Theme 12-An Overview of Animal Diversity
1/109
Earn XP
Description and Tags
About animals
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
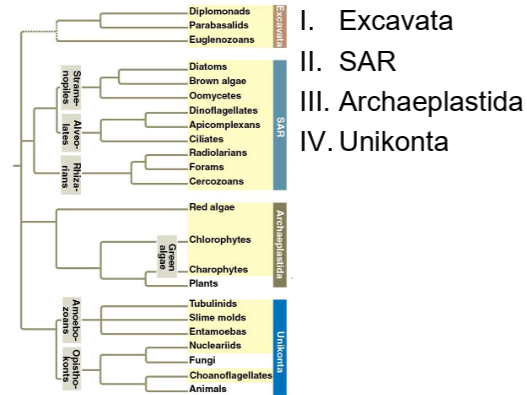
What are the four supergroups of Domain Eukaryote?
Excavata, SAR, Archaeplastida, and Unikonta.
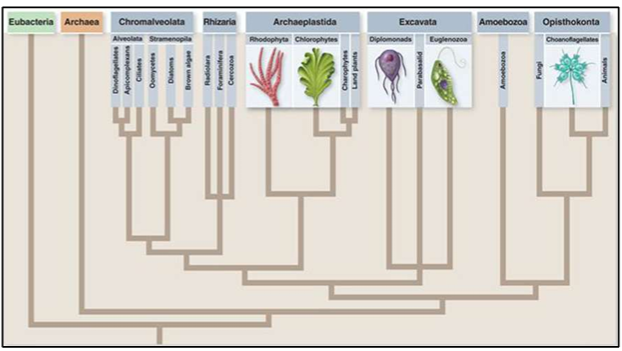
What types of organisms are included in Domain Eukaryote?
Plantae, Fungi, Animalia, and Protists.
What do all eukaryotes have in common?
Cells with a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
Which eukaryotic supergroup includes animals and fungi?
Unikonta.
Which eukaryotic supergroup includes plants and green algae?
Archaeplastida.
Which eukaryotic supergroup includes many protists with unique flagella and feeding grooves?
Excavata.
Which eukaryotic supergroup includes Stramenopiles, Alveolates, and Rhizarians?
SAR.
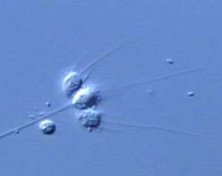
What are choanoflagellates?
Unicellular protists that are the closest living relatives of animals.
How do choanoflagellates move?
They use a single posterior flagellum for propulsion.

What cell type in animals are choanoflagellates morphologically similar to?
Choanocytes (collar cells) found in sponges.
Where are modern choanoflagellates commonly found?
In shallow freshwater and marine environments.
What is the typical structure of modern choanoflagellates?
They are tiny, stalked organisms that attach to surfaces.
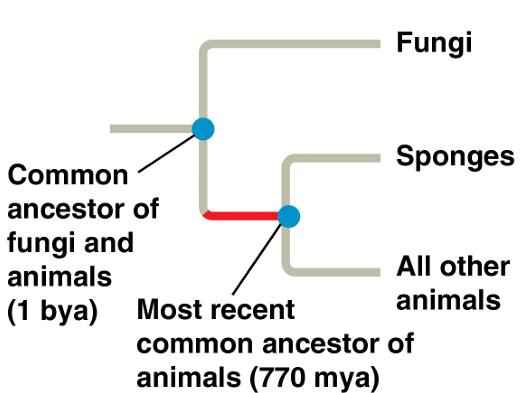
What is the most primitive animal group?
Sponges (Phylum Porifera).

To which phylum do sponges belong?
Phylum Porifera.
What is the Cambrian Explosion?
A period of rapid diversification of animal life that occurred during the Cambrian era (540–485 million years ago).

