(3) BIOCHEM fr and antioxidants
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
the primary free radicals (explain each)
superoxide= Generated through incomplete reduction of oxygen in ETC or as a product of an enzymatic reactions.
nitric oxide= Generated by a series of specific enzymes (NO synthase). reactive nitrogen species. best known for vasodilation.
what are free radicals produced by?
enzymes
can free radicals purposely produce?
yes
do molecules(FR) have the ability to leave cells and affect/impact on near by cells?
yes
how are free radicals formed?
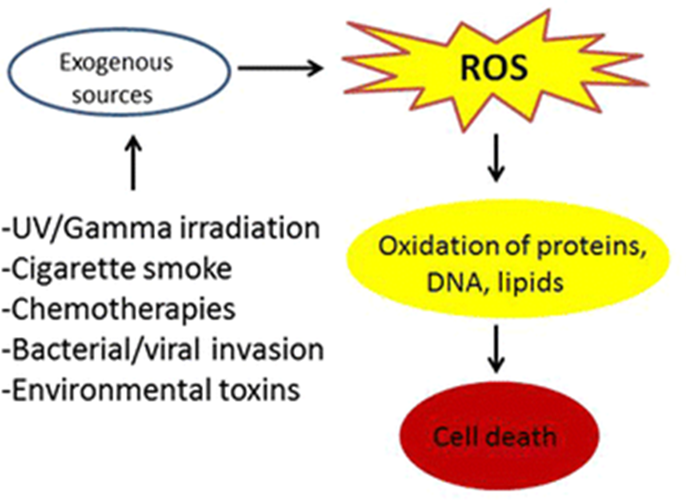
•Generated through outside sources that damage or break bonds (like from smoking, radiation)
•incomplete oxidation reaction (electrons leak backwards, which generates superoxides)
•Enzymatic reactions
normal metabolic process of the cell generate free radicals as part of the reaction
what does incomplete oxidation reaction mean?
electrons leak backwards, which generates superoxides
non-enzymatic sources of ROS (why FR formed);
•Environmental sources disrupt electrons in molecules in the body.
•Why oxygen
present in high concentrations
2 unpaired electrons
•“Accidental” Generation
Any reaction involving oxygen has the possibility of incomplete oxidation
endogenous production of ROS (why FR formed). what is it’s purpose?
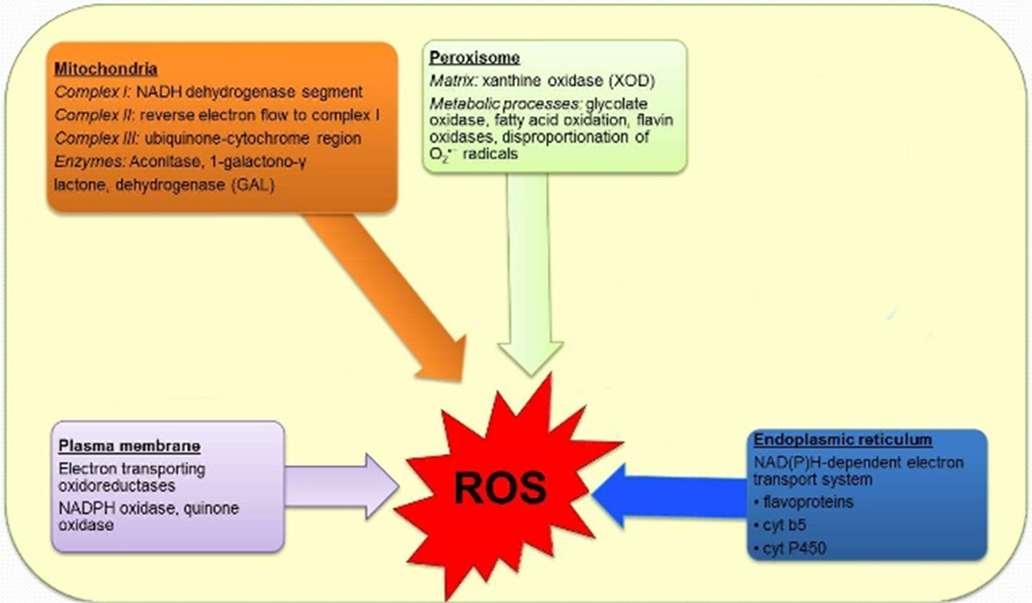
→ often compartimentalized
→ enzymes in cell are producing them
why? because they are a signaling molecule
what is often compartimentalized?
