Clin Lab Med Exam II Study Guide
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
137 Terms
What clinical states increase albumin?
dehydration
What clinical states decrease albumin?
liver disease, renal disease, malnutrition, malabsorption (Chron's, Whipples, Sprue), and muscle-wasting diseases
What is the clinical significance of AAT?
decreases with severe, degenerative emphysematous pulmonary disease
-associated with chronic smokers or genetic link
What is a scenario where an acute-phase reactant would be elevated?
inflammation or stress
What is the significance of high AFP levels during pregnancy?
open neural tube defect in the fetus, atresia of the GI tract, and fetal distress
What is the significance of low AFP levels during pregnancy?
down's syndrome and trisomy 18
What is another clinical setting (besides pregnancy) that AFP would be utilized?
liver cancer and adult gonad cancer
-tumor marker
What disease is associated with low ceruloplasmin levels?
wilson's disease
-causes copper to be present in the whole body
What is the major function of transferrin?
transport iron and prevents loss of iron through the kidneys
-made in the liver
What types of reactants are complement proteins?
acute phase reactants
What clinical scenarios would acute phase reactants be elevated?
inflammation
What clinical scenarios would acute phase reactants be decreased?
systemic lupus erythematosis
What is the function of fibrinogen?
formation of fibrin clot when activated with thrombin
What happens to the fibrinogen level in the presence of DIC?
decreases
-also decreases with severe liver disease
What is the clinical significance of CRP in an acute setting (ED or inpatient)?
elevated with MI, viral infections, bacterial infections, and RA
-CVD marker
What is the downfall to drawing a CRP?
one of the first proteins to increase with inflammation, so it is non-specific
When would you see elevated IgA levels?
liver disease, autoimmune disease, and infections
When would you see elevated IgD levels?
liver disease, infections, connective tissue disorders, and multiple myeloma
When would you see elevated IgE levels?
asthma, allergic rhinitis, and parasitic infections
When would you see elevated IgG levels?
liver disease, infections, and collagen disease
When would you see elevated IgM levels?
immune response (1st to arrive) and waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia (lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma)
How would there be excessive protein loss from the renal system?
damage to the glomerulus of the nephron which results in proteinuria
How would there be excessive protein loss from the GI tract?
protein leaking into GI tract due to protein losing enteropathy (PLE)
