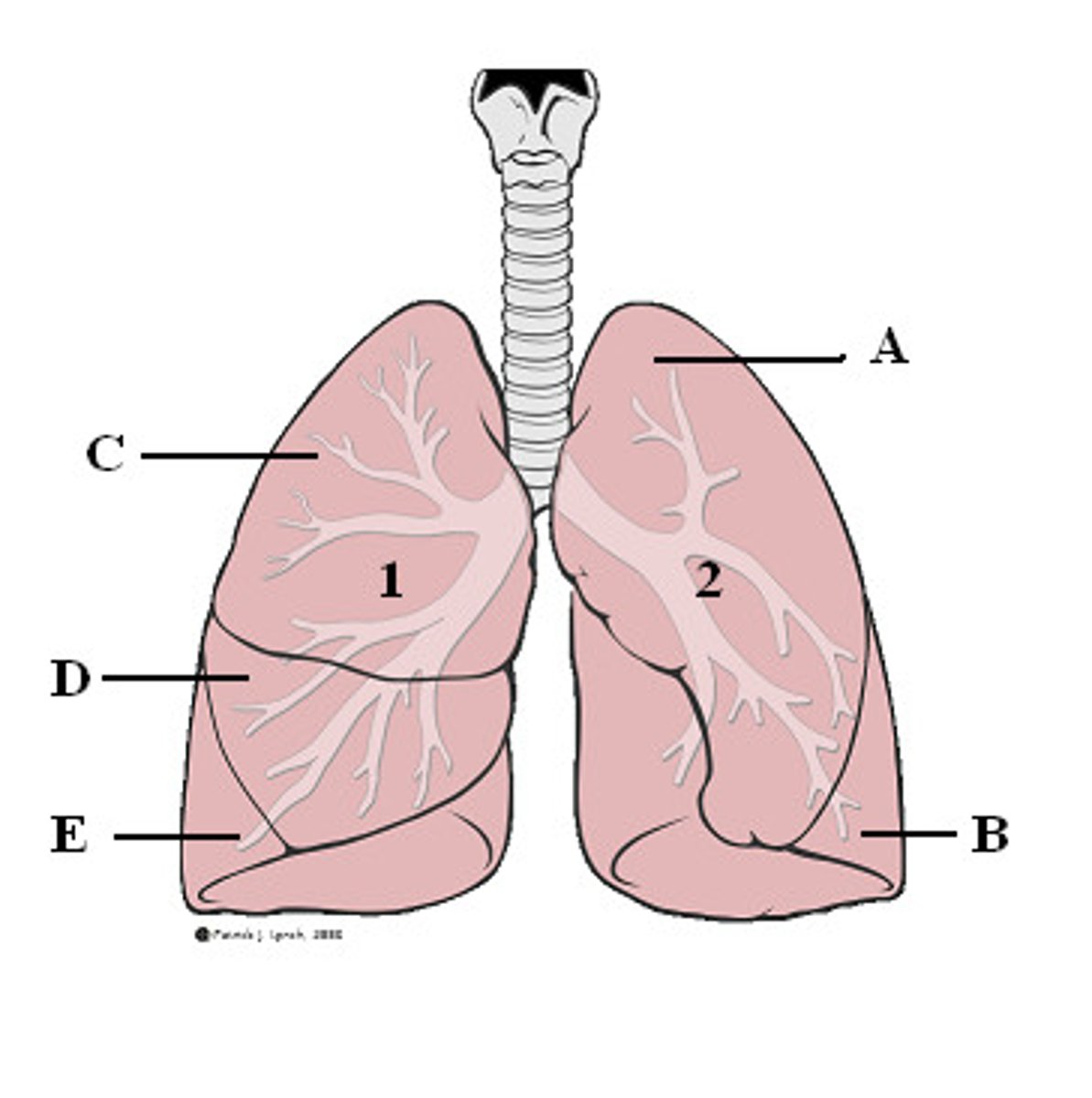
lungs
An organ found in air-breathing vertebrates that exchanges oxygen and carbon dioxide with the blood
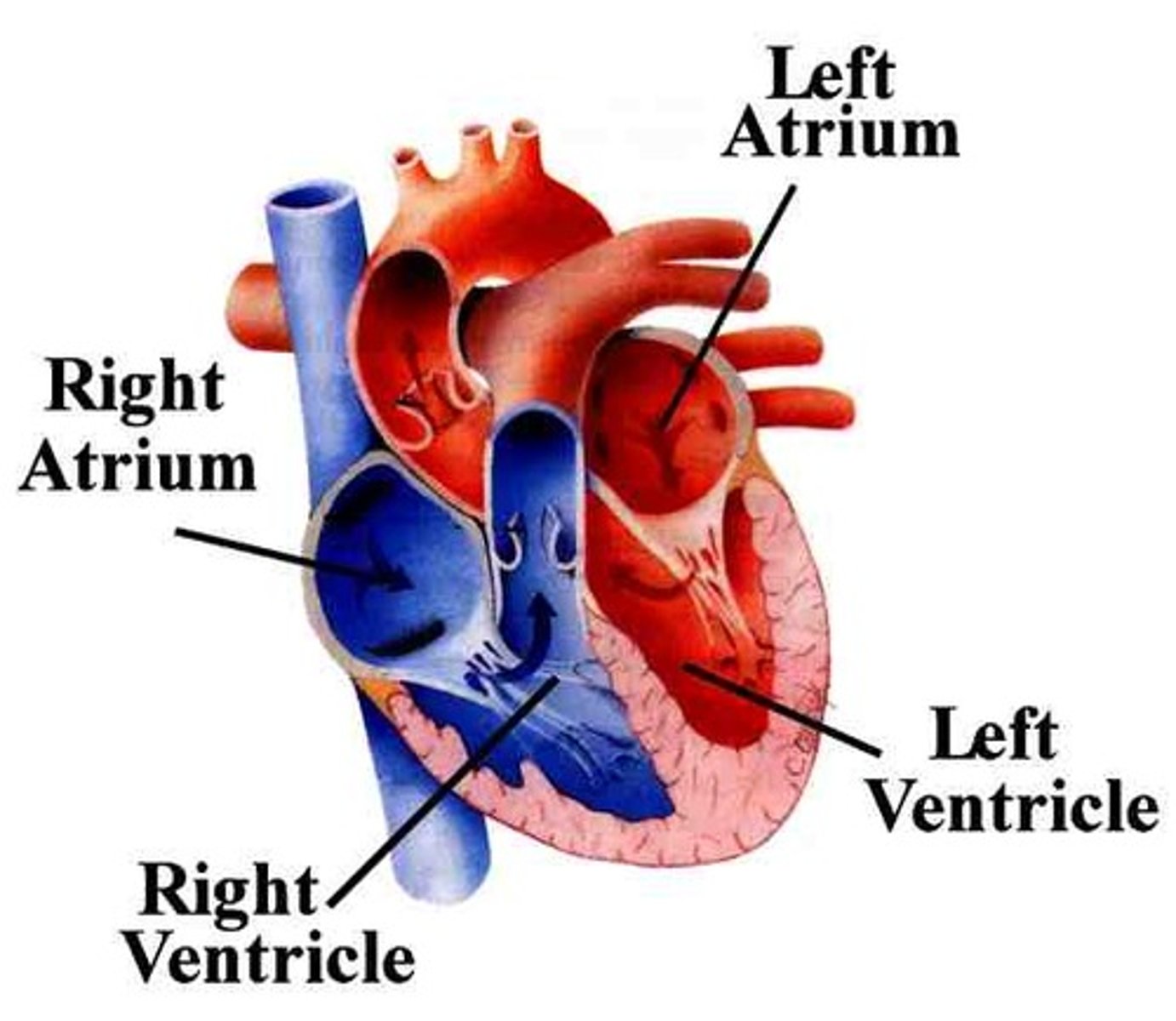
heart
A hollow muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body
kidney
an organ that filters the blood and removes excess salt, water and urea.

ureter
A duct leading from the kidney to the urinary bladder.
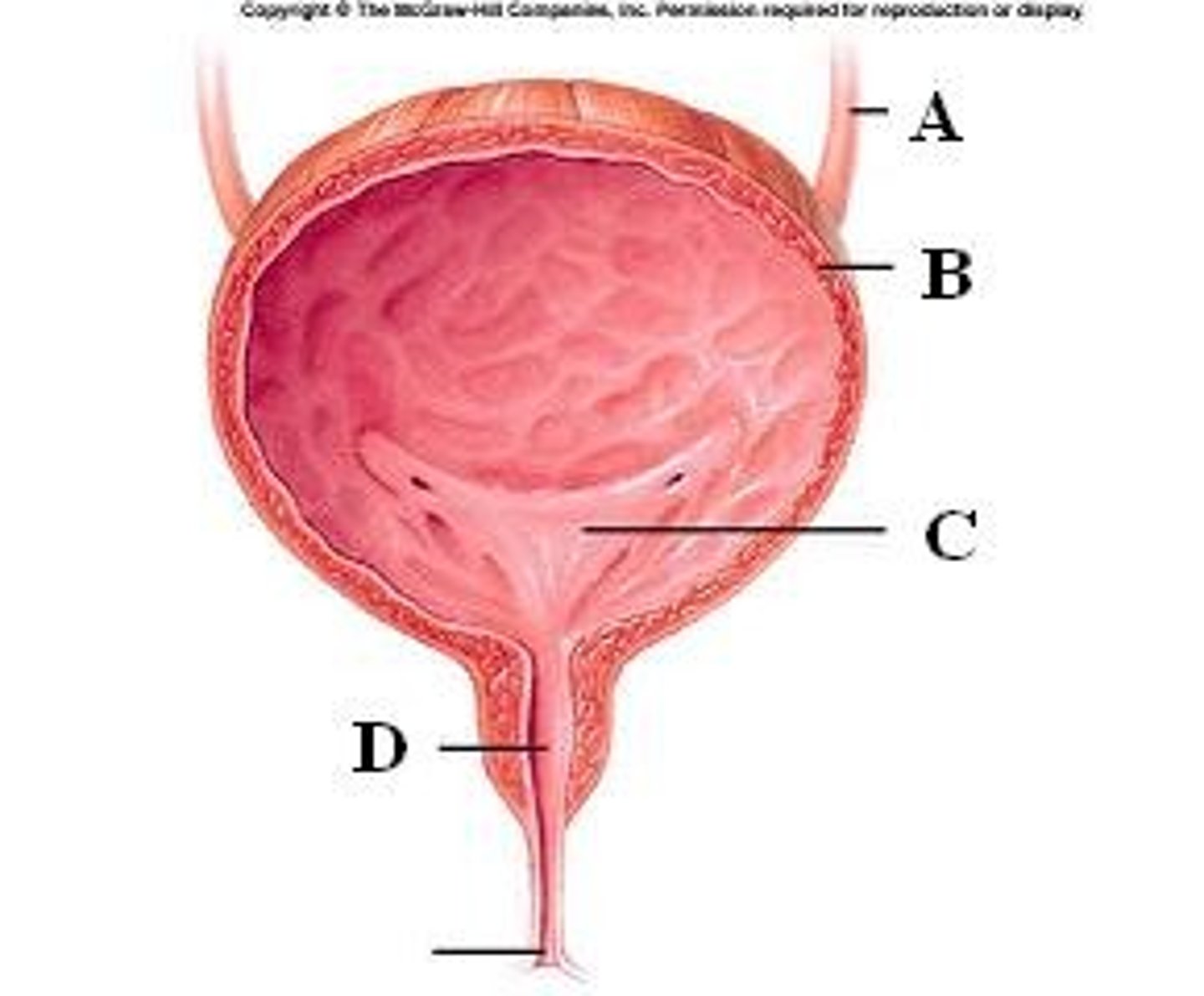
bladder
Holds urine
trachea
Allows air to pass to and from lungs. The windpipe
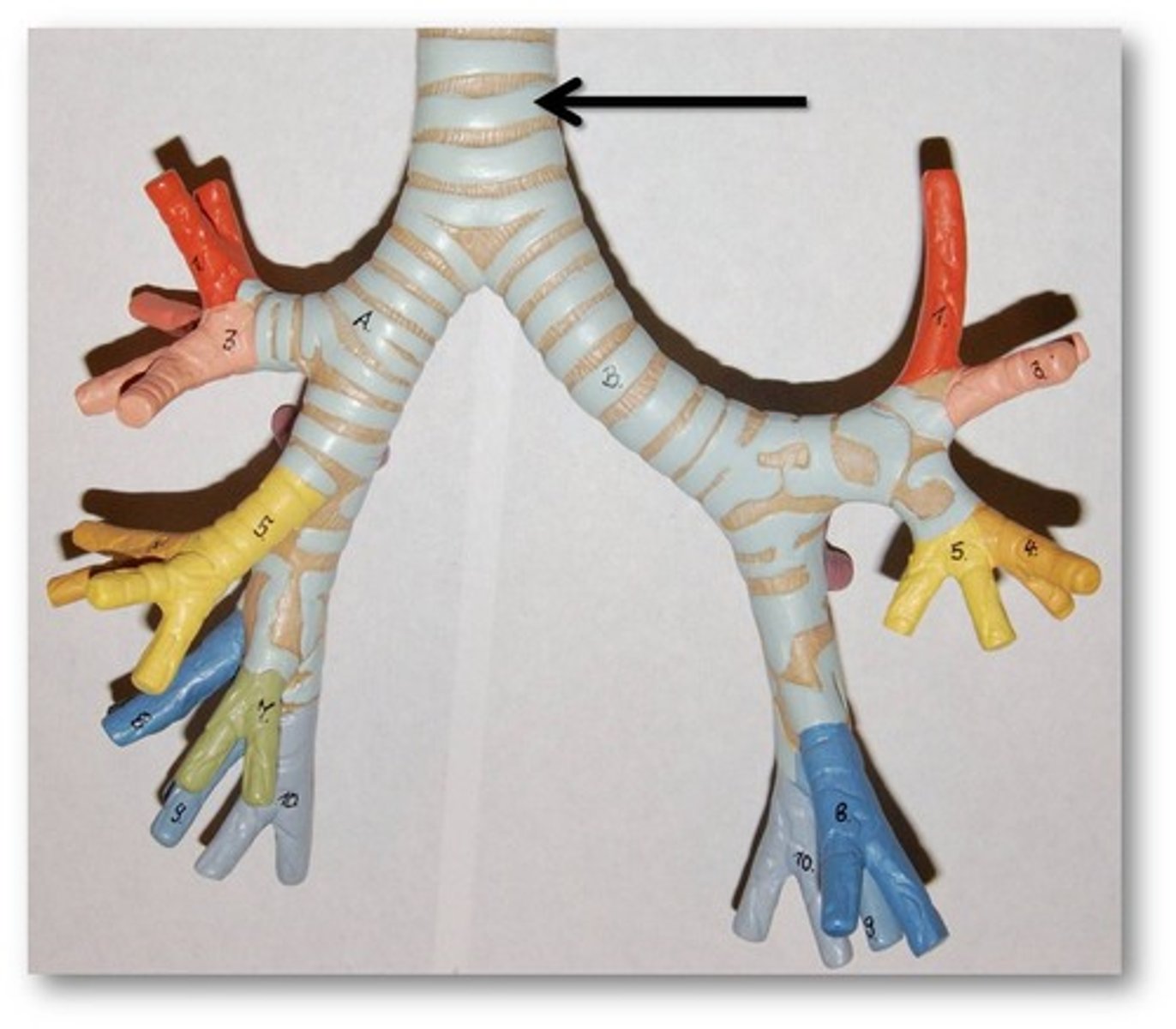
bronchial tubes
one of the two tubes that connect the lungs with the trachea
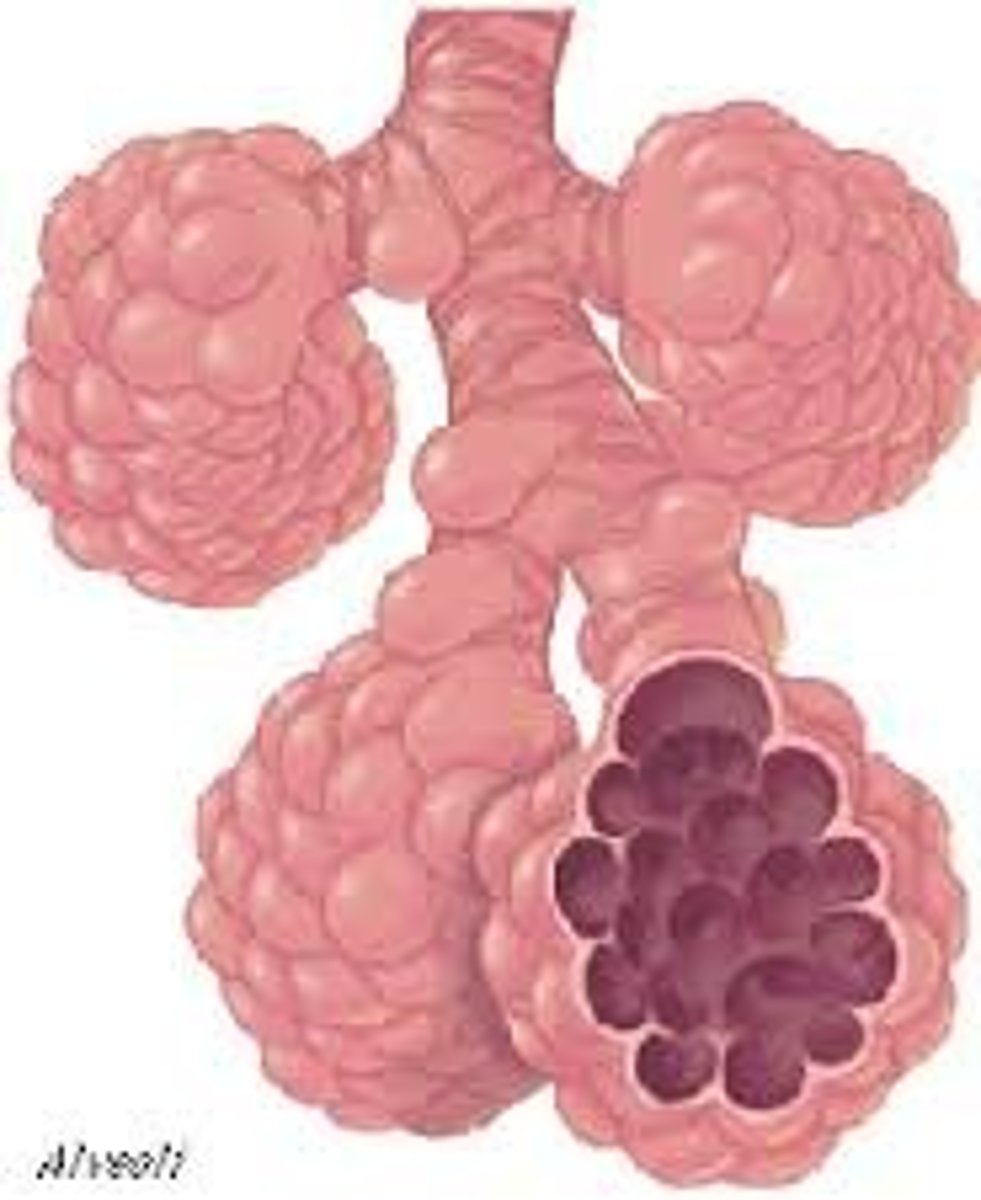
alveoli
(singular alveolus.) Tiny sacs, with walls only a single cell layer thick found at the end of the respiratory bronchiole tree; the site of gas exchange in the respiratory system.
hemoglobin
a protein containing iron, found in red blood cells, which carries oxygen
small intestine
Digestive organ where most chemical digestion and absorption of food takes place
stomach