endogenous (production of ROS)
what does ROS stand for?
reactive oxygen species
do most ROS have a short or long life span?
extremely short.
even though ROS have a extremely short life span, what can they do well?
they can cause substantial damage to tissue and cellular components
main ROS we talk about:
superoxide radical
hydrogen peroxide
hydroxyl radicals
what is superoxide primarily formed as?
•Primarily formed as an intermediate in biochemical reactions
explain superoxides
•Primarily formed as an intermediate in biochemical reactions
•Has a relatively long half life
•Main precursor of other ROS
•Can be converted to H2O2 (hydrogen peroxide) by a dismutation reaction
•Relatively low cytotoxicity

what ROS has a relatively long half life?
superoxide
what is the ROS that is the main precursor for other ROS?
superoxide
what ROS can be converted into H2O2 (hydrogen peroxide) by a dismutation reaction?
superoxide
what kind of reaction can superoxide be converted into H2O2 (hydrogen peroxide) by?
dismutation reaction
does superoxide have a relatively low or high cytotoxicity?
low
explain hydrogen peroxide
Stable, permeable to membranes, and has a relatively long half life
Does not directly oxidize DNA or Lipids, but may inactivate some enzymes
Dangerous because it can generate hydroxyl radicals

what ROS is not actually a free radical?
hydrogen peroxide
what ROS is stable and permeable to membranes?
hydrogen peroxide
what ROS has a relatively long half life?
hydrogen peroxide
what ROS does not directly oxidize DNA or lipids, but may inactivate some enzymnes?
hydrogen peroxide
what ROS is dangerous because it can generate hydroxyl radicals?
hydrogen peroxide
explain hydroxyl radicals
•Widely considered the most damaging ROS in cells
•Incredibly reactive
•Do damage close to their site of generation
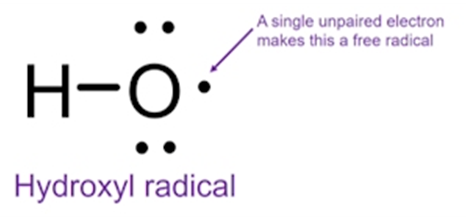
what ROS is considered the most damaging ROS in cells?
hydroxyl radicals
what ROS has a short half life and is incredibly reactive?
hydroxyl radicals
what ROS damages close to their site of generation?
hydroxyl radicals
what are H-atom abstraction and chain reactions aka/mean?
aka steal electron/abstracting electron
most common consequence of H-atom abstraction and chain reactions is what? explain
Most common consequence is lipid peroxidation
Membrane-bound proteins are damaged by propagation reactions (change reations)
Hydroxyl radicals remove a hydrogen atom from a PUFA creating a lipid peroxyl radical
This reacts with another PUFA to form another lipid radical
Creates a chain reaction causing large amounts of damage to the cell
what can happen in H-atom abstraction and chain reactions;
•Most common consequence is lipid peroxidation
Decrease in membrane fluidity (=increased stiffness; cells no longer able to function properly)
Increased “leakiness” of the membrane pores to substances which normally do not pass through the membrane
alter membrane; increase leak; more unwanted things in membrane
decrease membrane fluidity (cannot change shape relatively easy)
what does decreasing membrane fluidity do?
