cranial nerves and special senses
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
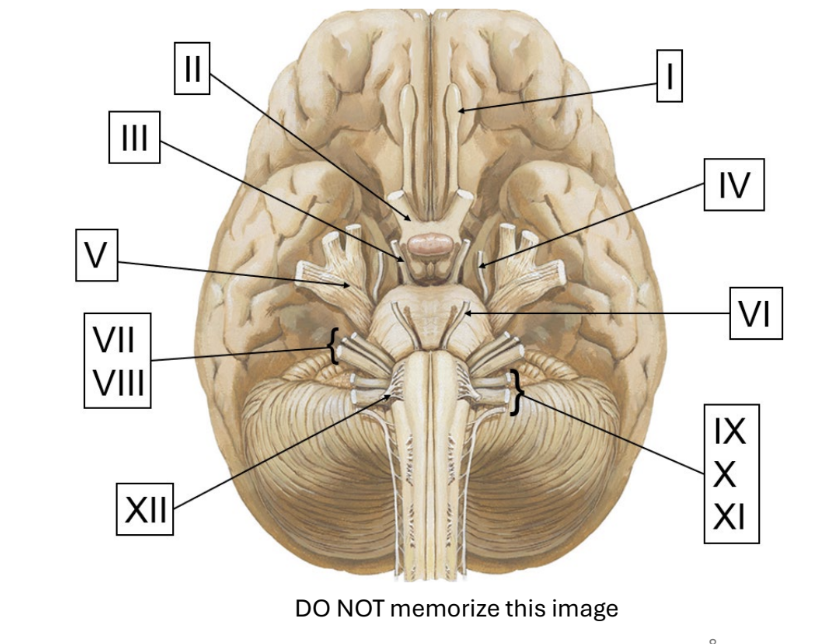
cranial nerves
olfactory
optic
oculomotor
trochlear
trigeminal
abducens
facial
vestibulocochlear
glossopharyngeal
vagus
spinal accessory
hypoglossal
olfactory nerve
special sensory: smell
small nerves in nasal cavity roof
pass through cribriform plate of ethmoid
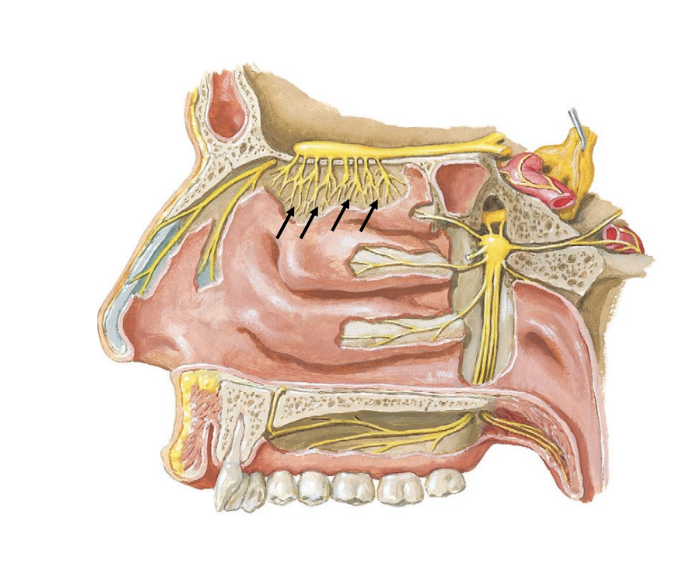
odorants
CN 1:
scent molecules that bind to olfactory nerves in two ways:
nostrils during breathing
oropharynx during chewing
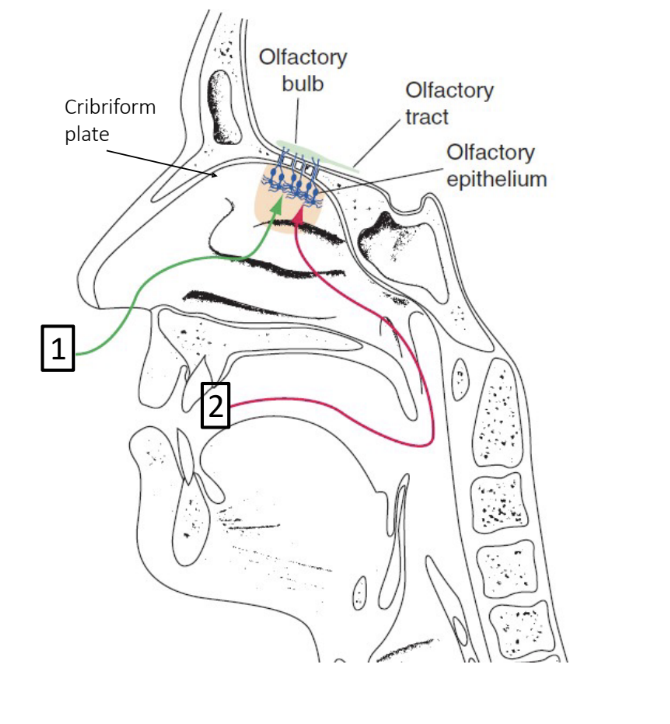
olfaction
CN 1:
—> many areas of the brain
affects memory, emotion, behavior, salivation, taste, etc.