A muscular and elastic sac that serves mainly to store food, break it up mechanically, and begin chemical digestion of proteins.
gastric juice
Stomach acid that allows the protease enzymes to break down protein. Stops amylases from breaking down starch
large intestine
Absorbs water and forms feces.
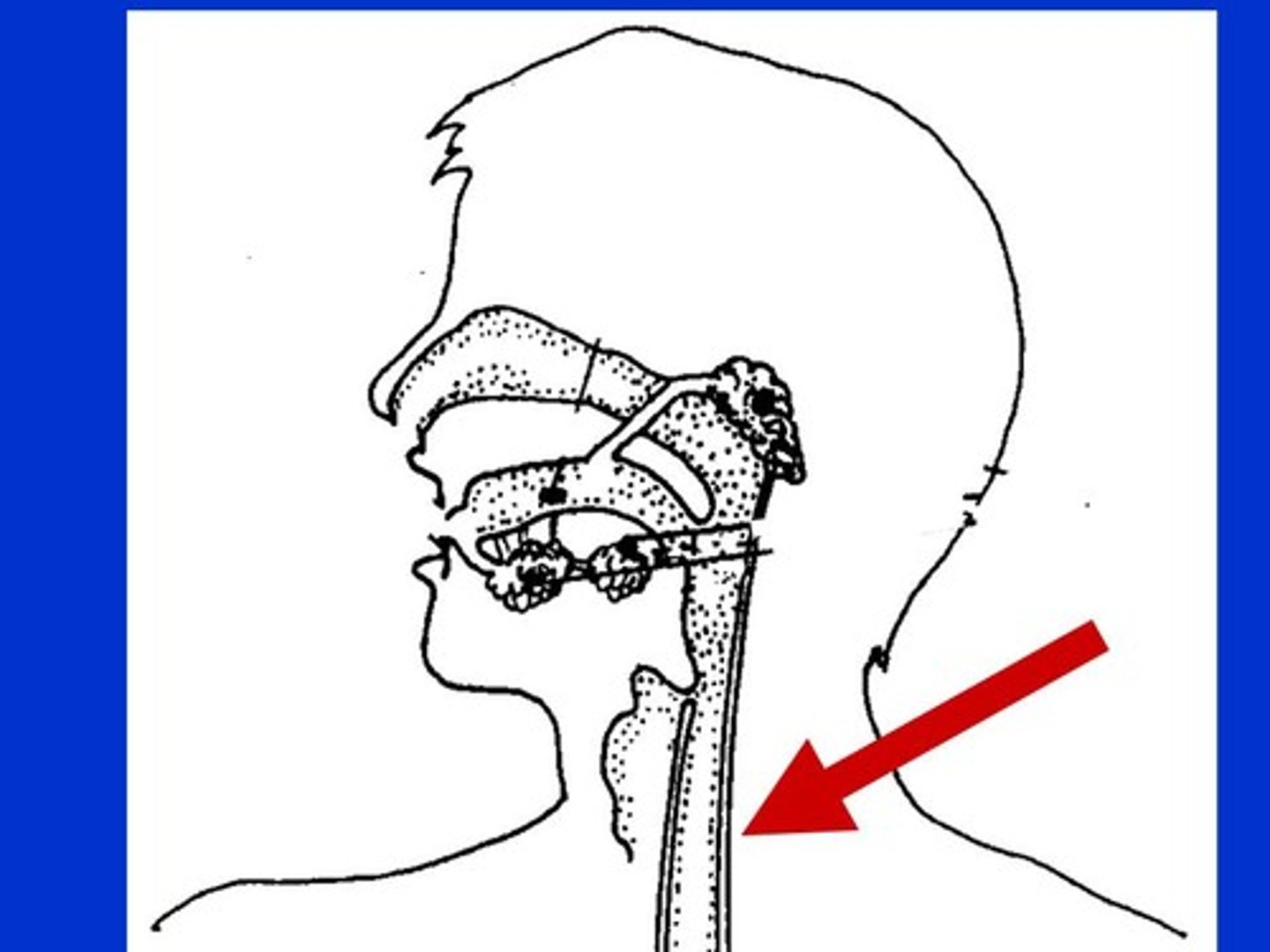
esophagus
Tube connecting the mouth and the stomach.
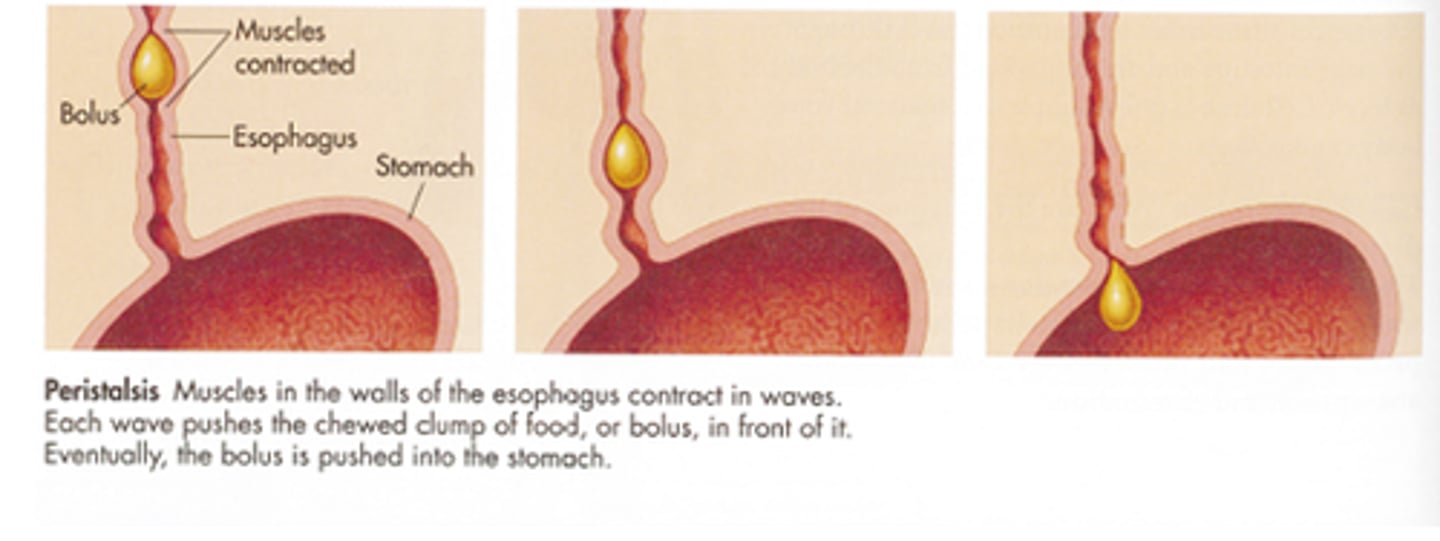
peristalsis
Involuntary waves of muscle contraction that keep food moving along in one direction through the digestive system.
Blood
Fluid that transports substances throughout the body. Made up of plasma and blood cells.
Platelets
Form blood clots
Muscle Cells
Shorten to cause movement of the body. They move the skeleton, heart, and internal organs
Skeletal muscle
a muscle that is connected to the skeleton to form part of the mechanical system that moves the limbs and other parts of the body.

Smooth muscle
muscle tissue in which the contractile fibrils are not highly ordered, occurring in the gut and other internal organs and not under voluntary control.
