🍆 | Chapter 26: Reproductive System
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
Gonads
Primary sex organs that produce sex cells called gametes.
Ovaries
Female gonads that produce oocytes.
Testes
Male gonads that produce sperm and hormones.
Gametes
Sex cells produced by gonads; oocytes in females and sperm in males.
Scrotum
Skin and superficial fascia surrounding the testes, providing a cooler environment for sperm production.
Dartos muscle
Smooth muscle in the skin of the scrotum that regulates testicular temperature.
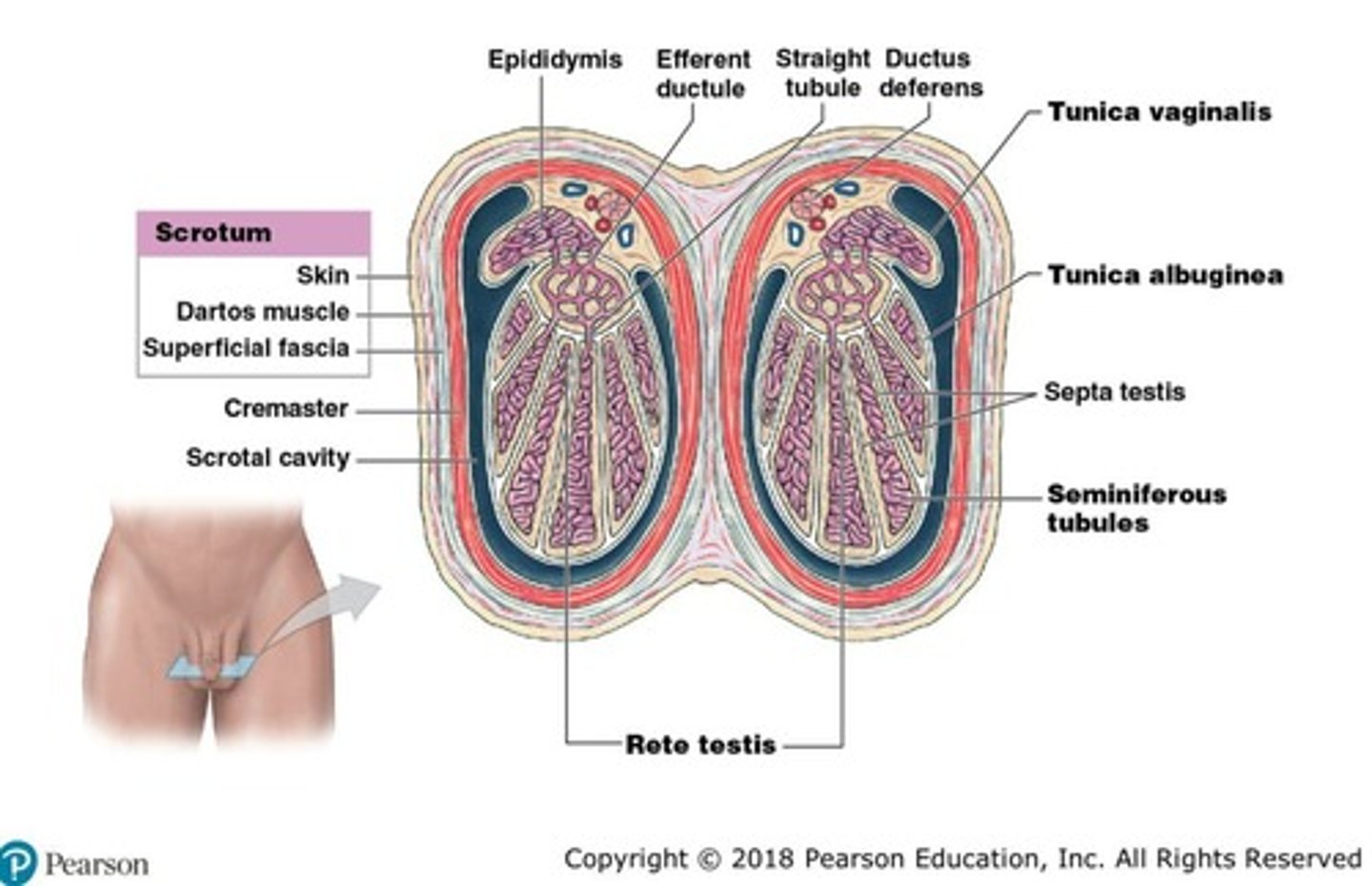
Tunica vaginalis
Serous membrane lining the scrotal cavity that reduces friction.
Tunica albuginea
Tough, fibrous capsule covering the testis and continuous with septa subdividing testes.