increase stiffness
decreases ability to change shape
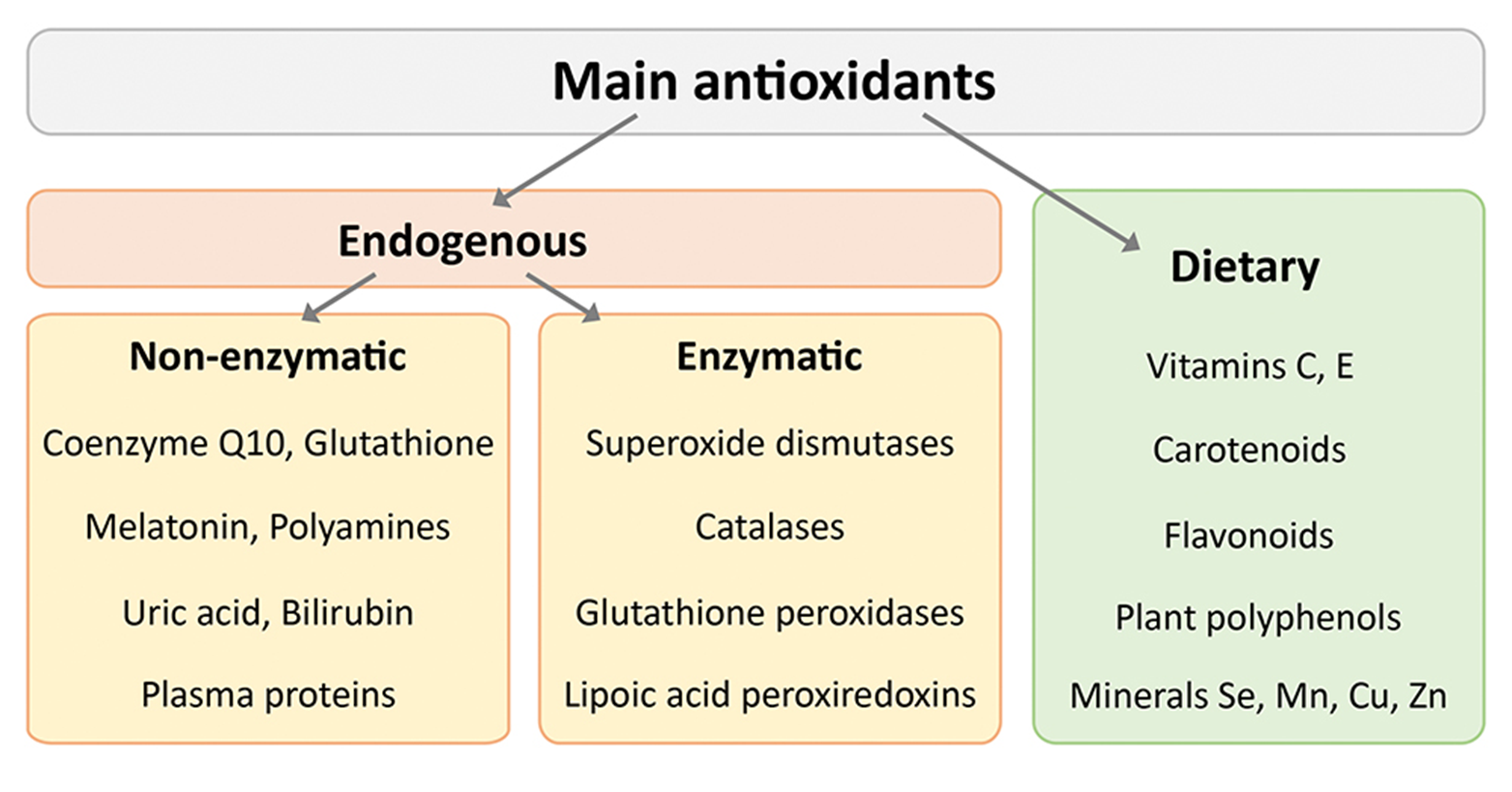
explain the model of superoxide dismutase if radicals produced
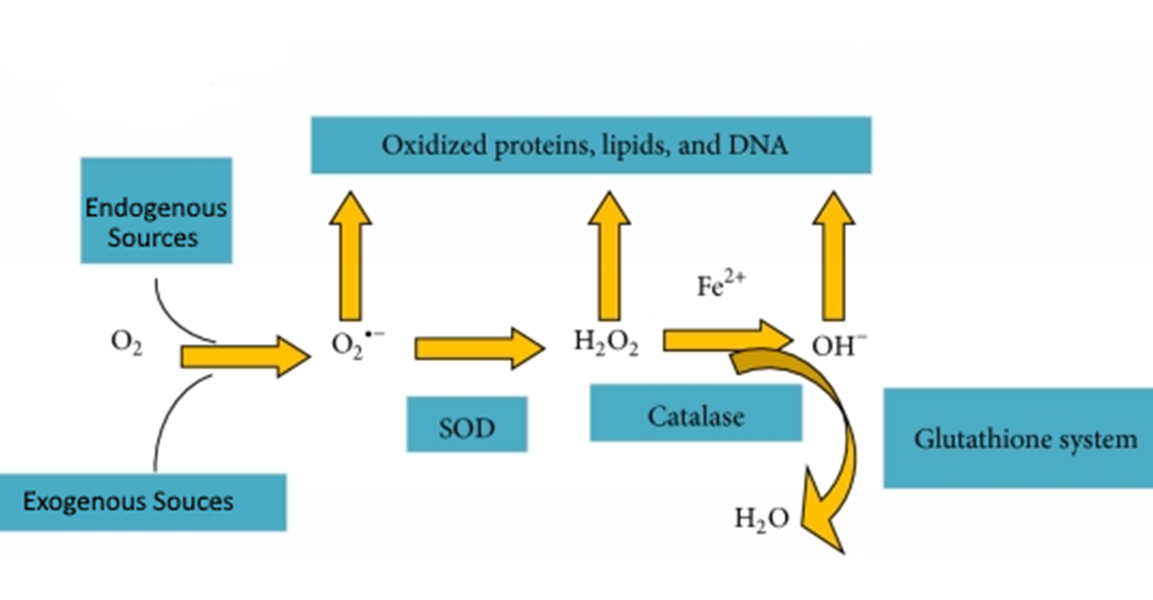
superoxide dismutase
Converts superoxide to hydrogen peroxide and oxygen
