Abdomen
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
Abdominal wall
what compresses and supports the abdominal viscera
intra-abdominal pressure
when contracted, the interior abdominal wall increases …
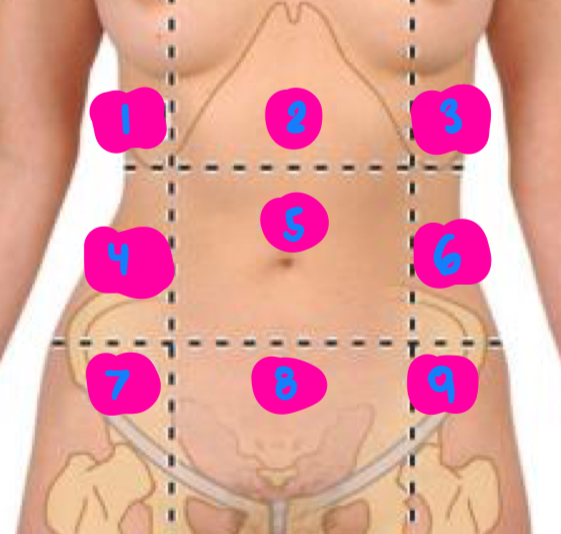
right hypochondrium
1
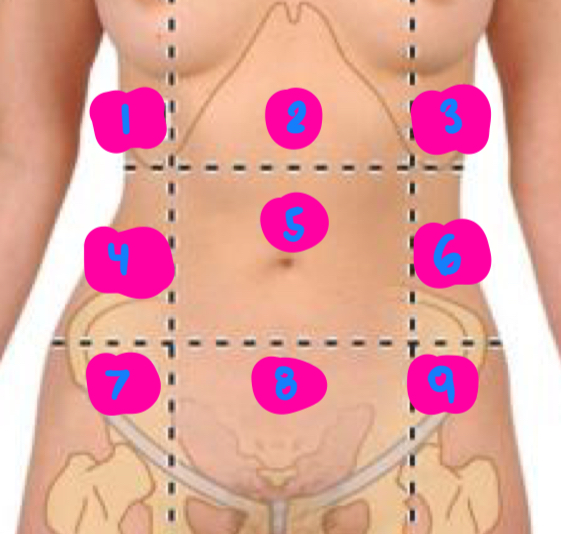
epigastric
2
left hypochondrium
3
right flank
4
umbilical
5
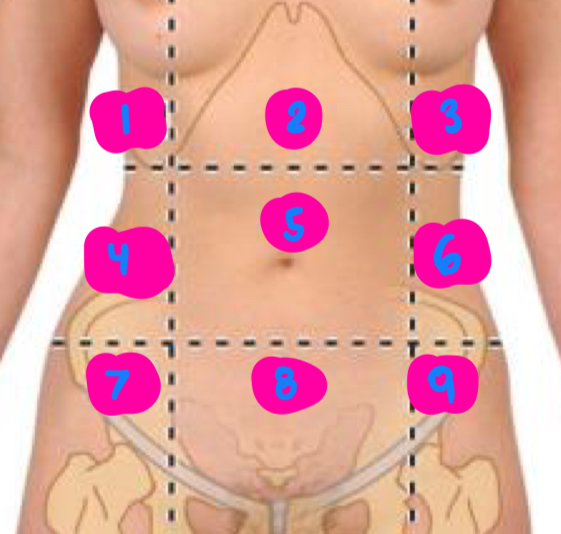
left flank
6
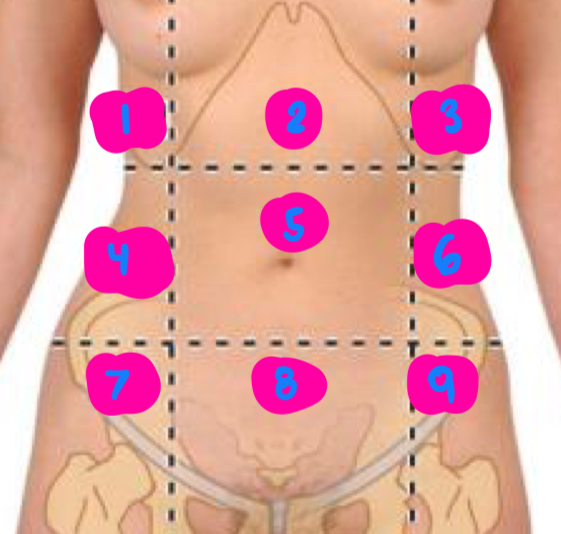
right inguinal
7
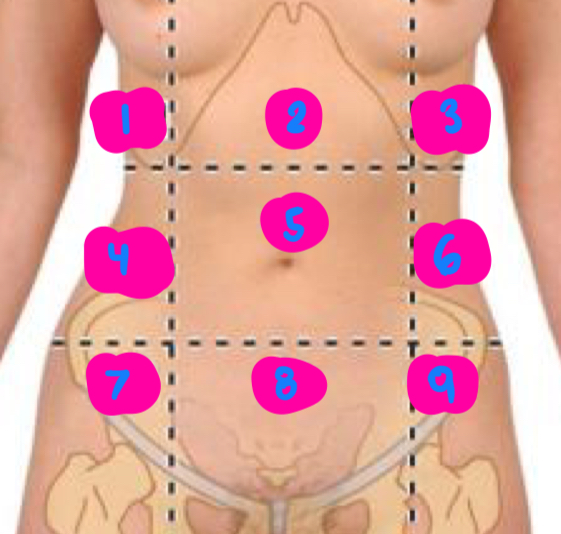
pubic
8
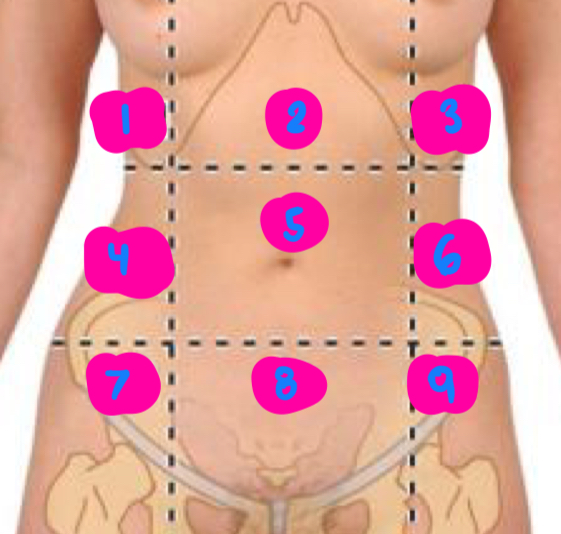
left inguinal
9
5-12 ribs
Linea alba, Pubic tubercle, Iliac crest
External Oblique
origin:
insertion:
Flexion of trunk
Unilateral → contralateral rotation
External Oblique
action:
Thoracolumbar fascia, lllac crest, Inguinal ligament
10-12 ribs, Linea alba, Superior ramus of pubis
Internal Oblique
origin:
insertion:
Flexion of trunk
Unilateral → ipsilateral rotation
Internal Oblique
action:
7-12th costal cartilages, Thoracolumbar fascia, Iliac crest, Inguinal ligament
Linea alba, Aponeurosis of internal oblique, Pubic crest/superior ramus
Transverse Abdominis
origin:
insertion:
transverse abdominus
what muscle compresses the abdominal cavity
Pubic symphysis, Pubic crest
Xiphoid process, 5-7 costal cartilages
Rectus Abdominis
origin:
insertion:
Flexion of trunk
Posterior pelvic tilt
Rectus Abdominis
action:
external oblique
internal oblique
transverse abdominus
rectus abdominus
abdominal muscles superficial —> deep
External oblique
Internal oblique
Transversus abdominus
what 3 muscles does the rectus sheath include?
rectus abdominus
tendinous intersections cross what muscle
tendinous intersections
what makes the “6 pack” appearance
psoas major
psoas minor
what 2 muscles in the posterior abdominal wall cause trunk flexion
quadratus lumborum
what muscle in the posterior abdominal wall cause ipsilateral lateral flexion
internal oblique
what abdominal muscle causes ipsilateral rotation
external rotation
what abdominal muscles causes contralateral rotation
parietal peritoneum
_____ is deep to the transverse abdominis & lines the abdominal cavity walls
visceral peritoneum
____ lines the abdominal organs and helps anchor to body wall
kidney’s
retroperitoneal means….
