Honors Biology Final Study Guide - Unit 5
Gene
section of DNA that determines a specific trait
Genetically Modified Organisms
to alter an organism's DNA using genetic engineering techniques to introduce/modify specific traits
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Gene
section of DNA that determines a specific trait
Genetically Modified Organisms
to alter an organism's DNA using genetic engineering techniques to introduce/modify specific traits
nucleic acid
a complex organic molecule that carries genetic instructions for the development of living organisms
DNA
the molecule that carries genetic instructions for the development and functioning of an organism
nucleotide
the basic building block of nucleic acids
RNA
a nucleic acid molecule similar to DNA but containing ribose rather than deoxyribose
protein
a complex molecule made up of amino acids that performs a wide variety of functions in living organisms
chromosome
a structure within a cell that contains DNA, organized into genes
specialized cells
cells that have specific structures and functions
gene expression
the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product
mutation
a change in the DNA sequence of an organism virus, or extra chromosomal DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid
Genetic information found in every cell
Function of DNA
Provide genetic information to every cell (generation to generation, new cells) and Direct the production of proteins
Structure of Nucleotides in DNA
Composed of nucleotides, Deoxyribose sugar, Phosphate, Nitrogenous base
Four Different Bases in DNA
Adenine (A & T), Guanine (G & C), Thymine (T & A), Cytosine (C & G)
Structure of DNA
DNA is arranged in a double helix, Two strands of DNA form opposite one another and then twist, Looks like a ladder that is twisted or a spiral staircase
Replication Fork
Y-shaped region where parental DNA strands are being unwound
DNA Replication
the copying of DNA
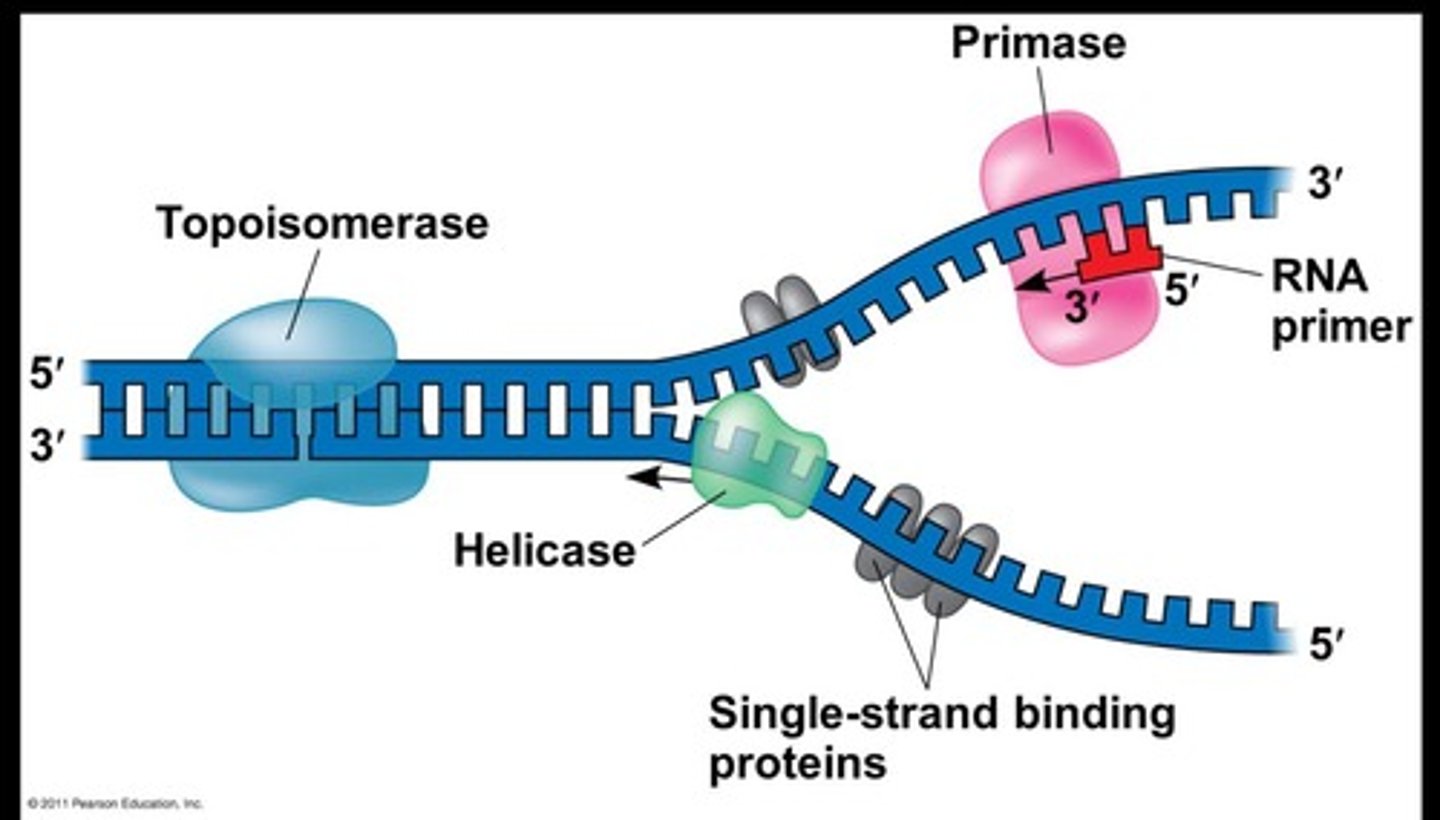
Topoisomerase (Gyrase)
relaxes supercoiled DNA ahead of the replication fork so that replication moves forward
Helicase
unwinds portion of the DNA double helix & makes it single stranded
single-stranded binding proteins
bind to the single stranded DNA and keep the two strands apart
Complementary strands of DNA
Strands that are synthesized using single parent strands as templates.