SOD1 – found in cytosol and mito
SOD2 – found in mito matrix
SOD3 – extracellular
explain the model of superoxide relating to glutathione peroxidase and catalase conversion
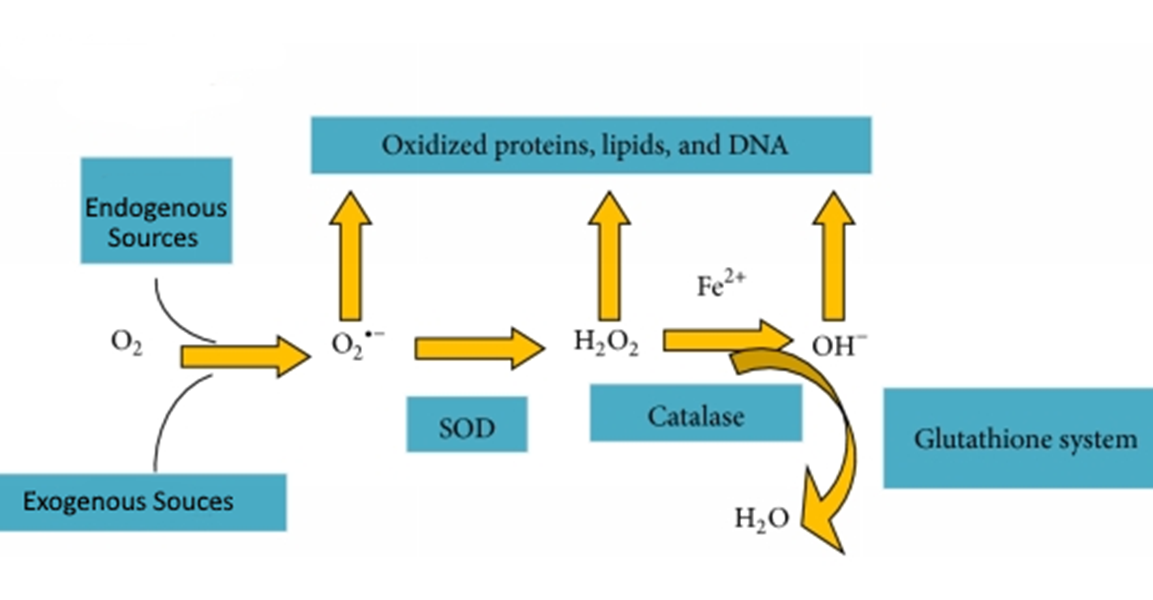
glutathione peroxidase and catalase
Converts hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen
GPx1 – cyt and mito
GPx2 – cyt
GPx3 – ec and cyt
GPx4 – mito and nuclei
GPx5 – ec and membrane
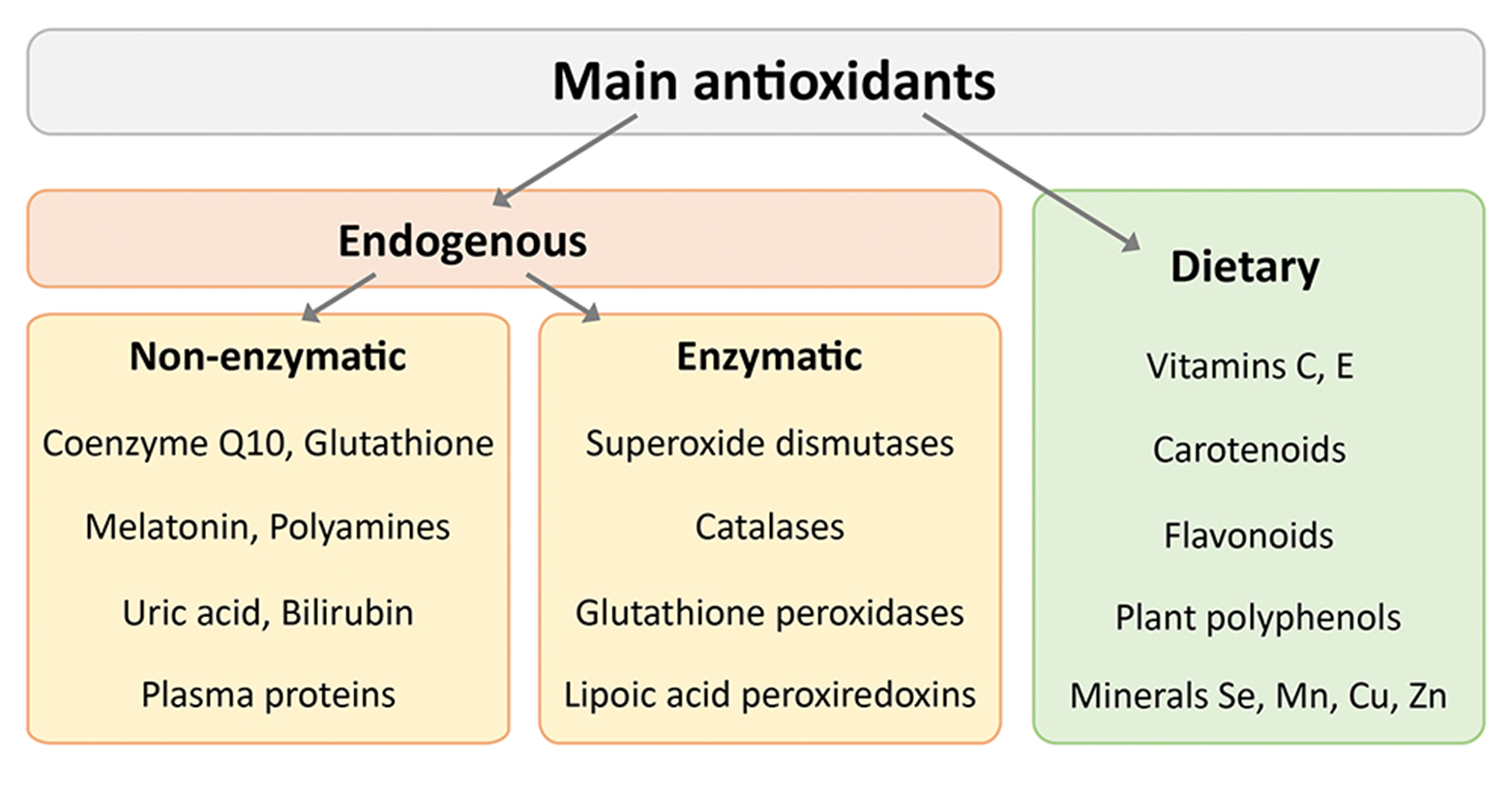
exogenous antioxidants are commonly associated with what? what are the examples?
