Online Biochem
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
What is the angle of a sp3 bond?
109.5
What are the major elements in living organisms?
H,C,N,O,Na,P,S,Cl,K,Ca
What are the angles in a sp2 bond?
120
What shape are sp2 bonds?
Planar trigonal
What the angles in a sp bond?
180
Stereoisomer
Same composition but a different configuration
Configurational isomer
Different arrangements of groups around a chiral center, a single bond must break
Enantiomers
Mirror images, can never be rotated to get the other enantiomer (a bond must break)
Confromations
From rotation around a single bond
Eclipsed
Higher energy, less stable
Staggered
Lower energy, more stable
Configuration
Fixed arrangement of atoms directed by the bonds of a molecule
Biochemical reactions
Matter and energy exhanged
Catabolism
Converting energy to be used
Why does energy need to be convereted?
To do work and anabolism
Phototroph
Uses sunlight as energy
Chemotroph
Energy from chemical molecules
Lithotroph
Inorganic molecules used as fuel
Organotroph
Organic molecules are used as fuel
Autotroph
Fix CO2 to get carbon
Heterotroph
Use organic molecules to get carbon
Energy
The capacity to do work
What is the first law of thermodynamics
Energy is constant, never created or destroyed, only changes forms
What is the second law of thermodynamics?
Energy is transferred to increase entropy
What is gibbs free energy equation?
G=H-TS or DG=-RTln(keq)
Enthalpy
Total energy in a system
Free energy
Energy available to do work
Spontaneous
Negative DG, exergonic, DH<TS, energy released, products more stable than reactants
Nonspontaneous
Endergonic, positive DG, products less stable than reactants
Equilibrium
No net change between products and reactants, no work is done
What is the equation to find the equilibrium constant?
K=[P]/[R]
Le Chateliers principle
When equilibrium is disturbed, the system will correct this change and move back to equilibrium
Draw the structure of an amino acid
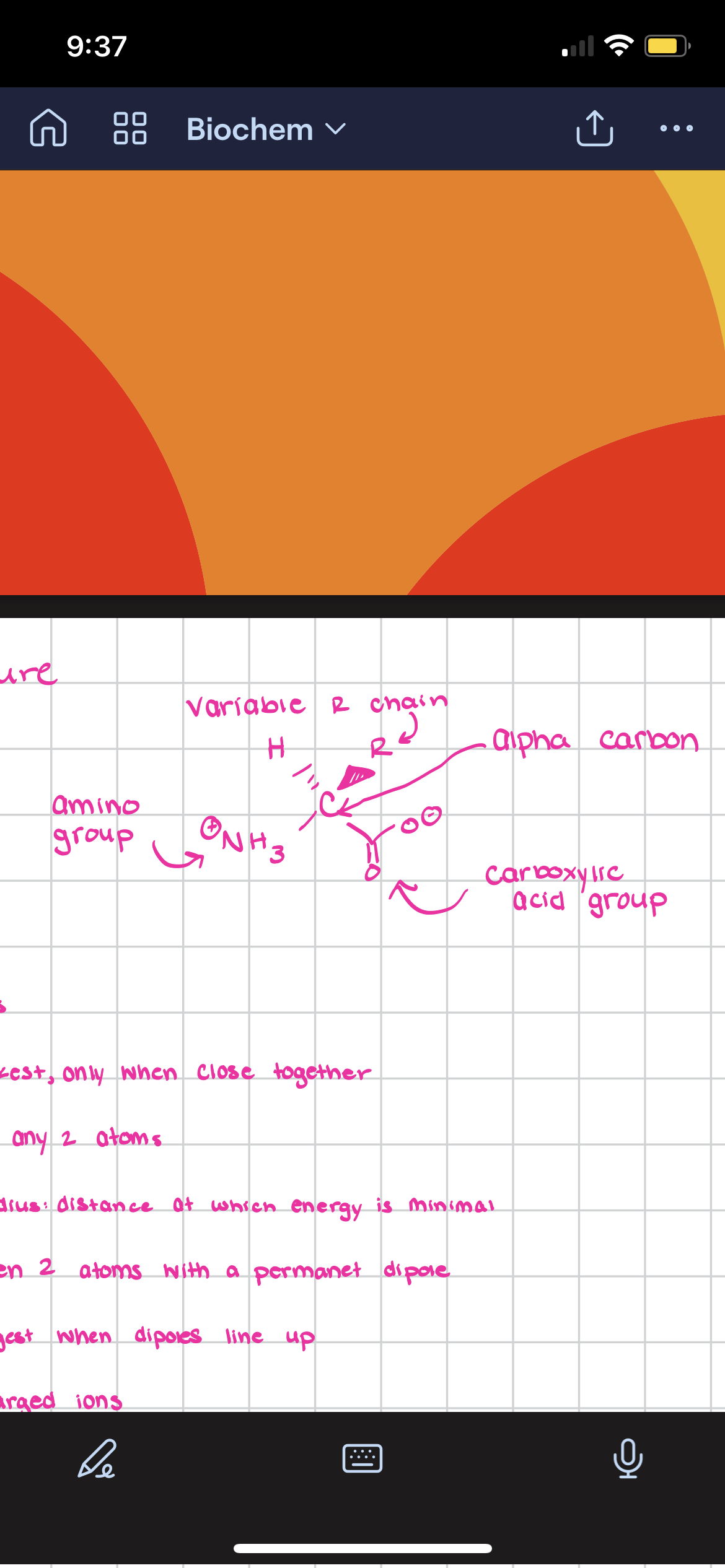
Zwitterion
Has a positive and a negative charge
Why does binding need energy input?
Due to loss of entropy
Sulfhydryl
Very reactive, forms disulfide bonds in extracellular conditions
Where do disulfide bonds form?
In extracellular conditions (oxidizing), inside of cells it is reducing
Glycine
Not chiral, important for folding
Proline
Cyclic, conformationally restricted
What are the types of secondary structures of proteins?
Helix, beta sheet, and loop
How do peptide bonds form?
Condensation reaction
Peptide bond
Unbranched, planar, no rotation, must be cis or trans
Is cis or trans favored for a peptide bond?
Trans, except when proline is the terminal amino acid
Phi
Bond between N and the alpha C
Psi
Between carbonyl carbon and alpha carbon
How are phi bonds measured?
Look down the bond from the N to the terminal alpha carbon, then measure the angle between the carbonyl carbons
How are psi bonds measured?
Look down N to the terminal alpha carbon, measure the angles between the Ns
Ramachadran plot
Areas of dihedral angles that phi/psi that are allowed for regular proteins, have minimized steric clashses
What allows secondary structures to form?
Multiple bonds in a row being in the same plot area, polar groups forming H-bonds
Helix
carbonyl of x bonds with the amino group of x+4, 3.6 residues per turn, side chains point out
Beta sheet
Multiple beta strands joined through H-bonds, side chains perpendicular to H-bonds, can be parallel anti parallel or both, sides of sheets have different properties
Loop
Can be any combination of plot areas, connect secondary structures, many small and polar residues, form active sites, flexible, proline and glycine here often
How are peptide bonds named?
Cis (0) and trans (180)
Alcohol dehydrogenase
Enzyme that is important in energy metabolism
Primary structure
Amino acid sequence
What geometry does an alpha carbon have?
Tetrahedral
What geometry does a carbonyl carbon have?
Trigonal
What atoms connect to form a peptide bond?
Carbonyl carbon and nitrogen
Imino acid
R group connects with N and carbonyl C, no h to h bond with, breaks alpha helixes