Wound Healing and Cancer Biology Overview
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
130 Terms
What is the role of vasoconstriction in haemostasis?
Vasoconstriction, mediated by the SNS, reduces blood flow out of the wound by causing smooth muscles to contract.
What are the three main functions of a fibrin clot?
1. Scaffold for cell migration 2. Reservoir for growth factors and cytokines 3. Haemostasis.
What triggers the inflammatory response?
Immune cells and proteins migrate to the tissue in response to injury or infection.
How do macrophages recognize invading pathogens?
Macrophages recognize pathogens through Toll-like receptors (TLR) that detect pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and NOD-like receptors (NLR) that detect damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs).
What cytokines do macrophages release during inflammation?
Macrophages release IL-1, IL-6, IL-12, TNF-alpha, CXCL8, and GM-CSF.
What is the effect of GM-CSF released by macrophages?
GM-CSF stimulates the bone marrow to increase the production of neutrophils and monocytes.
What are the effects of IL-1 and IL-6?
IL-1 and IL-6 cause fever and increase the production of acute phase proteins.
What is the role of mast cells in inflammation?
Mast cells release histamine, which increases vasodilation and permeability of blood vessels.
What are the five signs of inflammation?
1. Rubor (redness) 2. Calor (temperature) 3. Dolor (pain) 4. Tumor (swelling) 5. Loss of function.
What causes rubor (redness) in inflammation?
Rubor is due to increased blood flow caused by vasodilation, which is mediated by nitric oxide (NO) and histamine release.
What causes calor (temperature) in inflammation?
Calor is caused by macrophages releasing IL-1 and IL-6, which induce fever.
What causes dolor (pain) in inflammation?
Dolor is caused by damaged cells releasing prostaglandins that act on nerve endings.
What causes tumor (swelling) in inflammation?
Tumor is caused by increased vascular permeability, leading to fluid accumulation in tissues.
When are neutrophils most prevalent at the site of infection?
Neutrophils are most prevalent at the site of infection 0-48 hours after infection.
What is the function of NETs released by neutrophils?
NETs trap microbes through the protrusion and expulsion of chromatin.
When are macrophages most common at the site of infection?
Macrophages are most common 48-96 hours after infection.
What role do macrophages play in monocyte production?
Macrophages secrete GM-CSF, which stimulates bone marrow to increase monocyte production.
How are macrophages activated?
Macrophages are activated by IFN gamma released by neutrophils.
What cytokines are involved in the switch from M1 to M2 macrophages?
IL-4 and IL-13 released by TH1 and TH2 cells facilitate the switch from M1 to M2.
What is the function of dendritic cells in the immune system?
Dendritic cells are antigen-presenting cells that activate naive T-cells in the lymph nodes.
How do dendritic cells present antigens to T-cells?
They phagocytose microbes and present them on MHC class II molecules.
What do natural killer (NK) cells identify in infected cells?
NK cells identify infected cells through stress receptors, lack of MHC, and Fc receptors.
What substances do NK cells release to kill infected cells?
NK cells release granzyme and perforin.
What are the functions of complements in the immune response?
Complements opsonize pathogens, act as chemoattractants, and form the membrane attack complex (MAC).
What types of fibroblasts are formed during proliferation?
Profibrotic fibroblasts produce ECM more than myofibroblasts, while myofibrotic fibroblasts produce ECM containing Type 1 collagen and glycosaminoglycans.
What growth factors are involved in fibroblast migration and proliferation?
TGF-beta, PDGF, and FGF promote fibroblast migration, while PDGF and FGF also stimulate proliferation.
What is the role of VEGF in angiogenesis?
VEGF is released by keratinocytes, macrophages, and platelets and is stimulated by fibroblasts to promote blood vessel formation.
What changes occur in keratinocytes during re-epithelialization?
Normal keratinocytes exhibit apical-basal polarity, increased E-cadherins, decreased MMPs, and decreased motility.
What is the significance of stem cells in wound healing?
Stem cells in the stratum basale allow for the proliferative phase of keratinocyte healing.
What is the remodeling phase in wound healing?
Remodeling involves replacing provisional ECM with mature ECM, with Type III collagen being replaced by Type I collagen.
What is the difference between scarring and regeneration in wound healing?
Scarring results in tissue that is not structurally and functionally the same as adjacent tissue, while regeneration restores tissue to its original state.
What factors influence wound healing?