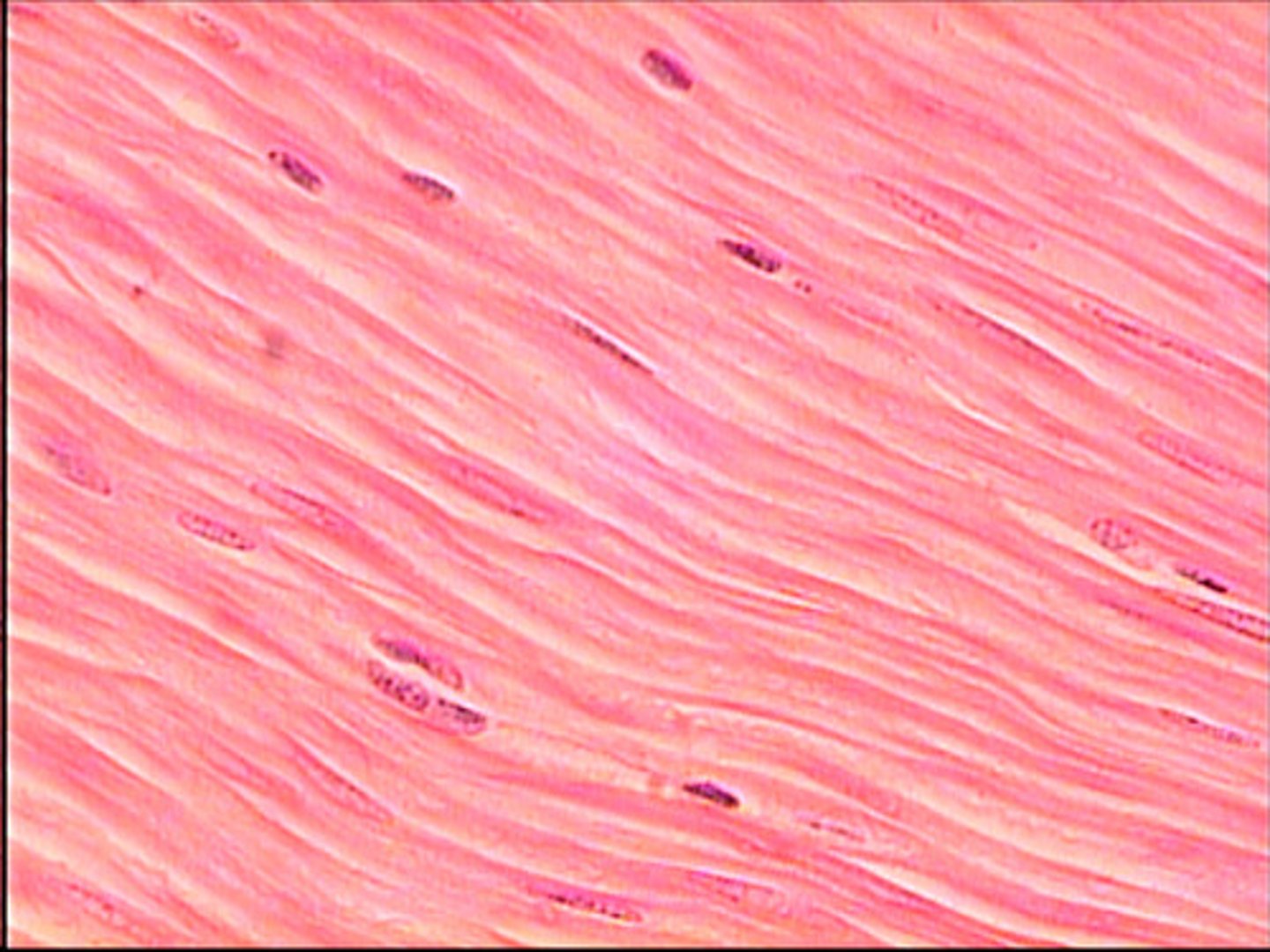
Cardiac Muscle
makes up the heart
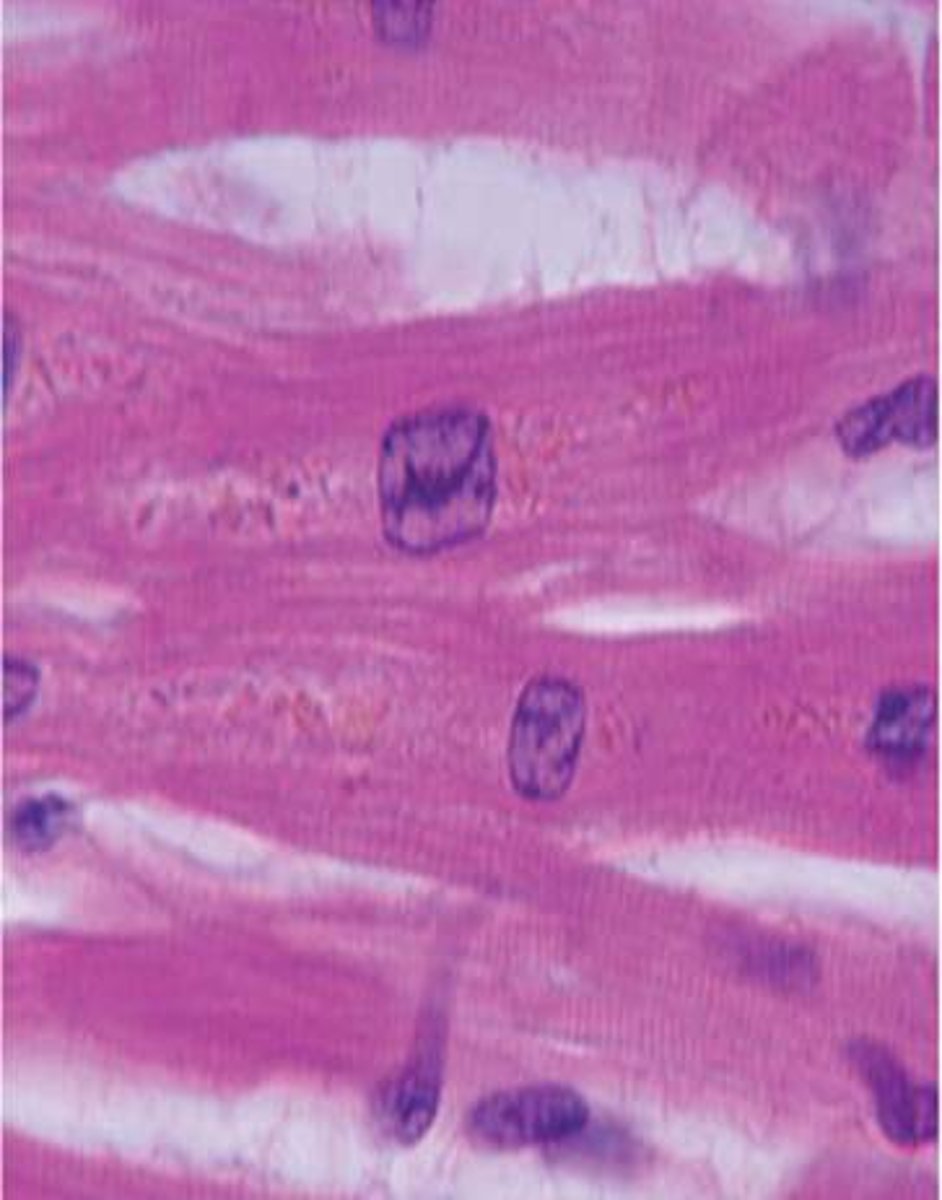
Muscle cells
have many mitocondria
Epithelium cells
form the lining of structures
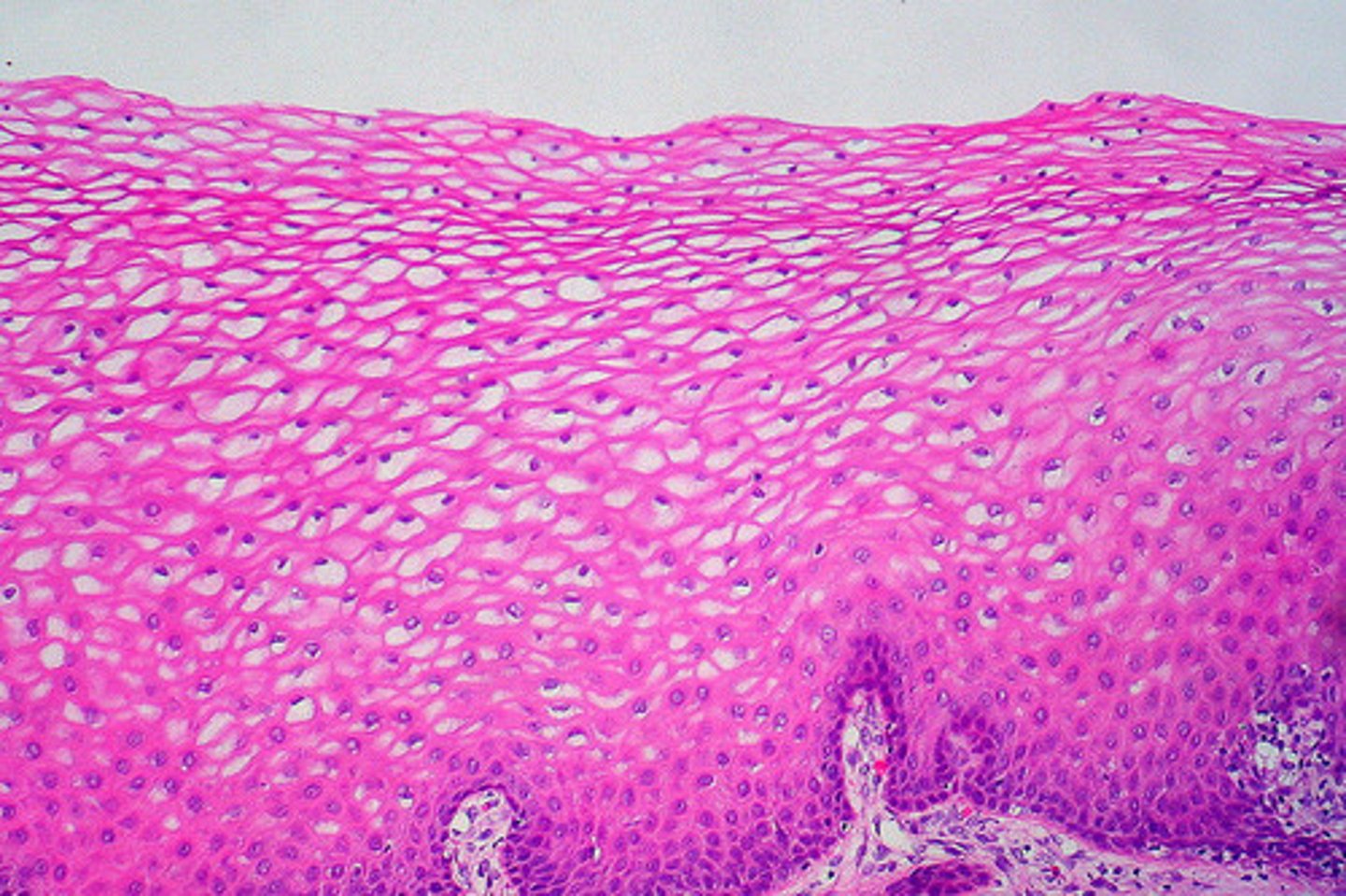
squamous
Flat, thin and soft. These line the cheeks, blood vessels, lungs, and other body cavities.
