Reactivity 1.1 - 1.4 : What drives chemical reactions?
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Heat
measure if the total energy of a substance
Temperature
measure of the avergae kinetic energy of the particles ina subtance
Enthalpy change △H
heat absorbed/released at constant temperature (Break-Make)
Standard enthalpy change △Hº
The enthalpy transferred under standard conditions: 100kPa + 298 K (Products - Reactants)
Average bond enthalpy
the energy required to break one mole of bonds in a gaseuous molecule averaged over similar compounds
Bond breaking is
endothermic
Bond making is
exothermic
Enthalpy change of formation △Hf
Enthalpy change when 1 MOL of a compound is formed from its elements in their standard states under standard conditions
Enthalpy change of Combustion △Hc
Enthalpy change when 1 MOL of a substance is complteley burned in oxygen under standard conditions
△Hºc
Reactants - Products
Born-Haber cycle
energy cycle for formation of an ionic compound
Lattice enthalpy change △Hºlat
the enthalpy hange when 1MOL of a solid ionic compound is broken down into gaseous ions under standard conditions
△Hºlat equation for MgCl2
MgCl2 (g) → Mg2+(g) + 2Cl- (g)
E. Atomisation △Hºatom
enthalpy change when 1MOL of gaseuous atoms is formed from an element in its gaseous state under standard conditions
△Hºf formula
Biofuel
fuel whose energy is obtained from biological carbon fixation (like photosynthesis): Bioethanol, Biodiesel, and Biogas
Biodiesel?
renewbale vegetable oil → esters of methanol (fuel)
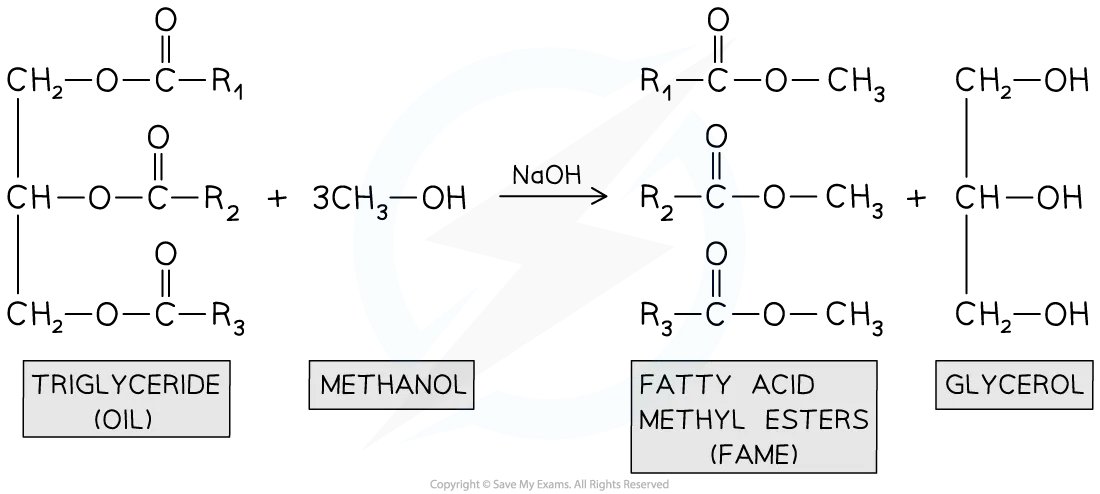
Bio Gas?