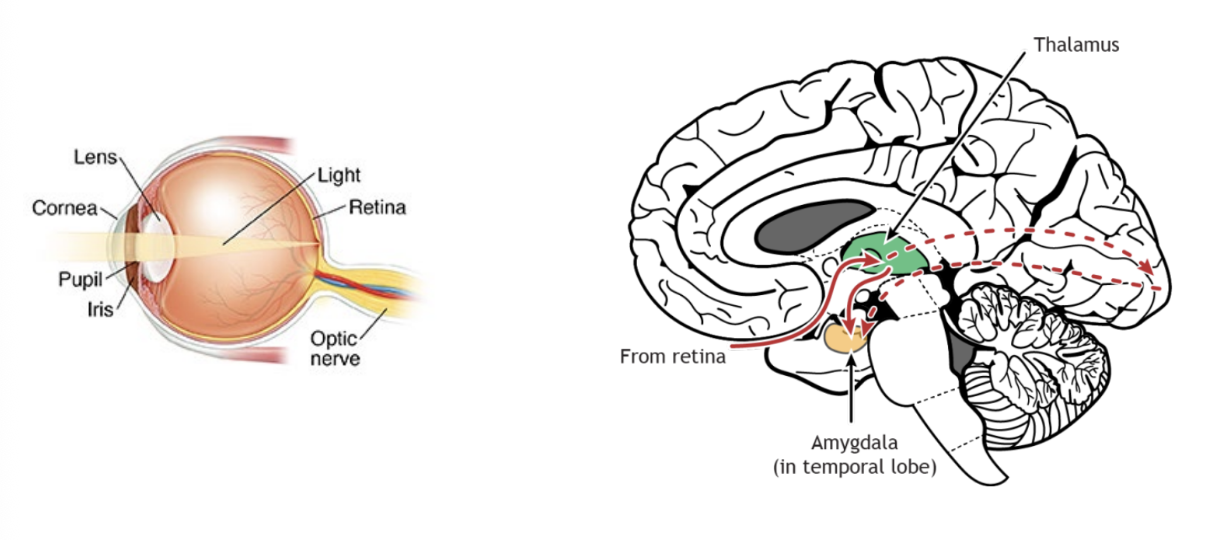
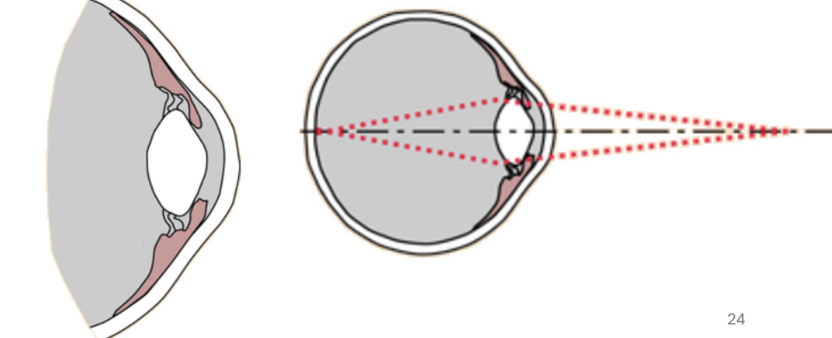
optic nerve
vision
formed by axons of the ganglionic cells in the retina of the eye
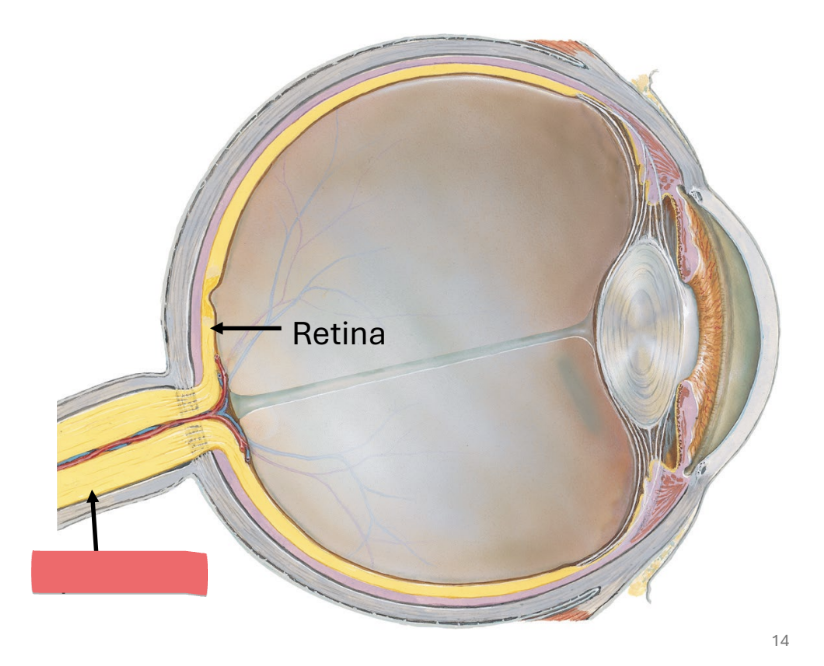
sclera
white outer layer of eye
dense CT
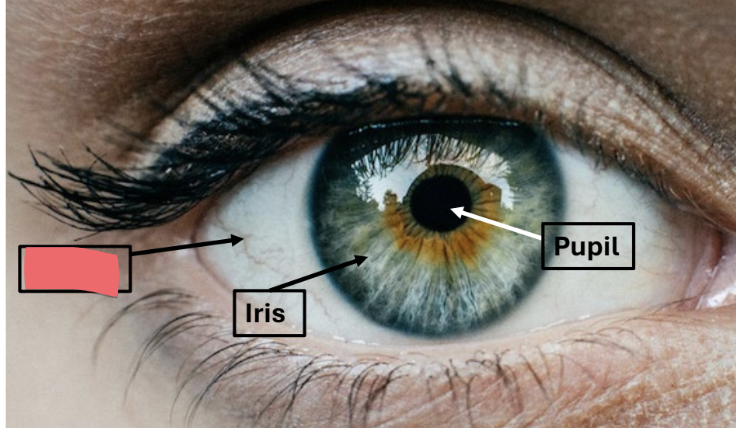
iris
pigmented ring of smooth muscle
pigment = melanin
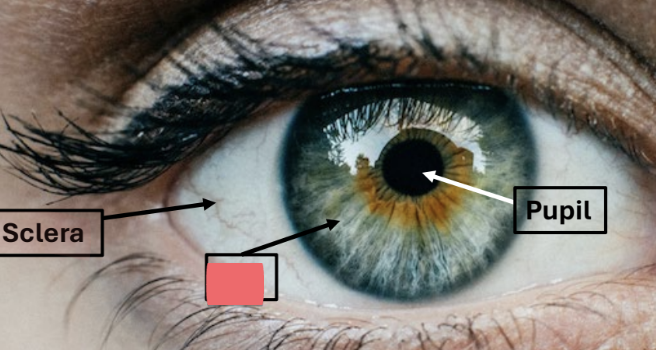
pupil
central hole in iris
allows light into eye
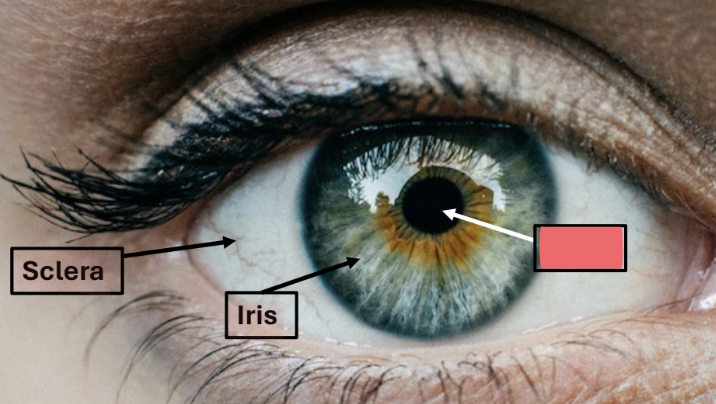
conjunctiva
membrane protecting eye and inner eyelid
present but not visible
eyelids
dense connective tissue core
skin on external surfaces
conjunctiva on inner surface