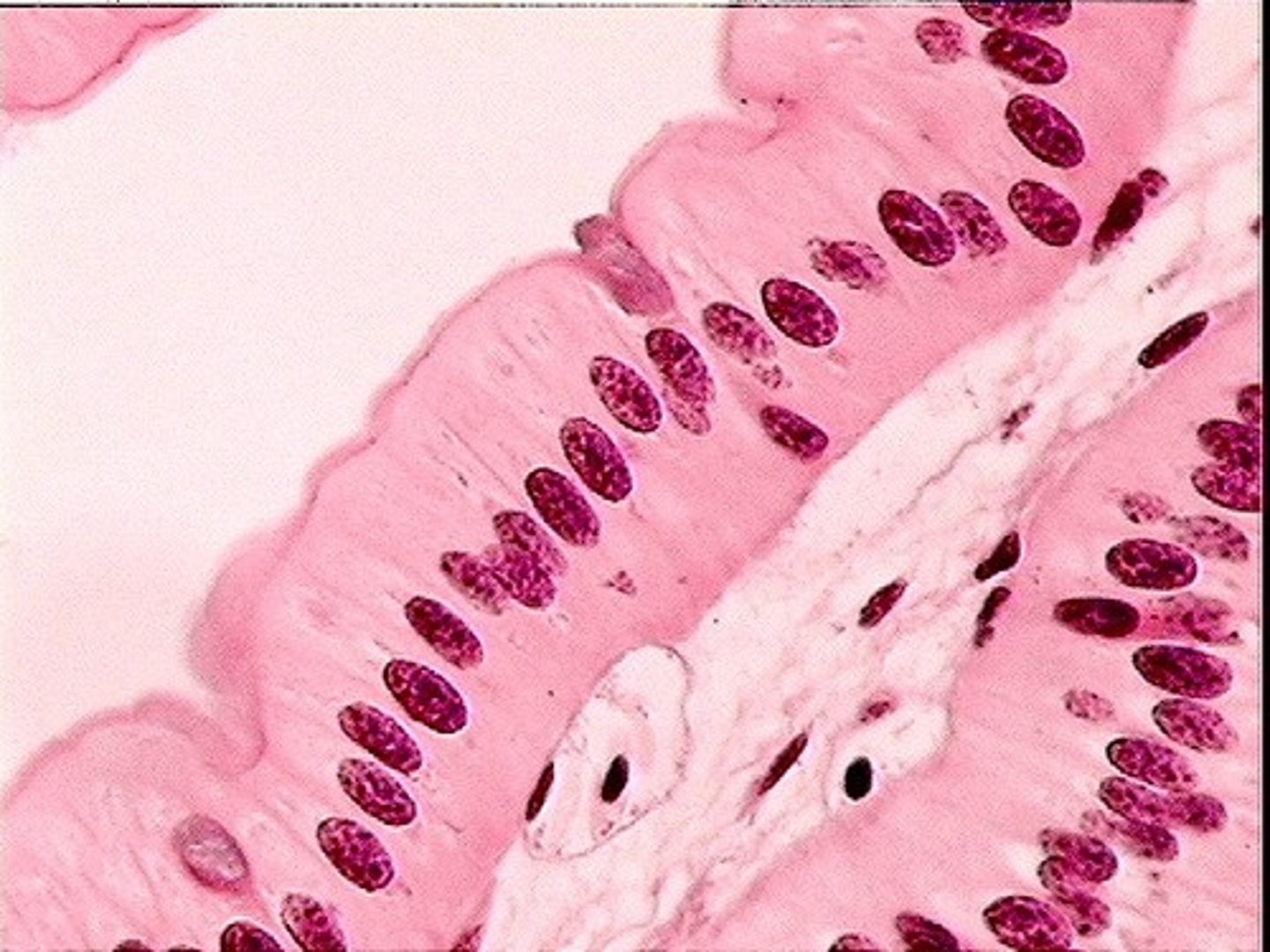
Columnar
Line the small intestine
Cuboidal
cube-shaped epithelial cells
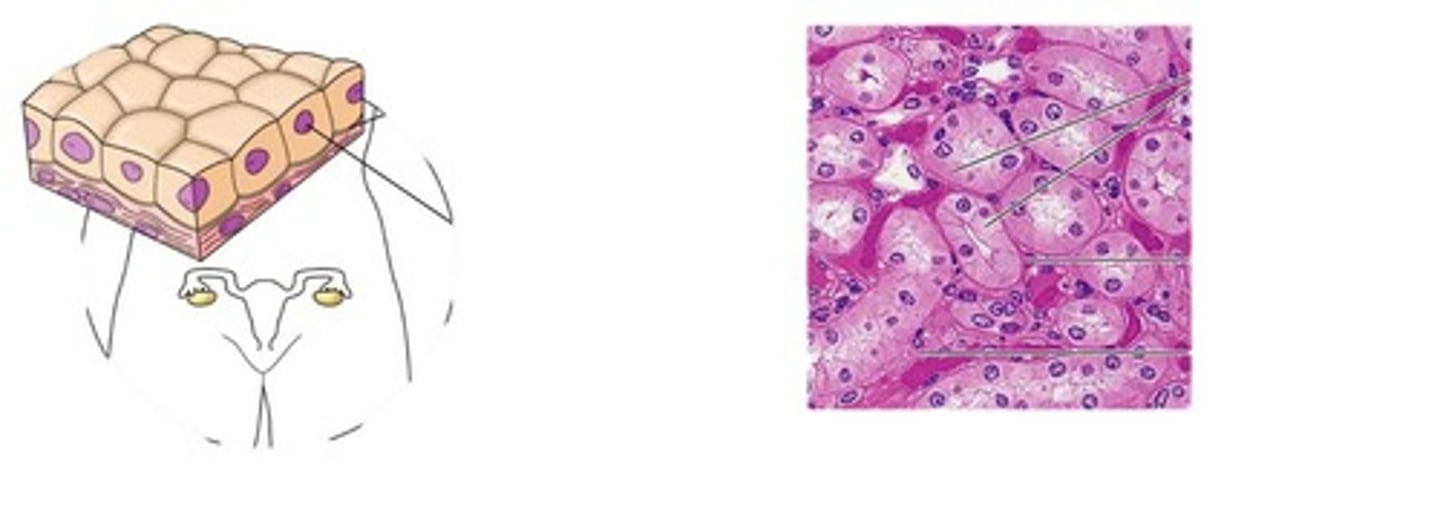
Bones
made up of calcium phosphate (CaPO4
Joints
where bones come together
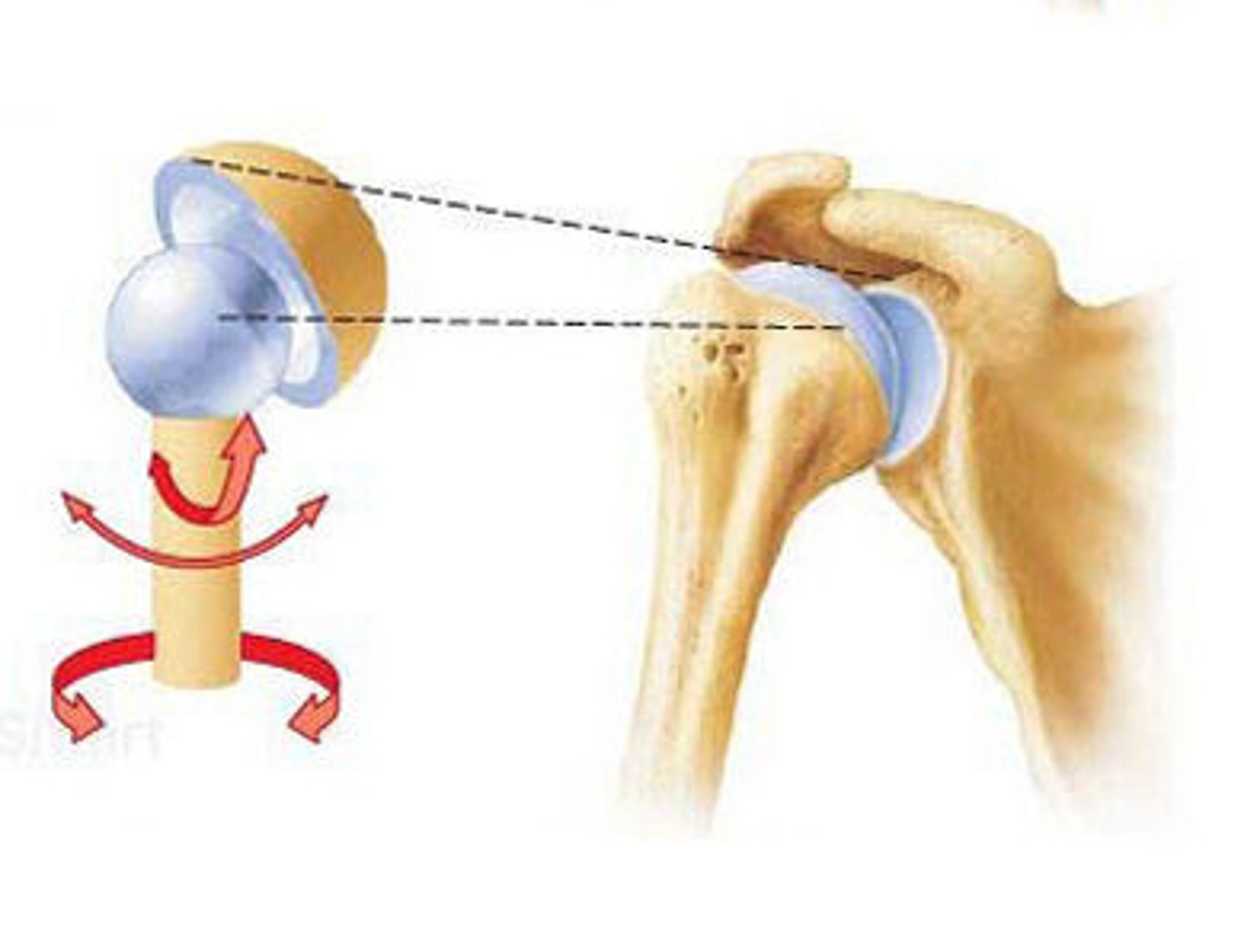
ball and socket joint
like hip or shoulder
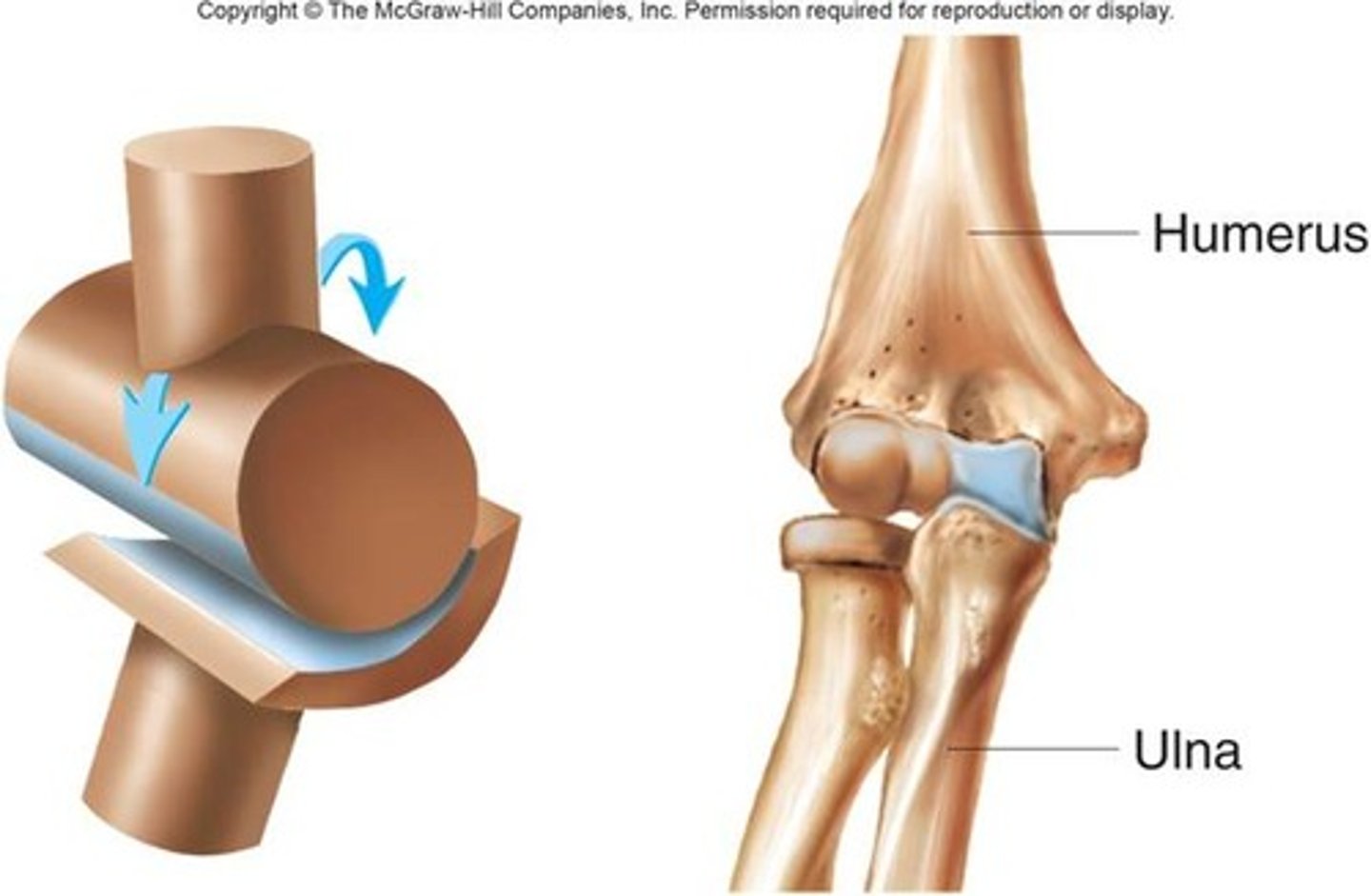
hinge joint
like knee or elbow