Factors include injury type, tissue type (labile, stable, permanent), patient factors (age, sex, comorbidity), and local factors (hypoxia, infection).
What characterizes chronic wound healing?
Chronic wound healing is marked by no switch from M1 to M2, increased inflammatory response, and an imbalance of MMPs to TIMPs.
What are the characteristics of malignant tumors?
Malignant tumors have no clear boundaries, are poorly differentiated, invade the basement membrane, and can spread throughout the body.
What distinguishes benign tumors from malignant tumors?
Benign tumors have well-defined boundaries, are well differentiated, do not invade the basement membrane, and cause no real damage.
What is the significance of the MMPs to TIMPs ratio in wound healing?
A balanced ratio of MMPs to TIMPs (1:1) is necessary to maintain a stable basement membrane during healing.
What is the role of fibroblasts in tissue repair?
Fibroblasts are involved in the production of extracellular matrix and play a crucial role in wound healing.
What is the impact of age on wound healing?
Older individuals tend to heal more through scarring compared to younger individuals.
How does sex influence wound healing?
Females generally heal better than males due to the effects of estrogen.
What are the direct effects of cancer growth?
Obstruction, pressure, damage to blood vessels, and bleeding due to ulcerations.
What are the indirect effects of cancer growth?
Cachexia, fever, and paraneoplastic syndrome, where cancer cells produce cytokines and hormones that can induce immune cells to destroy both cancerous and normal cells.
What is the difference between sarcoma and carcinoma?
Sarcoma is a malignant cancer of connective tissue (mesenchyme), while carcinoma is a malignant cancer of epithelial cells.
Why are carcinomas more common than sarcomas?
Carcinomas are more common because epithelial cells have a higher turnover rate, leading to increased proliferation and a higher likelihood of cancer development.
What causes death in cancer patients?
Death by cancer is caused by secondary tumors spreading to vital organs, not the primary tumor itself.
What are the gross appearances of benign tumors?
Benign tumors can appear sessile (flat), as polyps, or papillary (like fingers).
What are the gross appearances of malignant tumors?
Malignant tumors can appear fungating (explosion of cells), ulcerating (depression in center with heaped edges), or annular (growing mainly in hollow organs, producing an apple core shape).
What are the microscopic features of cancerous tissue?
Increased nucleus to cytoplasm ratio, large nuclei, increased mitotic bodies, disorganized appearance, individual cells differing from each other, no clear boundaries, and loss of features in some cells.
What is the first step in the pathway of cancer growth?
A genetic mutation occurs.
What follows hyperplasia in the cancer growth pathway?
Dysplasia, where cells begin to look different from the tissue they arose from.
What characterizes in situ cancer?
In situ cancer is when the cells do not invade through the basement membrane and remain above it.
What defines invasive cancer?
Invasive cancer occurs when cells penetrate through the basement membrane and use blood and lymphatic vessels as conduits to spread.
What is the adenoma-carcinoma pathway?
It involves a mutation leading to the growth of an adenoma (benign tumor), which then undergoes carcinomatous change and spreads throughout the body.
What happens during the development of an adenoma?
There is hyperproliferation with abnormalities in the crypts and glands, leading to increased mutations and the progression to carcinoma.
What is the significance of understanding cancer pathways?
Detecting cancers early allows for better treatment preparation, as earlier cancers have fewer mutations and are better differentiated.
What is cachexia in the context of cancer?
Cachexia is a syndrome characterized by weight loss, muscle wasting, and fatigue often associated with cancer.
What is paraneoplastic syndrome?
A syndrome where cancer cells produce substances like cytokines and hormones that can affect normal cell function and immune response.
What does an increase in mitotic bodies indicate in cancerous tissue?
It indicates continuous proliferation of cells.
What does a loss of defined boundaries in cells suggest?
It suggests a disorganized and malignant growth pattern.
What is the role of the basement membrane in cancer progression?
The basement membrane acts as a barrier; invasion through it indicates a transition from in situ to invasive cancer.
What is the relationship between differentiation and mutation in cancer?
The earlier cancer develops, the fewer mutations it has, leading to better differentiation.
What indicates that cancer has not yet metastasized?
If the cancer has not invaded through the basement membrane, it can be resected.
What are three methods for cancer detection?
Pap smear, colonoscopy, mammogram.
What is the origin of cancer?
Cancer originates from a single cell that proliferates, leading to mutations.
What are the causes of cancer mutations?
Mutations can be spontaneous, induced by mutagens, and result in faulty protein production.