organic matter/waste → microorganisms in the absence of oxygen → Methane and CO2
Benefits and Negatives of Biofuels
+ves:
renwable + readily available
crops regrown : sustainable
reduces landfill waste
-ves:
↓ land for food
less specififc energy than fossil fuels
fertilisers
Fuel cell
converts chemical potential energy stored in a fuel into electrical energy
Proton Exchange membrane / Hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell:
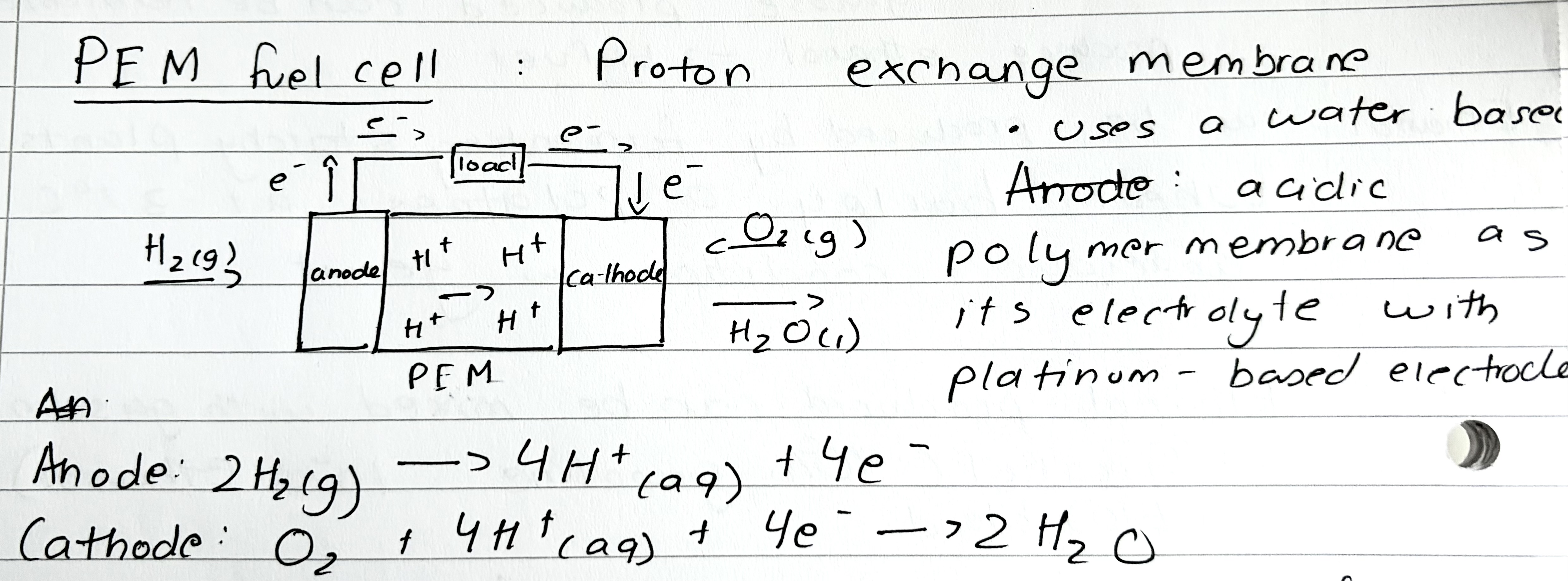

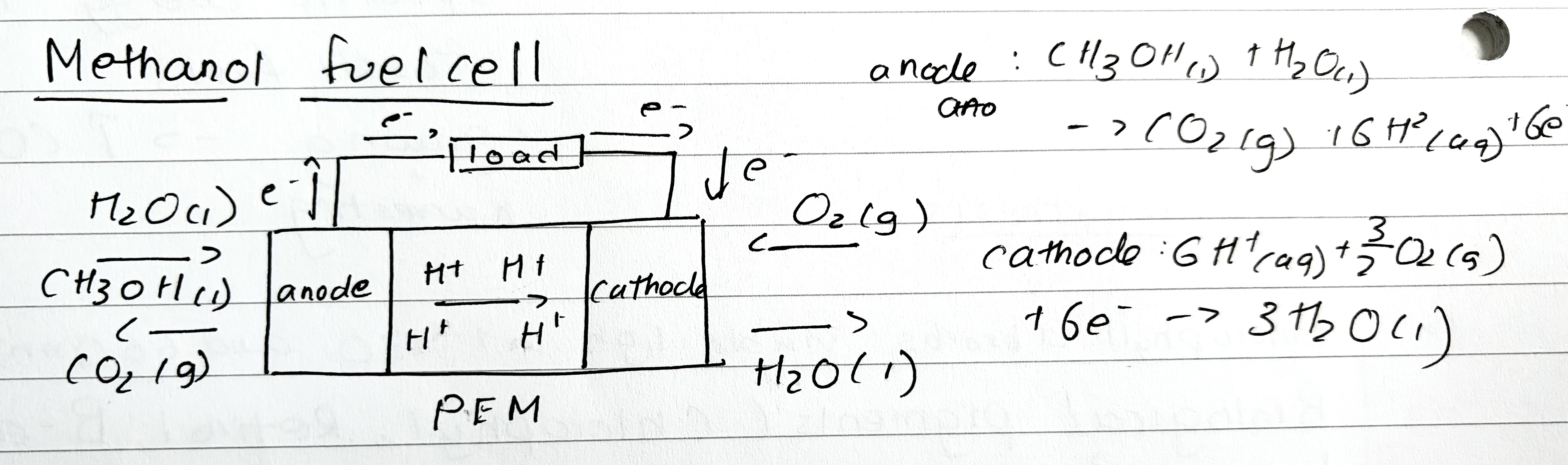
Methanol Fuel cell

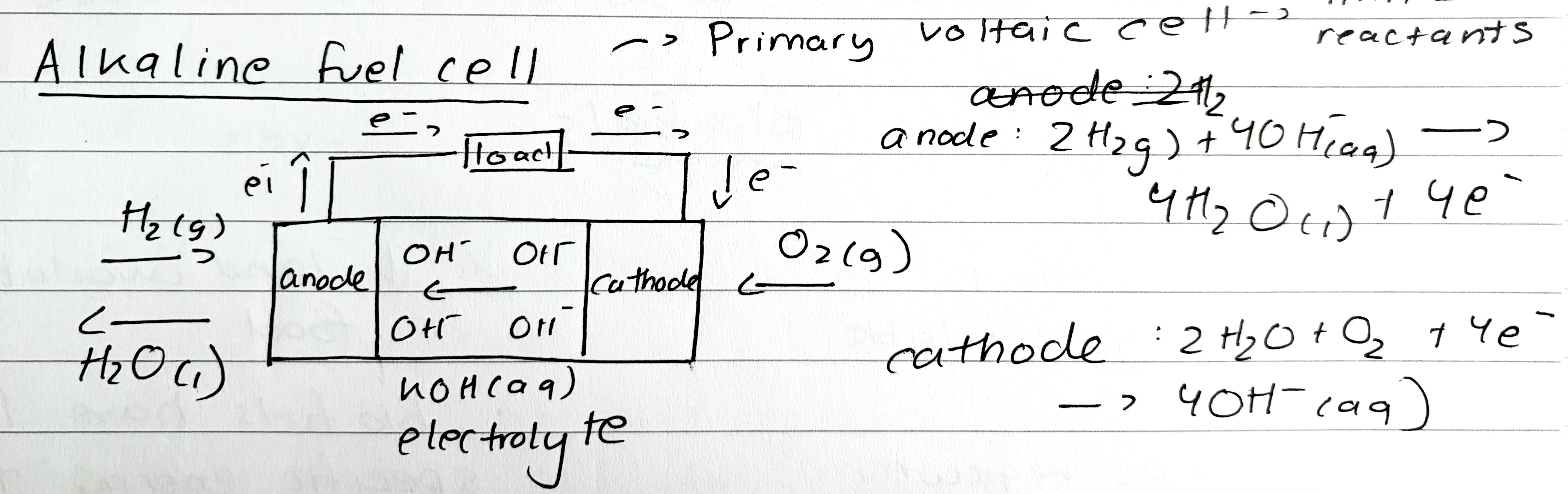
Alkaline fuel cell

Benefits and negatives of hydrogen fuel cells vs Methanol fuel cells
Pem +ves
| M +ves
|
Pem -ves
| M -ves
|
Factors that affect the entropy of a system:
temperature
change in state
dissolving/crystalising
change in no. of gaseuous reactants
Spotaneous process:
process that occurs without adding energy other than the energy required to overcome the energy barrier
△Stotal= +ve
△Stotal =
system - surroundings
Spontaeinty and Gibbs free energy
If ΔH .... | And if ΔS .... | Then ΔG is | Spontaneous? | Because |
|---|---|---|---|---|
is negative < 0 exothermic | is positive > 0 more disorder | always negative < 0 | Always | Forward reaction spontaneous at any T |
is positive > 0 endothermic | is negative < 0 more order | always positive > 0 | Never | Reverse reaction spontaneous at any T |
is negative < 0 exothermic | is negative < 0 more order | negative at low T positive high T | Dependent on T | Spontaneous only at low T TΔS < H |
is positive > 0 endothermic | is positive > 0 more disorder | negative at high T positive low T | Dependent on T | Spontaneous only at high T TΔS > H |
