transcription and translation and protein synthesis
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Number of protein coding genes in human genome
Around 20,000
Why is the study of gene expression central in modern drug development
Most drugs cause long term effect through changes in gene expression contributing to both action of drugs and their side effects
Three steps in protein production
Regulation of transcription
Regulation of mRNA processing and decay
Regulation of translation
How can RNA fold into secondary and tertiary structures?
By internal base pairing
What conditions is RNA most unstable
Alkaline conditions
Why are ribose sugars less stable than deoxyribose
Have a hydroxyl group on 2 carbon so more prone to hydrolysis and chemical reactions
Role of promoter
Determines where the transcription start site
Found at upstream of gene which RNA polymerase binds to
Chromatin rearrangement
Open conformation and low nucleosome density permit RNA polymerase access
What structure do transcription factors have ?
Modular structure ( discrete inteconnected structures)
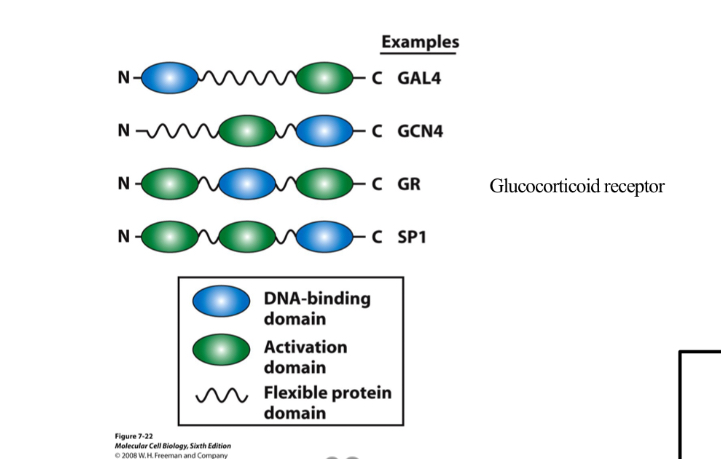
Gene
A section of DNA that directs transcription of one or more overlapping mature RNA molecules (mRNA , rRNA, tRNa)
Unit of transcription
How many codons are there out of the 64
61
How many stop codons are there within the 64
3
What is the start codon
AUG
stop codons examples
UAA
UAG
UGA
Coding region
A reading frame encoding a protein
What amino acid does AUG code for (start codon)
Methionine(Met )
Role of rRNA (Ribosomal)
Links the amino acid
Aminoacyl tRNA site
Where the aminoacyl tRNA recognises codon
P: peptidyle tRNA site
Peptidyl tRNA placement before Peptide formation
E
Where the uncharged tRNA exiting ribosome is located
3 main steps of protein synthesis
Initiation
Elongation
Termination
Initiation
Finding the start codon and assembling the ribosome with the first tRNAs
Elongation
Coupling amino acids from tRNAs to a growing peptide chain
Termination
Recognising the stop codon and releasing the new protein
Release factor
TRNA shaped protein that recognises the stop codon
Steps of translation elongation
Amainoacyl tRNA binding
Peptidyl transfer
Translocation
What is Peptidyl transfer catalysed by?
Ribosomal RNA
Replication
DNA synthesis by copying of existing DNA
Transcription
RNA synthesis by copying DNA
RNA processing
Modification of RNA in the nucleus and cytoplasm
Translation
Protein synthesis by decoding of RNA
Example of antibiotics that target bacterial protein synthesis
Tetracycline, streptomycin, chloramphenicol
An anti-microbial drug that inhibits thymidine monophosphate synthesis in bacteria
Trimethoprim
A drug that affects a viral DNA polymerase
A cancer therapy drug that affects the synthesis of building blocks of DNA
Methotrexate
Function of tRNA
Decodes the genetic code
Role of mRNA
Encodes protein