Lobules
Subdivisions of the testes containing seminiferous tubules.
Seminiferous tubules
Coiled tubules within lobules where sperm production occurs.
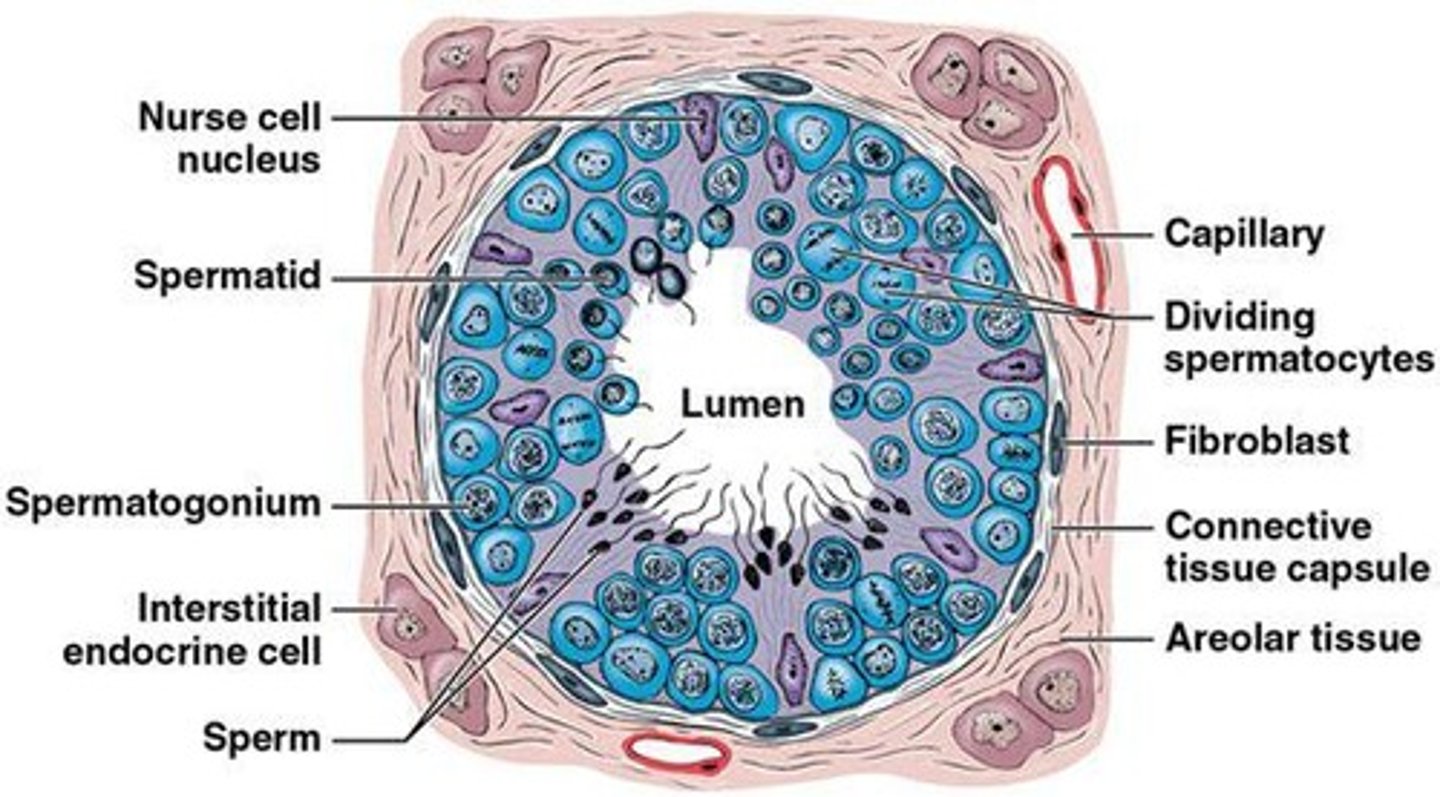
Spermatogenesis
The process of sperm production occurring within the seminiferous tubules.