What are epigenetic changes in cancer?
Epigenetic changes, such as hyperphosphorylation, can increase or decrease protein production.
List the hallmarks of cancer.
Activation of oncogenes, inactivation of tumor suppressor genes (TSG), decreased apoptosis, immortalization, angiogenesis, invasion and metastasis, cancer metabolism, evasion from the immune system.
Do all hallmarks of cancer occur in the same order?
No, the hallmarks do not occur in the same order and vary in different cancers.
What enabling characteristic allows cells to metastasize?
Inflammation facilitates metastasis through epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT).
What is genetic instability in cancer?
Genetic instability leads to cells acquiring different characteristics due to mutations.
Who discovered oncogenes and how?
Oncogenes were discovered by Peyton Rous as a retrovirus.
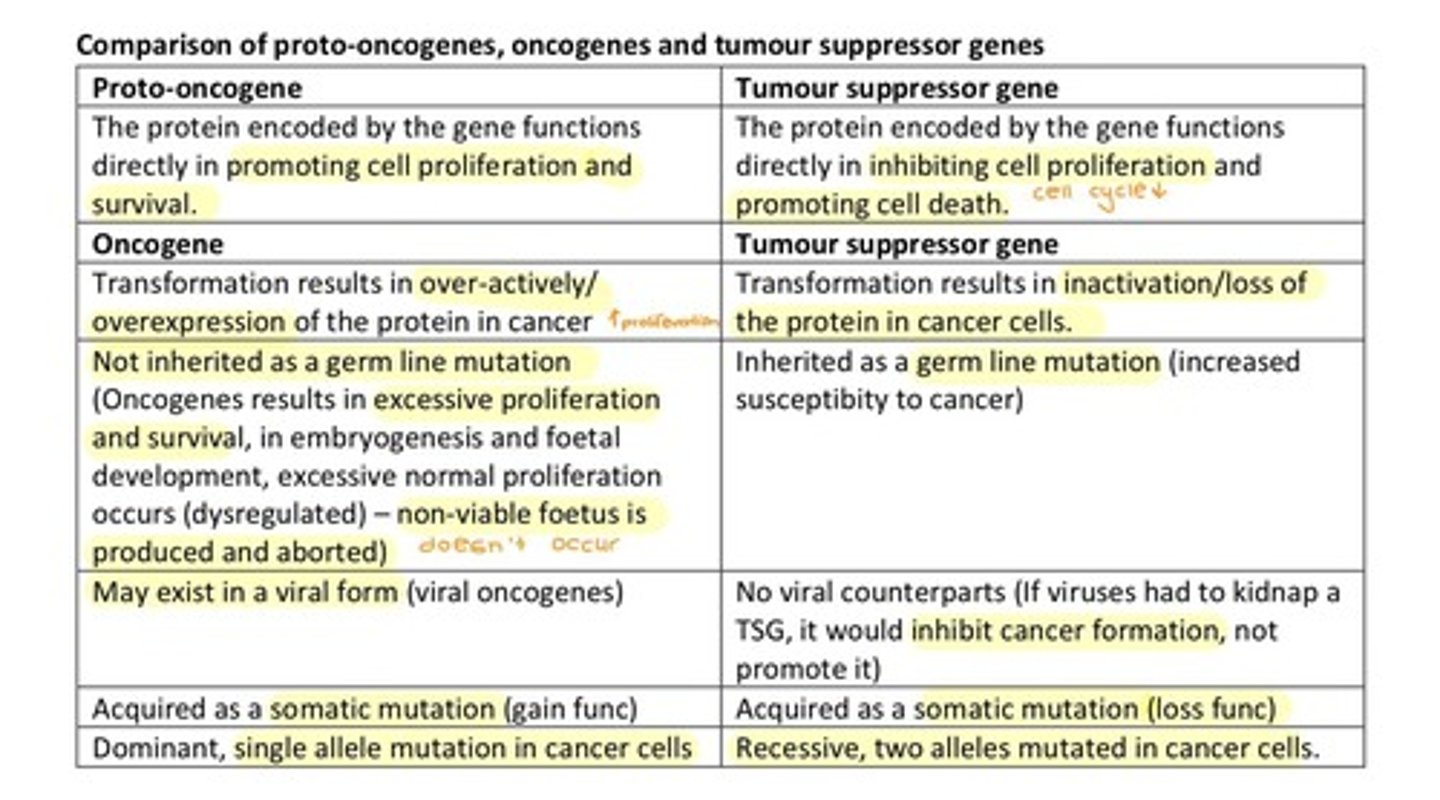
What are proto-oncogenes?