What is significant about the Cambrian Explosion in evolutionary history?
It marks the earliest fossil appearance of many major groups of living animals.
What is the central principle of biology regarding organisms?
Biology is ultimately about survival and reproduction — passing genes to the next generation.
Why is evolution considered a “race” or a “competition”?
Because individuals compete to pass more of their genes to the next generation than others.
How can an organism gain an advantage in survival and reproduction?
Through changes in morphology, physiology, behavior, or life history that:
Make it superior to others
Allow it to exploit alternative resources
What does it mean to “exploit alternative resources” in an evolutionary context?
Using different food sources, habitats, or strategies to reduce competition and increase reproductive success.
What cellular feature separates animals from prokaryotes and many protists?
Being multicellular eukaryotes.
Are all animals multicellular?
Yes, all animals are multicellular eukaryotes.
How does multicellularity benefit animals?
It allows cell specialization, tissue formation, and greater complexity compared to unicellular organisms.
What does “advanced animal” imply in this context?
It refers to animals with complex organization, including tissues, organs, and specialized systems.
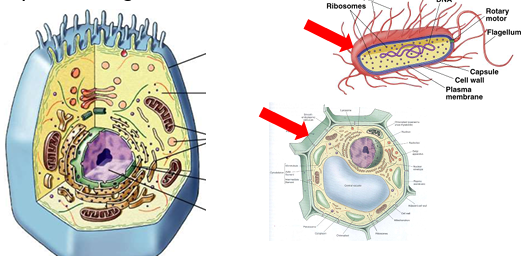
Do animal cells have cell walls?
No, all animal cells lack cell walls.
What structural feature do cell walls provide in other organisms?
They provide structural support for prokaryotes, some protists, plants, and fungi.
How does the absence of cell walls distinguish animals from plants and fungi?
Animal cells are flexible and can form tissues and organs, unlike the rigid cells of plants and fungi.
Why is the lack of a cell wall important for animal cells?
It allows cell movement, shape change, and complex interactions, which are crucial for multicellularity and tissue specialization.
If animal cells lack cell walls, what holds them together?
Extracellular proteins, especially collagen.
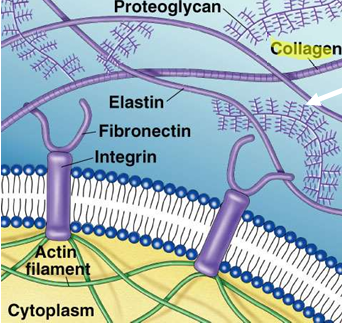
What are the evolutionary advantages of animal cells lacking cell walls?
Flexibility and shape change — allows cells to move and adopt diverse forms.
Complex tissue and organ formation — enables specialization and multicellularity.
Motility — facilitates movement of cells (e.g., during development, immune response).
Dynamic interactions — allows cells to communicate and respond to environment more efficiently.
Are animals autotrophic or heterotrophic?
Heterotrophic — animals cannot synthesize their own food.
How do animals obtain nutrients?
By ingesting preformed organic molecules.
What types of food sources do animals consume?
Animals may eat:
Other living organisms
Parts of living organisms
Dead organic materials
Why is heterotrophy important in animals?
It drives feeding behaviors, digestion, and energy acquisition, which are central to survival and reproduction.
What are the evolutionary advantages of animals being heterotrophs?
Energy efficiency — allows use of preformed organic molecules instead of producing them.
Flexibility in diet — animals can exploit a variety of food sources.
Supports mobility and active lifestyles — energy from heterotrophy fuels movement and predation.
Facilitates complex behaviors — feeding strategies drive competition, social interactions, and adaptation.
How do most animals reproduce?
Sexually, with the diploid (2n) stage dominating the life cycle.
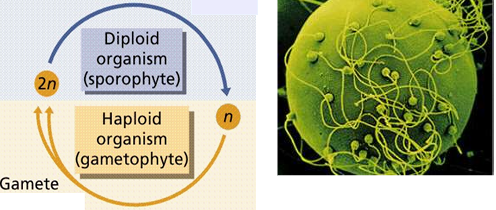
What are the typical gametes in animals?
A small, flagellated sperm and a larger, non-motile egg.
Which stage dominates the animal life cycle?
The diploid (2n) stage.
Why is sexual reproduction advantageous in animals?
It increases genetic variation, enhancing adaptation and survival in changing environments.
What happens to most animal zygotes after fertilization?
They undergo embryonic development, producing multiple tissue layers.
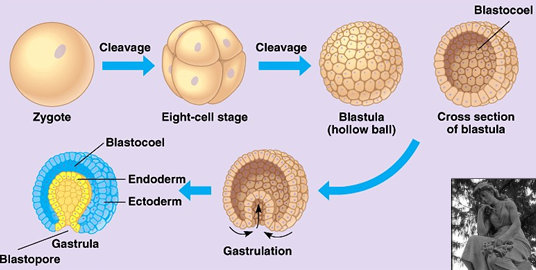
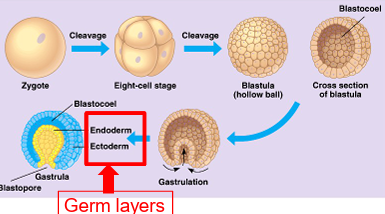
What is a blastula?
A hollow ball of cells formed after successive mitotic divisions of the zygote.
What is gastrulation?
A process where part of the blastula folds inward, forming a blind pouch and producing germ layers.
What are the two germ layers produced in early embryonic development?
