ABA and stomatal closure
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What do guard cells do
Surround the stomata to control the entry of carbon dioxide into leaves and can respond to environmental stimuli in order to control the internal environment of the leaf
What do stomata open in response to
increasing light intensity
Low carbon dioxide concentration within air spaces within the leaf
What do stomata close in response to
darkness
High carbon dioxide concentration in leaf air spaces
Low humidity
High temperature
Water stress - when high rates of transpiration are not matched by high water uptake from the soil
What is the disadvantage of closed stomata
Photosynthesis rates decreases
What advantage is there to closing the stomata
Water is retained within the leaf.
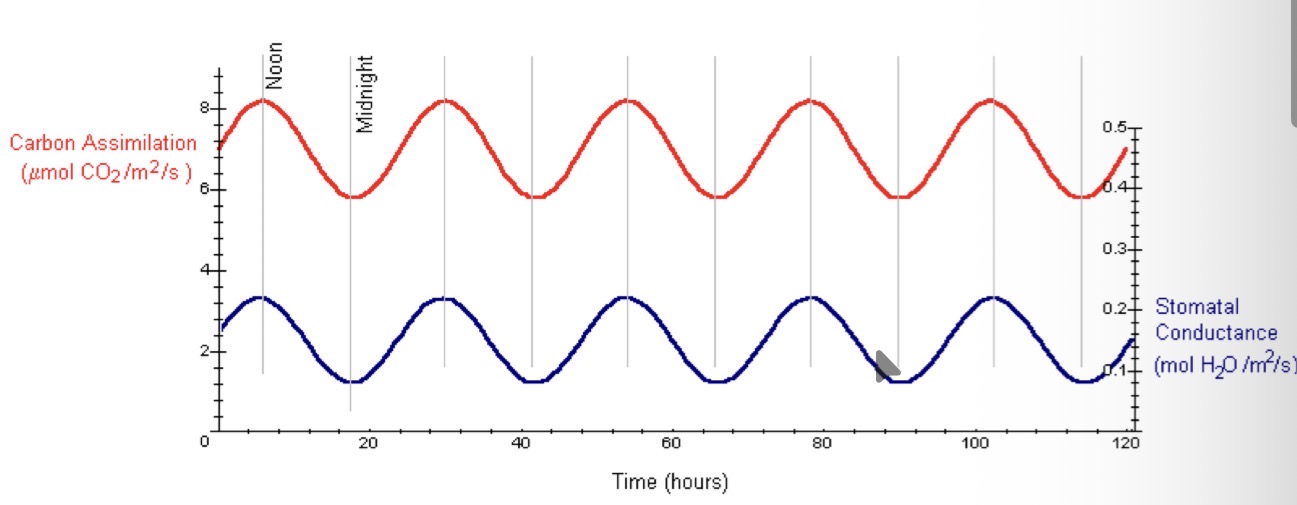
What can be said from this graph
The stomata close at regular intervals even when kept in constant light or dark - they have natural circadian rhythms.
How do stomata open?
guard cells either side of a stomach open when they gain water by osmosis (turgid) and close when they lose water by osmosis (flaccid)
As the two guard cells are joined at the top and the bottom, when the cells become turgid, the guard cells move apart at their centre and the pore opens.
