LAB 4: PHYLUM PLATYHELMINTHES AND BODY SYMMETRY
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
PHYLUM PLATYHELMINTHES
Flatworms; bilaterally symmetrical, acoelomate invertebrates with a flattened body.
Class Turbellaria
Mostly free-living flatworms, often found in aquatic environments; characterized by ciliated epidermis.
Class Trematoda
Parasitic flatworms, commonly known as flukes; they infect various hosts, including humans.
Class Cestoda
Parasitic flatworms known as tapeworms; live in the intestines of vertebrate hosts and absorb nutrients through their skin.
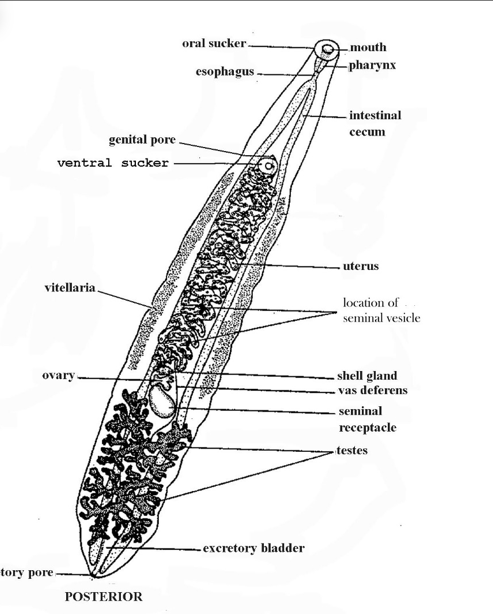
Opisthorchis
A genus of parasitic liver flukes that infect the liver, gallbladder, and bile ducts of humans and animals.
Schistosoma
A genus of parasitic blood flukes responsible for schistosomiasis in humans.
Platyhelminthes exhibit what kind of Symmetry
bilateral symmetry ; body can be divided into mirror-image halves.
Cercaria
The free-swimming larval stage of trematodes that leaves the first intermediate host to find a second intermediate or definitive host.
Cephalization
The development of a head region where sensory organs and nerve cells are concentrated.
Complex Life Cycle
A life cycle involving multiple hosts and stages, typical of parasitic flatworms like trematodes and cestodes.
Cysticercus
The larval stage of certain tapeworms, encysted in tissues of the intermediate host.
Eggs
Reproductive structures produced by flatworms, which hatch into larval forms.
Eyespots
light-sensitive organs found in some flatworms (e.g., Turbellaria) used to detect changes in light intensity.
First Intermediate Host
The host in which the larval stage of a parasite develops before moving to the next host
Flukes
Parasitic flatworms belonging to Class Trematoda, typically infecting organs like the liver, lungs, or blood vessels.
Hooks
Structures found on the scolex of tapeworms used to attach to the host’s intestinal lining.
Incomplete Digestive Tract
A digestive system with only one opening that serves as both mouth and anus, seen in many flatworms.
Intestine
The part of the digestive system where nutrient absorption occurs; in some flatworms, it branches extensively.
Metacercaria
The encysted, infective larval stage of trematodes, typically found in the second intermediate host.
Miracidium
The free-swimming ciliated larval stage of trematodes that infects the first intermediate host.
Oral Sucker
A muscular structure around the mouth of parasitic flatworms used for attachment and feeding.
Parasitic
Organisms that live on or in a host, deriving nutrients at the host's expense.
Pharynx.
A muscular tube through which food passes from the mouth to the intestine in some flatworms
Sporocyst
A larval stage of trematodes that develops within the first intermediate host, producing more larvae.
Strobila
The body of a tapeworm, consisting of a chain of segments called proglottids.
Suckers
Muscular structures used by parasitic flatworms for attachment to host tissues.
Tapeworms
Parasitic flatworms (Class Cestoda) that live in the intestines of vertebrates and absorb nutrients through their body surface
Tegument
The outer covering of parasitic flatworms, adapted for nutrient absorption and protection from the host's immune system.
Uterus
The reproductive organ in flatworms where eggs are stored and developed before being released.
Ventral Sucker
A sucker located on the underside of parasitic flatworms, aiding in attachment to the host.
Primary/Definitive Host
host in which a parasite reaches sexual maturity and reproduces.
Proglottids
Reproductive segments of a tapeworm, each containing male and female reproductive organs.
Redia
A larval stage of trematodes that develops within the sporocyst and produces more larvae.
Scolex
\
The head of a tapeworm, equipped with hooks and suckers for attachment to the host’s intestinal wall.
Second Intermediate Host
The host in which the parasite undergoes additional development before infecting the definitive host.
