Practice Problems
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What is the total number of known stable
isotope in the universe?
a) 7000
b) 250
c) 118
d) 82
B
Which of the following is incorrectly matched with its
approximate energy?
a) Nuclear fusion: 103 kJ/mol
b) Covalent bonds: 102 kJ/mol
c) Hydrogen bonding: 101 kJ/mol
d) Dispersion forces: 100 kJ/mol
A
What is the isotope formed from a single beta decay of
the 14C isotope?
a) 14C+ion
b) 14N atom
c) 13C atom
d) 14N— ion
e) 14C atom
B
Consider the reaction
2 N2O5 (g) → 4 NO2 (g) + O2 (g)
with rate = k[N2O5]. If the initial concentration of N2O5 is 0.80 M,
what is the concentration after 5 half-lives?
a) 0.032 M
b) 0.11 M
c) 0.025 M
d) 0.16 M
C
For the formation of ammonia below, if rate of consumption of
H2 is 0.1 atm per second, what is the rate of production of NH3?
N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) → 2 NH3 (g)
a) 0.067 atm/s
b) 1.33 atm/s
c) 0.33 atm/s
d) 0.2 atm/s
A
A chemical reaction as a rate constant of 2.46 x 10-4
s-1.
What is the order of reaction?
a) 0th order
b) 1st order
c) 2nd order
d) Need more information
B
What is the rate constant for a reaction in which the
rate is 0.02 atm s-1 for a bimolecular reaction of NO2
that has an initial pressure of 0.2 atm?
a) 0.1 s-1
b) 0.05 s-1
c) 0.1 atm-1s-1
d) 0.5 atm-1s-1
D
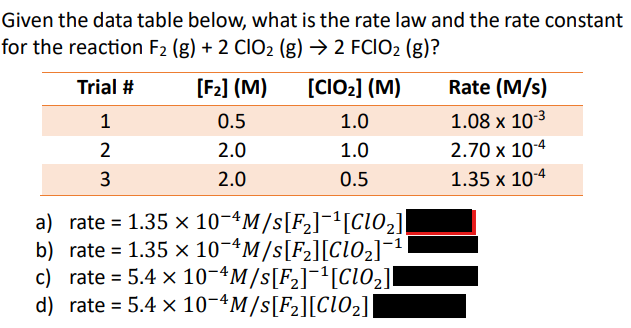
C
For the reaction N2O5 (g) → 2 NO2 (g) + ½ O2 (g), k = 0.5 mMs
-1. Starting with 20 millimolar (mM) N2O5 (g), what is the concentration after 10 seconds?
a) 5 mM
b) 10 mM
c) 15 mM
d) 25 mM
C
For the reaction SO2Cl2 (g) → SO2 (g) + Cl2 (g), k = 0.3 min-1. Starting with 16 mM SO2Cl2 (g), what is the concentration after 14 minutes?
a) 2 mM
b) 8 mM
c) 32 mM
d) 128 mM
A
For the reaction 2 NO2 (g) → NO (g) + O2 (g), k = 0.05 M-1s-1. Starting with 0.25 M NO2, what is the concentration after 20 seconds?
a) 0.16 M
b) 0.20 M
c) 0.33 M
d) 0.05 M
A
What must be plotted to obtain a straight line that yields a rate
constant of 0.1 sec-1?
a) [A] vs t
b) ln[A] vs t
c) 1/[A] vs t
d) [A]0 vs t
B
While doing data analysis for a kinetics experiment, a researcher plots 1/[A] vs t, yielding a straight-line graph. They use this to find the y-intercept is at 5 mM. What was the initial concentration of the species?
a) 5 mM
b) 0.2 mM
c) 10 mM
d) 1 mM
B
Which of the following statements about the Arrhenius
equation is FALSE?
a) The pre-exponential factor provides a measure of the
frequency of collisions and therefore is larger for gases.
b) The activation energy term describes an endothermic
process.
c) Because the T2 term is subtracted from the T1 term, it is
acceptable to use either Celsius or Kelvin.
d) Because the temperature term is the denominator of
the exponent term, as temperature increases, the rate
constant increases.
C
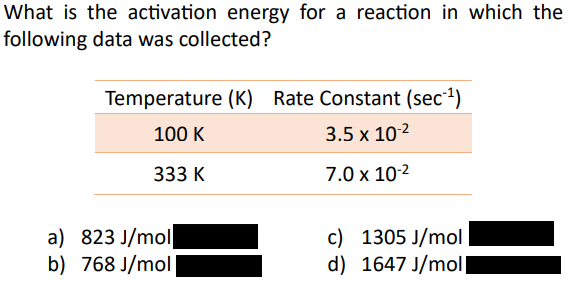
A
Which of the following is TRUE with respect to collision theory?
a) Colliding molecules react no matter their orientation or energy.
b) With the appropriate orientation, molecules will react
regardless of their energy.
c) As long as molecules have high enough energy, the orientation
of collision does not matter.
d) Molecules must have the correct orientation and high enough
energy to react.