→ Commonly associated with compounds found in your diet or in supplements
vit E
vit C
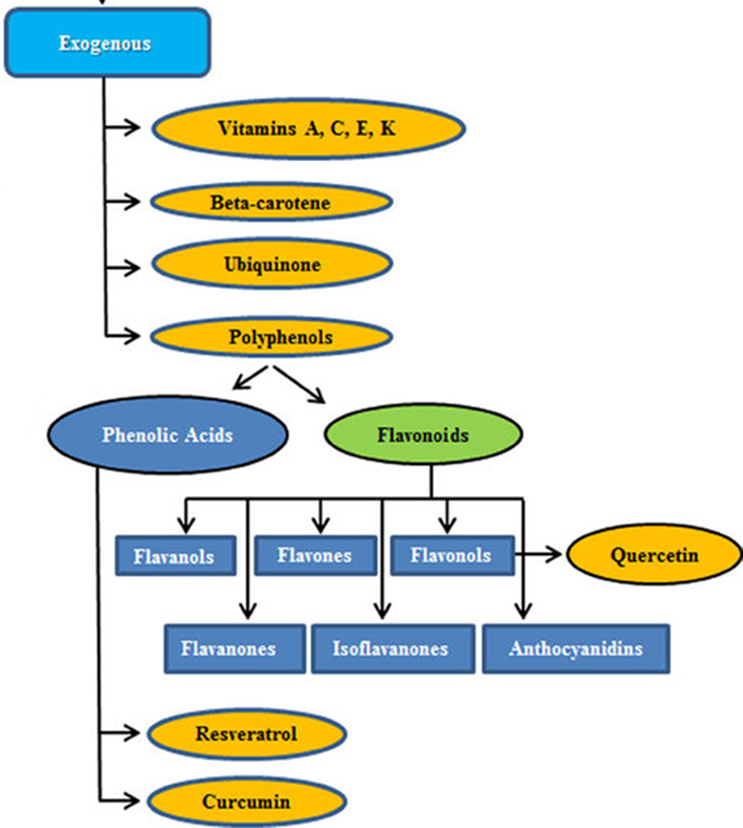
explain vit E
•fat soluble
•Protects against lipid peroxidation
explain vit C
•Water soluble
•Electron acceptor
•Reduces oxidized Vit E
fill in the blank:
vit ___recycles vit____
vit C recycles vit E
balancing free radical chart
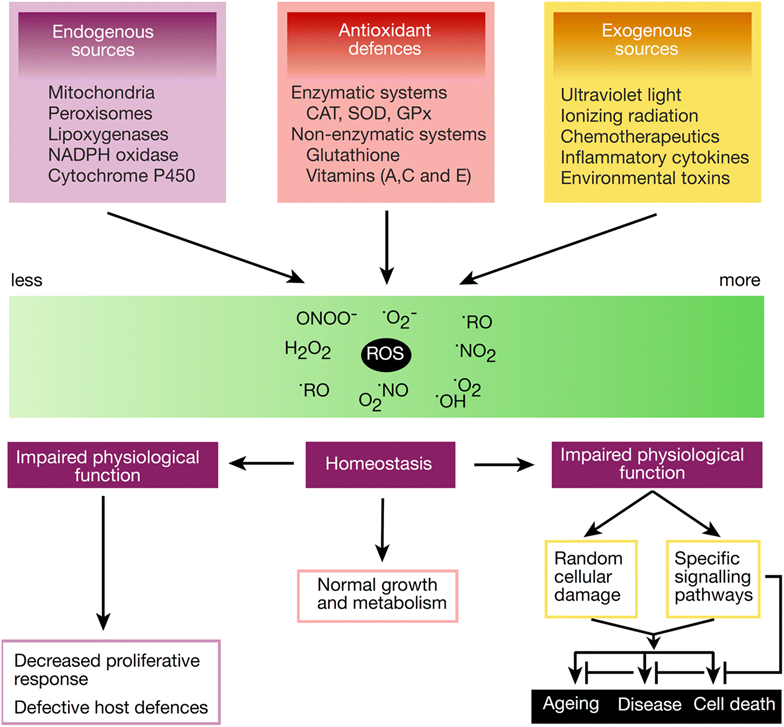
(left side is reductive stress)