How are the guard cell walls adapted to be effective for the opening/closing of stomata
have unevenly thickened cell walls - inside wall is very thick and quite inflexible but outside wall is thinner and easier to bend

How is cellulose used in guard cells to help them be better adapted to their function
Cellulose is arranged in hoops around the cells preventing them from expanding width-ways, so any changes in size affect the length
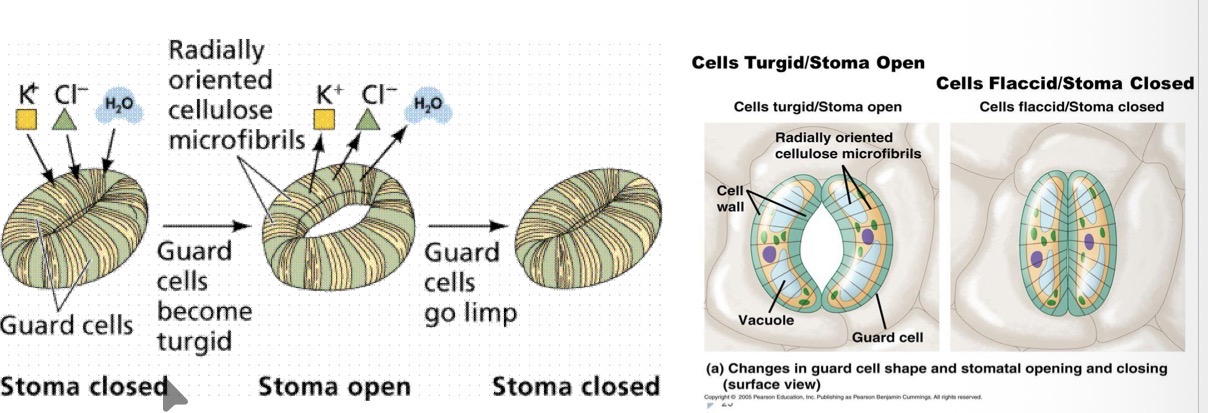
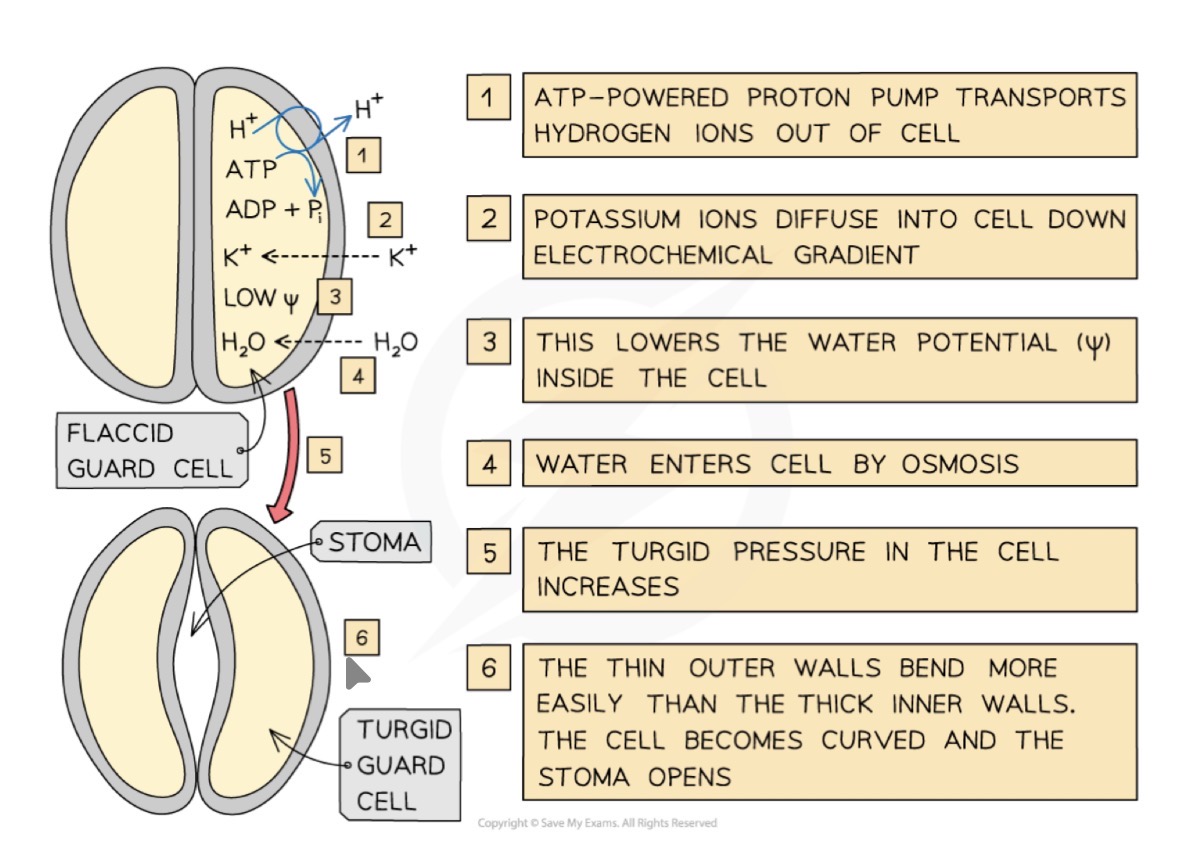
What is the process by which stomatal opening is controlled
H+ ions actively pumped out of guard cells via proton pumps in the cell surface membrane
Causes K+ channels in cell surface membrane so K+ diffuse into cell down electrochemical gradient and Cl- ions also diffuse in
Extra Cl- and K+ in cell lowers water potential causing water to move in through aquaporins
Increases turgidity of cell so stomata opens
What does ABA stand for
Abscisic acid
What is the role of ABA and when is it released
‘stress hormone’
Under conditions of water stress ABA is released and causes stomatal closure to reduce transpiration
How does ABA affect closure of stomata by binding to receptors
binds to receptors on cell surface membrane of guard cells
Inhibits proton pumps
Stops H+ leaving cell
Causes closure of K+ channel which were allowing K+ into cell
Solute conc in cytoplasm decreases, water potential becomes higher than epidermal cells and water moves out of cell
Guard cells become flaccid and stomata close.