Endoderm and ectoderm, which later develop into true tissues.
What is a tissue in animals?
An ensemble of similar cells from the same origin that together carry out a specific function.
Why is the formation of germ layers important?
Germ layers are the foundation for specialized tissues and organs, enabling complex multicellular organization.
What are “true tissues” in animals?
Tissues derived from germ layers that perform specific functions.
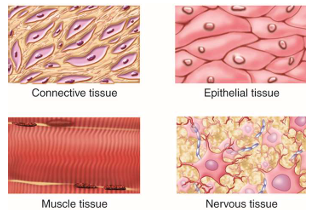
Do most animals have unique tissue types?
Yes, most animals have specialized tissue types.
What is the function of nervous tissue?
Impulse conduction — transmitting signals throughout the body.
What is the function of muscle tissue?
Movement — enabling locomotion and internal movements.
Why are true tissues evolutionarily important?
They allow specialization of cells, leading to more complex body functions and higher adaptability.
Do most animals have a larval stage?
Yes, most animals have at least one larval stage.
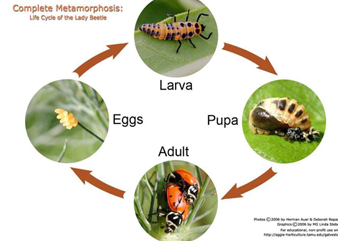
What is a larva?
A sexually immature stage that is morphologically and behaviorally distinct from the adult.
What happens after metamorphosis in animals?
The larva becomes a juvenile, which resembles the adult but is still sexually immature.
Why is a larval stage evolutionarily important?
It allows different life stages to exploit different resources, reducing competition between juveniles and adults.
What are Hox genes?
A unique family of regulatory genes in animals that control development.
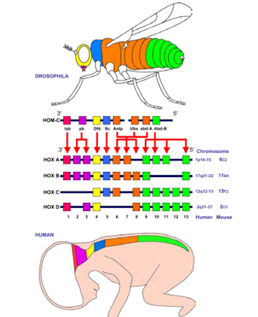
What is the main function of Hox genes?
They regulate the expression of genes that determine body plan and organization during development.
Why are Hox genes evolutionarily important?
They allow for complex body structures and diversity of animal forms.
Are Hox genes found in all animals?
Yes, most animals share this conserved set of developmental genes.
What key characteristics of animals make them efficient consumers?
Heterotrophy – animals ingest preformed organic molecules for energy.
Motility – ability to move to find and capture food.
Specialized tissues – nervous and muscle tissues enable rapid response and movement.
Digestive systems – complex organs allow efficient breakdown and absorption of nutrients.
Sensory and behavioral adaptations – detect, pursue, and exploit various food sources effectively.
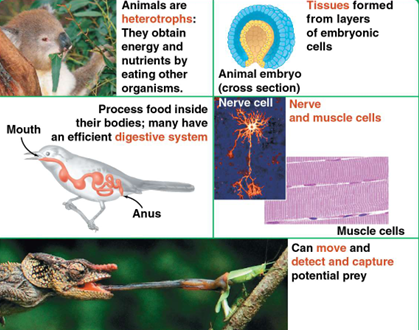
What are the five key events in the evolution of the animal body plan?
1. Tissues
2. Symmetry
3. Body cavity
4. Patterns of development
5. Segmentation
Why is the evolution of tissues important?
Tissues allow specialization of cells to perform specific functions, increasing complexity.
What is the significance of symmetry in animals?
Symmetry (radial or bilateral) helps with movement, sensory perception, and body organization.
Why is the evolution of a body cavity important?
A body cavity (coelom) provides space for organs, organ development, and better movement.
What is meant by patterns of development in animal evolution?
Refers to embryonic development processes, like cleavage, gastrulation, and germ layer formation, that determine adult body plans.
Why is segmentation significant in animals?
Segmentation allows repetition of body units, specialization of segments, and greater flexibility and mobility.
What does totipotent mean in animal zygotes?
Can become any cell type.
Are totipotent cells reversible in all animals?
No, except in sponges.
From what do true tissues develop?
Germ layers.
What is special about tissue cells?
They have specialized, irreversible functions.
Why are sponges simple regarding tissues?
No true tissues, cells are unspecialized and flexible.
Why is tissue specialization important evolutionarily?
Enables complexity and diversification.
What is the earliest and simplest animal group?
Sponges (Phylum Porifera).
Do sponges have true tissues?
No, they have unspecialized cells but not true tissues.
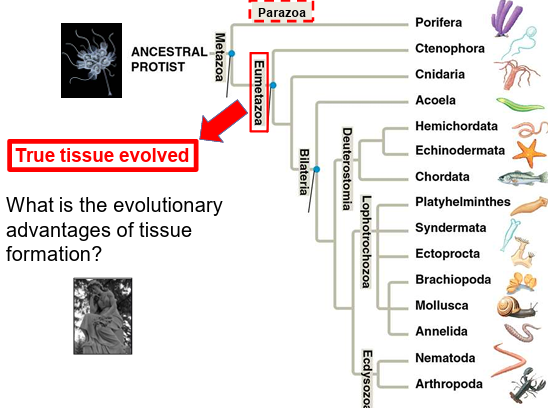
What are the two main branches of animals?
Parazoa and Eumetazoa.
What are the characteristics of Parazoa?
Lack true tissues and lack symmetry.
What are the characteristics of Eumetazoa?
Have true tissues and have symmetry.
Which animals have radial symmetry?
Cnidaria and Ctenophora.