Simple Life Cycle
A life cycle involving only one host and fewer developmental stages, contrasting with complex life cycles.
phylum Platyhelminthes (flatworms)
bilateral symmetry, acoelomate body structure, well-defined organs, dorsoventrally flattened body, incomplete digestive tract with one opening, and mostly parasitic members.
Class Turbellaria (Planarians)
Free-living flatworms; ciliated epidermis, branched gastrovascular cavity a mid-ventral oral opening with an eversible pharynx
least extensive reproductive structure out of the 3
Planarian Anatomy
Features include eyespots for light detection, a gastrovascular cavity (gut), pharynx, and reproductive structures like ovaries and testes.
Class Cestoda (Tapeworms)
endoparasites within vertebrate intestines. They have no mouth/ digestive tract , highly developed reproductive system, scolex w hooks& sucker (PROGLOTTIDS).
Tapeworm Anatomy
Composed of a scolex (head) with hooks and suckers for attachment, a neck, and a strobila made of proglottids containing reproductive organs
Platyhelminthes Taxonomy
Phylum: Platyhelminthes
Class: Turbellaria, Trematoda, Cestoda
Genus: Opisthorchis, Schistosoma
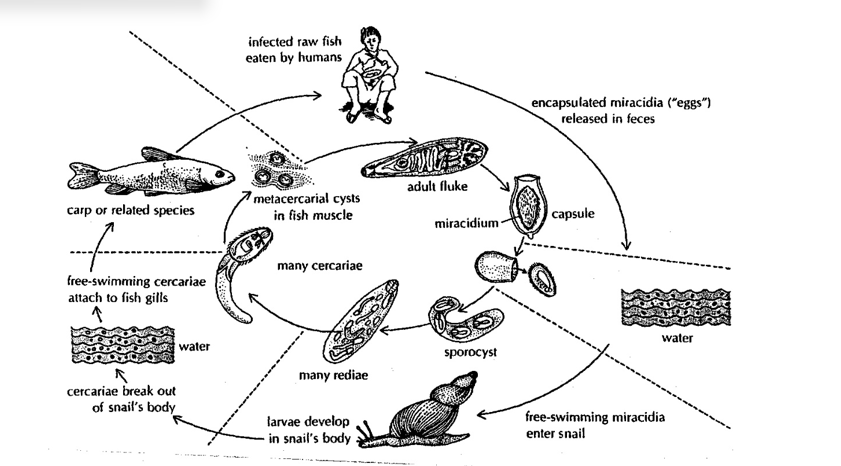
Opisthorchis Life Cycle
Eggs are released in feces.
Miracidium enters a snail (first intermediate host).
Develops into sporocyst, then redia.
Cercaria escapes into water, attaches to fish (second intermediate host).
Forms metacercaria in fish muscle.
Humans eat infected fish; adult fluke develops in the intestine (primary host)
class Trematoda
parasitic
mouth, pharyx, gastrovascular cavity divided into 2, ventral suckers (FLUKES)
Genus : Opisthorchis, Schistosoma
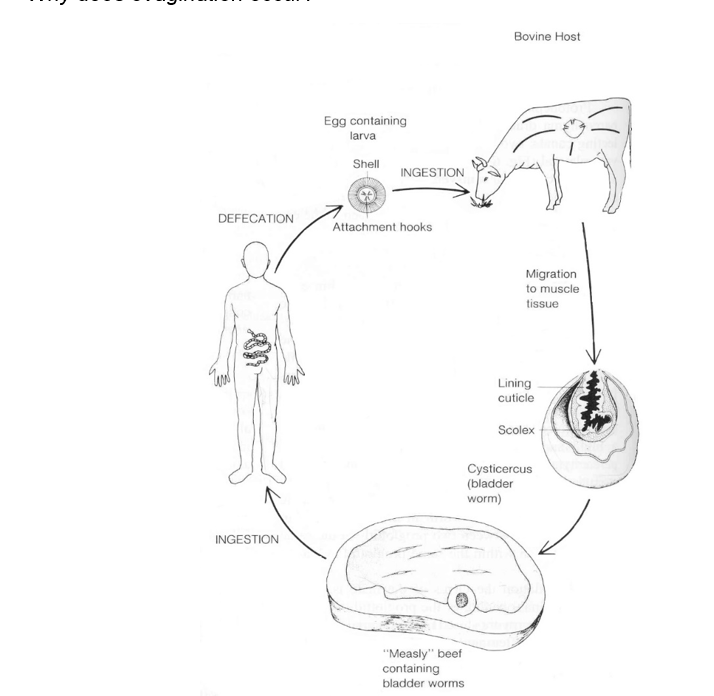
tape worm life cycle