How would there be excessive protein loss from the skin?
extensive burns
How would there be excessive protein loss from the blood?
large loss of proteins with blood loss
What are the levels of proteins in liver disease?
-decreased plasma protein and albumin
-increased gamma globulin
What is the most commonly used screening test for serum protein abnormalities?
total protein and albumin assay
What are the 5 protein fractions that are identified in a total protein and albumin assay?
1. albumin
2. alpha-1 globulin
3. alpha-2 globulin
4. beta globulin
5. gamma globulin
Label the SPE scan
see picture
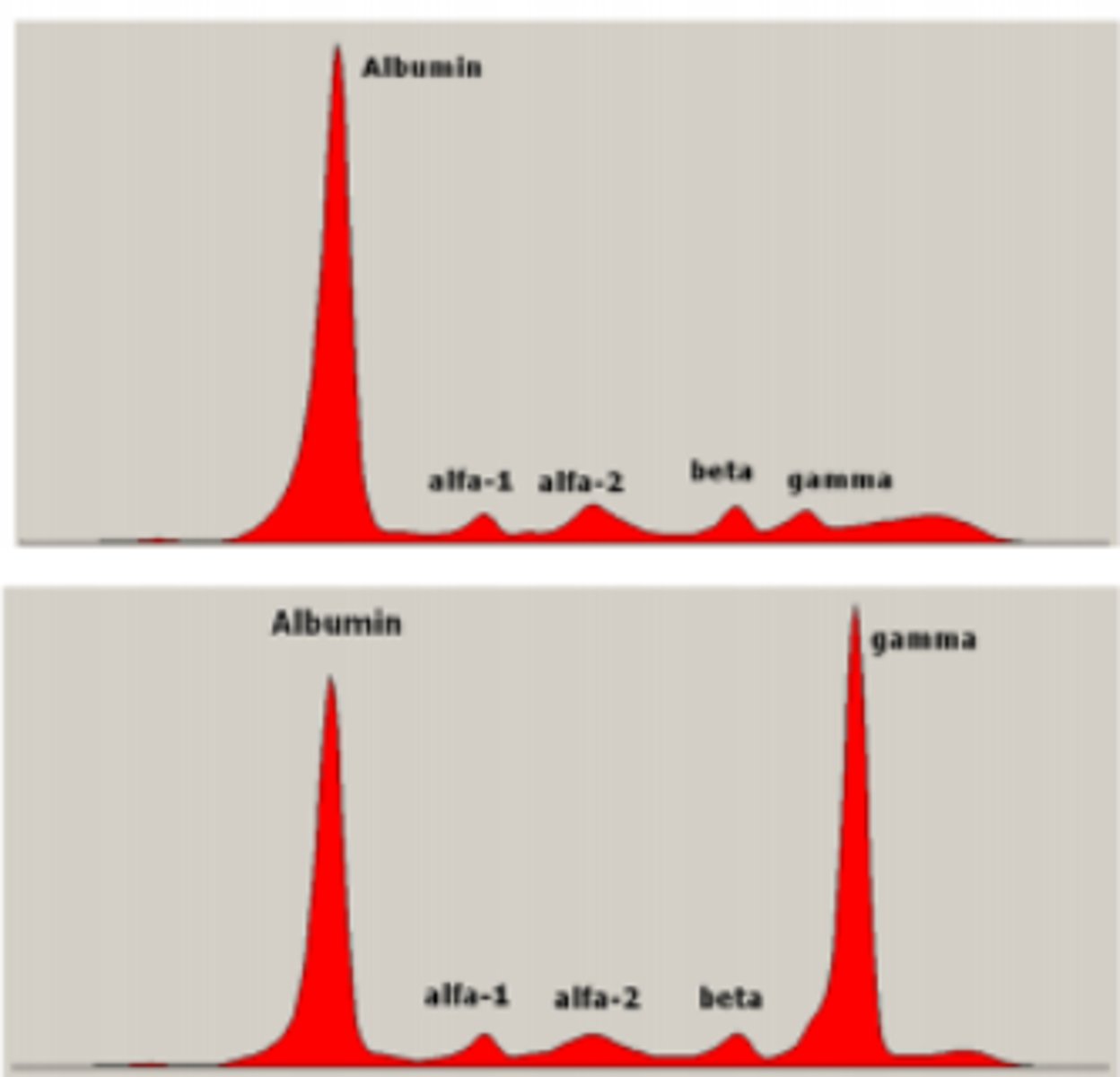
What would alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency look like on an SPE?
no alpha 1 bump
What would chronic inflammation look like on an SPE?
spikes in alpha 1, alpha 2, beta, and gamma (all globulins)
What would nephrotic syndrome look like on an SPE?
decreased albumin and increased alpha-2 bump
What would severe cirrhosis look like on an SPE?
decreased albumin and increased gamma bump
Glycolysis
oxidation of glucose to use as energy
Glycogenesis
glucose to glycogen for storage
Glycogenolysis
glycogen to glucose from storage
Gluconeogenesis
new glucose made from amino acids
What role does insulin play in the control of plasma glucose?
decreases
What role does glucagon play in the control of plasma glucose?
increases
What are the diagnostic criteria for diabetes?
-hyperglycemia with a fasting blood sugar level > 126 mg/dl
-symptoms and a random plasma glucose > 200 mg/dl
-A1c > 6.5%
-2 hour OGTT > 200 mg/dl
What is the pathology of type I diabetes?
-insulin dependent (no insulin production)
-autoimmune destruction of pancreatic beta cells
*diagnosed in juvenile patients
What is the pathology of type II diabetes?
-high insulin production but target cells are unresponsive
-decreased insulin receptors cause by obesity receptors destroyed by antibodies
*diagnosed in obese, adult patients
If a 7 yo patient came in with complaints of polyuria and polydipsia with a high glucose level based on her UA, what would the diagnosis most likely be?
type I diabetes mellitus
What is the pathophysiology behind DKA?
diabetic ketoacidosis occurs from a missed insulin dose (type I diabetes) and leads to increased ketoacids (ketones) and hyperkalemia
What is the hallmark finding for DKA?
postive plasma ketone level
How many weeks does HgbA1c reflect glucose control?
8-12 weeks
What are the HgbA1c ranges for prediabetes?
5.6-6.4%
What are the HgbA1c ranges for diabetes?
>6.5%
What test is most appropriate for gestational diabetes?
oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT)
What happens during a gestational OGTT?
1. patient performs 1 hour OGTT
2. patient will perform a confirmatory 3 hour OGTT
-measured in 4 increments : 0, 1, 2, 3 hours
*if 2/4 or more are above cutoff values: positive result
What is the role of microalbumin testing in patients with diabetes?
reveals early, reversible renal disease
What findings become more concerning in microalbumin testing?
albuminuria can suggest early onset of macroalbinuria
Where is Na found?
outside the cell
What regulates Na?
kidneys: ADH and aldosterone
Where is K found?
inside the cell
What regulates K?
kidneys: aldosterone
Where is Cl found?
outside the cell
What regulates Cl?
excretion in sweat/urine
-increased sweat -> aldosterone secretion -> conserve Cl and Na
Where is HCO3 found?
inside the cell (maintains buffer system)
What regulates HCO3?
kidneys
What is hypovolemic hyponatremia?
water and Na lost but Na loss is greater
What causes hypovolemic hyponatremia?
-loss of fluid (GI, burns) with hypotonic replacement
-thiazide diuretics
-hypokalemia
-hypoaldosteronism
What is normovolemic hyponatremia?
increased water but Na stays the same
What causes normovolemic hyponatremia?
-SIADH
-severe hyperglycemia (polyuria)
-polydipsia
-diuretics
-hypothyroidism
What is hypervolemic hyponatremia?
water and Na are elevated but water is greater
What causes hypervolemic hyponatremia?
-CHF
-hepatic cirrhosis
-overhydration
-nephrotic syndrome
-renal failure
What is hypovolemic hypernatremia?
decreased water and increased Na
What causes hypovolemic hypernatremia?
-dehydration
-excessive sweating
-vomiting
-diarrhea
What is normovolemic hypernatremia?
increased Na and same water
What causes normovolemic hypernatremia?
-skin/lung loss
-diabetes insipitus (DI)
What is hypervolemic hypernatremia?
increased Na and water
What causes hypervolemic hypernatremia?
-hypertonic saline treatment
-hyperaldosteronism
What are the causes of hypokalemia?
-decreased dietary intake
-diuretics
-increased insulin tx
-alkalosis
-hypomagnesia
-hyperaldosteronism
What are the causes of hyperkalemia?
-increased dietary intake
-acidosis
-decreased insulin
-drugs
-ACE inhibitors
-decreased excretion
What other electrolyte does chloride parallel?
Na
How do you calculate anion gap? (will be on exam)
AG = Na - (Cl + HCO3)
No K
Metabolic Acidosis
-in kidney
-acid
-decrease HCO3
Metabolic Alkalosis
-in kidney
-basic
-increase HCO3
Respiratory Acidosis
-in lung
-acid
-increase CO2
Respiratory Alkalosis
-in lung
-basic
-decrease CO2
What are the causes of high anion gap metabolic acid?
Methanol ingestion
Uremia (increased BUN)
Diabetic ketoacidosis
Polyethylene glycol
Iron and isonizaiades
Lactic acidosis
Ethanol and ethylene glycol
Salicyclates and starvation
What are the causes of normal anion gap?
Hyperalimentation
Acetolamide
Renal tubular acidosis
Diarrhea
Ureto-pelvic shunt
Post-hypocapnia
Spironolactone
Causes of metabolic alkalosis
-loss of HCl (vomiting and nasogastric suction)
-renal loss of H+ (some diuretics)
-increased aldosterone (conn's disease)
-increased cortisol (cushing's disease)
Causes of respiratory acidosis
-hypoventilation
-COPD
-neuromuscular disease
Causes of respiratory alkalosis
-hyperventilation
-stimulation of brainstem response center (stress, pregnancy)
-cardiac disease
-mechanical over-ventilation
What is the compensation mechanism for metabolic acidosis?
decreased CO2
What is the compensation mechanism for metabolic alkalosis?
increased CO2
What is the compensation mechanism for respiratory acidosis?
increased HCO3
What is the compensation mechanism for respiratory alkalosis?
decreased HCO3
What are the steps to determining states of acid-base disorders?
1. look at pH (high: basic and low: acidic)
2. look at pHCO3 (same direction as pH)
3. look at pCO2 (opposite pH)
What lab is associated with azotemia?
BUN/Creatinine ratio
What is the cause of an increased BUN/Cr ratio?
pre-renal
What is the cause of a decreased BUN/Cr ratio?
-acute tubular necrosis (kidney disease)
-decreased protein intake/starvation
-liver disease
What is the cause of an increased BUN and Creatinine?
-post-renal obstruction
-pre-renal azotemia superimposed on kidney disease
What lab value is needed to calculate GFR?
Creatinine
What will the BUN and Cr levels look like for pre-renal azotemia?
increased BUN and decreased Cr
What will the BUN and Cr levels look like for post-renal azotemia?
increased BUN and Cr
What lab is associated with gout?
uric acid
What is the relationship between Ca2+ and PTH?
proportional (Ca2+ is regulated by PTH)
What happens to PTH in hypercalcemia?
increases