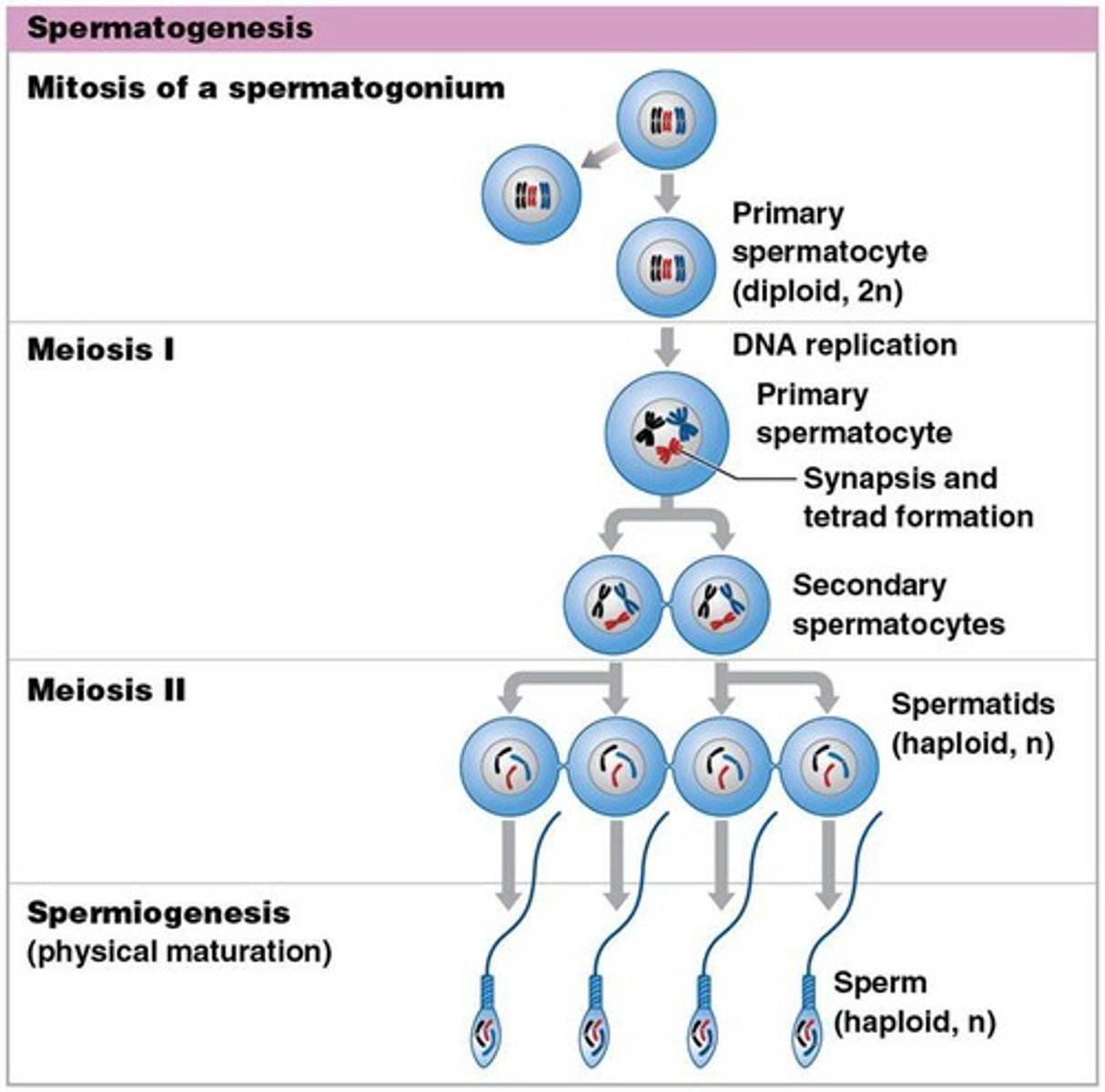
Spermatogonia
Stem cells in the seminiferous tubules that undergo mitosis.
Spermatocytes
Cells undergoing meiosis in the process of sperm production.
Spermatids
Cells undergoing spermiogenesis that develop into mature sperm.
Nurse cells (Sertoli cells)
Cells that extend from the tubular capsule to the lumen and form a blood-testis barrier.
Blood-testis barrier
Barrier formed by tight junctions of nurse cells protecting developing sperm from the immune system.
Mitosis
Process producing two identical daughter cells, each containing 46 chromosomes (diploid).
Meiosis
Cell division involved in gamete production resulting in haploid cells.
Haploid
Cells containing 23 chromosomes, produced during meiosis.
Diploid
Cells containing 46 chromosomes, produced during mitosis.
Spermiogenesis
The final stage of spermatogenesis where spermatids develop into mature sperm.
Leydig cells
Large interstitial endocrine cells in the spaces between tubules that produce androgens, such as testosterone.
Reproductive cycle
Major events occurring in the reproductive system over a defined period.