Free nucleotides
Nucleotides that form hydrogen bonds with complementary bases on template DNA to create new DNA strands.
DNA polymerase enzyme
An enzyme that catalyzes the formation of phosphodiester bonds during DNA synthesis.
Direction of DNA synthesis
New DNA is made in the 5' to 3' direction.
Daughter DNA strands
Each daughter DNA has one original parent (template) strand and one newly synthesized strand, known as semi-conservative replication.
Antiparallel strands
The two strands in a DNA molecule run in opposite directions, one is 5' to 3' and the other is 3' to 5'.
Leading strand
The new DNA strand that grows in the 5' → 3' direction.
Lagging strand
The new strand that grows in the 3' to 5' direction, replicated in pieces.
Replication of the lagging strand
DNA polymerase cannot catalyze DNA formation in the 3' → 5' direction, so it is replicated in pieces.
Okazaki fragments
Pieces of DNA that are replicated in a 5' → 3' direction on the lagging strand.
Primase enzyme
An enzyme that synthesizes short RNA primers, which are about 10 to 15 bases long, serving as a starting point for DNA synthesis.
DNA ligase
An enzyme that connects Okazaki fragments, resulting in a continuous 3' → 5' strand.
Proofreading
The process by which DNA polymerase acts as a 'spell checker' to ensure the correct bases are added during replication.
RNA Structure
RNA can be single or double stranded, combination.
Sugar in RNA
Sugar is ribose.
Nitrogenous Bases in RNA
Four nitrogenous bases: Adenine (A), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G), and Uracil (U).
Nucleotide Bonding
Nucleotides bound together on backbone by phosphodiester bonds (covalent).
Base Pairing in RNA
Base pairing in double stranded regions: A with U, G with C.
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
Carries genetic information from DNA (in the cell nucleus) to the ribosomes (in cytoplasm) for synthesis of proteins.
mRNA Production
Each gene segment of DNA produces a specific mRNA.
mRNA Template Function
The sequence of nucleotides in mRNA serves as a template for the arrangement of amino acids in a protein.
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
Combined with proteins in the ribosomes.
Ribosome Function
Ribosomes are sites of protein synthesis.
Location of rRNA
Free in cytoplasm or attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum (fixed).
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
Uses the sequence of nucleotides in mRNA to bring specific amino acids to the ribosome for protein synthesis.
tRNA for Amino Acids
Each of the 20 amino acids has one or more tRNA molecules.
Structure of tRNA
Cloverleaf structure due to hydrogen bonding between complementary base pairs in the single chain of nucleotides.
tRNA Acceptor Stem
Acceptor stem attaches to amino acid.
tRNA Anticodon
Series of three bases that complements three bases (codon) on mRNA.
Transcription
RNA Polymerase - enzyme that reads the template DNA and transcribes the DNA to RNA.
Transcription Initiation
Once DNA strands have separated and the promoter is exposed, transcription can begin.
RNA Polymerase Binding
RNA polymerase binds to the promoter region on the DNA then starts transcription to form RNA.
Transcription Elongation
Elongation - RNA polymerase attaches adenine, guanine, cytosine, & uracil to the growing mRNA chain.
Transcription Termination
Termination - At the termination signal in the DNA template, RNA polymerase & the new mRNA strand detach from the DNA (5' - 3%).
Synthesis of mRNA
Occurs only when protein is needed in the cell.