retroperitoneal
organs posterior to peritoneum
mesentary
double layer of peritoneum
intestines
vasculature
the mesentary suspends and supports the ____, and provides pathways for _____
omentums are avascular
what makes omentums different from the mesentary
connective tissue
omentums are forms of ____ that help keep everything in place
Lesser curvature of the stomach
the lesser omentum connects the liver to the _____
intestines
the greater omentum hangs from the greater curvature of the stomach and covers…
sphincters
part of the stomach where food enters and leaves
lower esophageal
pyloric
what are the 2 sphincters that allow for food to enter and leave the stomach
pyloric
what are the C rings on this diagram
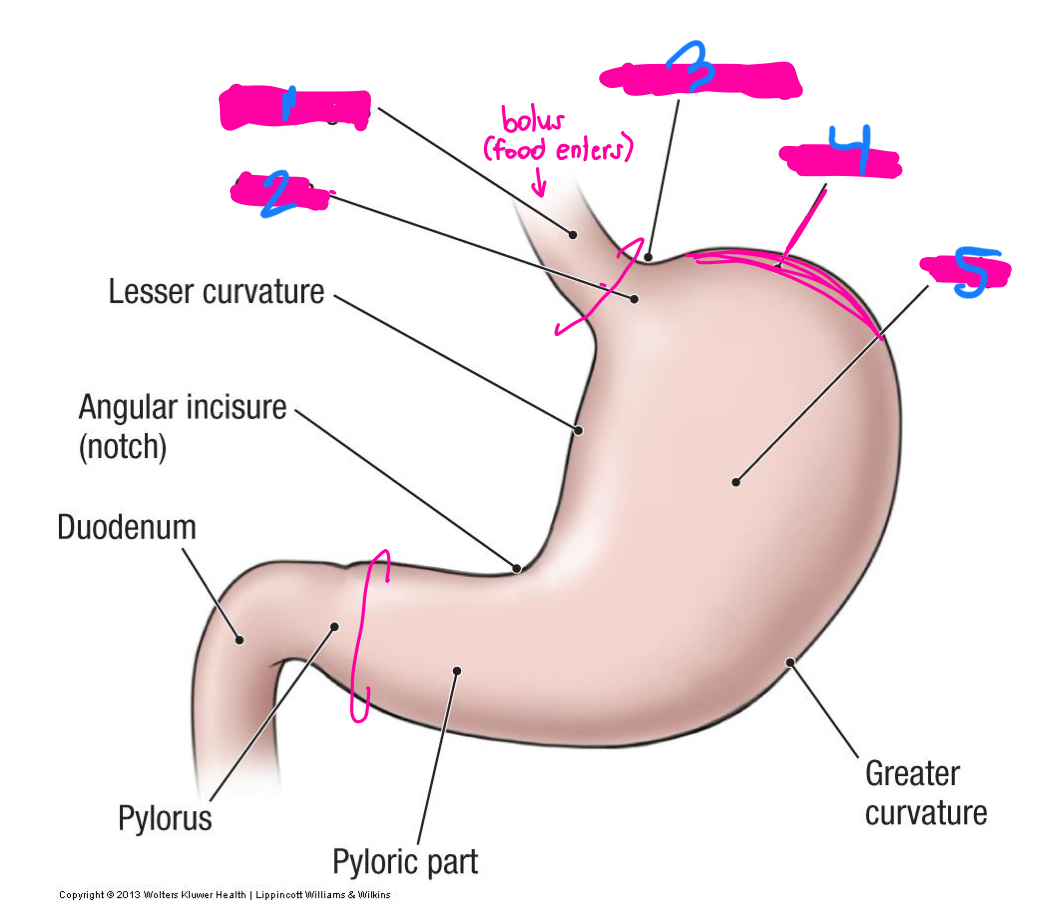
Lower esophageal
1
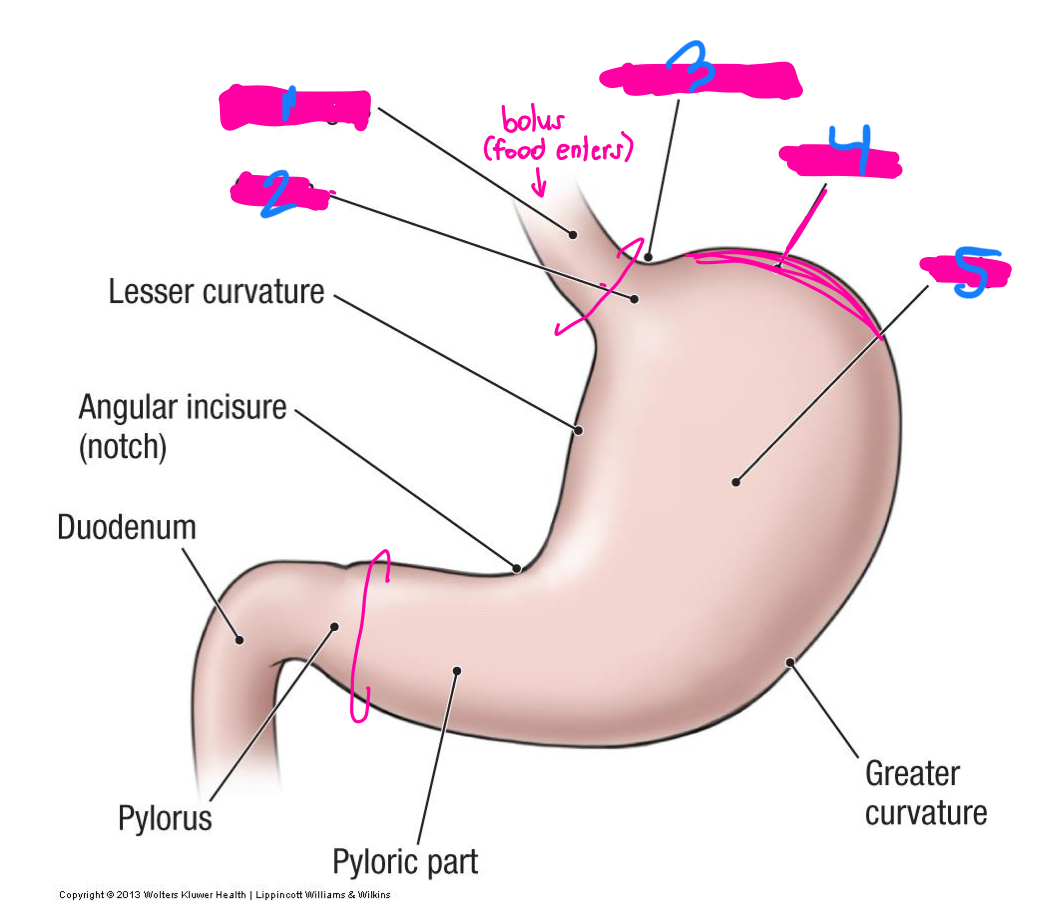
Cardial notch
3
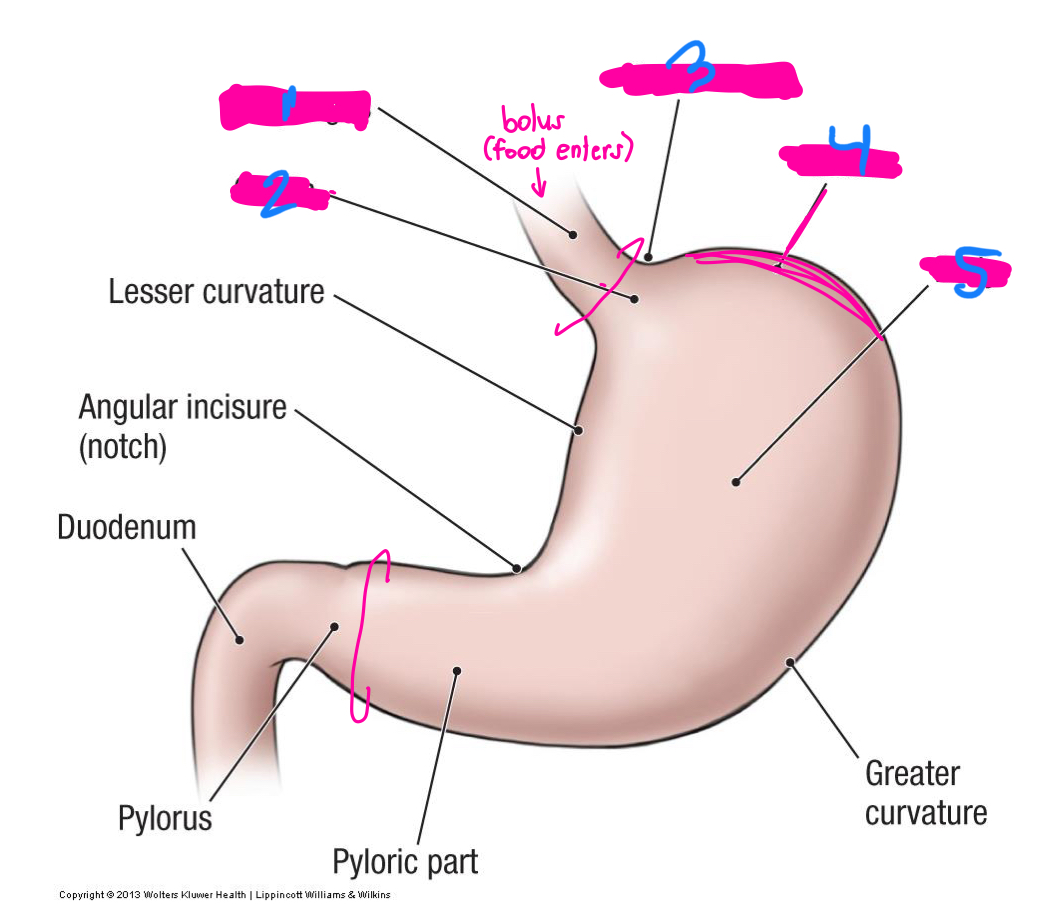
fundus
4
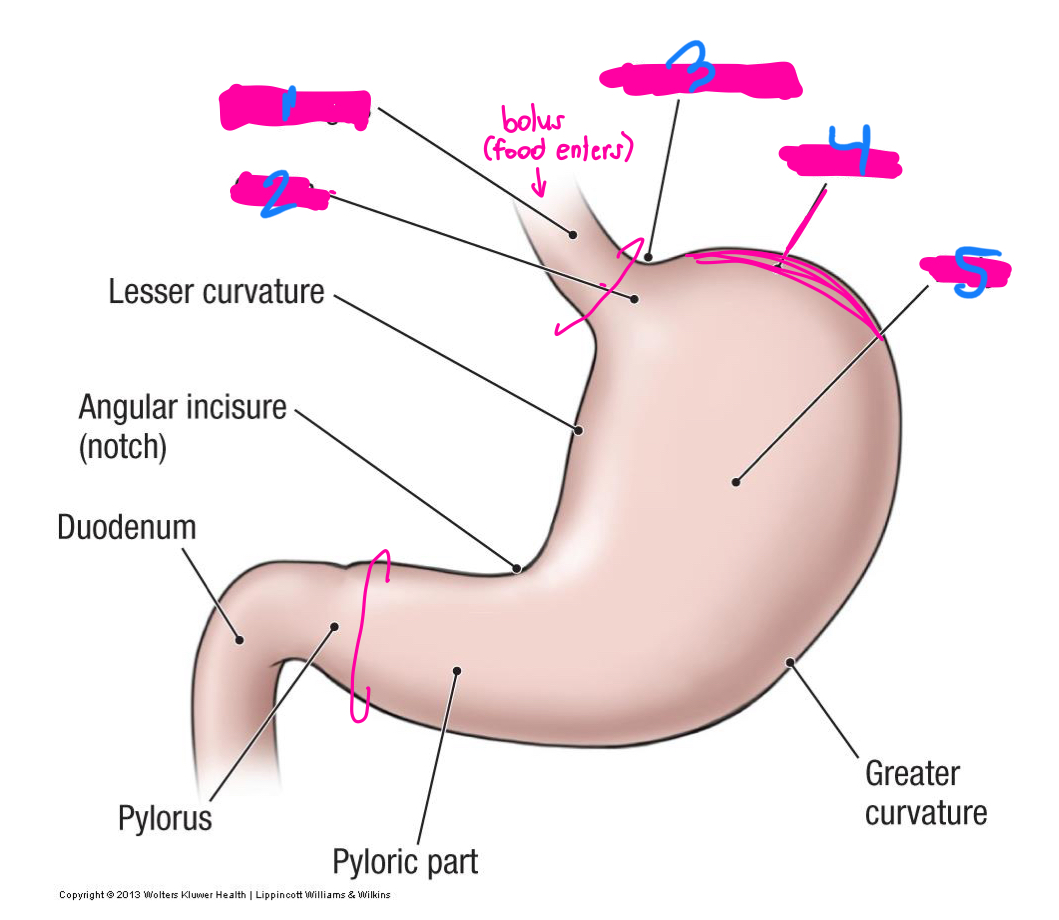
body
5
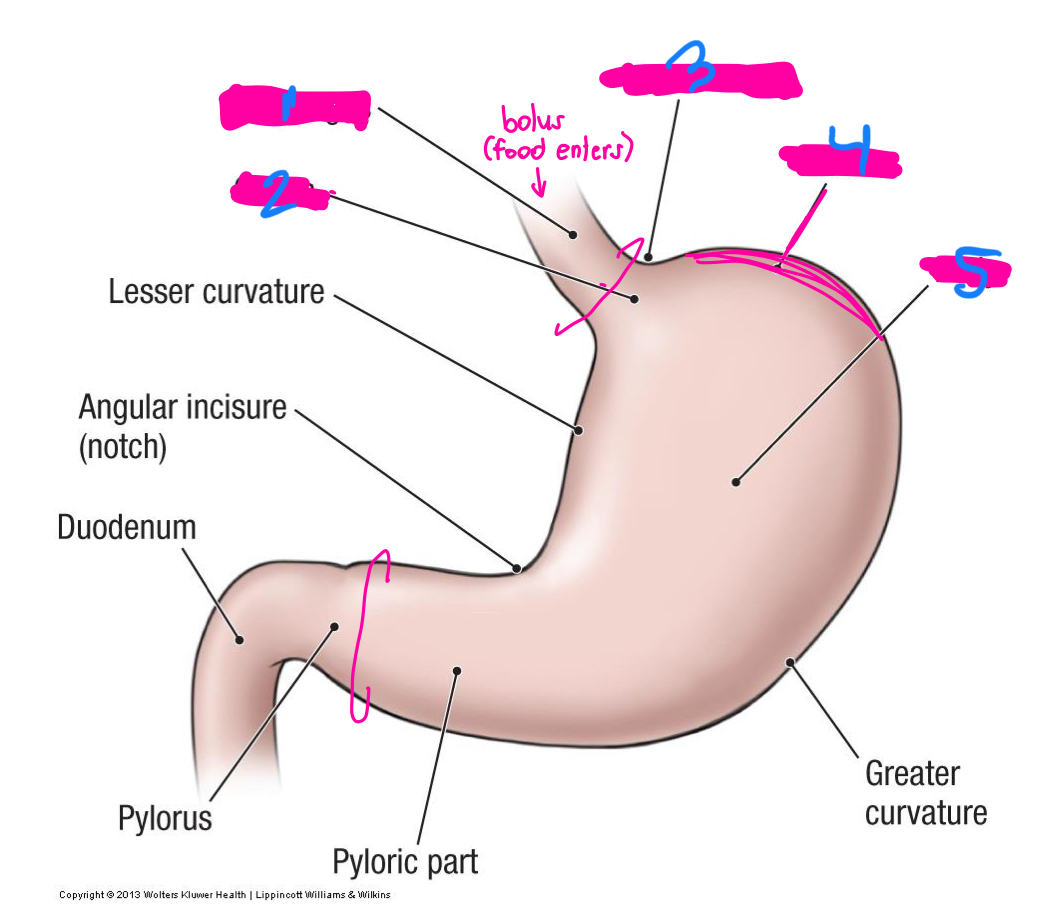
body
what is the vast majority of the stomach?
churring
The longitudinal, circular, and oblique muscular layers of the stomach allow for….