protect and spread tears
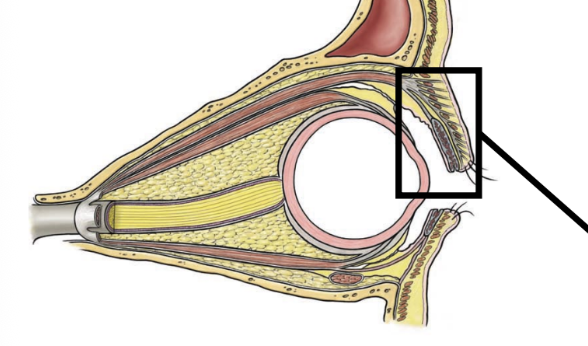
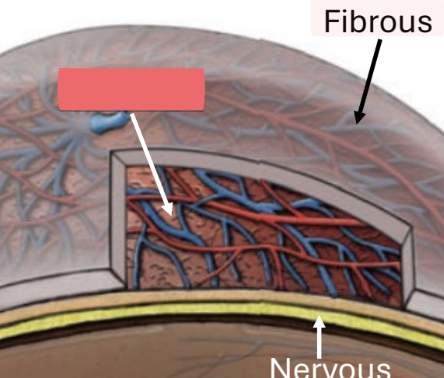
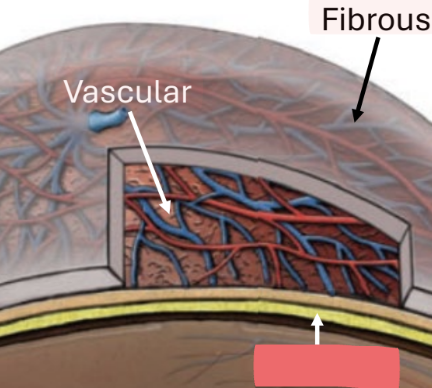
fibrous tunic
sclera
cornea
lens
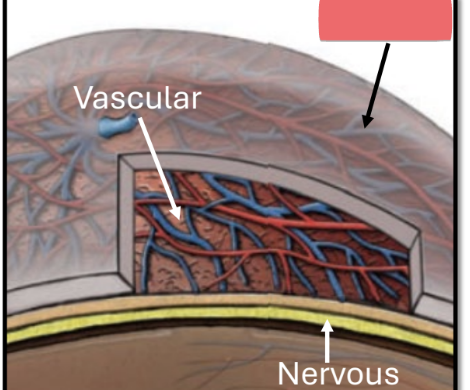
vascular tunic
major blood supply to/from eye
nervous tunic
sensory and autonomics
retinal cells
cornea
dome shaped protective outer layer
aqueous humor
watery fluid between cornea and lens
lens
curved, transparent structure that directs light towards retina
vitreous humor
gel-like, fills most of the eye
essentials of optic pathway
light passes through pupil, lens, humors, and strikes retina
optic nerve sends impulses to thalamus, brodman. areas 17.18,19, and other regions of the brain
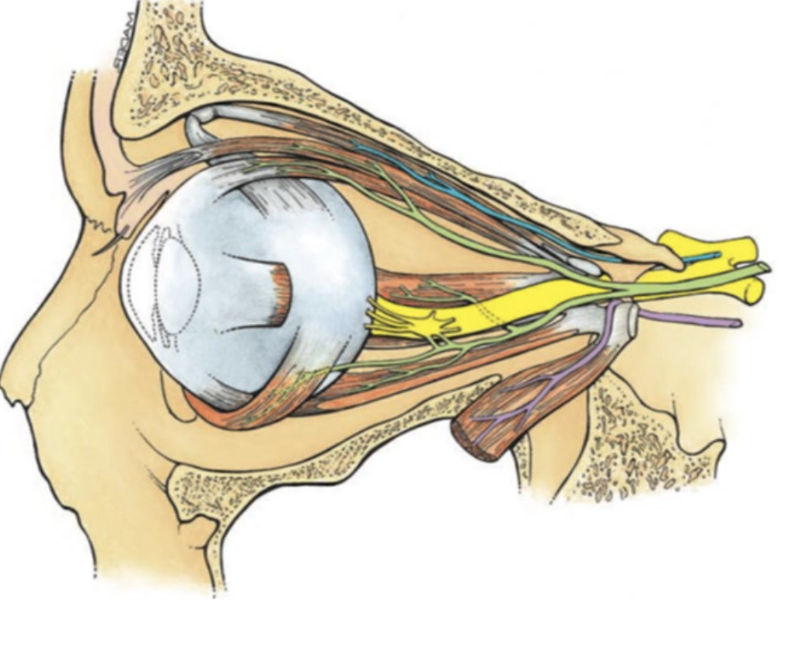
oculomotor nerve
trochlear nerve
abducens nerve
control skeletal muscles that move the eyeball as a group
oculomotor nerve
also supplies autonomic impulses that constrict pupil and change the shape of lens
viewing distant objects
lens under tension (smooth muscle)
flatter lens → see farther away
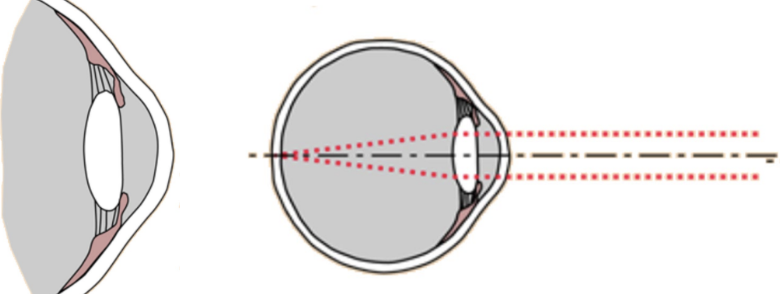
accommodation reflex
relaxation of lens
now more curved
see closer objects in focus
trigeminal nerve
sensation for the bones & skin of the face, teeth & cavities of the head