What is radial symmetry?
Body parts arranged around a central axis, bisected into equal halves in any 2-D plane.

Which animals have bilateral symmetry?
All other phyla and some Ctenophora.

What is bilateral symmetry?
Body has right and left halves that are mirror images, bisected only by the sagittal plane.
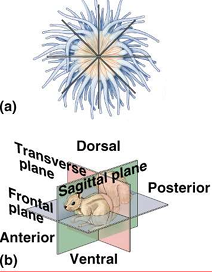
What are the two main advantages of bilateral symmetry?
1. Cephalization – brain development and directional movement
2. Greater mobility

What is cephalization?
Evolution of a definite brain area and purposeful, directional movement.
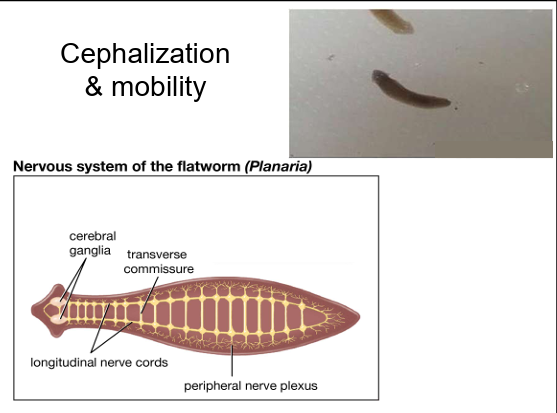
How many germ layers do radially symmetrical animals have?
Two (diploblastic): ectoderm and endoderm.

How many germ layers do bilaterally symmetrical animals have?
Three (triploblastic): ectoderm, endoderm, mesoderm.