Protect the inner lining because of how acidic it can get
why does the stomach secrete mucus?
duodenum
jejunum
ileum
the pathway of the small intestine
duodenum
this part of the small intestine receives bile and pancreas secretions
jejunum
this part of the small intestine absorbs CHO, amino acids, and fatty acids
upper left
what quadrant of the stomach is the jejunum located
2 lower
what quadrant of the stomach is the ileum located
ileum
this part of the small intestine involves B12 and other nutrients
cecum
Ascending
Transverse
Descending
Sigmoid
what is the pathway of the large intestine (5)
haustra
what are the bunched up sections of the large intestine called
spleen
posterior to the stomach in the left hypochondriac region
immune system
the spleen is a blood filter and aids in ___ function
the stomach
what does the visceral surface of the spleen touch?
pancreas
this organ is right of the spleen and is located in the left upper quadrant
Exocrine
duodenum
Pancreas (digestion aid)
____ function
Enzymes into _____
Pancreatic duct
glucagon
insulin
what does the pancreas secrete?
pancreas
this organs main function is endocrine function
glucagon
if you have not ate all day, the pancreas will secrete…
Insulin
if you ate something (big breakfast), the pancreas will secrete…
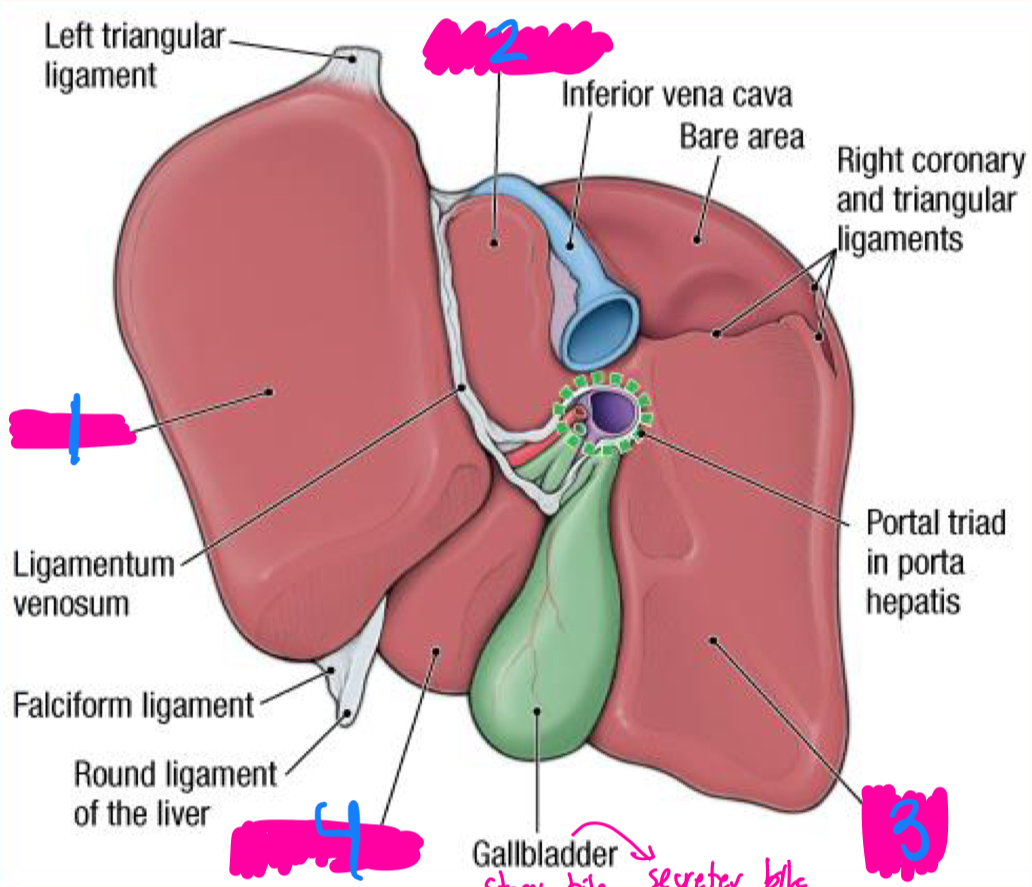
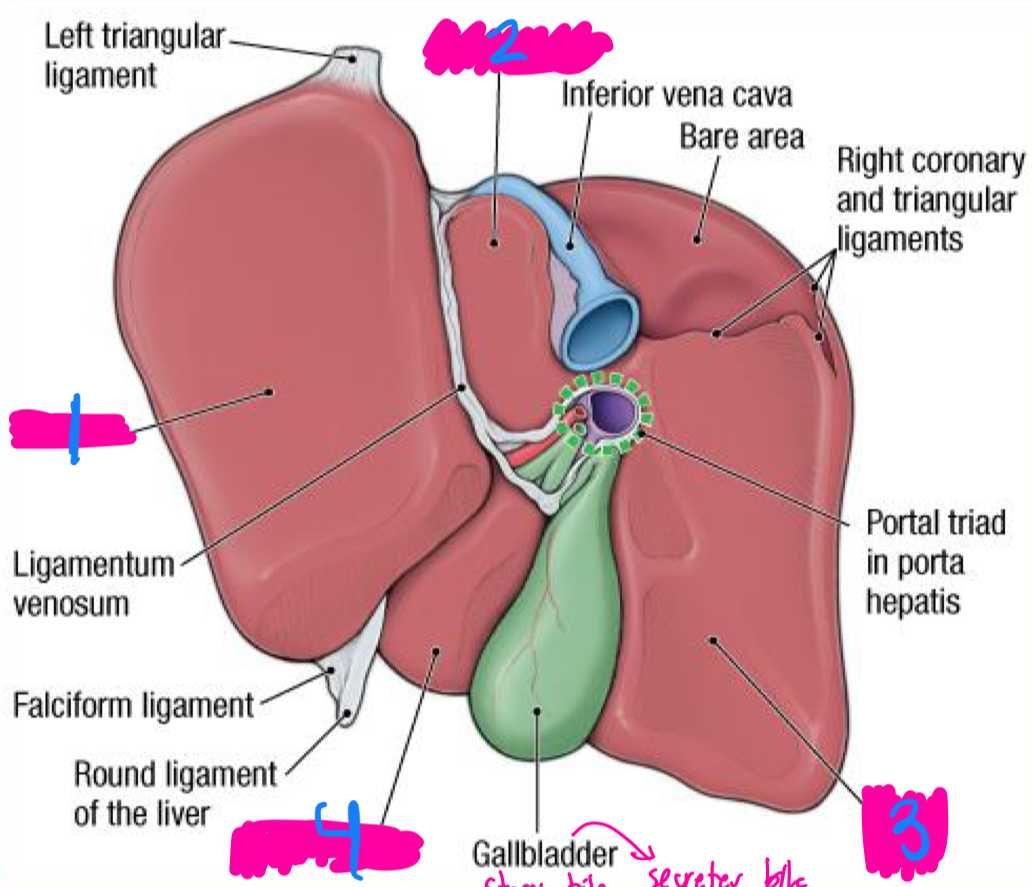
liver
gallbladder
the ___ produces bile
the ____ stores and releases bile to the duodenum
upper right quadrant
what quadrant is the liver mostly found in?
liver
hepatic =
liver
what organ has a role in cellular metabolism?
