Human Variation and Evolution
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
Evolution
The gradual change in the characteristics of a species over generations
Phenotype
The observable characteristics due to alleles (genotype)
Genotype
The combination of alleles for a gene
Population
A group of organisms of the same species living together in a particular place at a particular time.
Gene Pool
sum of all the alleles carried by the members of a population
Allele Frequency
How often each allele of a gene occurs in a population
Mutation
A change in a gene or chromosome leading to new characteristics in an organism
Mutant
an organism with a characteristic resulting from mutation
Gene mutation
changes in a single gene so that the traits normally produced by that gene are changed or destroyed
Chromosomal Mutation
a change in the structure and/or number of chromosomes in an organism
Cause of mutations
occur without any known cause, but agents are known to increase the rate at which they occur.
Mutagenic agents/mutagen
An environmental agent that increases the rate of mutation
Examples of mutagens
Mustard gas
Formaldehyde
Sulfur dioxide
Some antibiotics
Ionising radiation examples:
Ultraviolet light
X - rays
cosmic rays
radiation from radioactive waste
fallout from atomic and nuclear explosions
Albinism
an inherited inability to produce pigment in hair, skin and eyes. Extremely pale skin, whitish blond hair and pinkish eyes. Due to one missing protein.
Induced mutation
A mutation caused by a mutagenic agent
Spontaneous mutation
a mutation that occurs due to an error in a natural process (e.g. mitosis/meiosis
Somatic mutation
a change occurring in a gene in a body cell (cannot be passed on/inherited)
Germinal/germline mutation
a change in the hereditary material in the egg or sperm that becomes incorporated into the DNA of every cell in the body of the offspring (gametes; individual is usually not affected but offspring are).
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
an inherited disease resulting in damage to the growing brain and, thus, extreme intellectual deficiency, a tendency towards epileptic seizures, and failure to produce normal skin pigmentation.
Missense mutations
a mutation that causes a change in an amino acid resulting in a different protein being produced
Nonsense mutations
A mutation that results in a STOP codon, producing a shortened peptide chain
Neutral mutations
a mutation that causes a change in an amino acid; it does not cause an overall change in the protein
Silent mutations
a mutation that does not change the sequence of amino acids
Extent of mutation
Amount of DNA affected; from single base → whole chromosome.
Extent of gene mutation
affects only one single gene
Extent of chromosomal mutation
affects a number of genes; may change structure or number genes. Often course abnormalities so severe that miscarriage often occurs early in the pregnancy
Point mutations
a change in just one of the bases in a DNA molecule
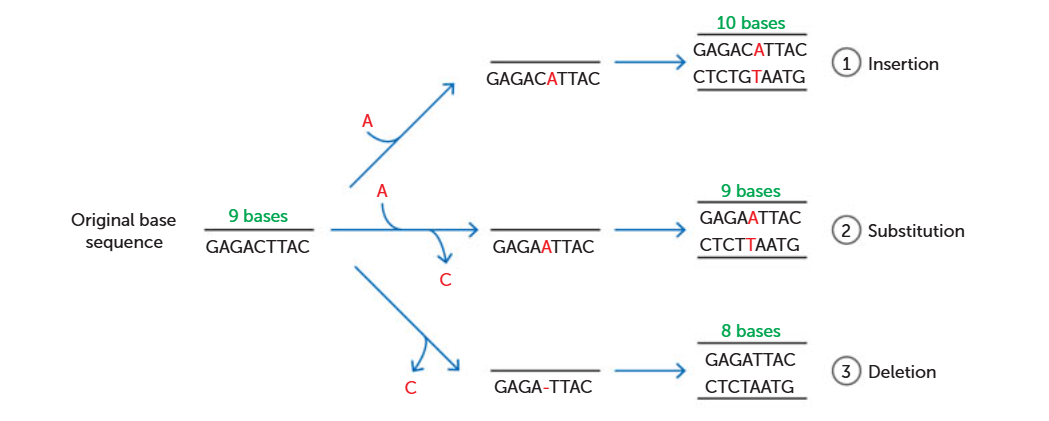
Actions of nucleotide in point mutations
Inserted - a new nucleotide is added to the DNA strand
Substituted - an existing nucleotide is replaced with another one, with a different base
Deleted - a nucleotide is removed from the DNA strand
Frameshift
a mutation involving an insertion or a deletion that results in a change in the way that the sequence is read
Duplication (insertion)
a section of chromosome occurs twice
Deletion
a piece of DNA is removed
inversion
breaks occur in a chromosome and the broken piece joins back in, but the wrong way around.
Translocation
part of a chromosome breaks off and is rejoined to the wrong chromosome
Non - disjunction
during meiosis, a chromosome pair does not separate and so one daughter cell has an extra chromosome, and one daughter cell has one less number.
Aneuploidy
a change in the chromosome number as a result of non - disjunction
Duchenne muscular dystrophy
a genetic disease resulting in wasting of leg muscles, and then arms, shoulders and chest. Occurs through gene mutation. May arise in mother and is inherited by sons or occur in male zygote so that the child develops the disease. Death occurs due to failure to of the respiratory muscles and those affected are unlikely to live more than 20 - 25 years.
Cystic fibrosis
Genetically determined disease, mutation occurs in a huge gene on chromosome 7. Gene codes for 1480 amino acids that make up a protein which regulates the passage of chloride ions across the cell membrane. Symptoms include salty - tasting skin, persistent coughing, wheezing or pneumonia, digestive and other problems. Recessive → must inherit from both parents.
Down syndrome (trisomy 21)
a genetic disorder resulting from an extra copy of chromosome 21 or an extra part of chromosome 21 (3 instead of 2). A chromosomal mutation, symptoms include characteristic facial expression, intellectual disability and weak muscles (can also suffer heart defects or digestive abnormalities)
Mechanism of evolution
the forces which alter allele frequences within a population leading to evolutionary change over time
Examples of Mechanisms of Evolution
Mutations
Migration
Natural Selection
Genetic Drift
Types of mutations
Point
Frameshift
Duplication (insertion)
Deletion
Inversion
Translocation
Non - disjunction
Gene flow
is the movement of genetic material from one population to another.
Migration
the movement of individuals between populations (enable gene flow)
Barriers to gene flow
Geographical
Sociocultural
Geographic Barriers
such as oceans, mountains, large lake systems, deserts and expansive ice sheets.
Sociocultural Barriers
e.g. economic status, educational background and social position. Religion and language → some religions do not allow marriages outside the religion. and
Variation
all members of a species vary
Birth Rate
all living organisms reproduce at a rate far greater than at which their food supply and other resources increase
Nature’s balance
each species’ numbers tended to remain at a relatively constant level