Which symmetry is associated with triploblastic animals?
Bilateral symmetry.
What does the ectoderm develop into?
Outer covering (epidermis, hair, nails, enamel) and central nervous system.
What does the endoderm develop into?
Lining of the digestive tract and associated organs (e.g., liver, lungs).
What does the mesoderm develop into?
Skeletal and muscle systems and most other organs between the digestive tract and outer covering.
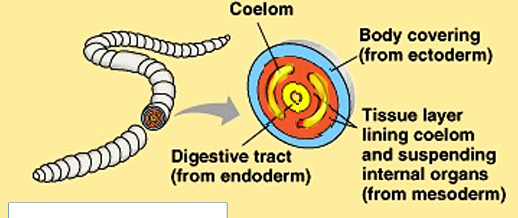
What is a body cavity (coelom)?
A space surrounded by mesoderm tissue, separate from the digestive cavity.
What are the functions of a body cavity?
1. Provides a rigid structure (hydroskeleton) for muscles to act against
2. Allows internal organs to grow and move independently
3. Cushions organs and helps transport nutrients and waste
What is the medium inside body cavities?
Fluid-filled in most animals, gas-filled in vertebrates.
How does a hydroskeleton function in animals?
Works like a tube man — fluid-filled cavity provides rigid support for muscles to act against.

How does water in a hydroskeleton help animals?
The fluid pressure stabilizes the body, allowing movement, especially in aquatic environments.
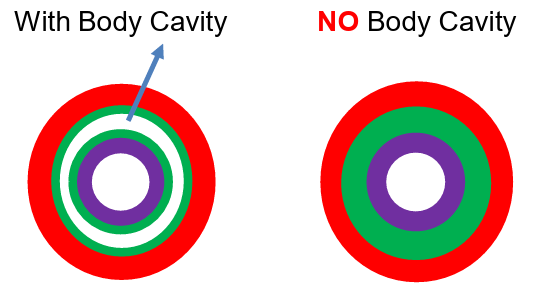
Do all animals with a mesoderm have a true body cavity (coelom)?
No, some have mesoderm but lack a true coelom.
What does this imply about animal body plans?
Presence of mesoderm does not always mean a coelom is present; body cavities vary in complexity.
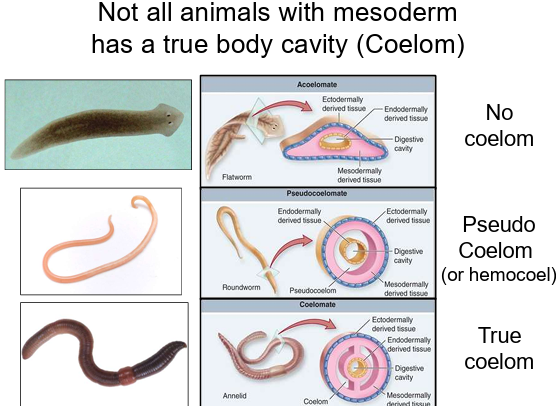

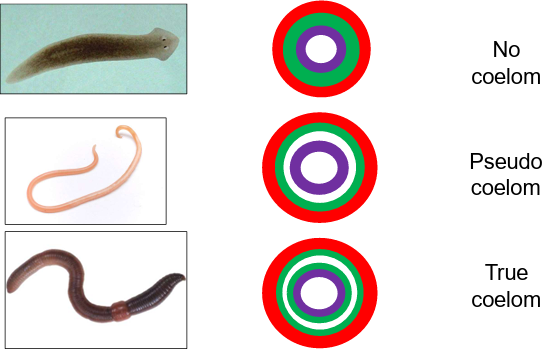
What is a coelomate?
Body cavity entirely within the mesoderm (e.g., earthworm).
What is a pseudocoelomate?
Body cavity between mesoderm and endoderm (e.g., roundworm), called pseudocoelom or hemocoel.

What is an acoelomate?
No body cavity (e.g., flatworm).

Do most bilaterians have a body cavity?
Yes, but the type varies (coelom, pseudocoelom, or none).
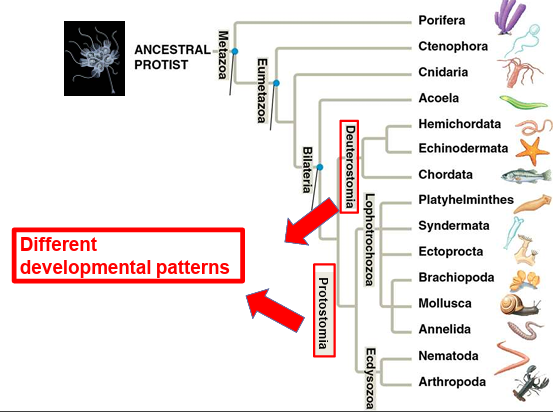
What are the two main developmental directions of the blastula in bilateria?
Protostomia and Deuterostomia.