quadrant and gallbladder
between what two lobes does the gallbladder sit between in the liver
duodenum
cystic duct
the gallbladder secretes bile into the ____ through the ____
left lobe
1
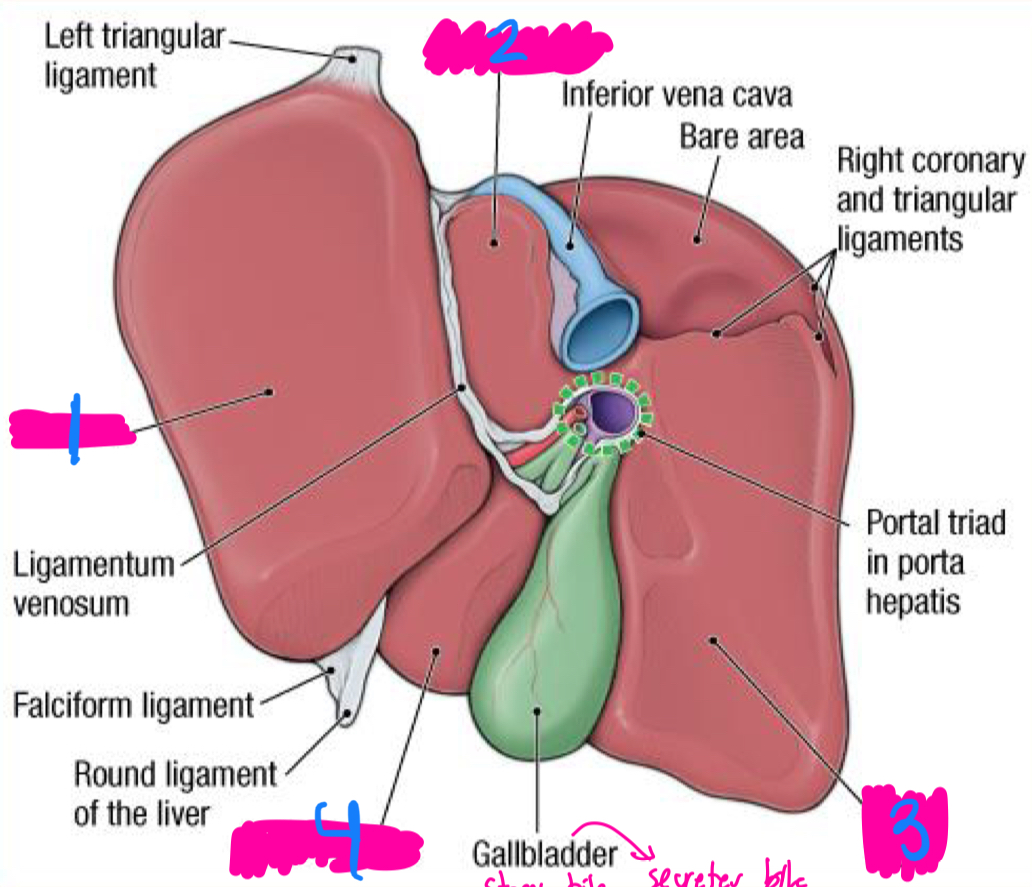
caudate lobe
2
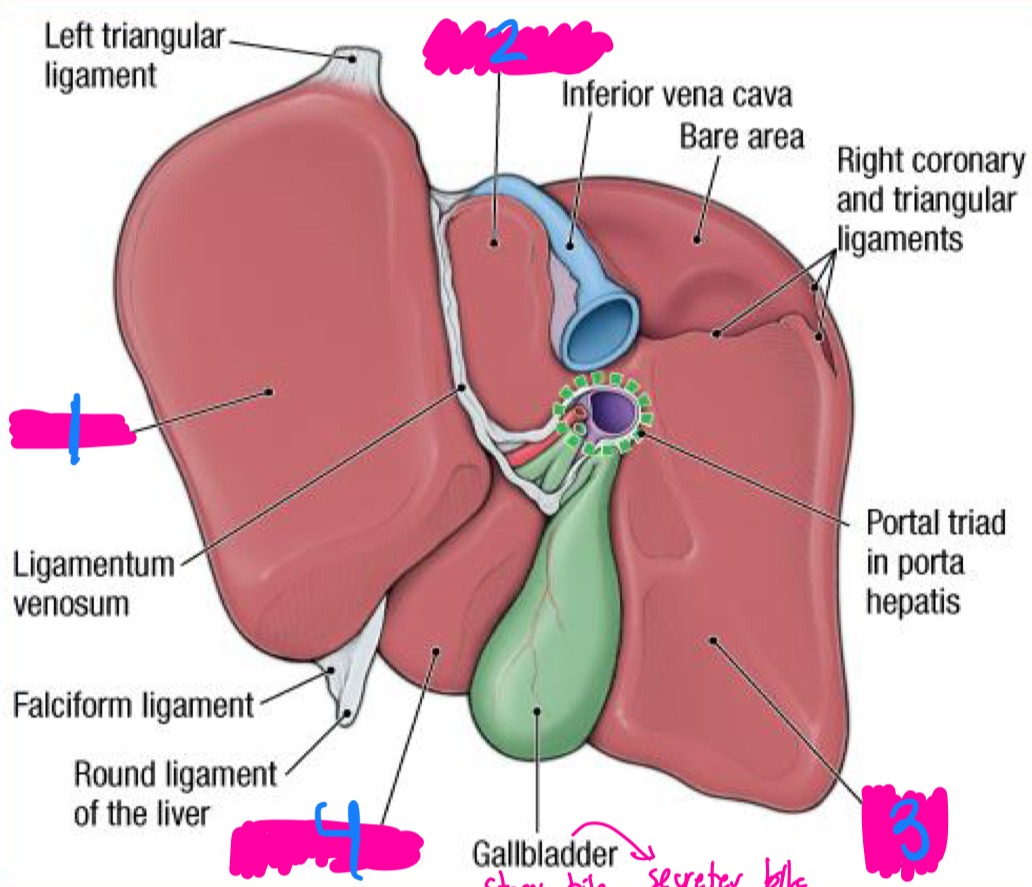
right lobe
3
quadrate lobe
4
floating ribs
what ribs are the kidneys anterior to
renal pyramids
where is urine made in the kidneys?
stomach
liver
spleen
the left gastric artery, hepatic artery, and splenic artery all innervate which 3 organs
celiac trunk
1
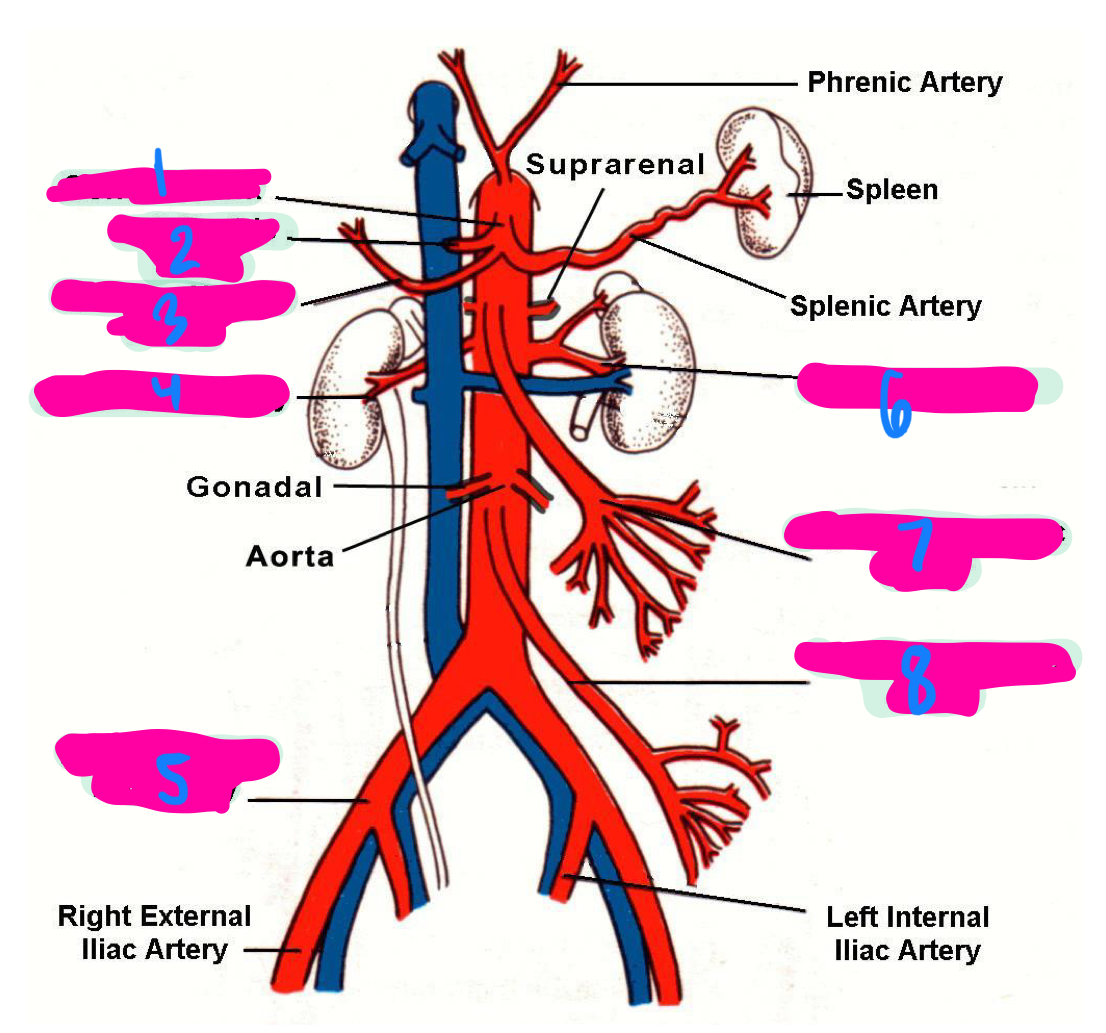
left gastric artery
2
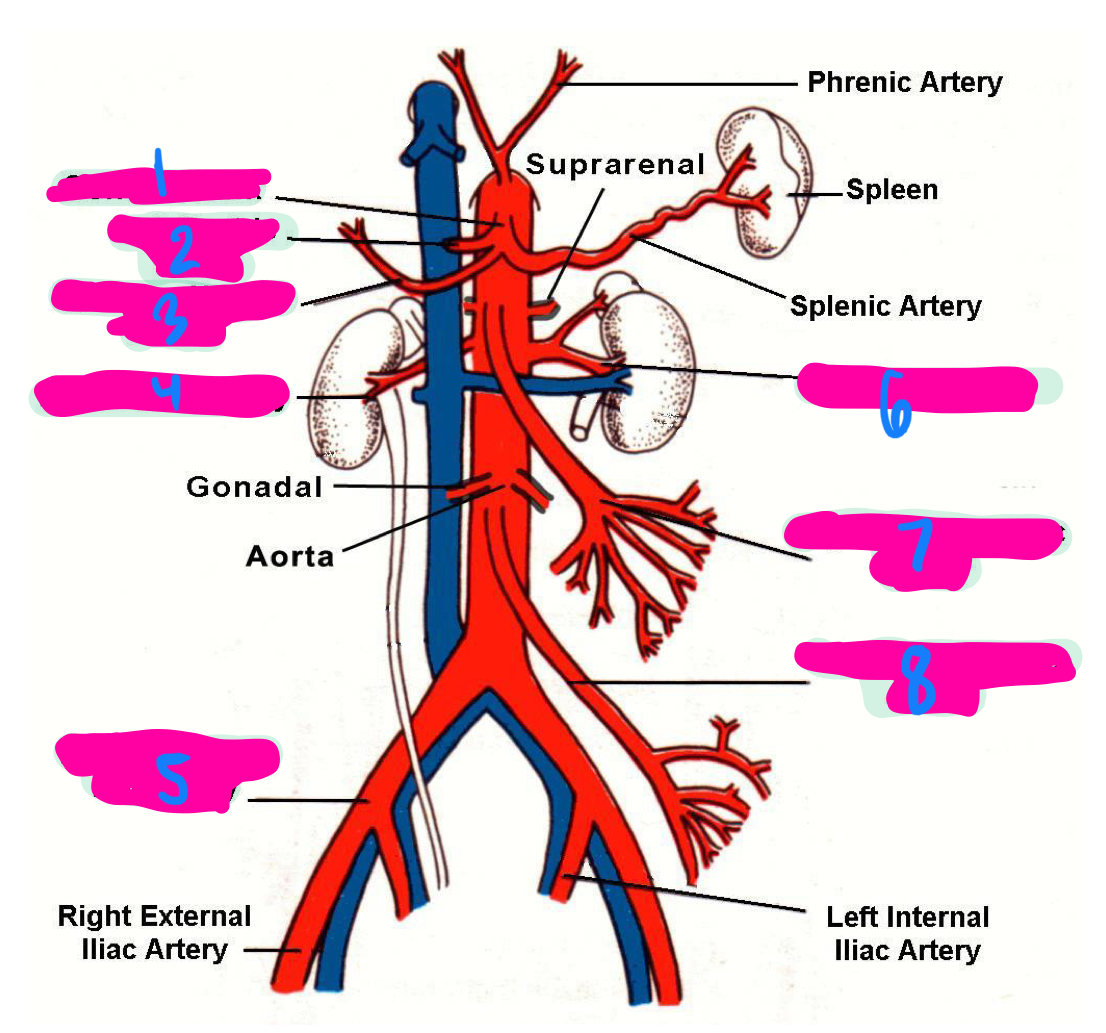
common hepatic artery
3
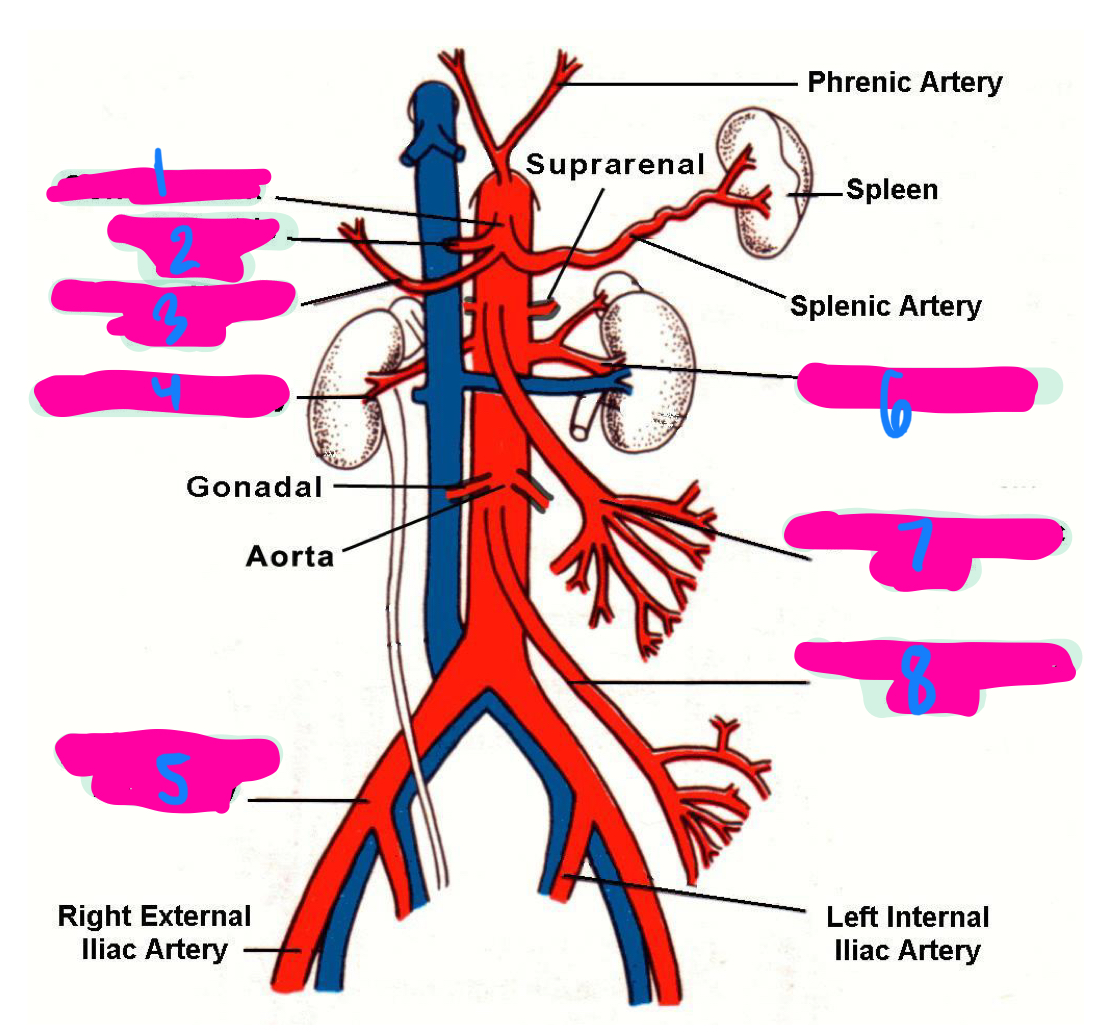
right renal artery
4
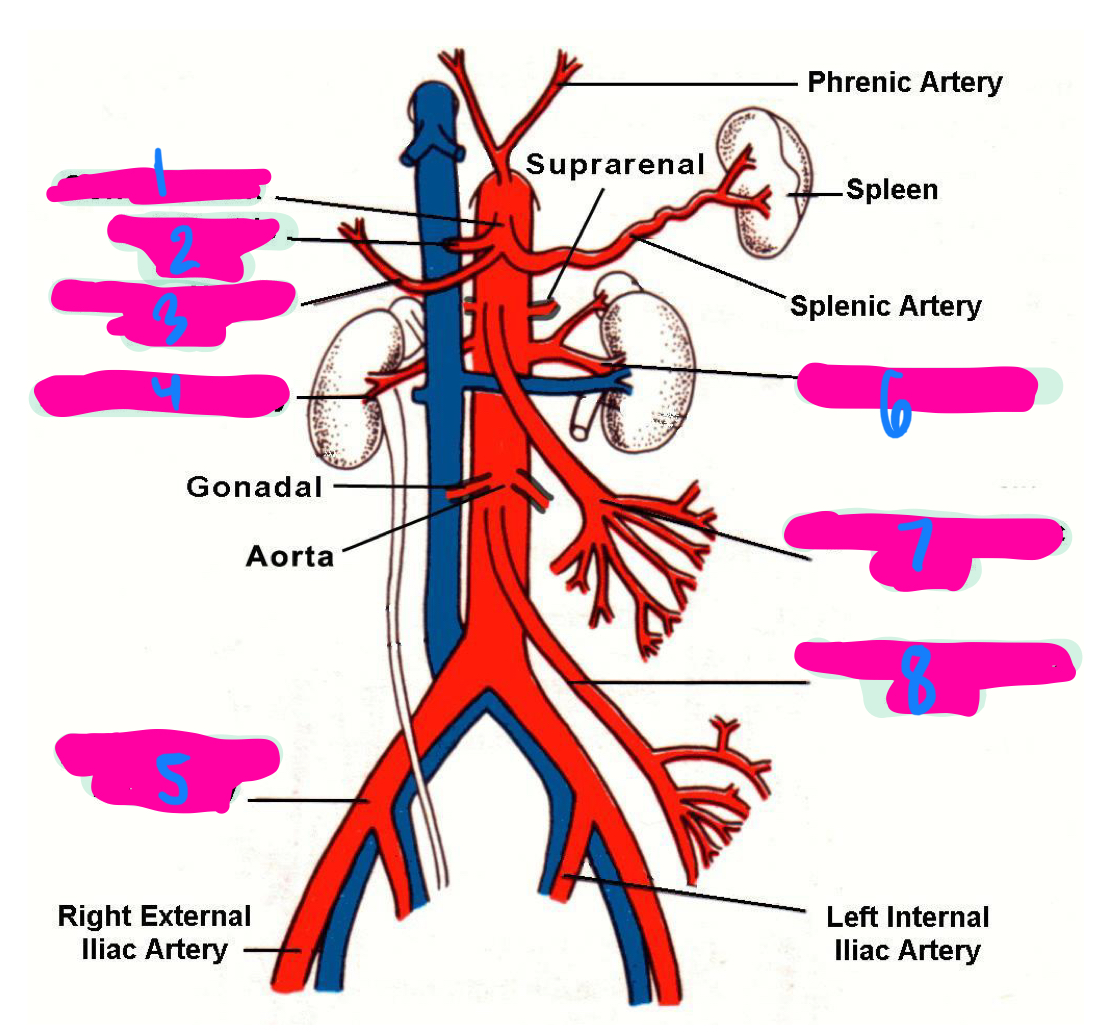
right common iliac artery
5