also innervates the muscles of mastication
collects sensory information
facial nerve
motor to muscles of facial expression
taste from anterior 2/3 of tongue
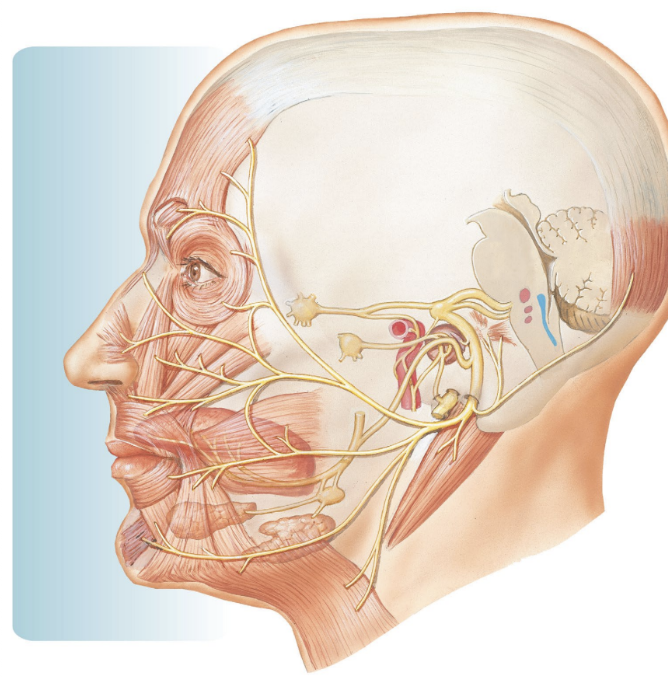
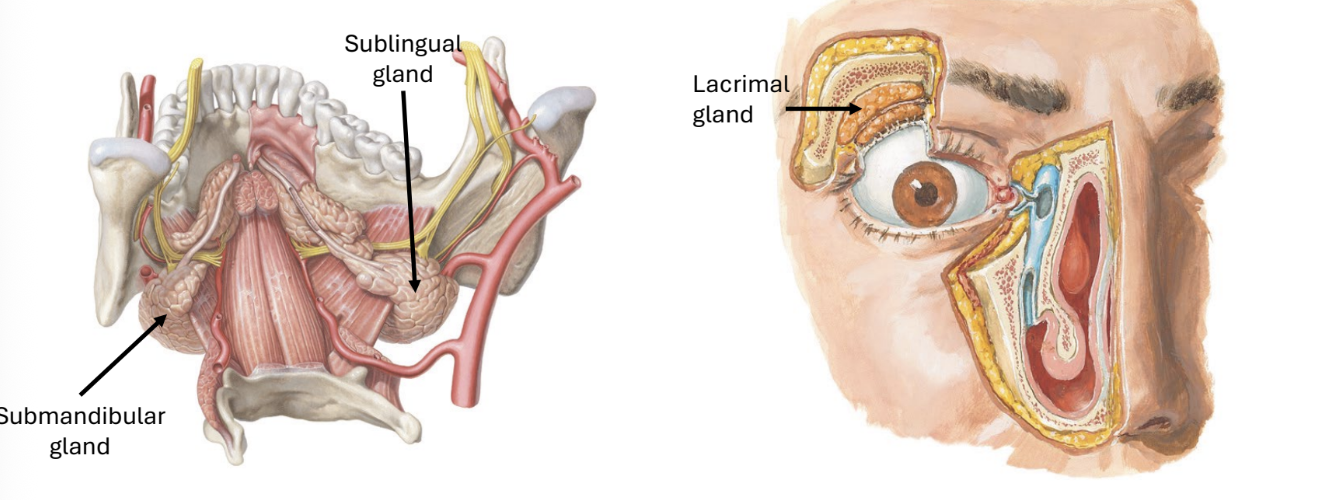
facial nerve parasympathetics
lacrimal glands (tears)
salivary glands (not the parotid)
vestibulocochlear nerve
two nerves — vestibular and cochlear nerves (balance + hearing)
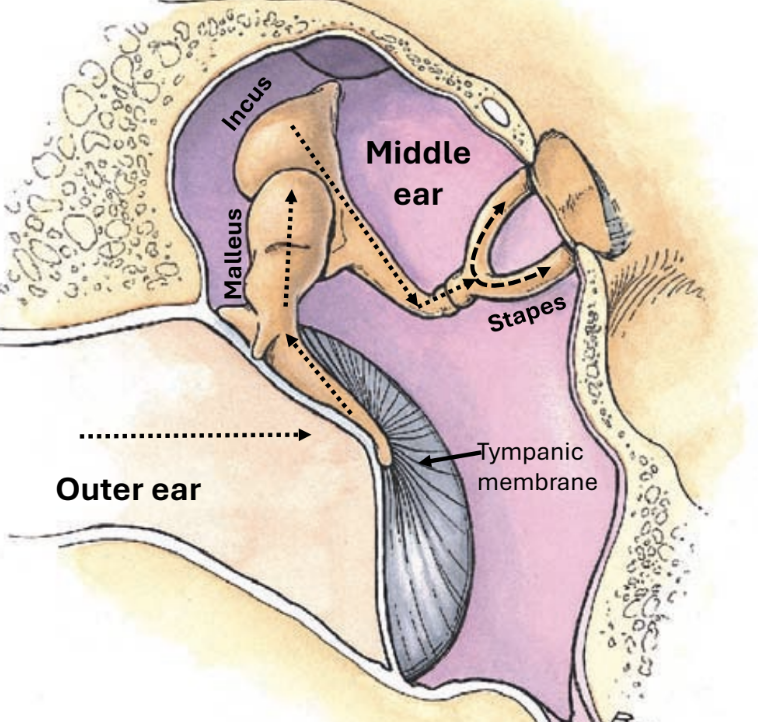
outer ear
the vibrations pass through the ______ ___ first via the ear canal and they strike the tympanic membrane (eardrum)
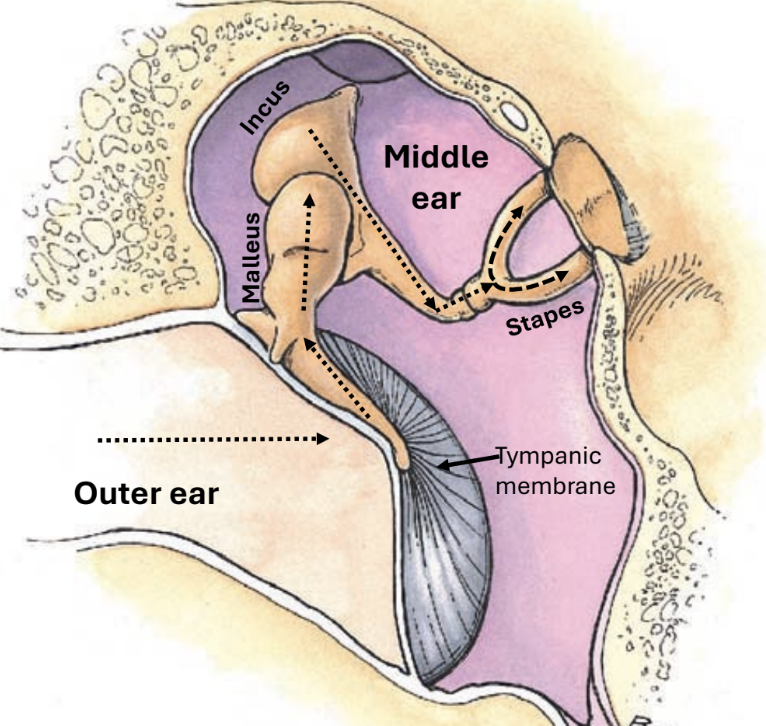
middle ear
vibrations are carried through 3 tiny ossicles in the ______ ___
ossicles: malleus, incus, stapes
cochlea
snail shell shaped spiral filled with fluid called endolymph
vibration of fluid causes cilia (hair cells) to bend and create an action potential
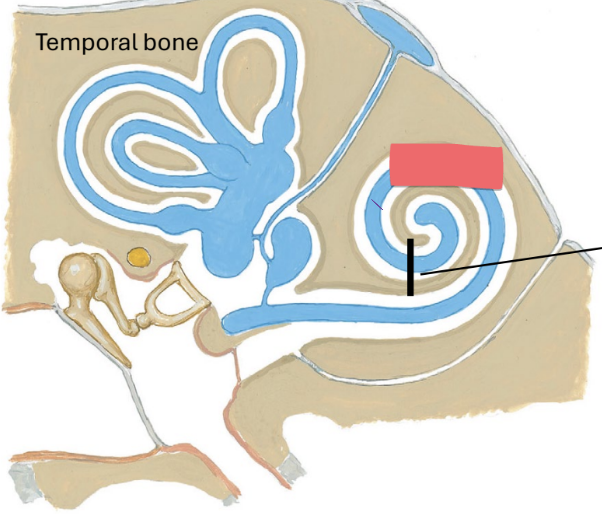
impulse
the _______ from the cochlea travels along the cochlear nerve to the pons
vestibular system
balance and proprioception
3 horseshoe-shaped semicircular canals, each one oriented differently
canals filled with endolymph like the cochlea

dynamic equilibrium
sensing angular movement and velocity
head moves
endolymph flows
hair cells bend
action potential generated along vestibular nerve
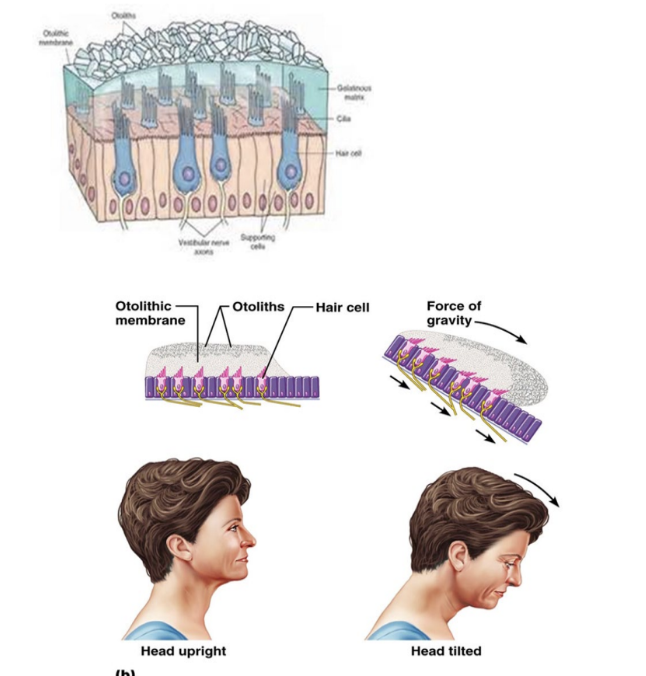
utricle and saccule
bulging chambers in vestibule contain fluid & hair cells with suspended crystals - otoliths
motion causes crystals to move the hair cells, creating an electrical impulse
important for static equilibrium: activated in acceleration
ex: car, elevator
glossopharyngeal nerve
autonomics to parotid gland (salvation), taste/touch posterior 1/3 of tongue
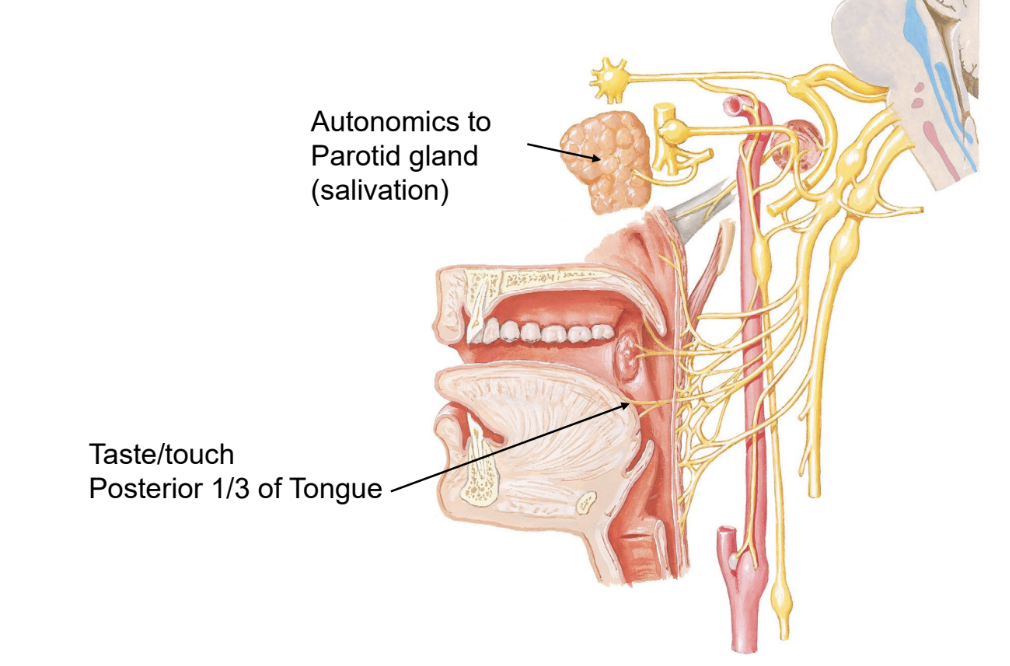
3 sensory inputs
mechanoreceptors, nociceptors, and chemoreceptors of oral cavity acquire taste — texture, spice, heat