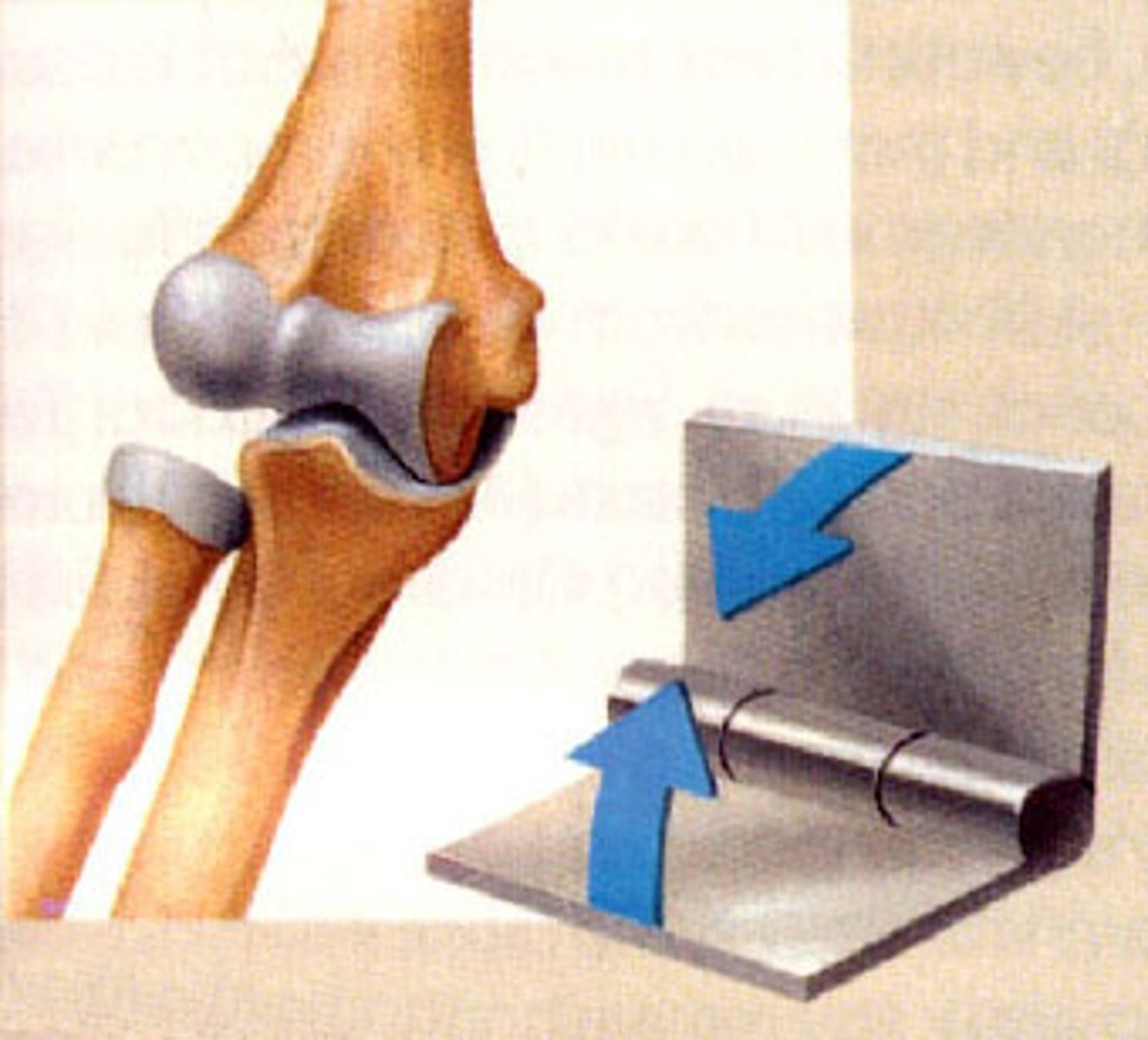
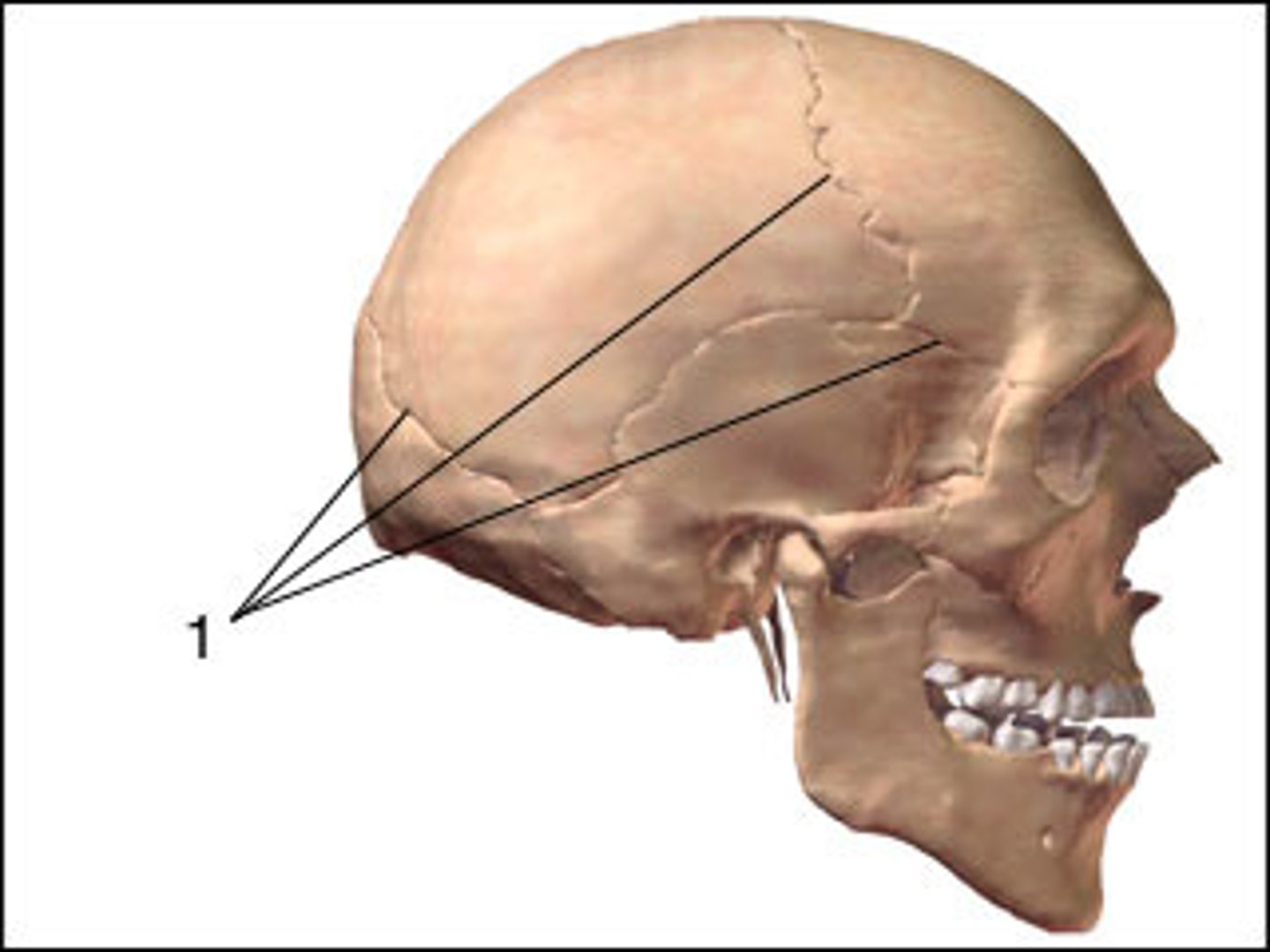
immovable joint
like the skull
cartilage
flexible tissue that provides additional support
Reproductive system
consists of testes and sperm; ovaries and eggs
Testes
glands that produce testosterone
ovaries
release eggs
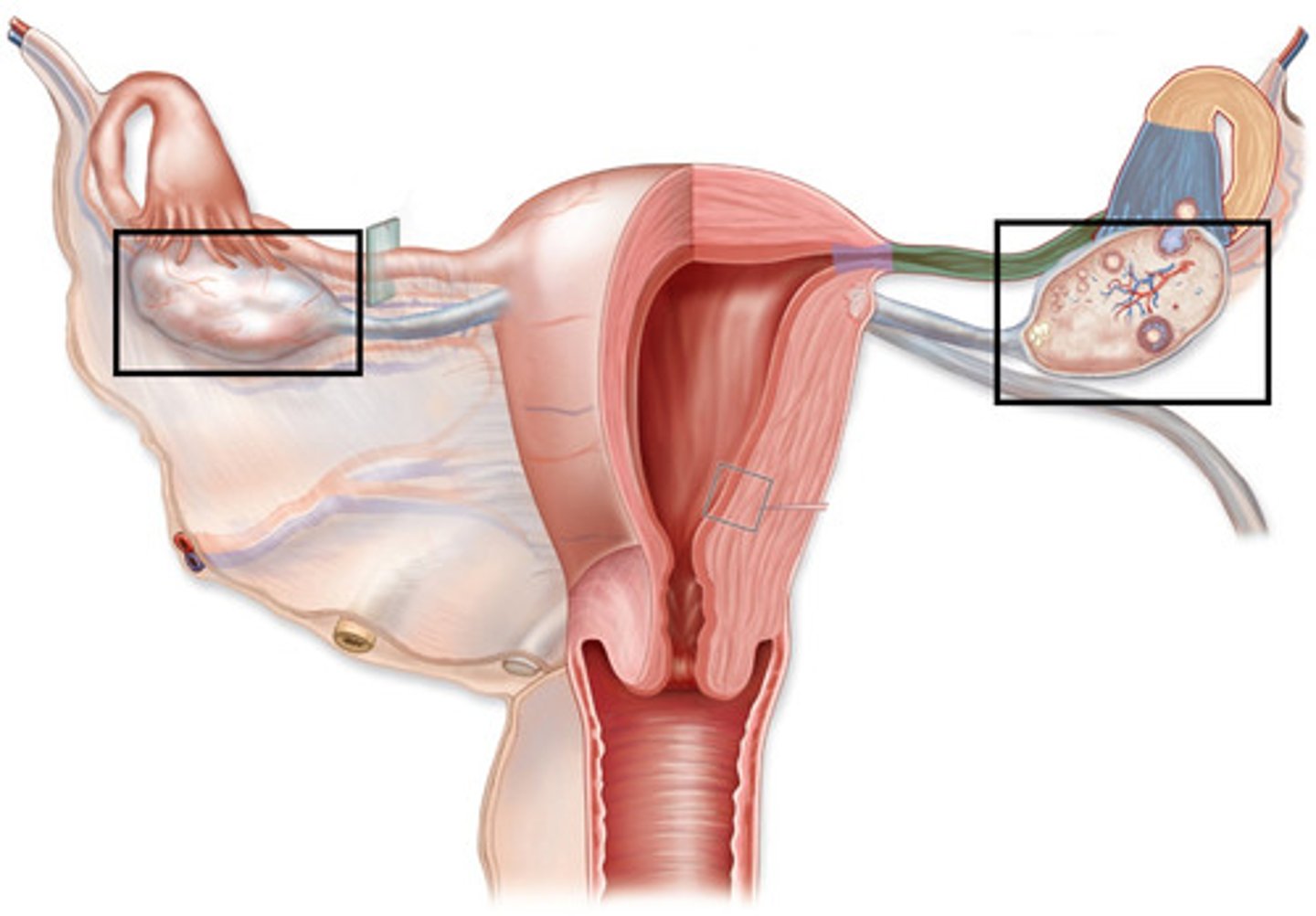
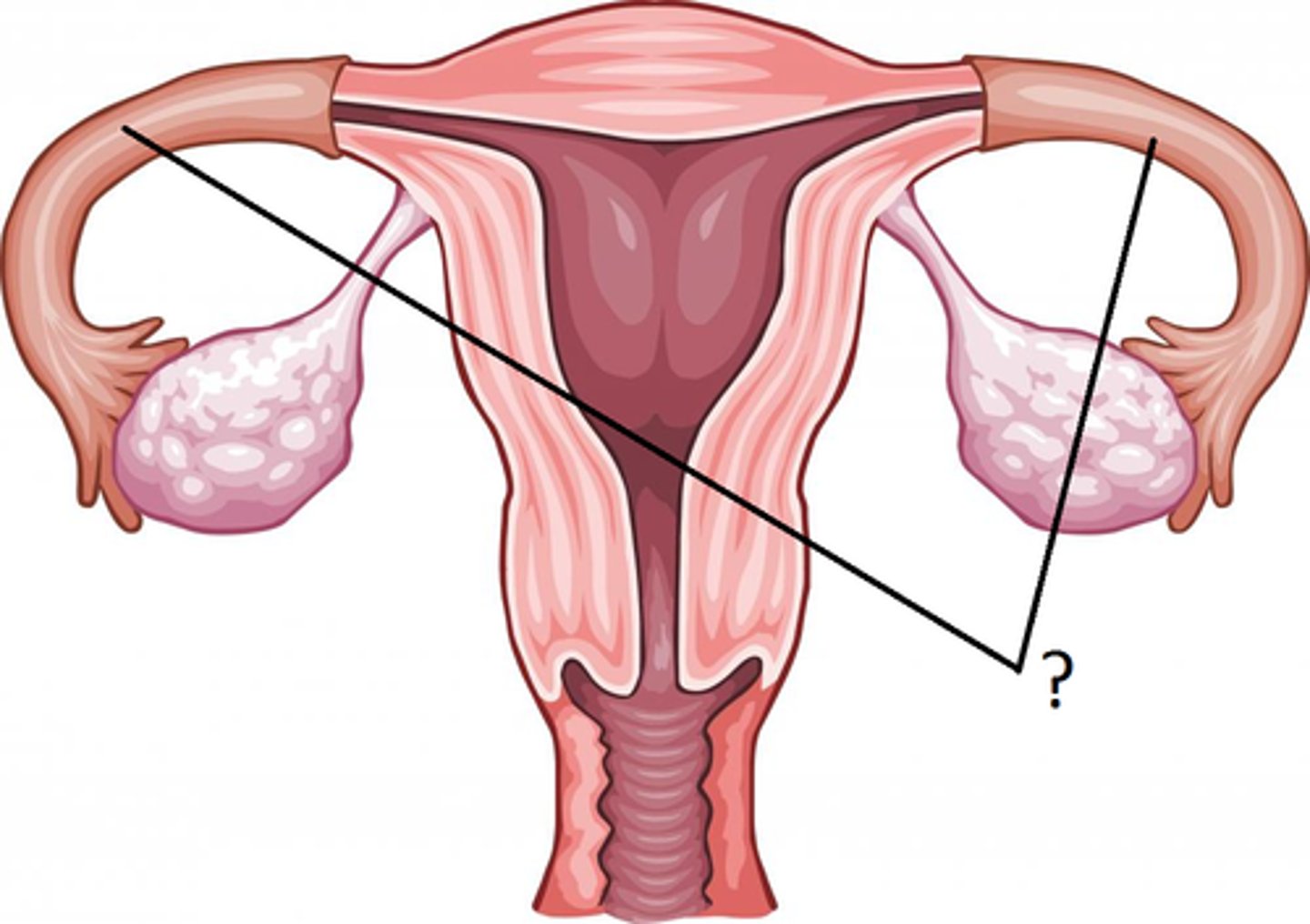
Fallopian tube
path of eggs to uterus