Structure of a sperm
Lacks most organelles and intracellular structures in order to reduce size and mass
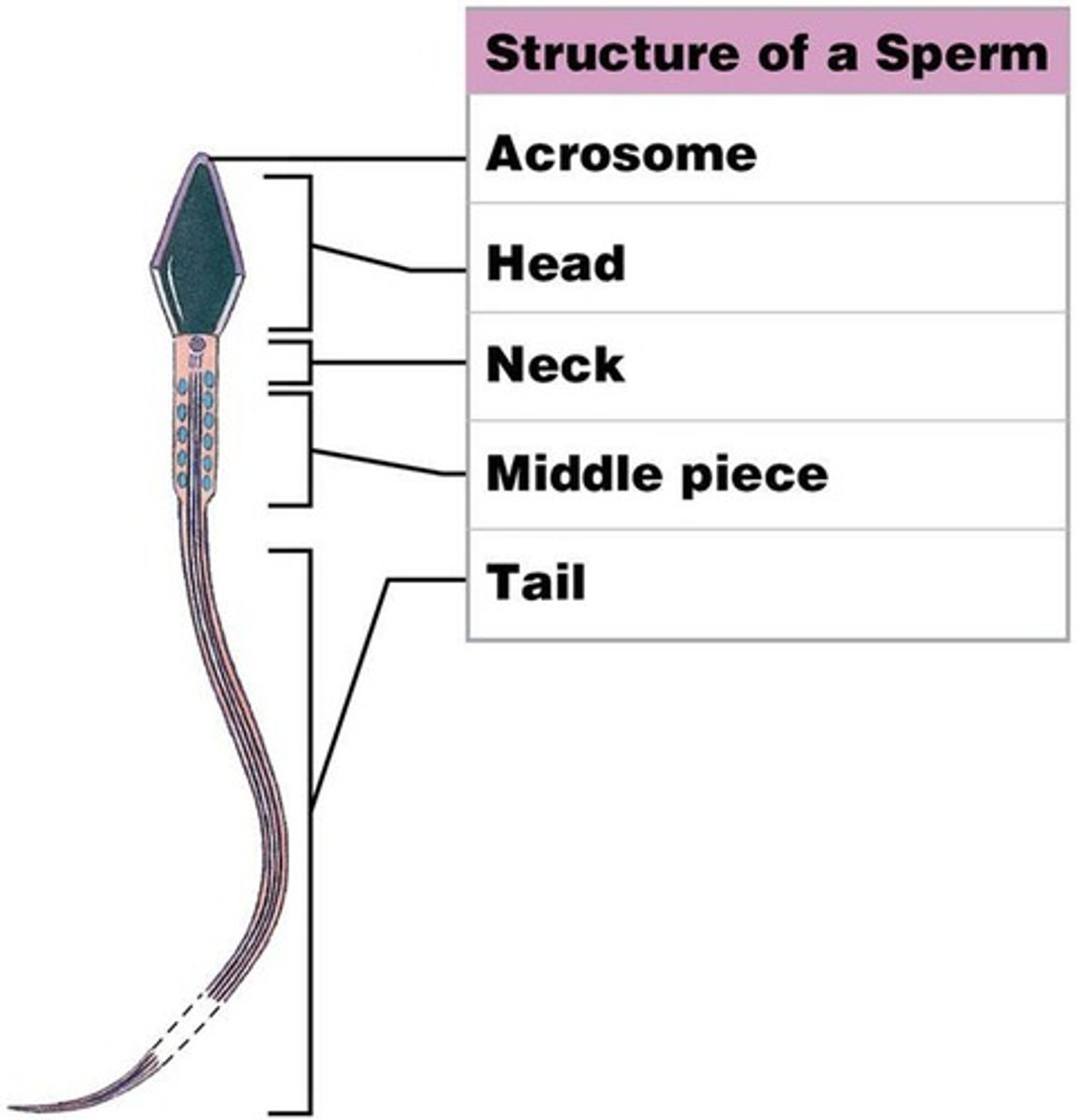
Acrosome
Containing enzymes essential to fertilization
Head of sperm
Contains nucleus with densely packed chromosomes
Neck of sperm
Contains both centrioles and microtubules
Middle piece of sperm
Contains mitochondria to provide ATP for tail movement
Tail (flagellum)
Whiplike organelle that moves the sperm
Spermatic cords
Extend between testes and abdominopelvic cavity
Cremaster muscle