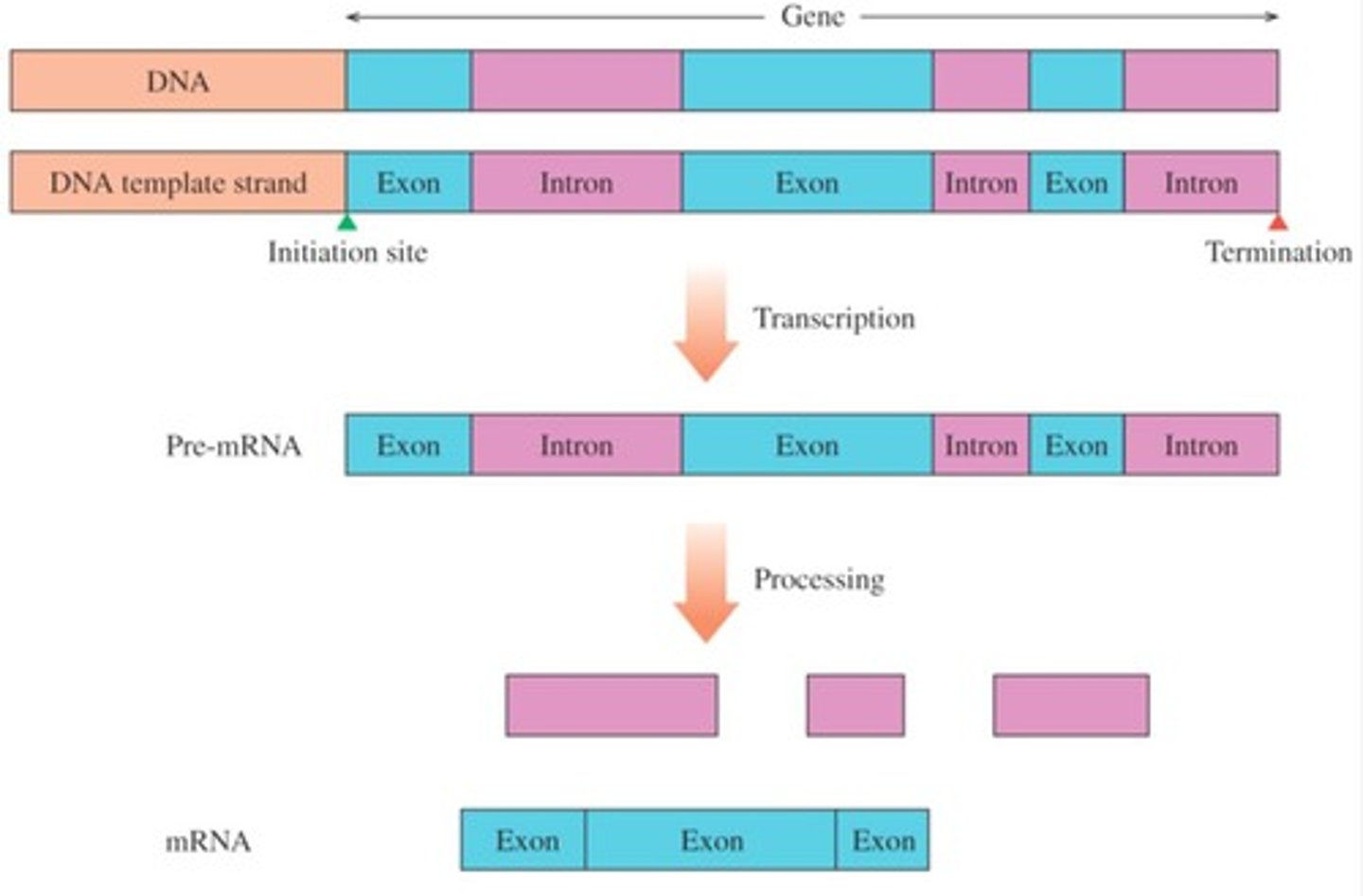
Immature mRNA transcript
Considered 'immature' at the end of transcription.
Exons
Sections of DNA in a gene that code for proteins.
Introns
Sections of DNA in a gene that do not code for proteins.
Intervening DNA
DNA that is 'in between' protein coding sections.
Pre-mRNA
A copy of the entire DNA template (introns and exons) at the completion of transcription.
mRNA processing
Involves removing introns and splicing together the remaining exons.
Functional mRNA
Ready to leave the nucleus and deliver genetic information to the ribosomes for protein synthesis.
7-Methyl Guanosine (7mG)
Added to the 5' end of the mRNA to protect it from nucleases and identify it as mRNA.
Poly A tail
Added to the 3' end of mRNA, consisting of 50 to 100 A nucleotides, to protect it from nucleases.
tRNA
Transfer RNA that translates mRNA's message.
Codons
Determine which amino acid is coded for by the DNA.
Initiation
Small ribosome subunit binds to mRNA at the START codon AUG.
Elongation
A site recognizes codon and pairs with the correct tRNA; peptide bonds form between amino acids.
Termination
Occurs when a STOP codon (UAA, UAG, UGA) is reached at the A site.
Release factor protein
Frees the new protein from the ribosome during termination.
Point Mutations
One base altered (base pair substitution).
Silent Mutation
No effect on the protein.
Missense Mutation
Changes an amino acid in the protein.
Nonsense Mutation
Creates a STOP codon in the sequence.
Insertion
Extra base(s) added to the DNA sequence.
Deletion
Removal of base(s) from the DNA sequence.
Frameshift Mutations
Created by insertion and deletion mutations.
Restriction Enzymes
Enzymes that cut DNA at specific nucleotide sequences (restriction sites).
Blunt ends
DNA ends cut straight across by restriction enzymes.
Sticky ends
Unpaired bases of DNA that can form bonds with complementary bases.
DNA ligase enzyme
Used to put together two different pieces of DNA via sticky ends.