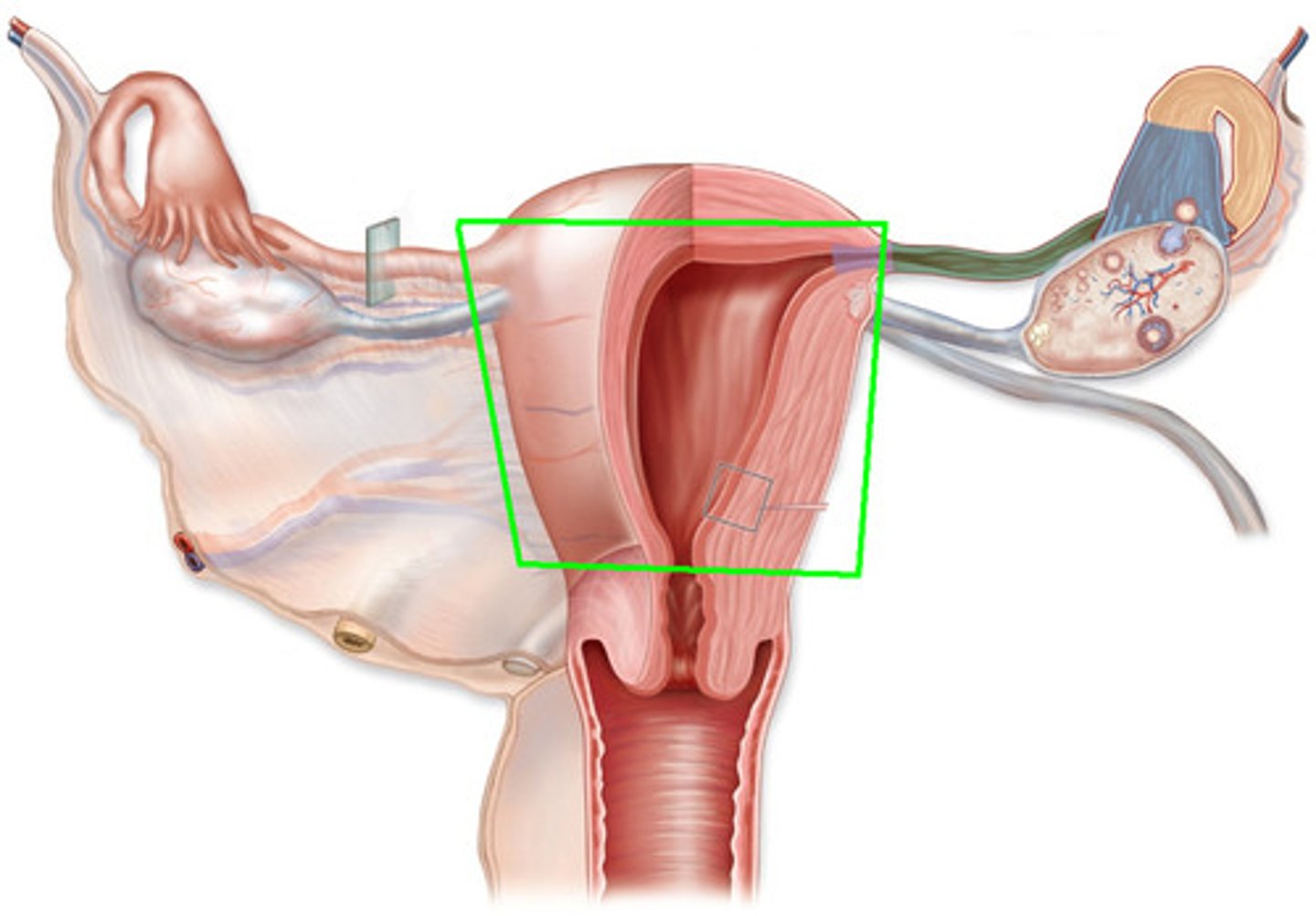
uterus
place for embryo to develop
muscular system
enables appropriate movement
Nervous system
Controls and communication network of the body
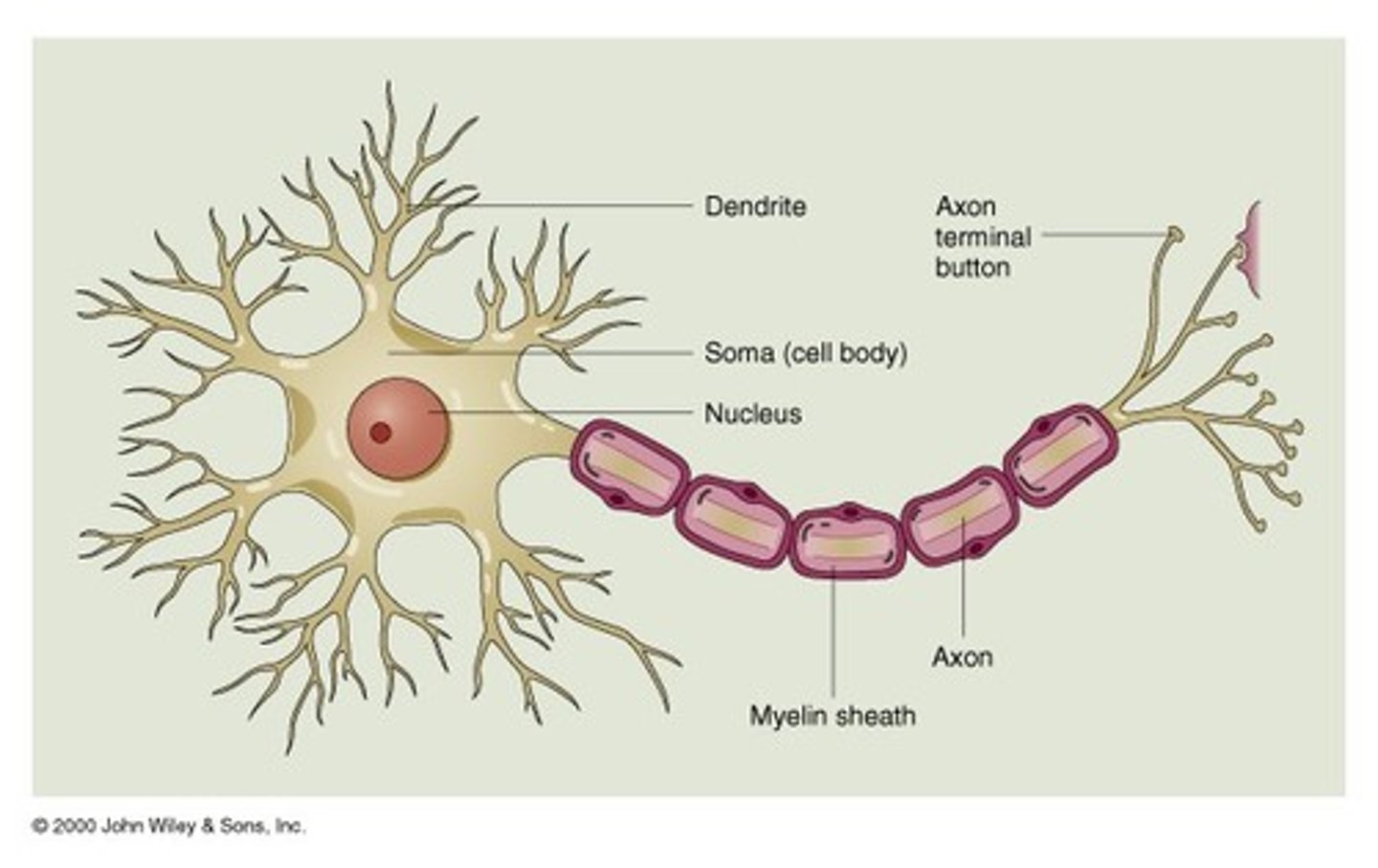
Neurons
nerve cells
sensory neurons
get information from the 5 senses
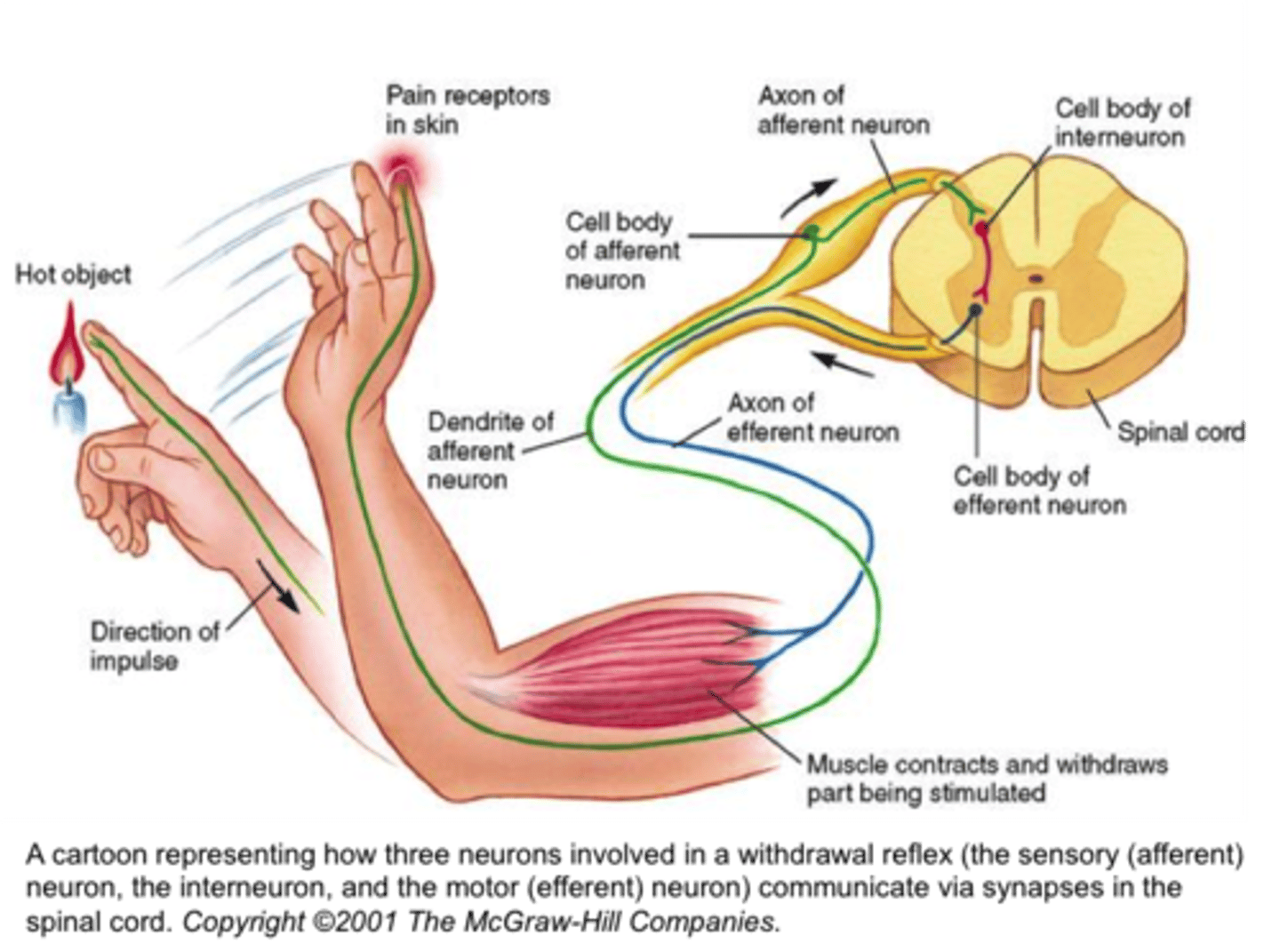
motor neurons
carry information from the brain to muscles to cause action