Proto-oncogenes encode proteins that regulate cell survival, proliferation, and cycling.
What is the difference between oncogenes and proto-oncogenes?
Oncogenes are mutated proto-oncogenes that are overexpressed or constitutively active, increasing cell proliferation.
What is one mechanism of oncogene activation?
Mutation can lead to a gain of function mutation resulting in constitutively active proteins.
What is the Philadelphia gene?
The Philadelphia gene (BCR-ABL) results from a translocation between chromosomes 9 and 22, leading to constitutively active proteins.
How can gene amplification contribute to cancer?
Gene amplification results in the gene being copied multiple times, leading to overexpression of proteins.
What role does miRNA play in cancer?
Loss of the 3' UTR region of mRNA where miRNA binds can increase mRNA levels and protein expression.
What is the effect of hypomethylation in cancer?
Hypomethylation results in increased gene expression and protein production.
What is the function of tumor suppressor genes (TSG)?
TSGs suppress cell proliferation, promote cell death, slow down growth, activate apoptosis, and repair DNA.
What is the 2 hit hypothesis related to TSG?
The 2 hit hypothesis states that both alleles of a TSG must be mutated for cancer to develop.
What can cause the second hit in the 2 hit hypothesis?
The second hit can occur due to deletion, non-disjunction, chromosome duplication, translocation, or point mutation.
How does increased miRNA affect TSG expression?
Increased miRNA can lead to decreased expression of tumor suppressor genes.
What is the result of hypermethylation in cancer?
Hypermethylation results in decreased expression of tumor suppressor genes.
What are the RTK pathways involved in cancer?
The MAPK and PI3K pathways are involved in cancer-related signaling.
What is the role of AKT in cell survival?
AKT increases cell survival by decreasing apoptosis, increasing glucose uptake, and phosphorylating proteins to prevent the production of death ligands.
How does AKT affect FASL transcription factor?
AKT phosphorylates FASL TF, preventing the production of the death ligand.
What is the function of PTEN in relation to PIP3?
PTEN converts PIP3 to PIP2, acting as a tumor suppressor gene.
What is the role of the JAK-STAT pathway in cancer?
The JAK-STAT pathway can lead to increased blood cell production and is associated with oncoprotein activity.
How does WNT signaling contribute to colorectal cancer?
WNT signaling increases proliferation and is associated with mutations in β-catenin, leading to uncontrolled cell growth.
What is the function of Rb protein in the cell cycle?
When hypophosphorylated, Rb binds to E2F, preventing it from entering the nucleus and promoting cell cycle progression.
What happens to Rb when G1 cyclins increase?
Active kinases phosphorylate Rb, releasing E2F, which promotes S cyclin and DNA replication.
What is the significance of p53 in cancer biology?
p53 is a transcription factor that regulates the cell cycle and apoptosis; mutations in p53 are associated with Li-Fraumeni syndrome.
What are the three regions of p53 and their functions?
1. MDM2 binding region: binds MDM2 for degradation; 2. DNA binding region: transcribes genes; 3. Oligomerization region: forms tetramers.
How does MDM2 regulate p53?
MDM2 ubiquitinates p53, leading to its degradation, and blocks its transcriptional activation domain.
What occurs when there is DNA damage in relation to p53?
p53 increases p21, leading to CDK inhibitors that halt the cell cycle and promote apoptosis.
What is the role of p21 in the cell cycle?
p21 inhibits CDKs, leading to cell cycle arrest.
What is the effect of increased DNA damage on cell fate?
Increased DNA damage can lead to apoptosis through the upregulation of death ligands and BAX.
What is the function of β-catenin in WNT signaling?
β-catenin is overexpressed or mutated in cancer, leading to increased transcription of genes that promote cell proliferation.
What is the relationship between oncoproteins and the cell cycle?
Oncoproteins like CDK and G1 cyclins promote increased cycling through the cell cycle without requiring growth factor signaling.
How do viral proteins interact with Rb?
Viral proteins can bind to Rb, leading to the release of E2F and promoting cell cycle progression.
What is the role of GSK-3 in WNT signaling?
GSK-3 phosphorylates β-catenin, leading to its degradation; inhibition of GSK-3 results in β-catenin accumulation.