Contracts to pull testes closer to body during sexual arousal or when exposed to cold temperature
Path of sperm
Testis to the epididymis, along the ductus deferens, then along the ejaculatory duct to the urethra
Epididymis
Start of the male reproductive tract, coiled tube bound to posterior border of each testis
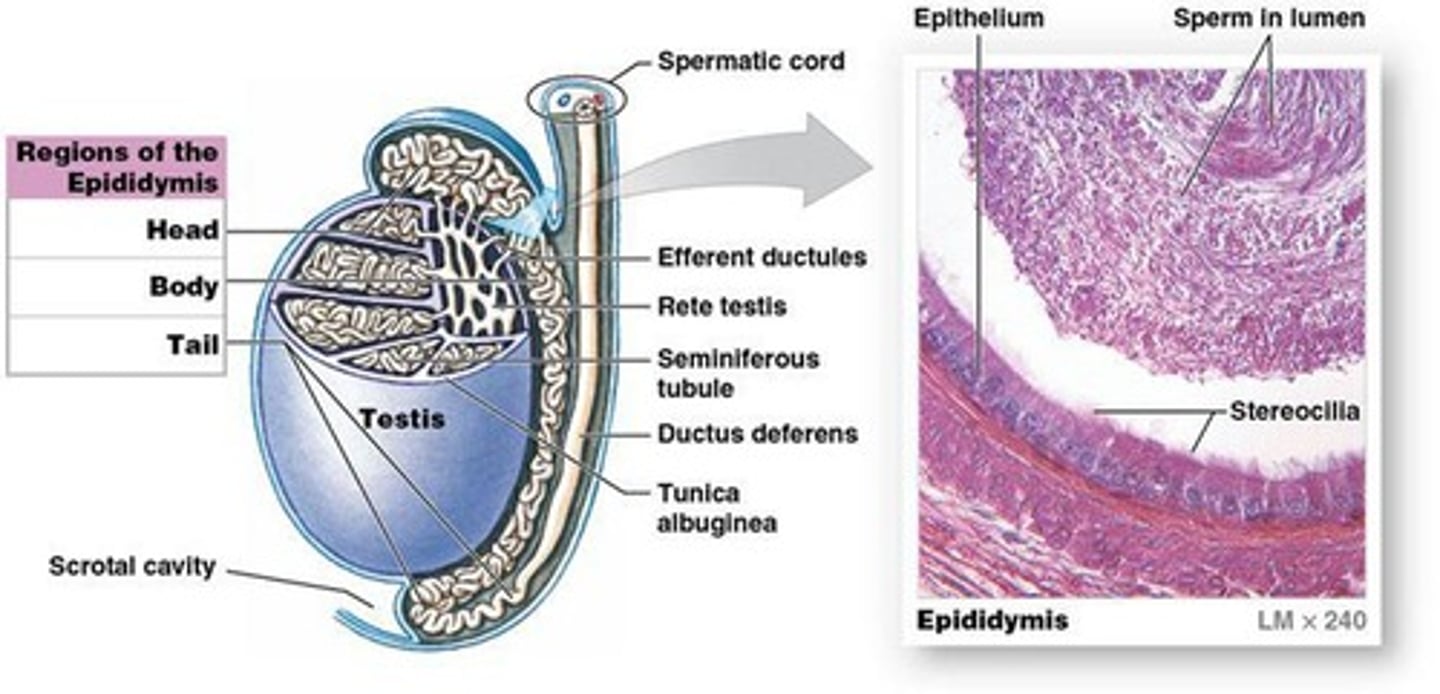
Ductus deferens (or vas deferens)
40-45 cm (16-18 in.) long, passes through spermatic cord, transports sperm from the epididymis
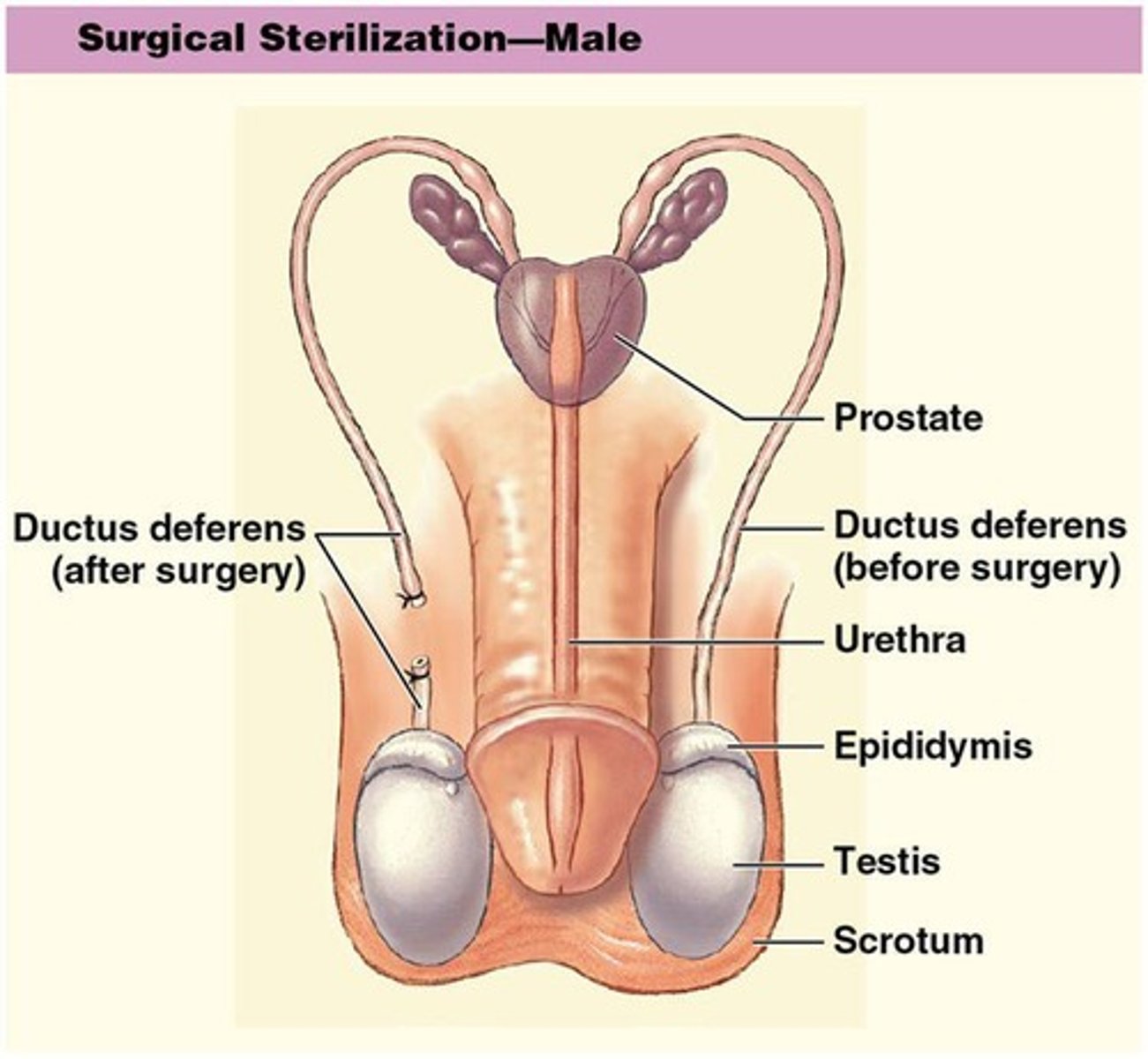
Ejaculatory duct