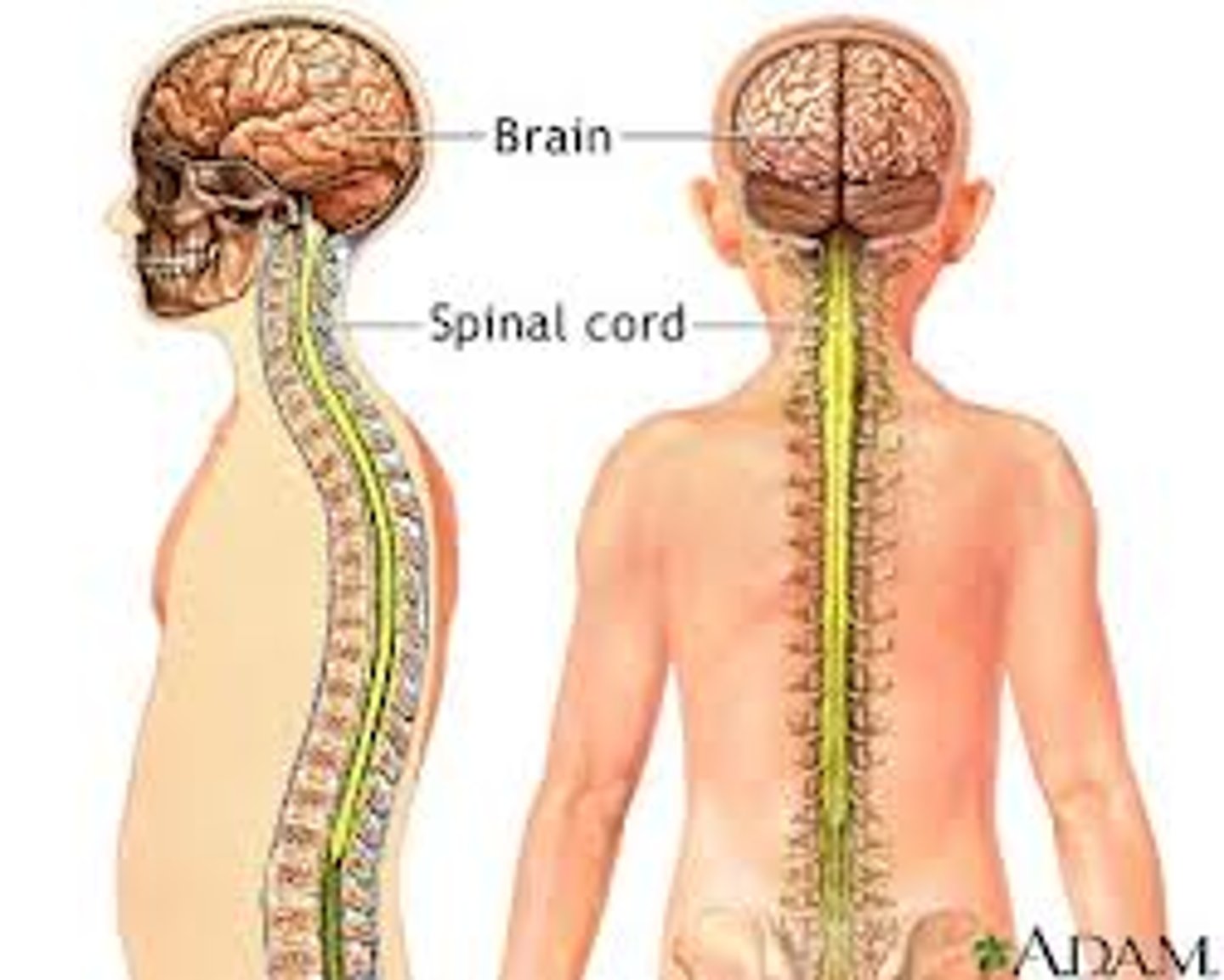
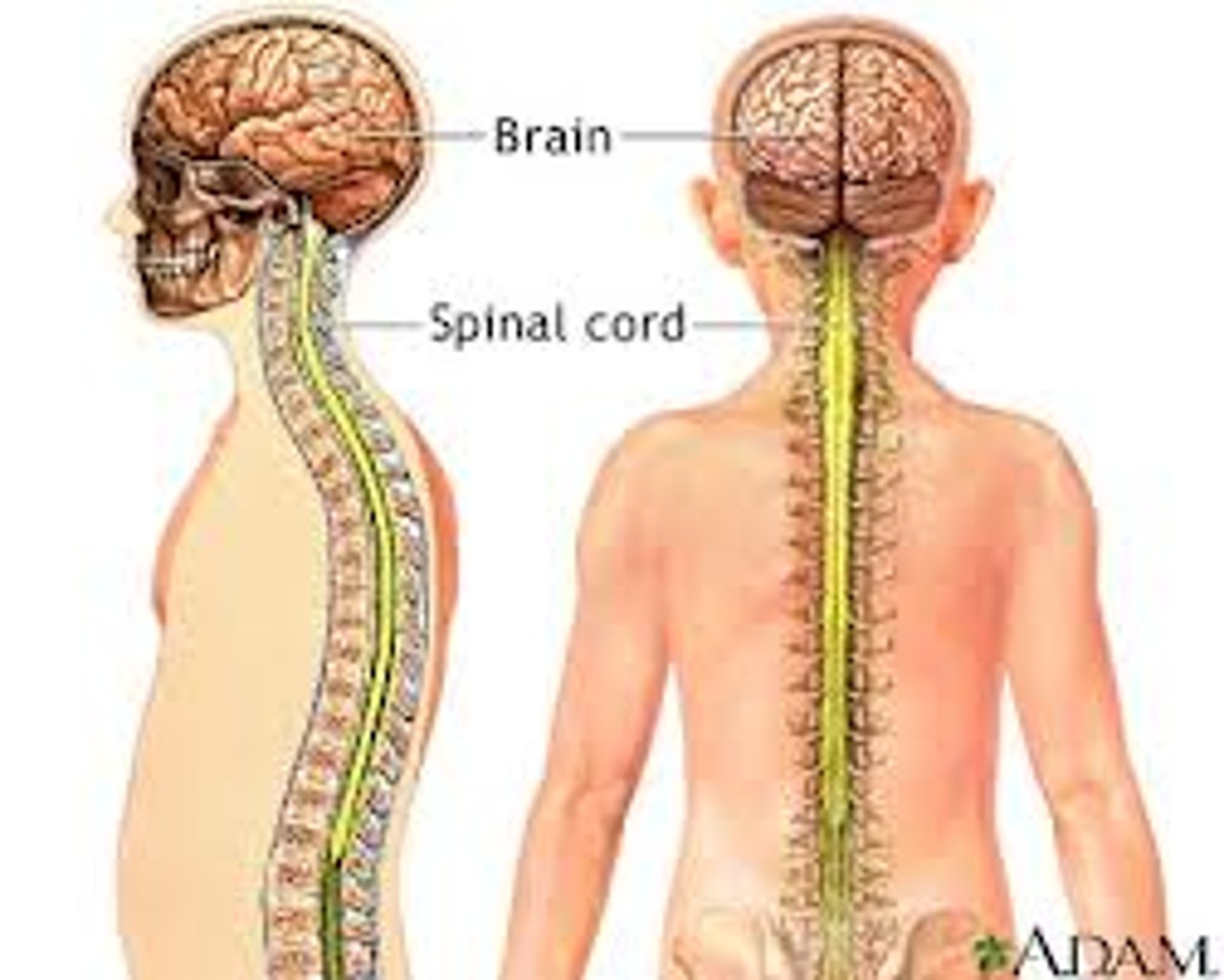
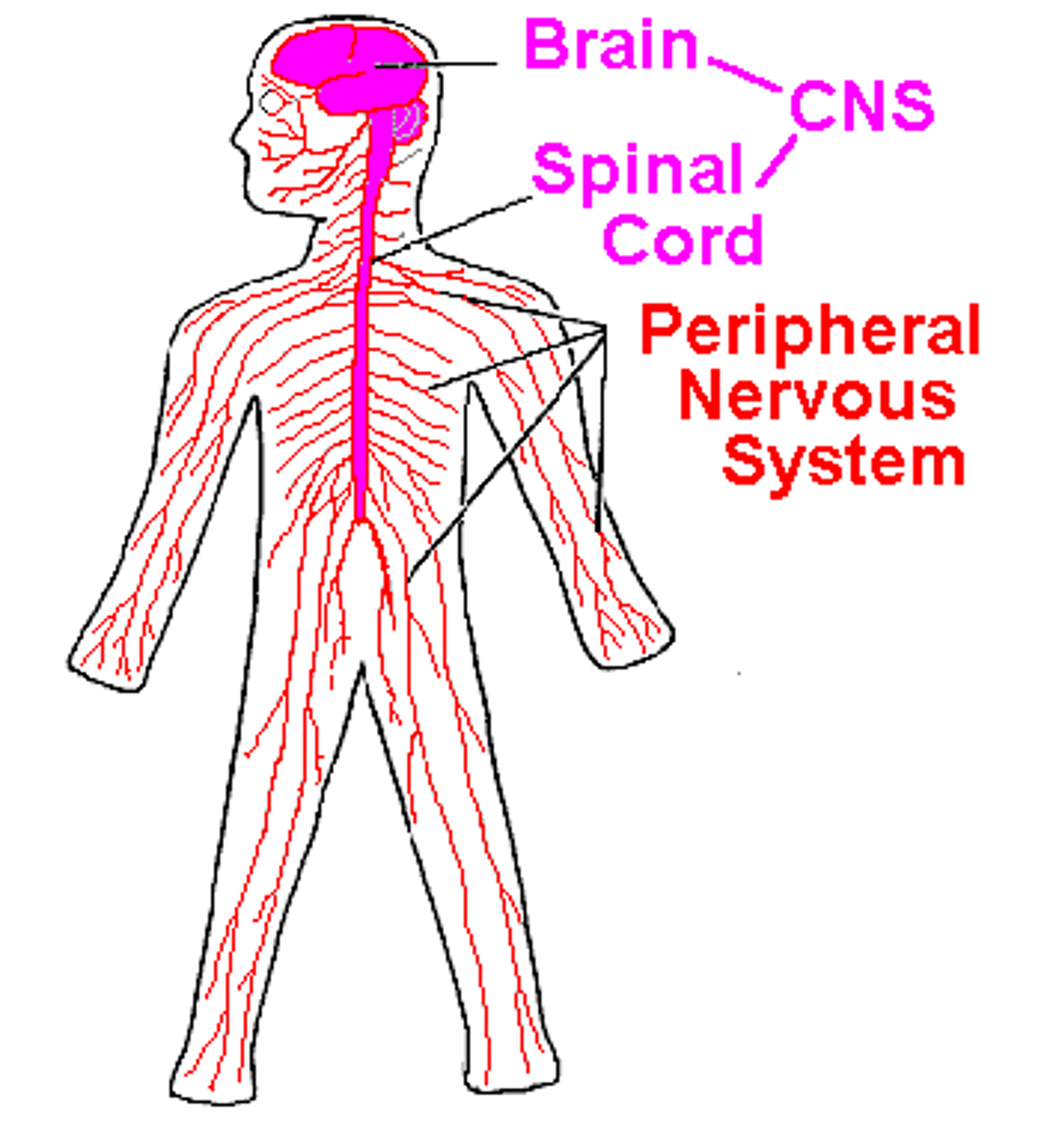
Central nervous system
Brain and spinal cord
peripheral nervous system
Carries impulses from brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body
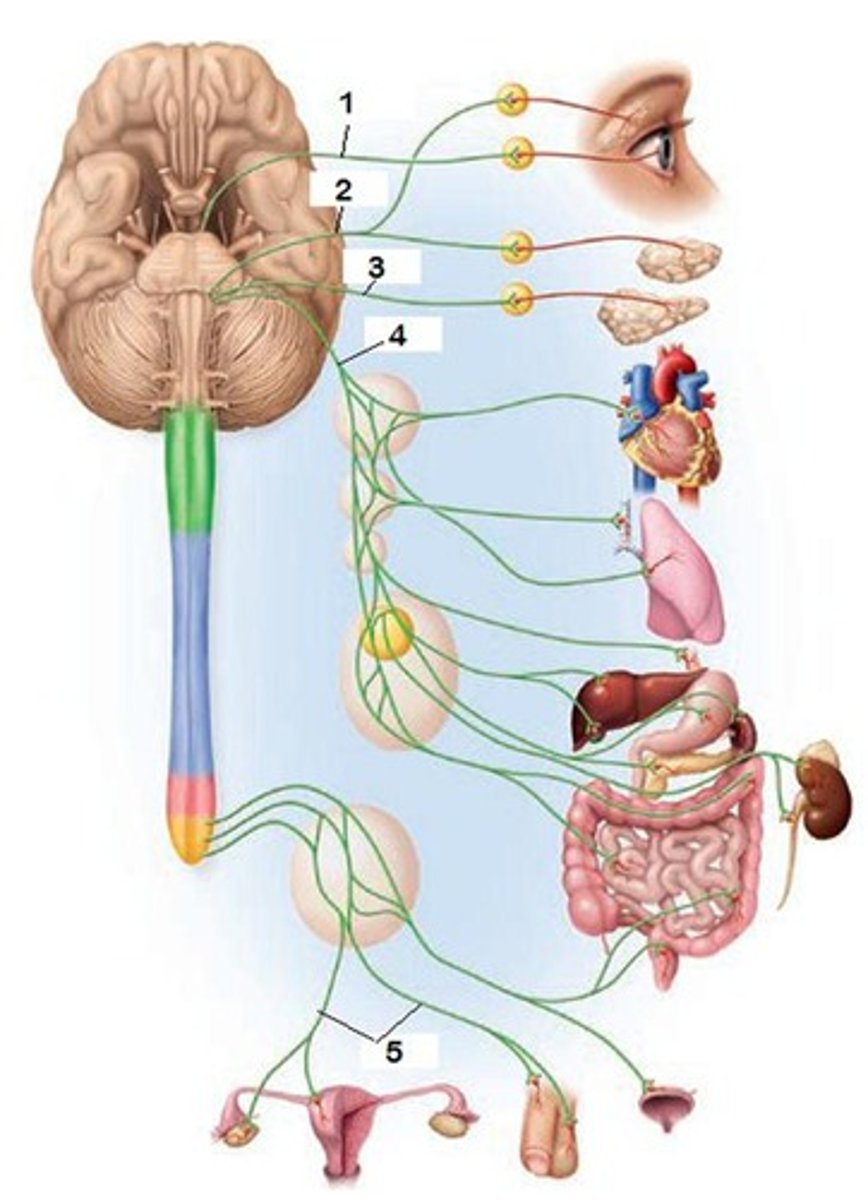
Autonomic system
controls involuntary systems, like glands & smooth muscles.