How do fossil fuels form?
from the reduction of biological compounds that contain carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, sulfur and oxygen →formed > million years ago in anerabic conditions
How does coal form?
giants plants die in swamps
trapped under layers of water and sediment
coal is formed under ↑ heat and ↑ pressure
Rank the coals on carbom content (low to high)
Peat
Lignite
Sub-bituminous coal
Bituminous coal
How does Natural gas/oil form?
Sea creatures die and are buried on the sea floor
remains burried deeper and ↑ heat + ↑ pressure forms oil + gas
oil+ gas reached by drilling
Crude oil/ petroleum
complex mixture of straight chain, branched, cyclic and aromatoc hydrocarbons
What is natural gas made up of?
Mainly Methane but also CO2
Coal +ves and -ves:
+ves
cheapish
↑ specific energy and energy density
can be converted into liquid fuels and gases
-ves
finite resource
produced CO2
produced SO2 (acid deposition)
mining = env. damage
Petroleum +ves and -ves:
+ves
cheap
↑ specific energy and energy density
easy to transport (gasoline)
feedstock for petrochemicals
-ves
non-renewable
produces CO2
drilling for and transporting →env. damage
uneven distribution worlwide
Clean fuel +ves and -ves:
+ves
clean fuel
↑ER specific energy than coal/oil
easy to transport: pressurised containers
no acid deposition
-ves
non-renewable
CO2
↓ ER energy density than coal/oil
uneven distribution
Stabdard Gibbs free energy of formation:
change in Gibbs free energy when 1MOL of a compound is formed from its elements in their standard states under standard conditions