taste buds
onion shaped cells on tongue, soft palate, and epiglottis
tastants (molecules from food/drink) bind to receptors in _____ ___
buds generate action potentials that ride along
facial (7)
glossopharyngeal (9)
vagus (10)
vagus nerve
somatic motor/sensory to epithelium and muscles of pharynx and larynx
parasympathetics to heart and airway
autonomics control of smooth muscle and gland secretion in digestive system
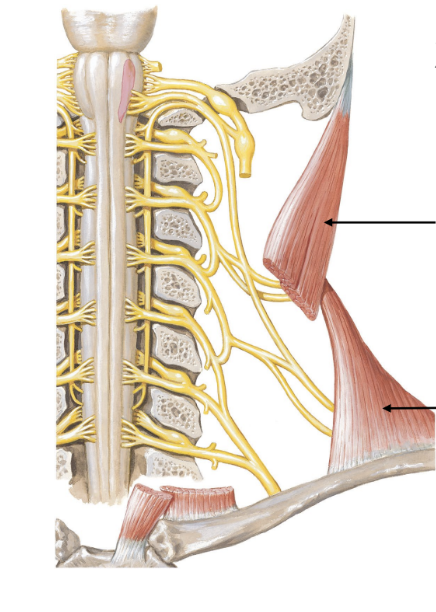
spinal accessory nerve
motor to 2 muscles:
sternocleidomastoid
trapezius
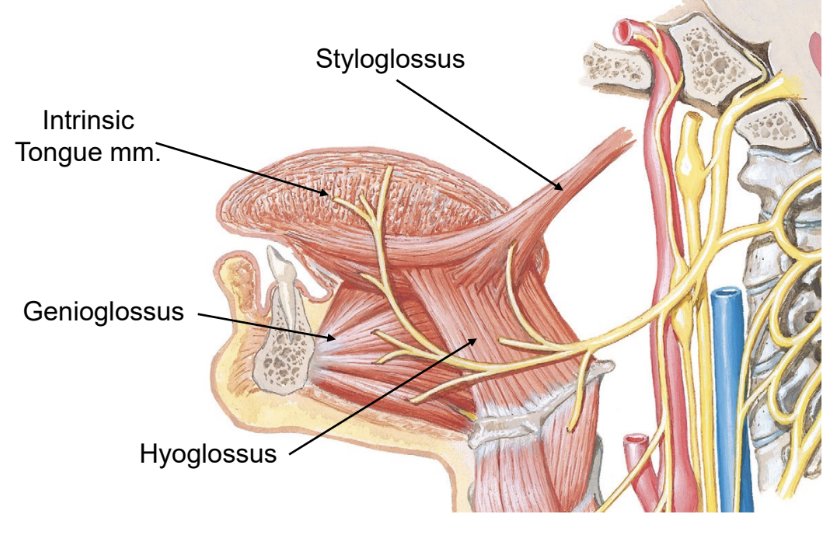
hypoglosseal nerve
muscles of the tongue