Short passageway formed where ampulla of ductus deferens joins with duct of seminal gland
Seminal glands
Also called seminal vesicles
Prostate
Encircles the proximal urethra as it leaves the bladder
Bulbo-urethral glands (Cowper's glands)
Located at the base of the penis, secrete thick, alkaline mucus that helps neutralize acids in the urethra
Root of the penis
A fixed portion that attaches the penis to the body wall
Body (or shaft) of the penis
A tubular, movable portion of the organ
Glans penis (head)
An expanded distal end that surrounds the external urethral orifice
Phases in the male sexual response
Arousal, release of nitric oxide, blood flow increases, erection occurs, ejaculation caused by sympathetic activation
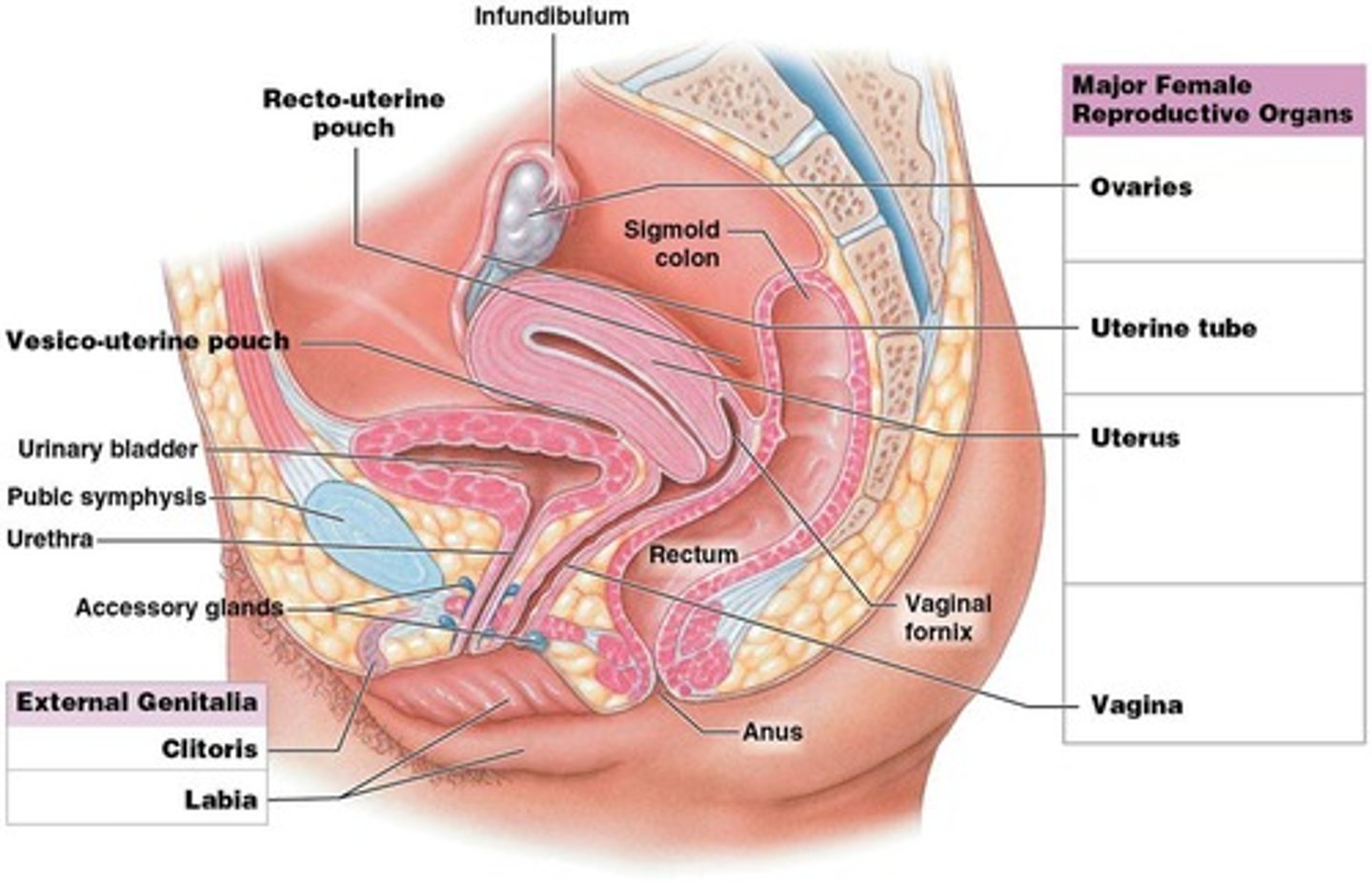
Ovary
Main structures of the female reproductive system, produces oocyte and hormones (estrogens and progesterone)
Oogenesis
Formation and development of the oocyte, begins before birth, accelerates at puberty, ends at menopause
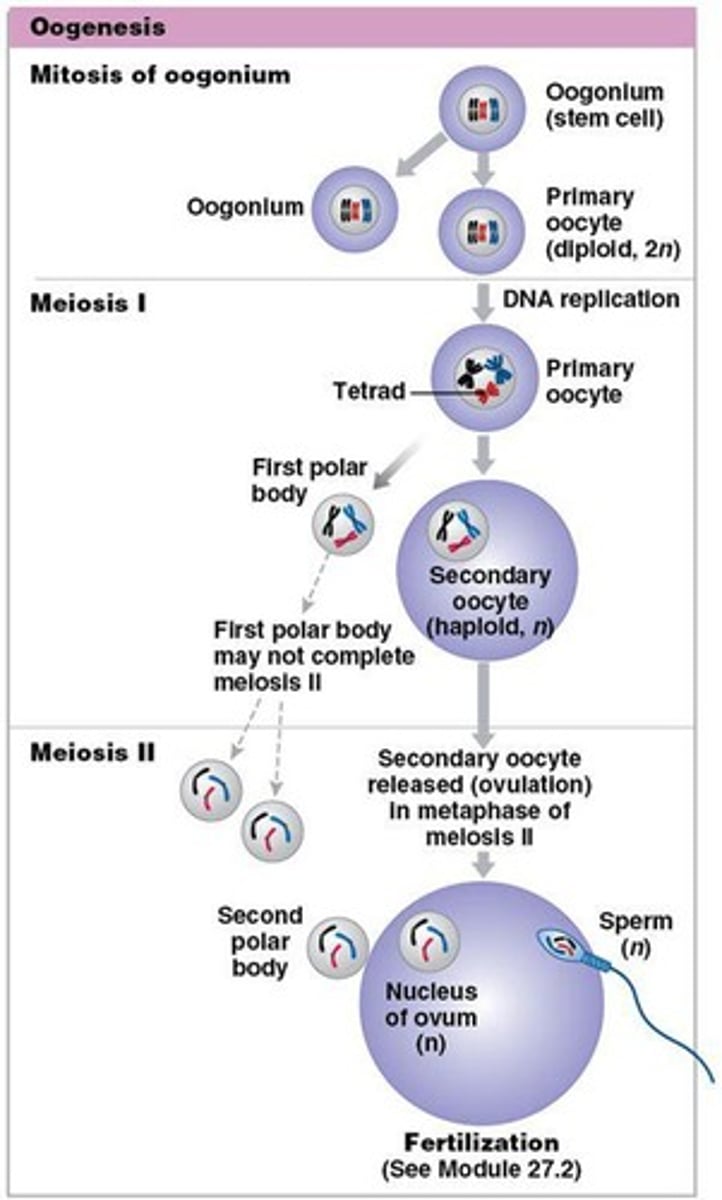
Polar body
A cell that holds discarded chromosomes.