D
Transition state theory…
a) Provides detailed structural models of transition states.
b) Predicts reaction rates in terms of the peaks on potential
energy surfaces.
c) Predicts reaction rates in terms of the frequency and
productivity of molecular collisions.
d) Is concerned with the relative stability of reactant and
products.
B
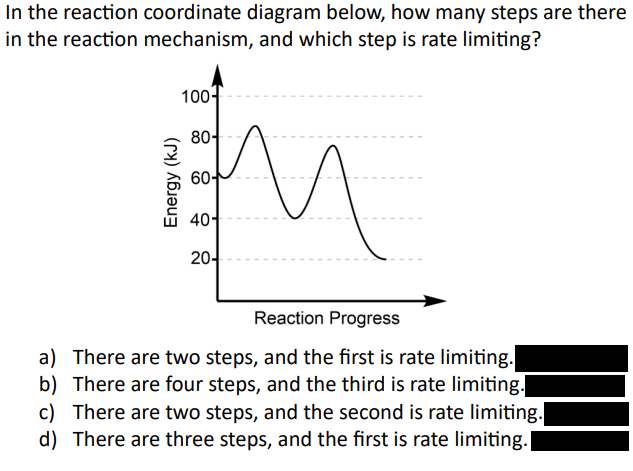
C

Given the reaction mechanism above, which species is a catalyst?
a) ClO
b) ClO2
c) NO2
d) None of these
e) N2O
D
![<p>Given the reaction mechanism above, what is the rate law?</p><p>a) Rate = k[NO2Cl]2[NO2]</p><p>b) Rate = k[NO2Cl]</p><p>c) Rate = k[NO2Cl]2[NO2]-1</p><p>d) Rate = k[N2O][NO2]-1</p><p>e) Rate = k[NO2Cl][NO2][NO2]-1</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/3a8c8b30-c6ca-492d-b12e-5ac0b3f9fb1a.png)
Given the reaction mechanism above, what is the rate law?
a) Rate = k[NO2Cl]2[NO2]
b) Rate = k[NO2Cl]
c) Rate = k[NO2Cl]2[NO2]-1
d) Rate = k[N2O][NO2]-1
e) Rate = k[NO2Cl][NO2][NO2]-1
C
Which of the following catalytic processes employ
heterogeneous metal catalysts?
I. The Haber process to produce ammonia.
II. The catalytic converter in automobiles.
III. Ozone Decomposition
a) I only
b) I and II
c) II only
d) I, II, and III
B
Which of the following is famously catalyzed by a
homogenous catalyst?
a) The reduction of nitrogen oxides in car
exhaust.
b) The formation of ammonia from elemental
nitrogen and hydrogen.
c) The conversion of incomplete combustion
products in car exhaust.
d) The breakdown of atmospheric ozone.
D
Which of the following statements about the Haber process is FALSE?
a) The Haber process transforms nitrogen into ammonia, crucial
for global agriculture.
b) The reaction releases heat, and higher temperatures push the
equilibrium to reduce ammonia production.
c) Raising the temperature speeds up ammonia formation,
despite the reaction being exothermic.
d) The catalyst involved is pure iron power.
D
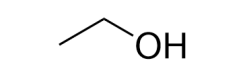
What functional group is shown
below?
a) Aldehyde
b) Ether
c) Ketone
d) Alcohol
D
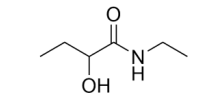
What functional group(s) is/are shown
in the molecule below?
a) Aldehyde and alcohol
b) Amide and alcohol
c) Amide and ether
d) Carboxylic acid and amine
B
Name the molecule below.
a) 2-hydroxybutanamide
b) 2-alcoholbutanamide
c) 2-hydroxy-1-amino-1-butanone
d) 2-hydroxybutanamine
A
Which of the following polymers is
formed via a condensation reaction?
a) Polyvinyl chloride
b) Polystyrene
c) Polyamide
d) Polyethylene
C
Which functional group do all
monomers undergoing addition
polymerization have in common?
a) Ester
b) Ketone
c) Amide
d) Alkene
D
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
a) Ether linkages are formed from carboxylic
acids and alcohols.
b) Ether linkages are formed from carboxylic
acids and amines.
c) Ester linkages are formed from carboxylic
acids and alcohols.
d) Ester linkages are formed from two alcohols.
C