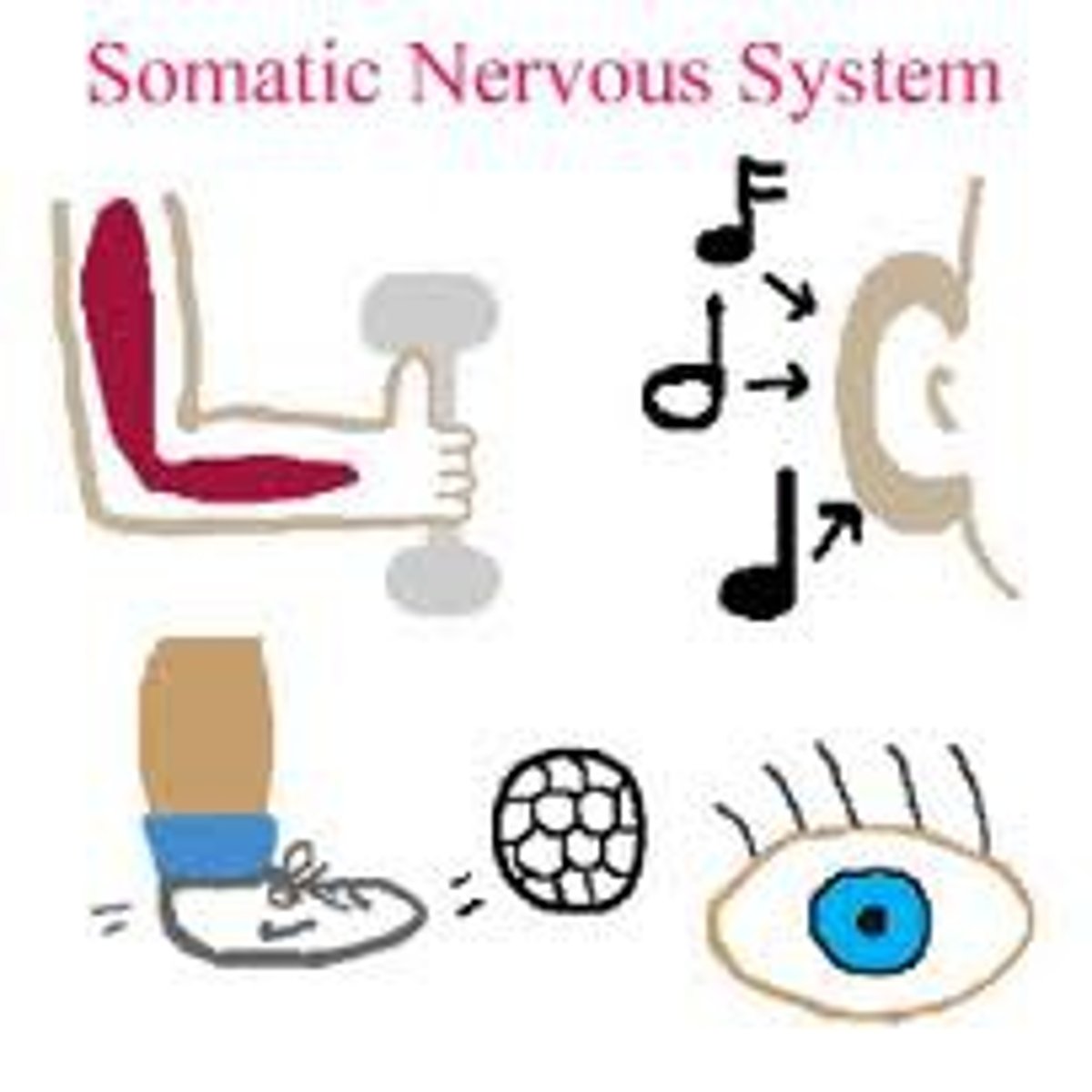
Somatic
controls voluntary systems, like skeletal muscles
urethra
tube that takes urine from the bladder out of the body.
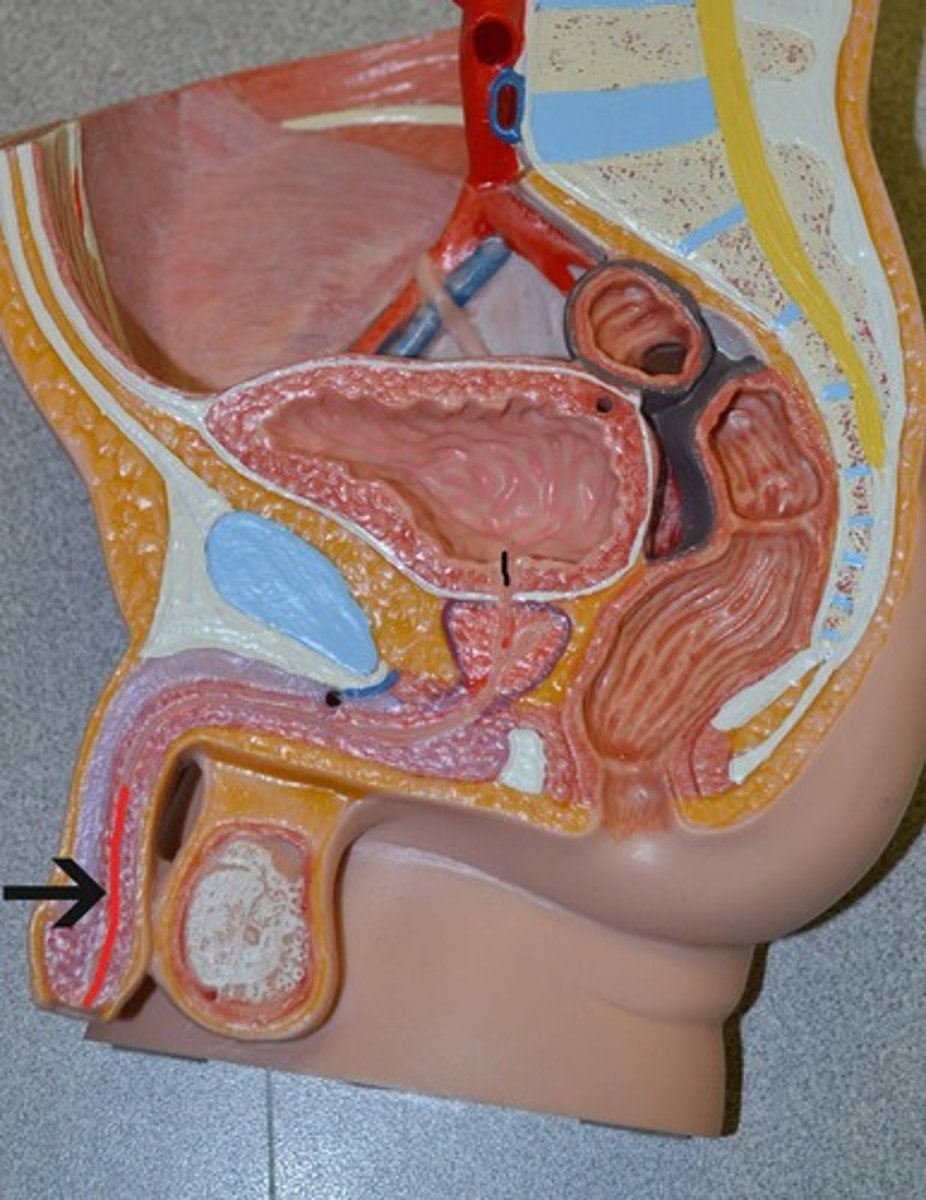
Endocrine system
regulates the effects of hormones on body function
Exocrine glands
secrete substances into body cavity or onto skin's surface. Ex. Sweat glands & mammary glands
Endocrine glands
secrete hormones into bloodstream.
Immune system
Cells and tissues that defend the human body against pathogens. Involves White blood cells (leukocytes)
lymphatic system
connecting network among parts of the immune system
Lymph
fluid contained in lymph vessels
Tissue fluid
surrounds cells and consists of water and leukocytes (WBC)
Lymph nodes
masses of tissue located at intervals along the lymph vessels
spleen
largest lymph organ
Inflammation
localizes the infection and allows the body to destroy pathogens
Fever
increase body temperature
Antigen
virus, bacteria, fungi (whatever the invading organism)
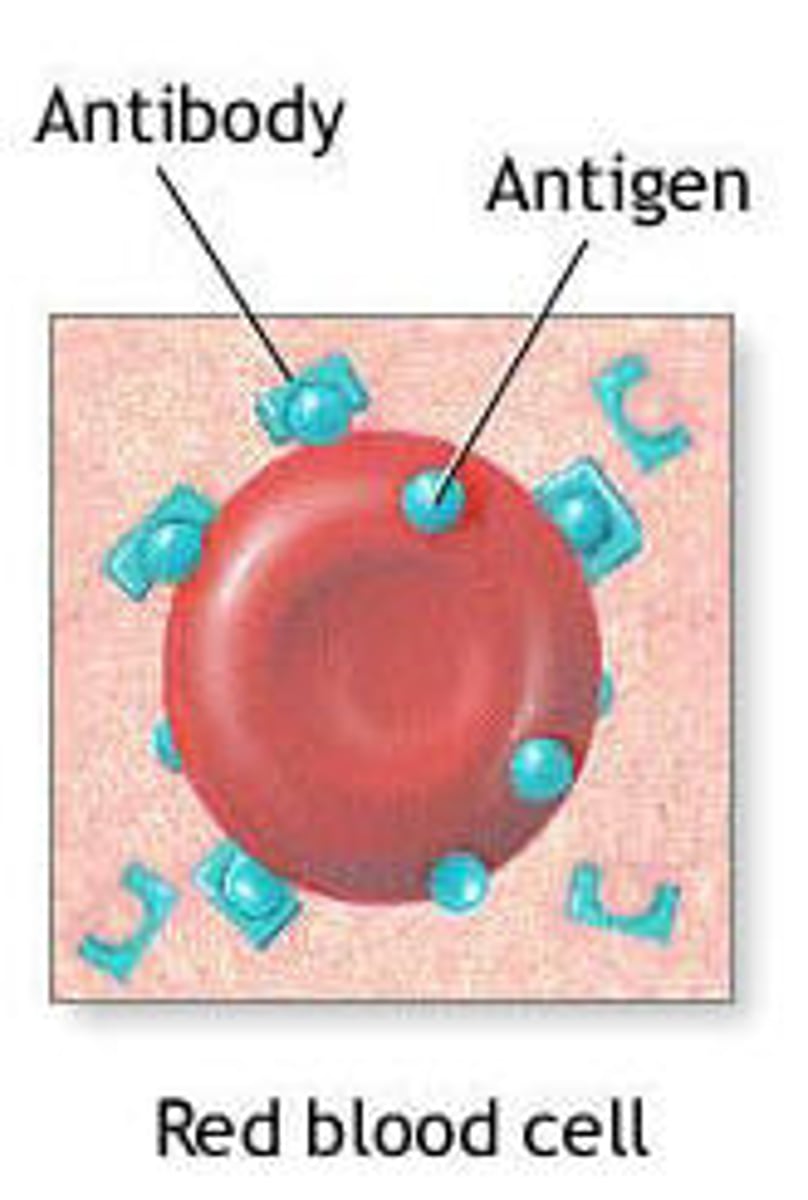
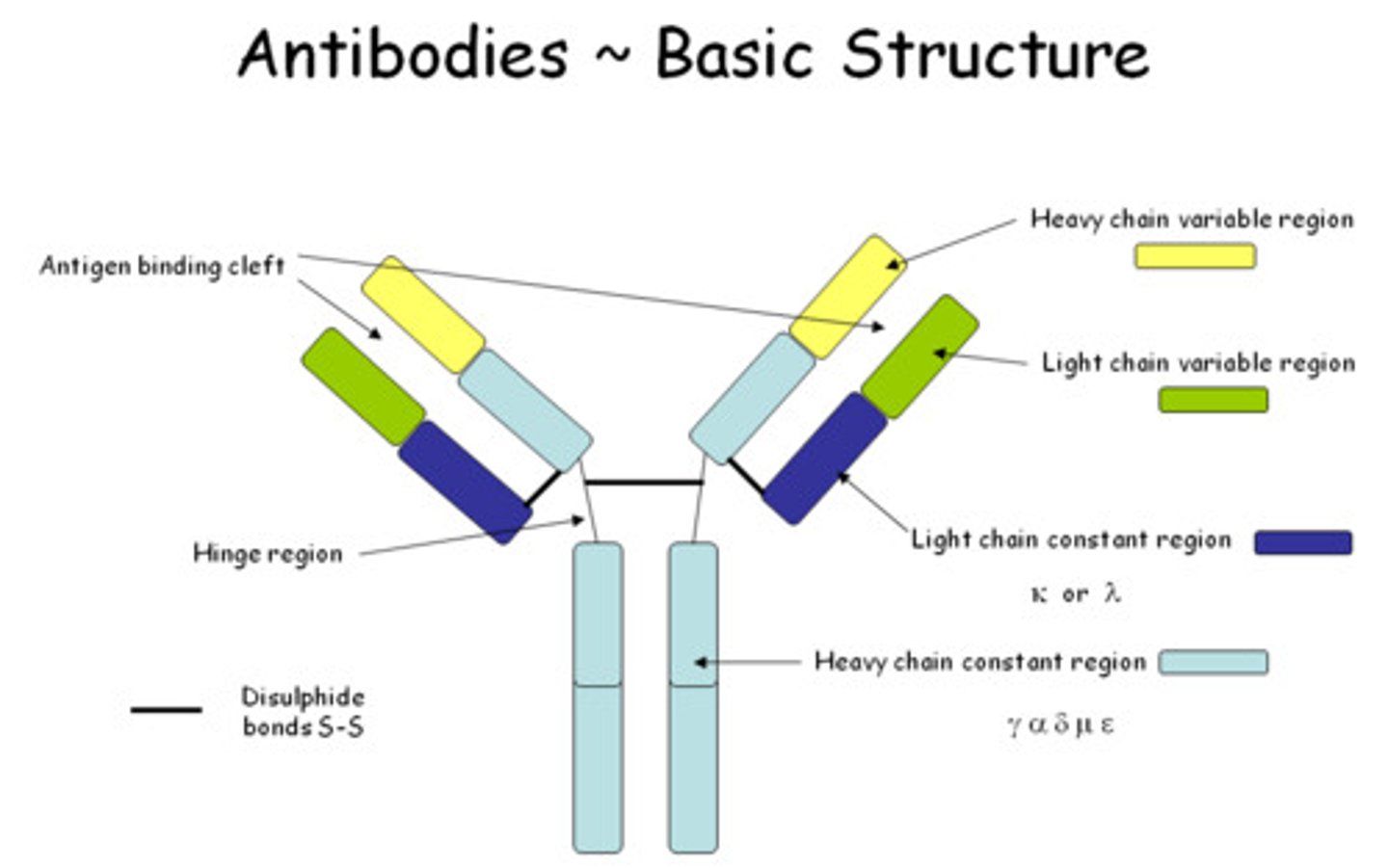
Antibodies
specific to one antigen. Binds to antigen and blocks effects.
Immunity
ability to resist disease.
Active immunity
acquired when an immune response is activated in the body. (You get sick and your body builds up its immunity). Long term immunity
Passive immunity
When antibodies are introduced into the body. (from mother to infant through breast-feeding). Short term immunity