Secondary oocyte
Undergoes meiosis II only if fertilized by a sperm cell.
Ovarian cycle
Consists of three phases: Follicular Phase, Ovulation, and Luteal Phase.
Follicular Phase
The first half of the ovarian cycle.
Ovulation
The midpoint of the ovarian cycle when the oocyte exits from one ovary.
Luteal Phase
The second half of the ovarian cycle where the remaining follicle becomes a corpus luteum.
Corpus luteum
Secretes progesterone and prepares for implantation of an embryo.
Corpus albicans
Pale scar tissue formed by degeneration of the corpus luteum when fertilization does not occur after 12 days.
Uterine tubes
Also known as fallopian tubes or oviducts, they are connected to the uterus.
Infundibulum
Funnel-like expansion adjacent to the ovary with fingerlike projections (fimbriae) that drape over the surface of the ovary.
Oocyte transport
Involves a combination of ciliary movement and peristaltic contraction of smooth muscle in the uterine tube.
Fertilization timing
Must occur within the first 12-24 hours after ovulation.
Uterus
Thick-walled, muscular organ that provides mechanical protection, nutritional support, and waste removal for embryo and fetus.
Perimetrium
The outer surface (serosa) of the uterine wall.
Myometrium
The thick muscular middle layer of the uterine wall, important in delivering the fetus at birth.
Endometrium
Mucosa whose characteristics change with each uterine cycle, consisting of a functional layer and a basal layer.
Fundus
Rounded portion superior to the openings of the uterine tubes.
Body of the uterus
The largest portion of the uterus, making up two-thirds of the organ.
Cervix
Inferior portion of the uterus that projects into the vagina; site for Pap test.
Uterine cycle
Monthly changes in the functional zone of the uterus in response to sex hormone levels.
Menstrual cycle length
Averages 28 days in length, with a range of 21-35 days.
Menarche
The first menstrual cycle, beginning at 11-12 years of age.
Menopause
Occurs between 45-55 years of age, marking the end of menstrual cycles.
Menstrual phase
Days 1-7 of the uterine cycle when the stratum functionalis is shed.
Proliferative phase
Days 8-14 of the uterine cycle when uterine gland basal cells multiply and restore uterine epithelium.
Secretory phase
Days 15-28 of the uterine cycle when uterine glands enlarge, stimulated by progesterone and estrogens.
Vagina
Elastic, muscular tube extending from the cervix to the vestibule, important during sexual intercourse and birth.
Mons pubis
Bulge of adipose tissue deep to the skin and superficial to the pubic symphysis.
Clitoris
Contains erectile tissue comparable to the corpora cavernosa and corpus spongiosum of the penis.
Labia majora
Folds of skin encircling the labia minora and adjacent structures.
Labia minora
Small folds of skin.
Vestibule
Central space bounded by labia minora.
Hymen
Elastic epithelial fold that usually partially blocks the entrance to the vagina.
Greater vestibular glands
Mucous glands activated during sexual arousal, homologous to bulbo-urethral glands of males.
Mammary glands
Located in the fat layer above pectoral muscles, responsible for milk production.
Lactiferous duct
Ducts carrying milk that leave lobules and merge into a single duct.
Lactiferous sinus
Where milk drains before opening onto the body surface through the nipple.
Areola
Brownish skin surrounding the nipple.
Site of spermatogenesis
Seminiferous tubules.
Primary site of fertilization
Fallopian tube.
Primary site of embryo implantation
Uterus.