golgi apparatus
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
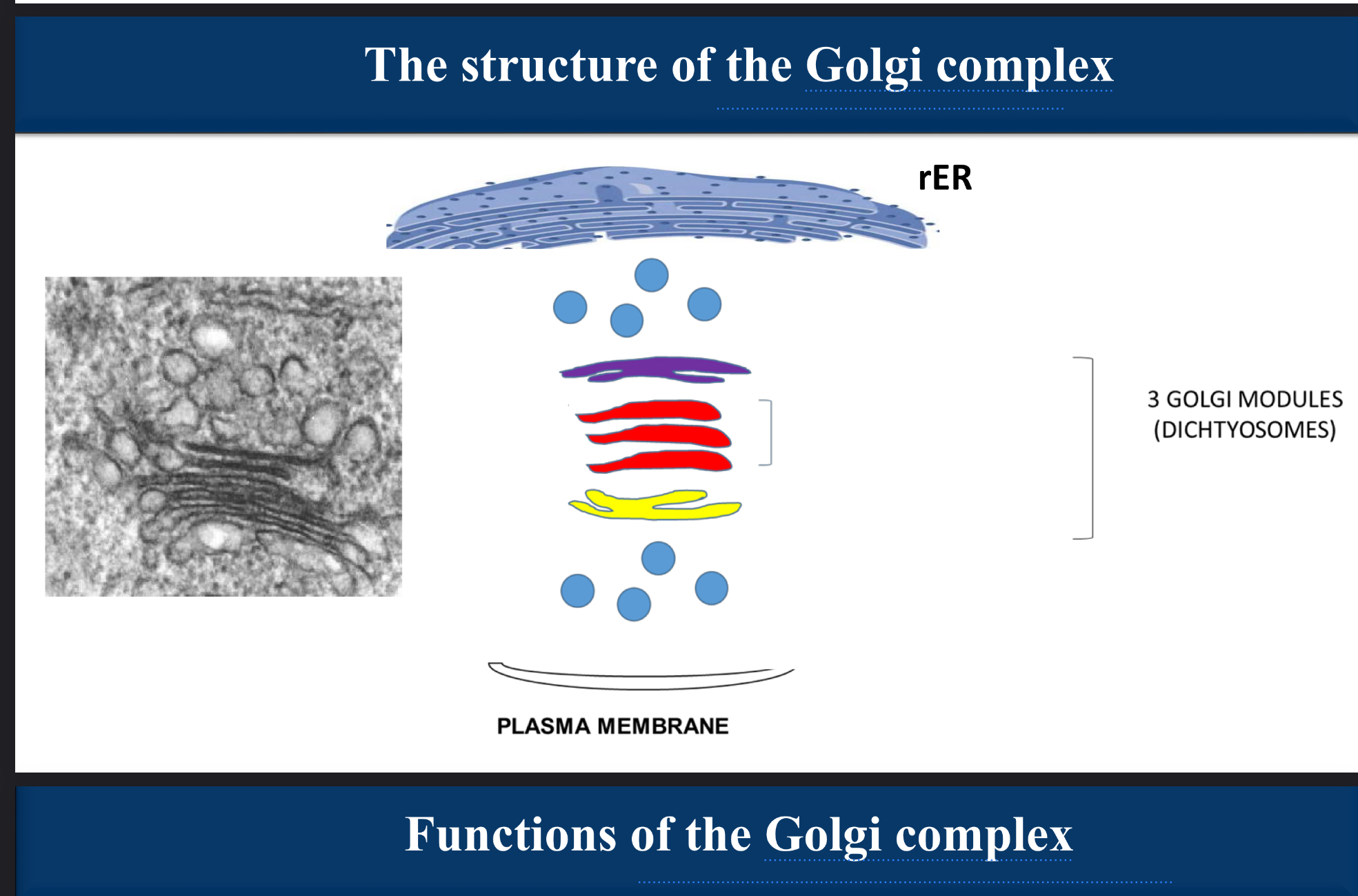
label the diagram
circles at the top → cis golgi network (CGN)
purple flattened area → cis golgi cisternae
red flattened area → medial golgi cisternae
yellow flattened area → trans golgi cisternae
circles at the bottom → trans golgi network (CGN)
whats the functions of the golgi apparatus
post translational modification factory
trafficking hub of proteins / lipids in cell
what are the 6 main roles of the golgi apparatus
glycan maturation
phosphorylation
sulfation
proteolysis
trafficking
sorting
describe in more detail the pathway of the golgi apparatus functions
once received the golgi passes these molecules (lipids and proteins from rer and ser) through cisternae from cis to trans (anterograde transport)
covalently modifies them (sulfation, phosphorylation, glycosylation lipid synthesis)
what does the rER and the sER each send to the golgi apparatus?
sER: sends lipids
rER: sends proteins with initial N-glycosylation and folding
what is anterograde transport (5) steps
transport from the er to the golgi apparatus
proteins made in rER are packaged into transport vesicles
which bud off rER membrane and move towards cis face of golgi
and fuse with the cis golgi network membrane (CGN)
and release their proteins inside of the golgi for sorting and modifications
what is retrograde
transport of vesicles from golgi back to rER
to return wrongly sent vesicles containing ER resident proteins (proteins meant to stay within the rER)