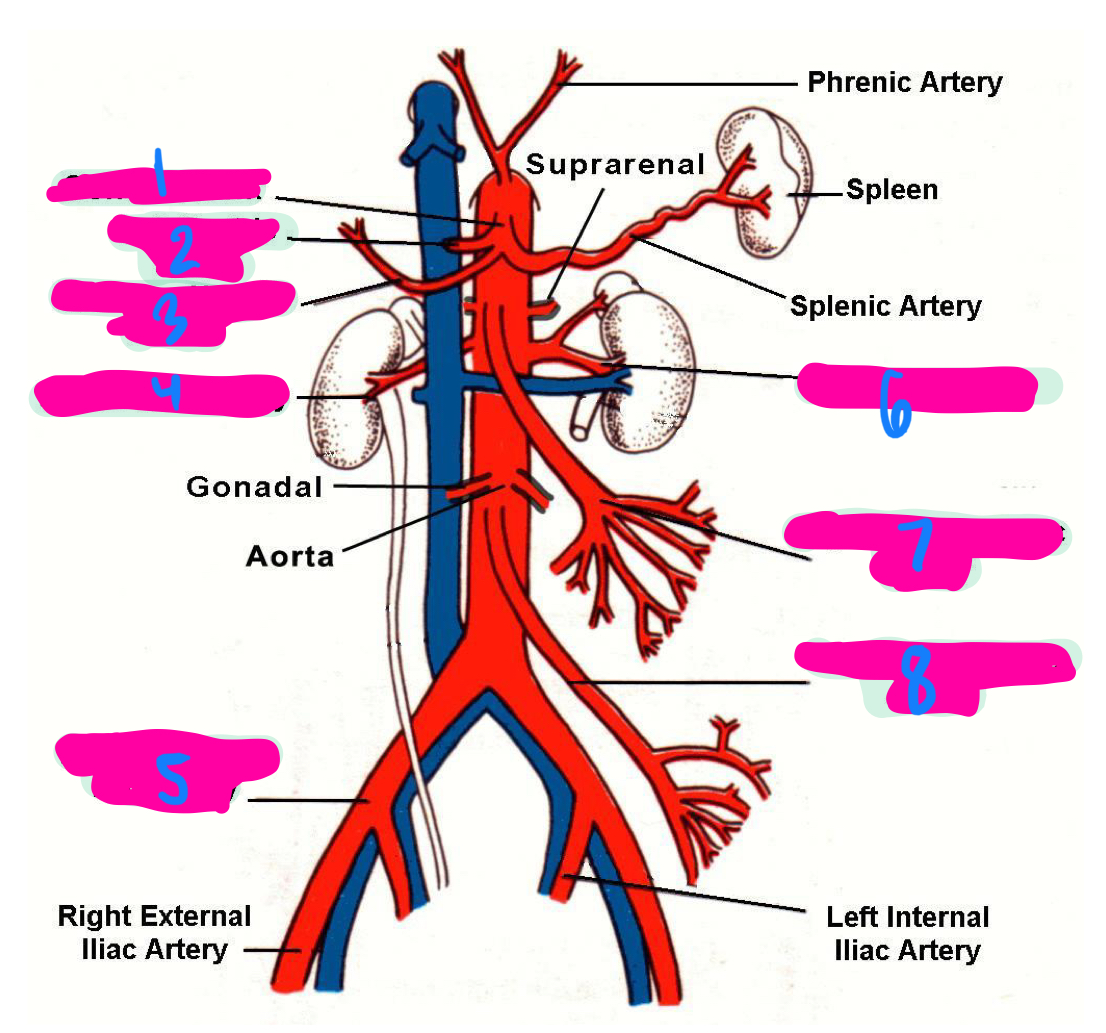
left renal artery
6
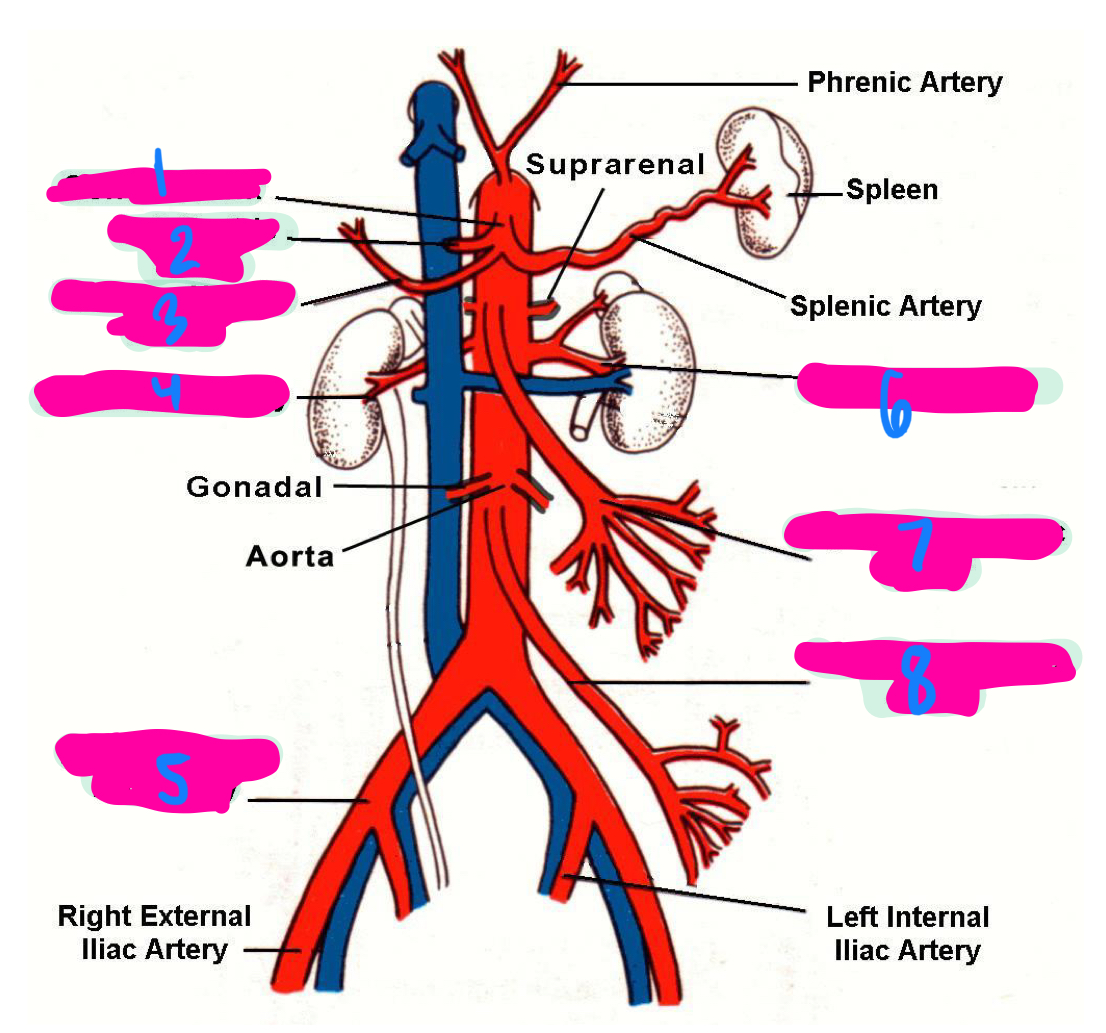
superior mesenteric artery
7
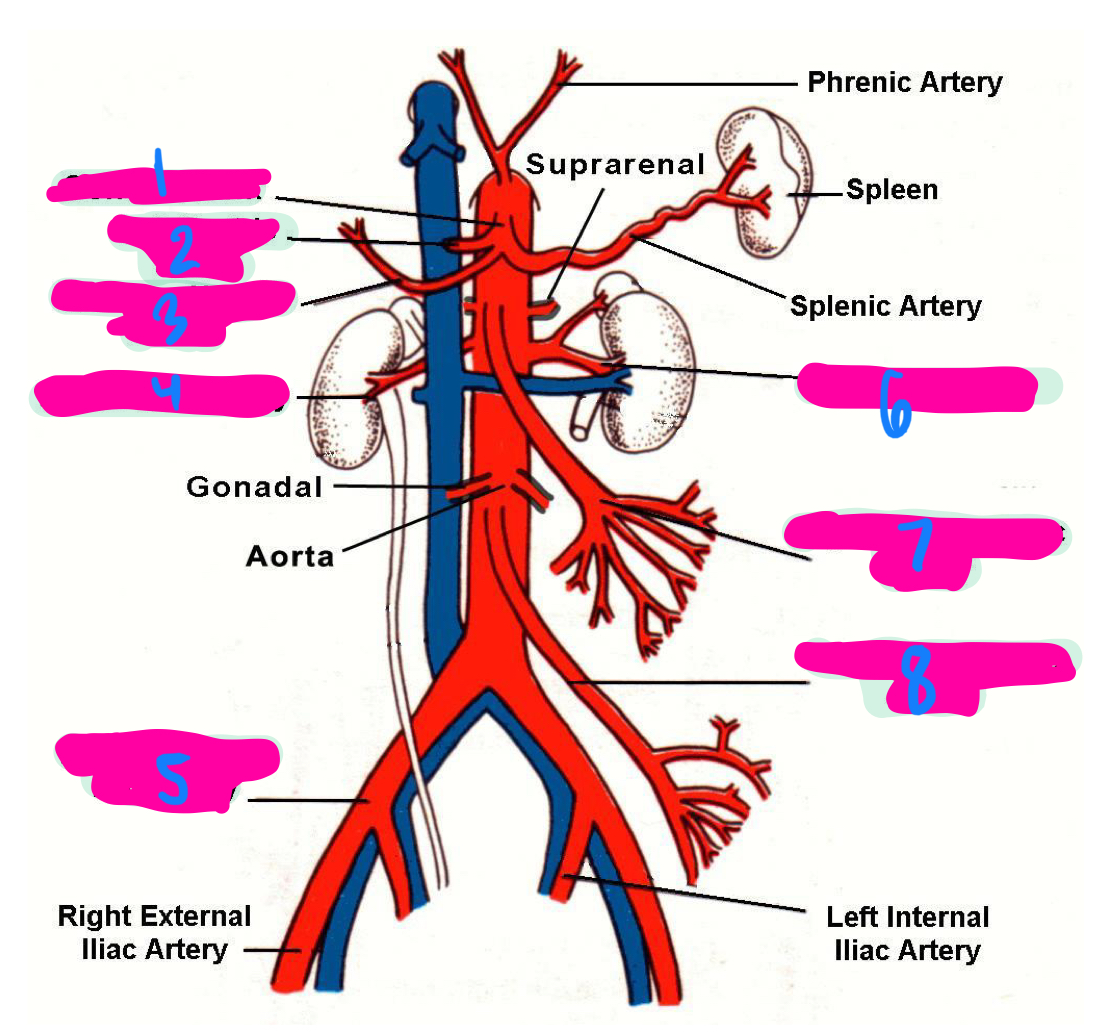
inferior mesenteric artery
8
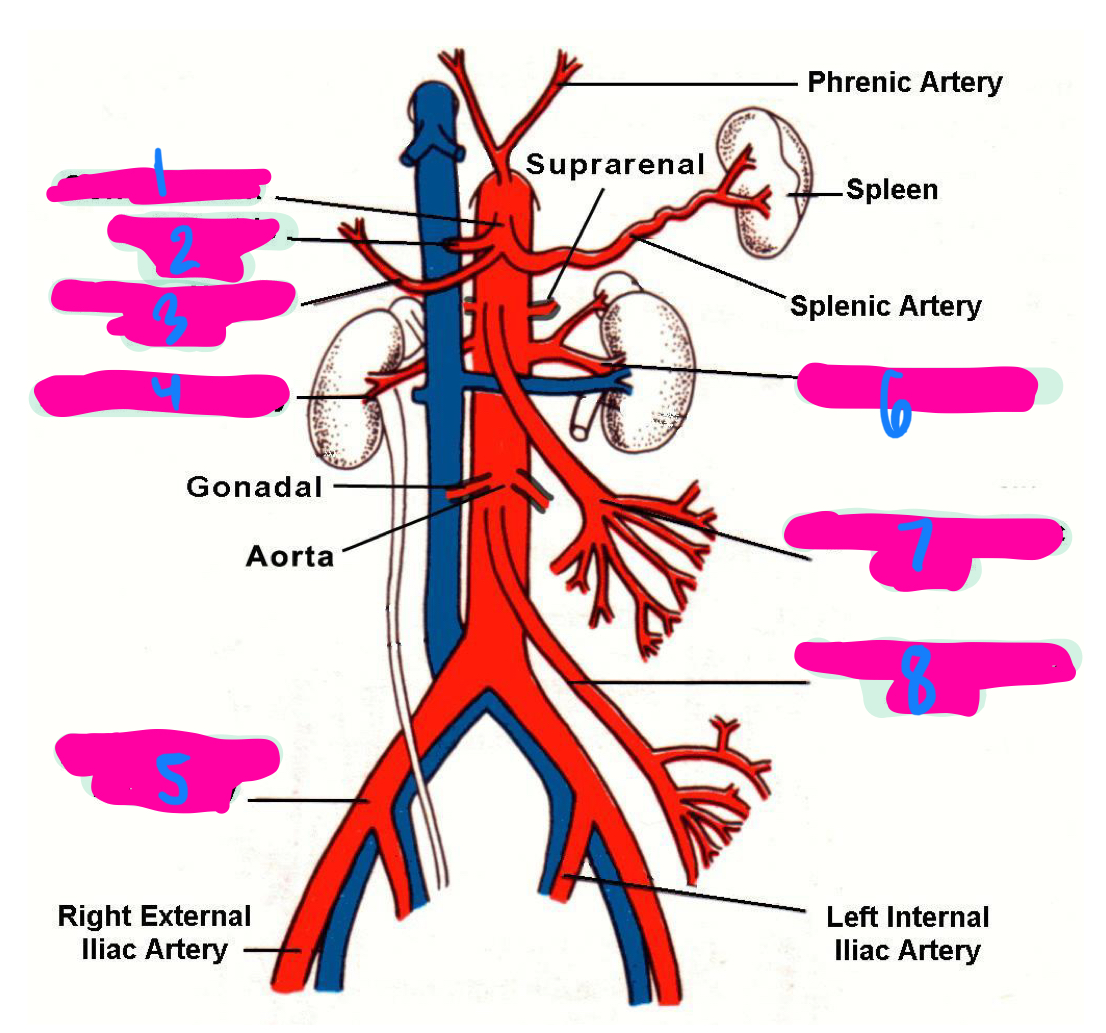
inferior vena cava
right and left common iliac vein
hepatic portal system
major veins inferior to the heart
___ —> ___ —> ____
liver
heart (inferior vena cava)
the hepatic portal vein takes blood back to the _____
the hepatic vein then takes it back to the _____ from that area
stomach, intestines, and gallbladder
the hepatic portal vein gathers blood from the what 3 areas
phrenic nerve (C3-C5)
what nerve innervates the diaphragm, mediastinal pleura, and pericardium
vagus (parasympathetic)
What nerve innervates the auricular, cardiac, laryngeal, pharyngeal, pulmonary, esophageal, and vagal trunks
hepatic
celiac
gastric
3 parts the vagal trunk includes
AIIS
the true pelvis is below what landmark?
Obturator Membrane
Greater Trochanter
Obturator Internus
origin:
insertion:
external rotation
ABD of flexed hip
Obturator Internus
action:
Sacrum and Sacrotuberous Ligament
Greater Trochanter
Piriformis
origin:
insertion:
external rotation
ABD of flexed hip
Piriformis
action:
Ischial spine
Sacrum and Coccyx
Coccygeus (ischiococcygeus)
origin:
insertion:
Flex Coccyx & supports pelvic viscera
Coccygeus (ischiococcygeus)
action:
Body of pubis, obturator fascia, ischial spine
Perineal body, Соссух, prostate/vagina, rectum, anal canal
Levator Ani
origin:
insertion:
Support Pelvic Viscera and resists increases in intra-abdominal pressure
Levator Ani
action: