Lecture 4: Spinal Fractures 1 (Intro, Upper and Lower C/S)
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What are the 2 Types of Spinal Injury?
Stabe Injury
Unstable Injury
Types of Spinal Injury:
Define:
Stable Injury
Unstable Injury
Stable:
Vertebral component will NOT BE displaced by normal movement
Unstable:
There is a risk that normal movement WILL LEAD TO displacement and resulting spinal tissue injury
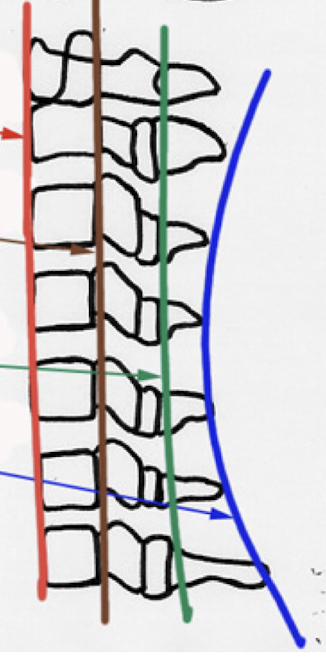
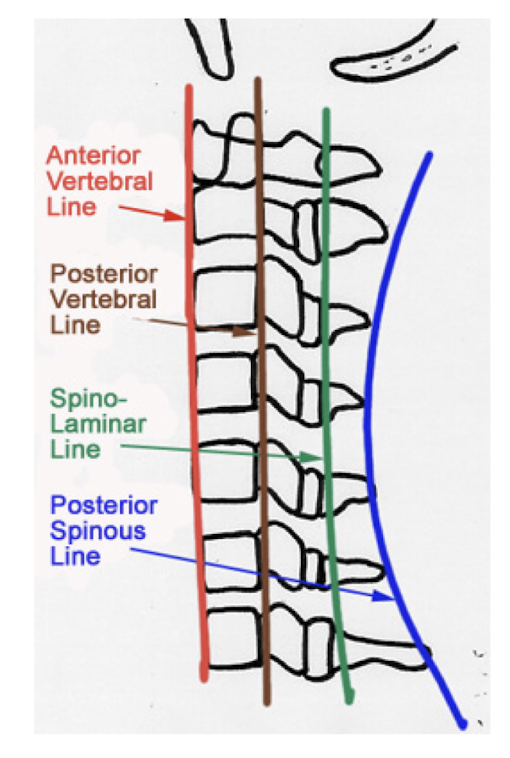
Label these 4 Lines? (C/S)
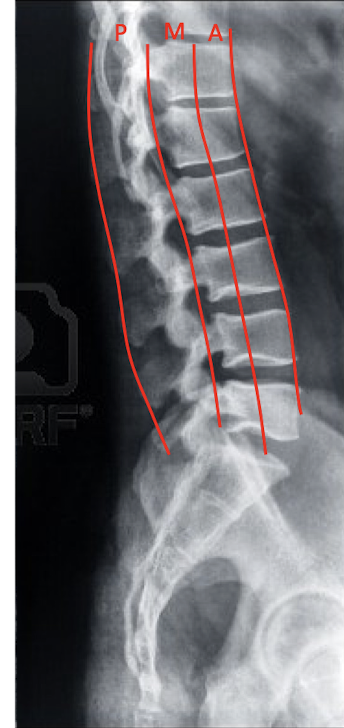
Spinal Column Fracture:
Define the 3 Column Concept:
Anterior Column
Middle Column
Posterior Column
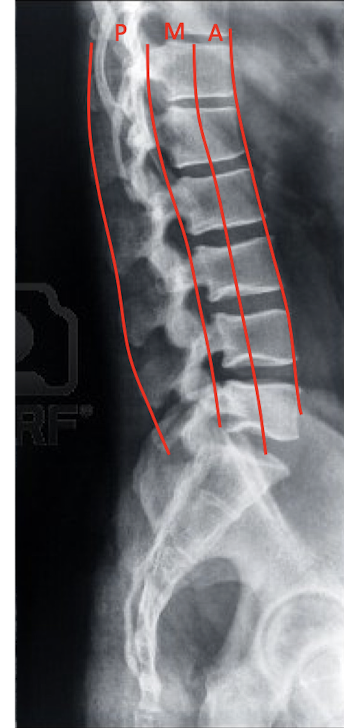
3 Column Concept:
What structures are included in:
Anterior Column:
2
Middle Column:
2
Posterior Column:
4
Anterior Column
Anterior Longitudinal Ligament
Ant. 2/3 of Vertebral Body
Middle Column
Posterior 1/3 of the Vertebrae
Posterior Longitudinal Ligament
Posterior Column
Posterior Ligament Complex
Vertebral Arch
Facets
Ligamentum Flavum
Spinal Column Rules:
What are the 3 Spinal Column Rules?
Spinal Cord and Canal are located Posterior to the Middle Column in the Posterior Column
Fx in the Posterior and Middle Column have potential to encroach on the Spinal Cord and Canal
MRI is needed to determine the level of injury, if any, to the spinal cord
Three Column Concept:
Fractures involving ONE COLUMN are ___.
Fractures involving THREE COLUMNS are ___.
Fractures involving TWO COLUMNS depends on what? (2)
If the Middle Column is Intact, it is usually a ___ injury.
One Column:
Stable
Three Columns:
Unstable
Two Columns
May or may not be unstable
Depends on the severity of the injury
Middle is intact
Stable
Upper C/S Fx
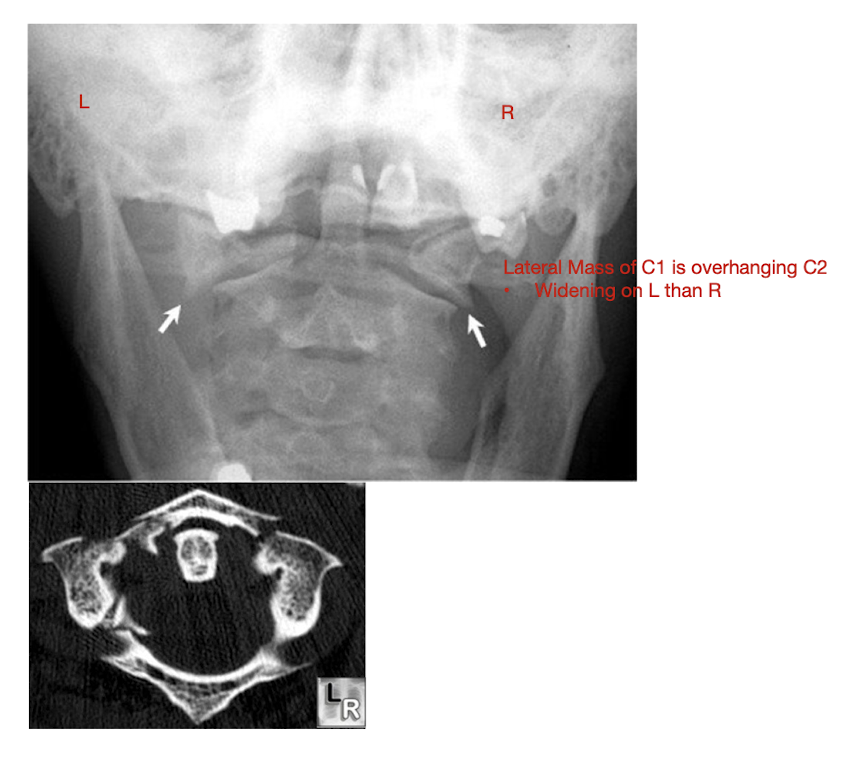
Fracture of C1: Jefferson Fx
What type of Fx is a Jefferson Fx?
AKA:
MOI:
Structures affected:
Compression Fx
MOI:
Hyper Ext or Flexion Injury of the Head
AKA:
Burst Fx
Structures affected:
Anterior and Posterior Arches of the Atlas
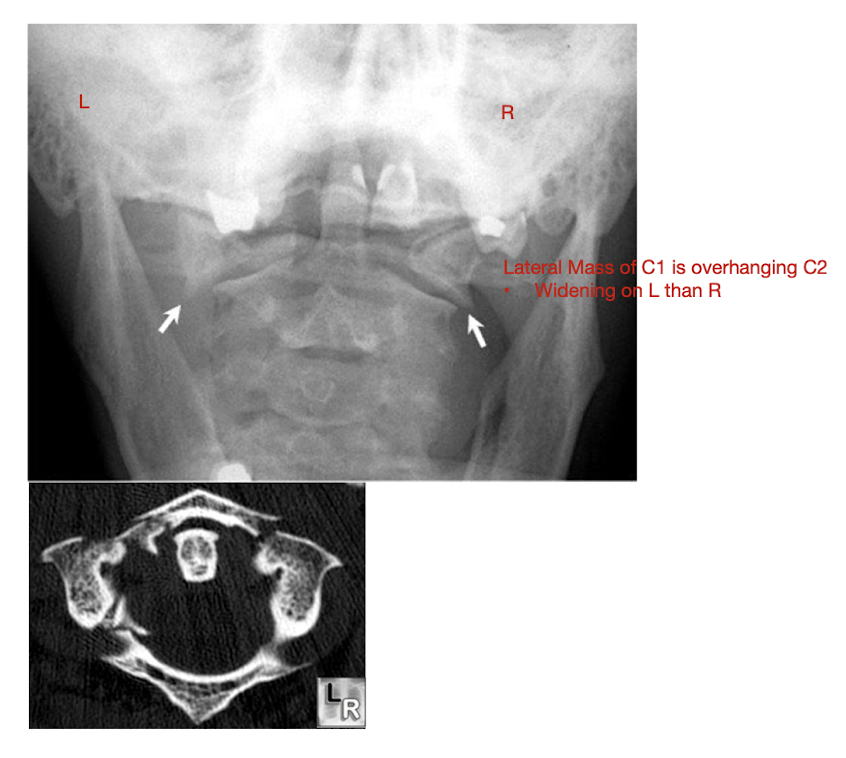
Fracture of C1: Jefferson Fx
Rarely causes ___ injury
What direction of neck movement can cause head to slide forwards and compress SC?
Requires what type of view to diagnose?
Note displacement of what structure?
Neurological Injury
Fwd flex w Jefferson Fx
Open mouth view
Lateral Mass Displacement
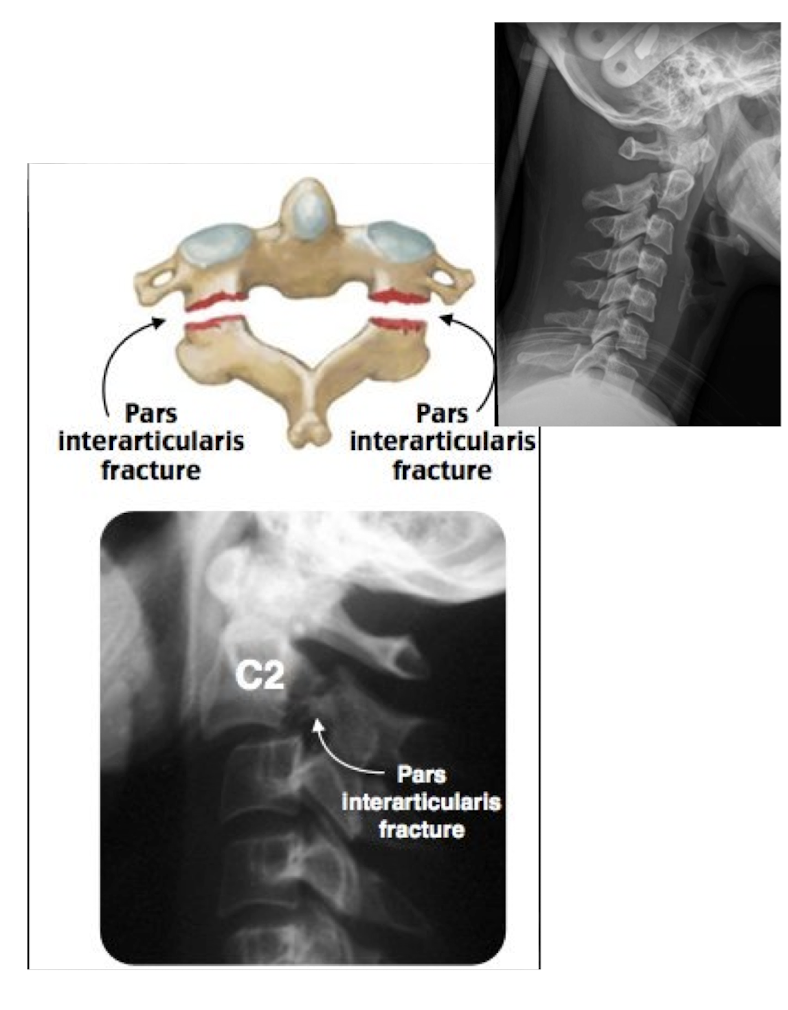
Fracture of C2: Hangman’s Fx
What type of Fx is this?
Bilateral Fx of the pedicles of C2 w dislocation of vertebral body C2 on C3
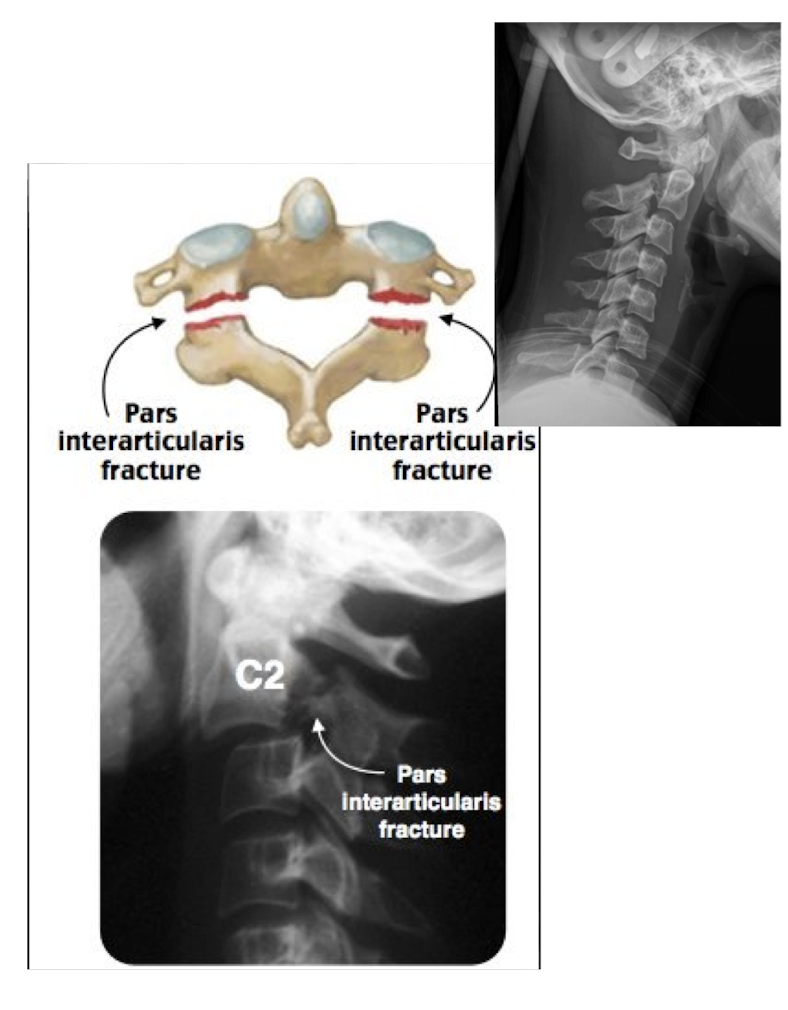
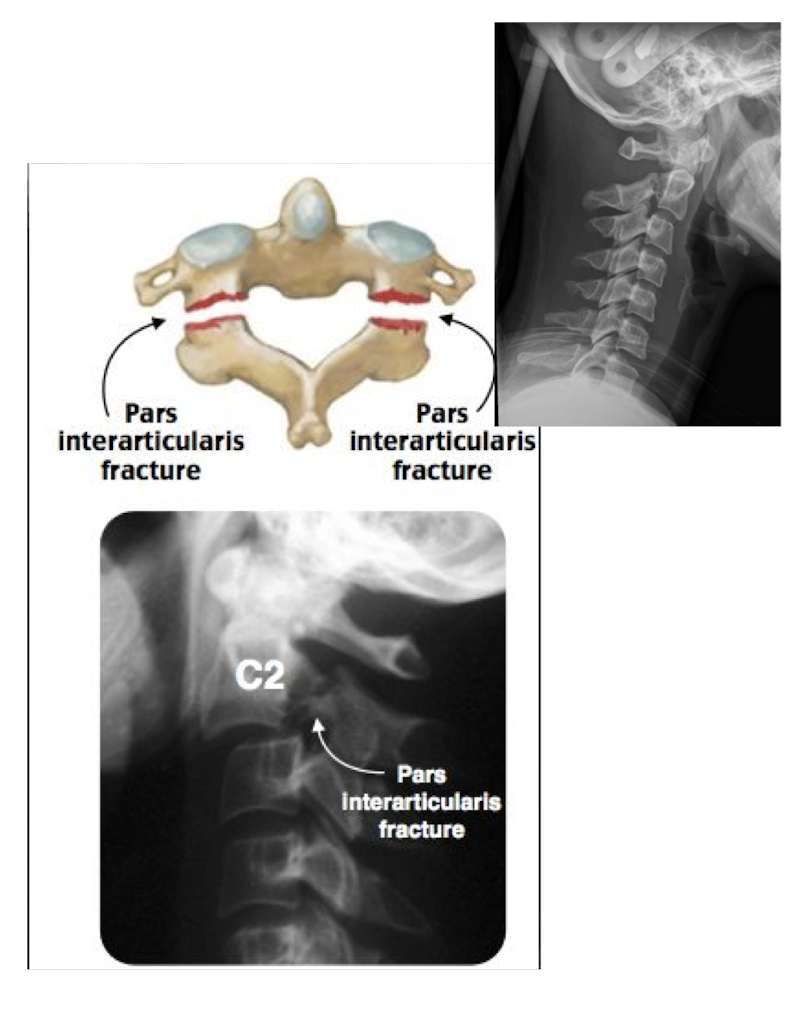
Fracture of C2: Hangman’s Fx
MOI:
__ for info on the SC
Stable or Unstable Fx
MOI:
Hyper Extension Injury in MVA
MRI
Unstable
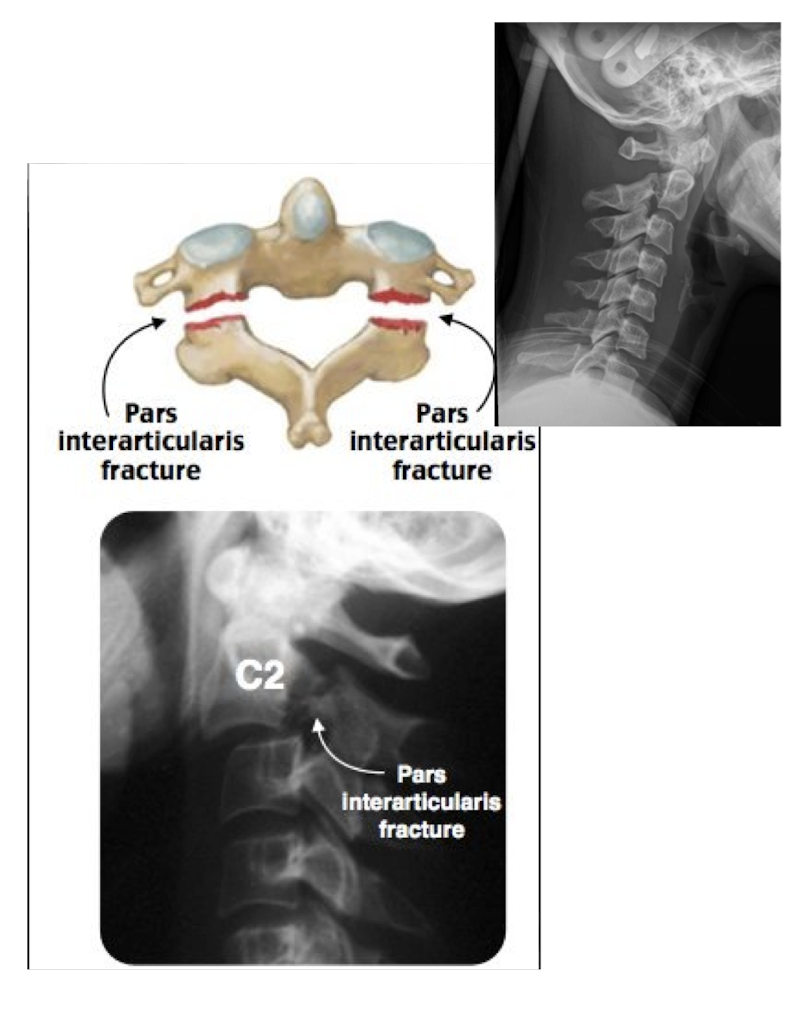

Fracture of the Axis: Dens
AKA:
__% of C/S Fx
Higher chance of __ involvement due to attachments of what 2 ligaments?
MC:
Often occurs w __ trauma
AKA:
Ondontoid Fx
20%
Neurological Involvement due to attachments of Alar and Transverse Ligs
MC C/S Fx for ≥ 65
Minimal Trauma
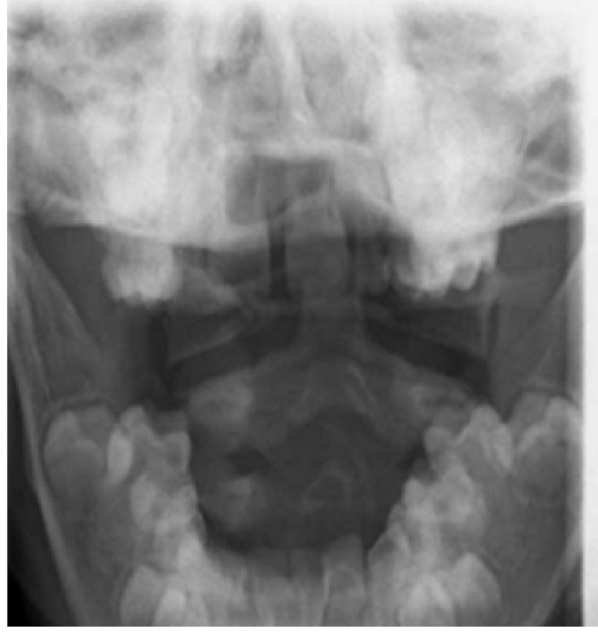
Fracture of the Axis: Dens
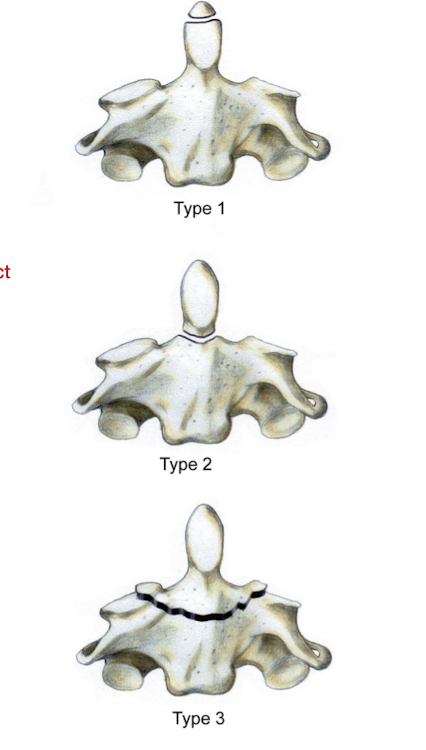
What are the 3 types of Odontoid Fractures?
Type 1:
Avulsion of the Hip
Type 2:
At junction of dens on the body of the axis
Type 3:
Below the junction of the dens
Fracture of the Axis: Dens
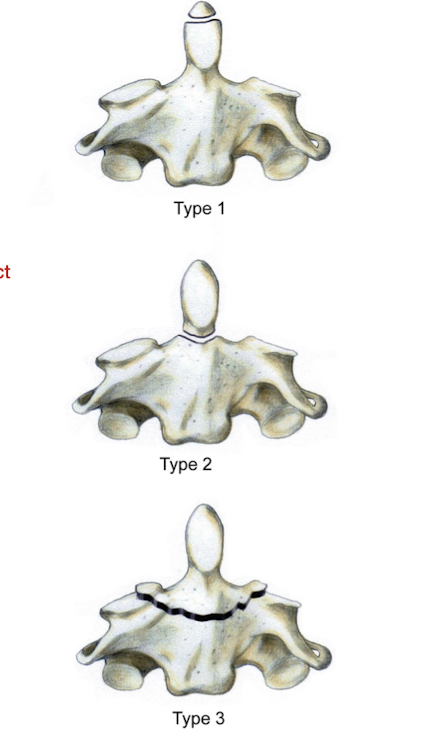
Which of the 3 types of Odontoid Fx is the most difficult to heal?
Why?
Type 2
Intact transverse and alar lig w poor bony contact
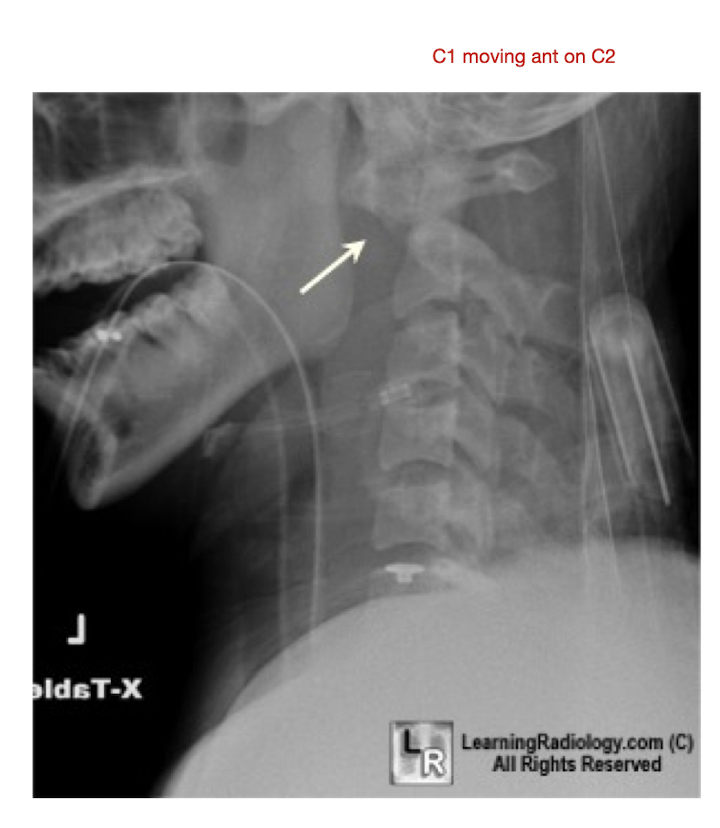
C/S: RA
What is it?
What does RA cause?
What 3 structures does it affect?
What is it?
Erosion and narrowing of the facet jts
Cause:
Increased Lig Laxity
Atlantoaxial Jt
Laxity of the Transverse Lig
Anterior Subluxation of C1 on C2
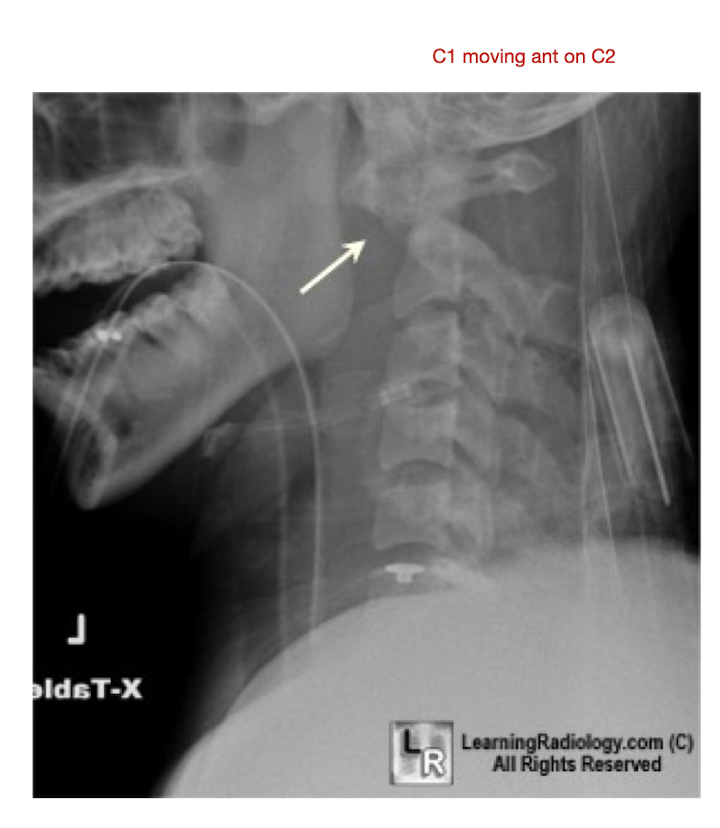
Lower C/S Fx: C3-C7
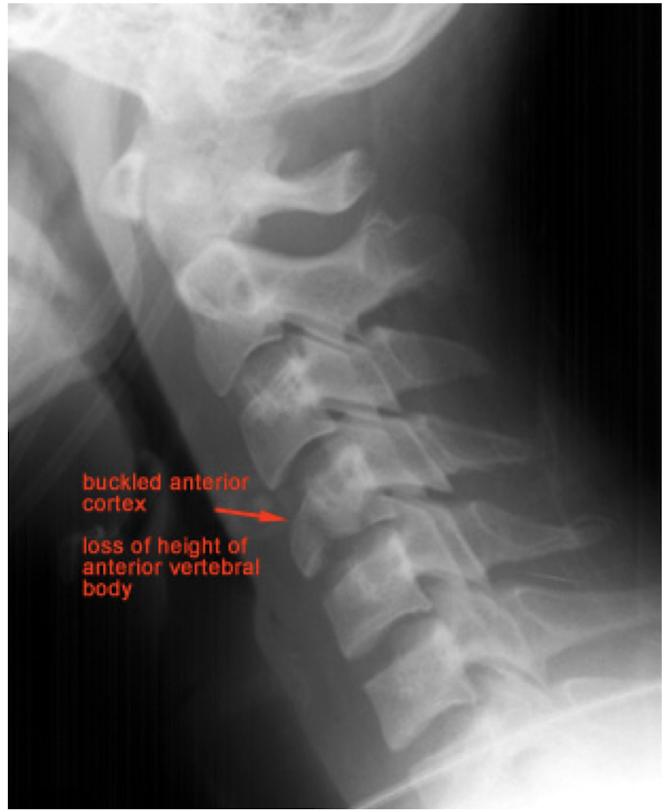
Fracture of C3-C7: Wedge Fx
MOI:
2
Stable or Unstable Fx?
MOI:
Hyper Flexion Injury
Ant Vertebral Compression of the vertebrae by adjacent vertebrae above and below
Stable
Notice: Post Vertebrae Intact, Ant Vertebrae w Fx
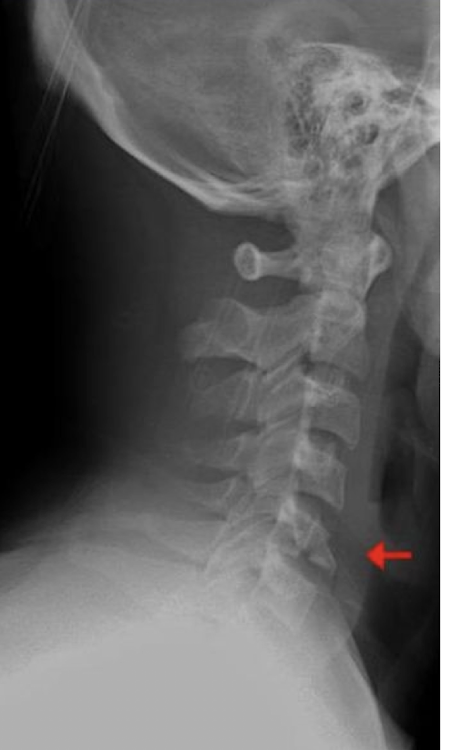
Fracture of C3-C7: Burst Fx
How does it occur?
2
Stable or Unstable Fx?
How:
Axially loaded Intervertebral Disc compressed through the adjacent vertebrae
Bursting of the vertebrae w comminution
Possibly Unstable
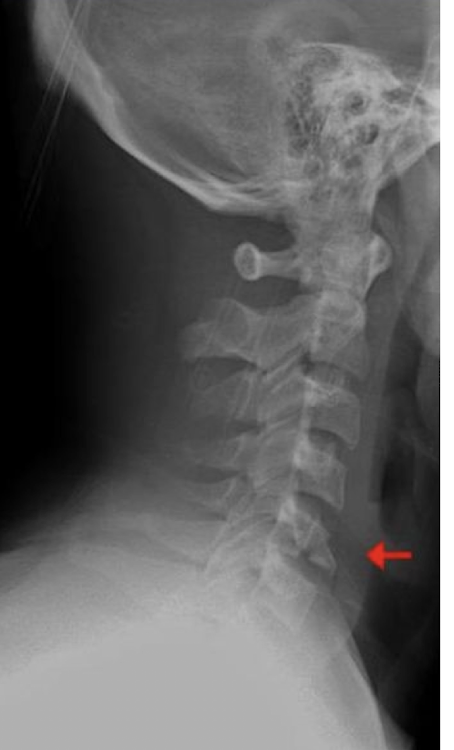
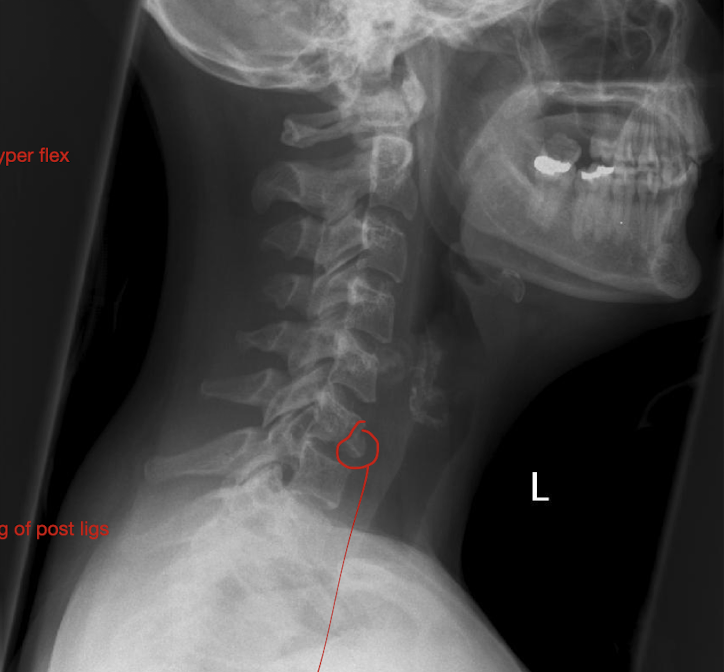
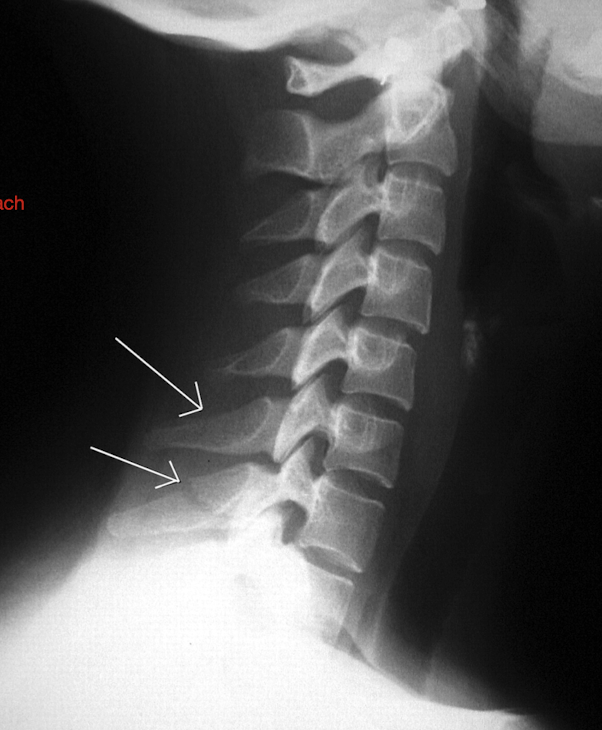
Fracture of C3-C7: Tear Drop Fx
What is this fx known as?
How does it occur?
2
Known as:
Most severe of the Lower C/S Fx (Hyper Flexion)
How:
Separation of a piece of bone from the Anterioinferior border of the vertebral border
Hyperflexion or Hyperextension
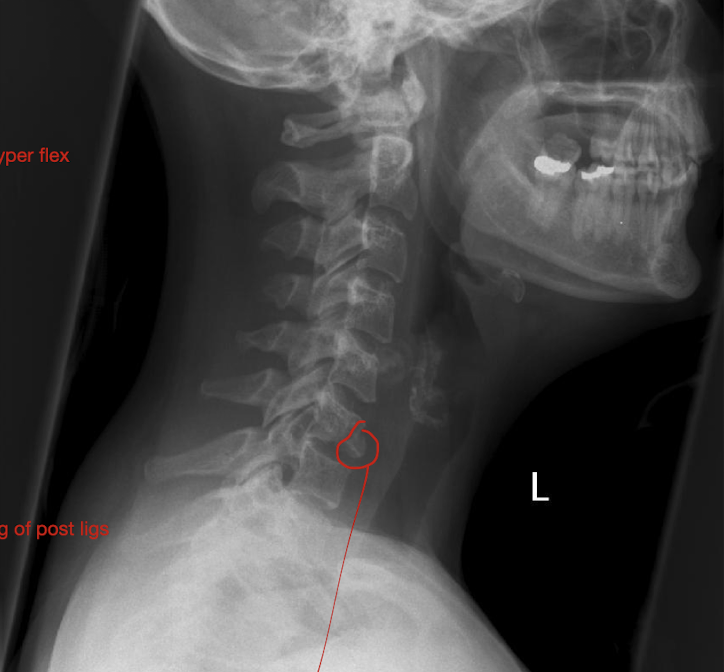
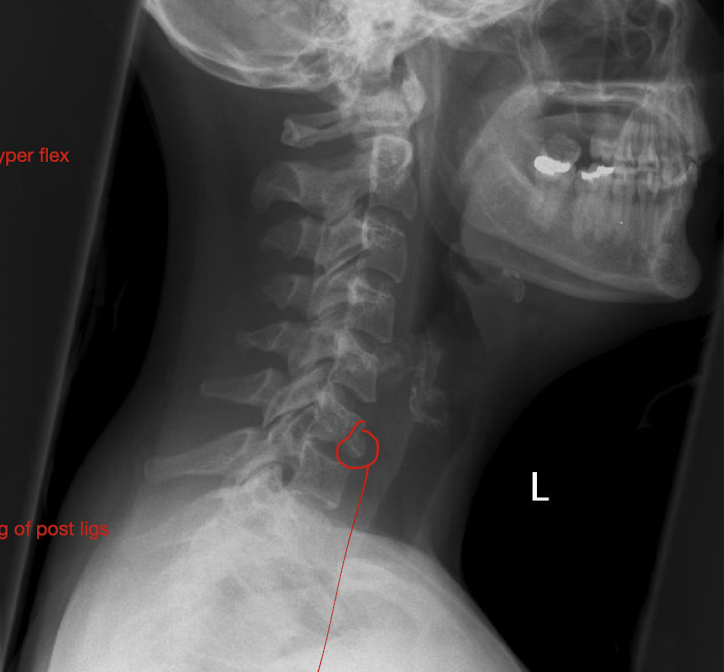
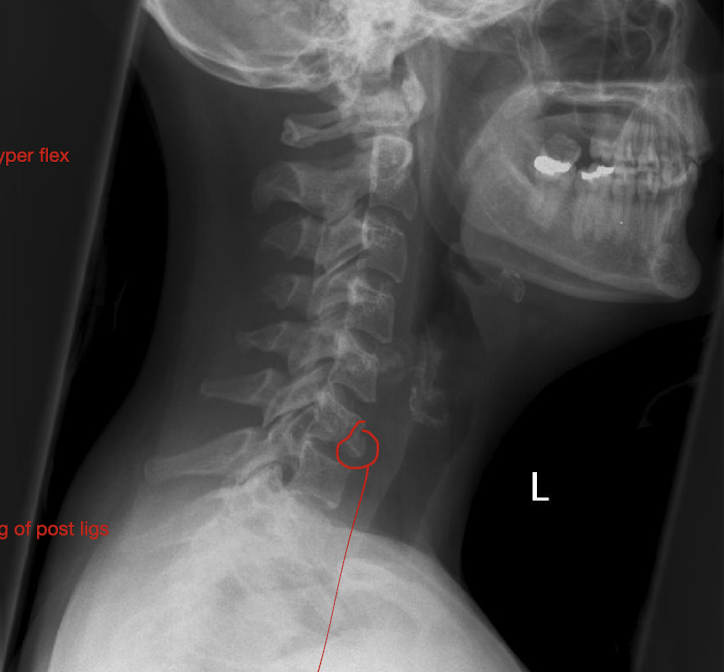
Fracture of C3-C7: Tear Drop Fx
How much force causes pieces to rupture off and tearing of post ligs.
Stable or Unstable Injury
Large Force
Unstabble
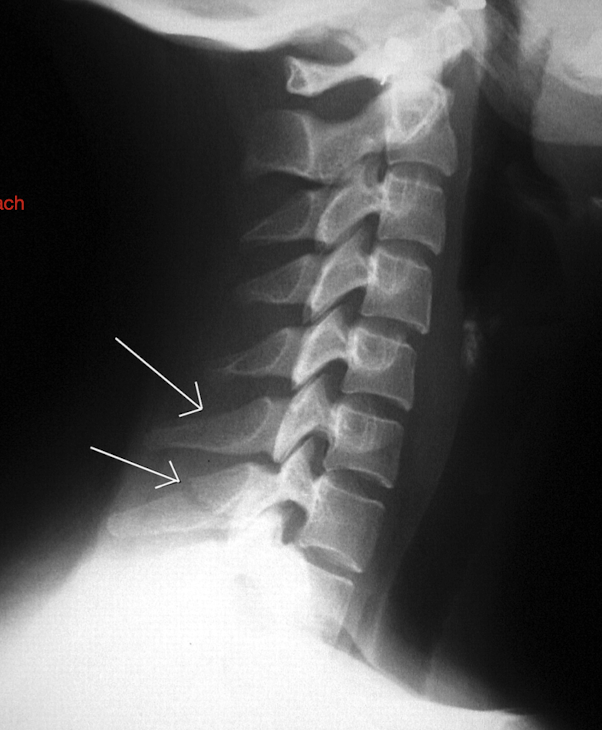
Fracture of C3-C7: Clay Shoveler’s Fx
What type of fx is this?
MOI:
What 3 segments does this fx MC occur?
Stable or Unstable Fx?
Type:
Avulsion fx of the Spinous Process (where Rhomboid or Traps attach)
MOI:
Hyperflexion Force
Forceful contractions of the Trapezius or Rhomboids
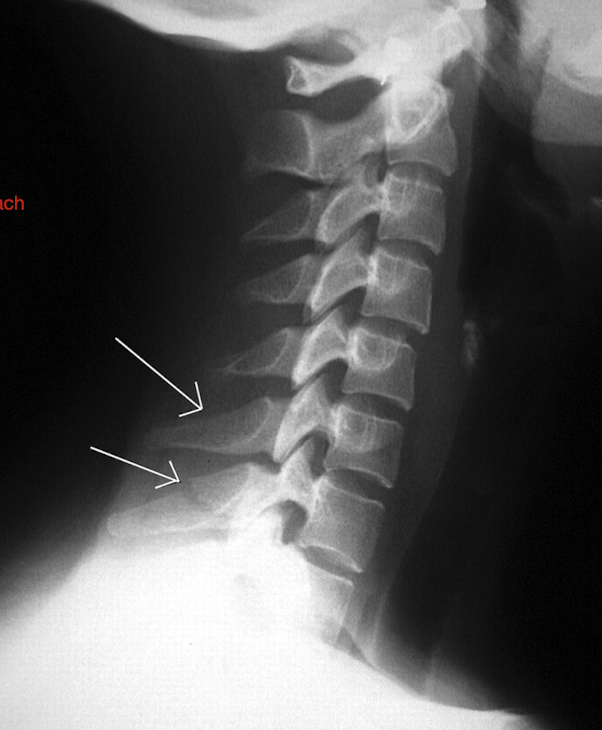
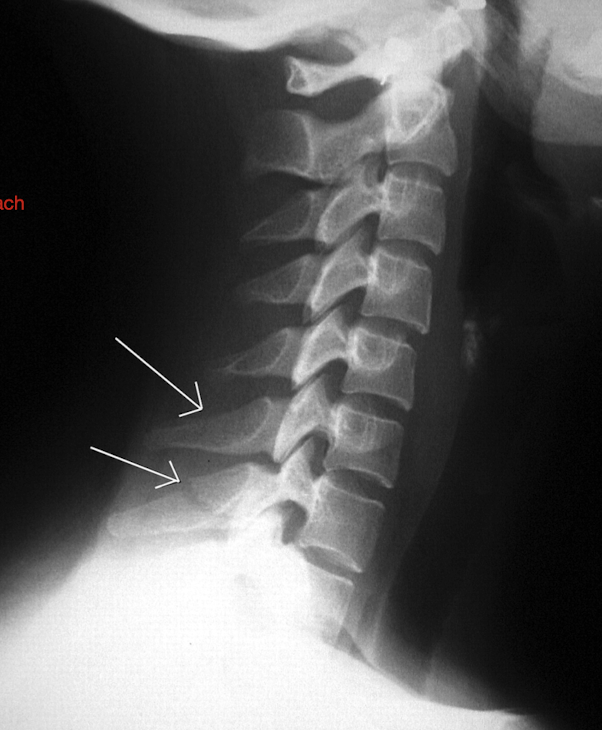
Fracture of C3-C7: Clay Shoveler’s Fx
What 3 segments does this fx MC occur?
Stable or Unstable Fx?
Common Pop:
3 Segments
C6, C7, T1
Stable
Pop:
Throwing Athletes
Dislocation of the C/S:
Dislocation of the C/S usually occurs how? (3)
Ligament rupture
Dens Fx WITH ligament rupture
Unstable Lower C/S
Dislocation of the C/S:
Define:
Dens Fx WITH ligament rupture
Fx dislocation of what 2 segments?
Unstable Lower C/S
Fx combine w what?
__ __ Injury
Dens Fx WITH ligament rupture
Fx dislocation occurs C1-C2
Unstable Lower C/S
Tear of the Post Lig may cause anterior displacement
SC Injury
Dislocations w/o Fx:
What are the 2 main types (in reference to the facet jts)
Self-Reducing
Complete
Dislocation w/o Fx:
Self Reducing:
Define:
Transient __ or __
Do not appear on __
May have __ __ signs of injury
Define:
Articulations are momentarily disengaged and then return to normal
Transient dislocation or subluxation
Radiographs
Soft Tissue signs of Injury
Dislocation w/o Fx:
Complete:
Define:
Can happen __ or __
Define:
Inferior articulating process will lie in front of the superior process
Unilateral or bilateral