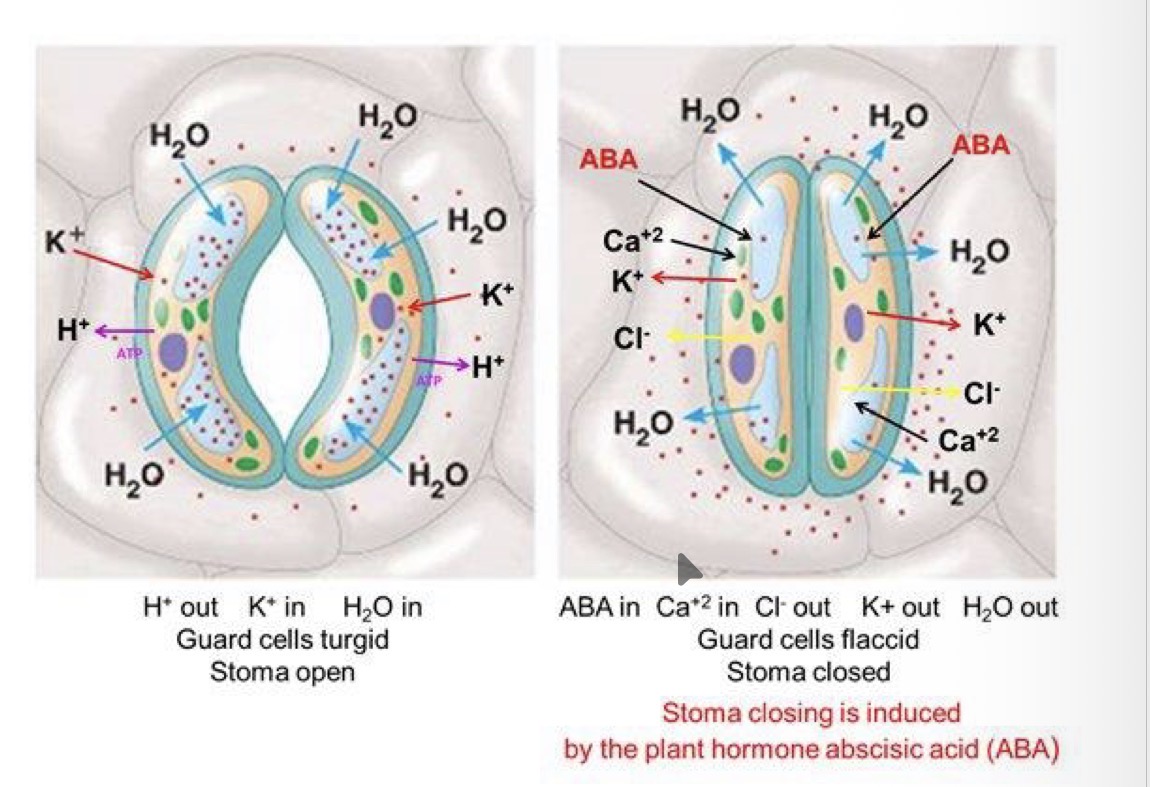
How does ABA affect closure of stomata by Ca2+ stimulation
ABA stimulates Ca2+ ions to move into cytosol from vacuole through tonoplast
Ca2+ acts as second messenger
Opening of channel proteins in cell surface membrane allowing Cl- out of cell
Opening of K+ channels which allow K+ to diffuse out of cell, down electrochemical gradient
Solute conc in cytoplasm decreases, water potential becomes higher than epidermal cells and water moves out of cell
Guard cells become flaccid and stomata close.