AP HUMAN GEOGRAPHY UNIT 5
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Mediterranean climate
a climate type characterized by hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters, typically found on the western sides of continents between 30° and 45° latitude
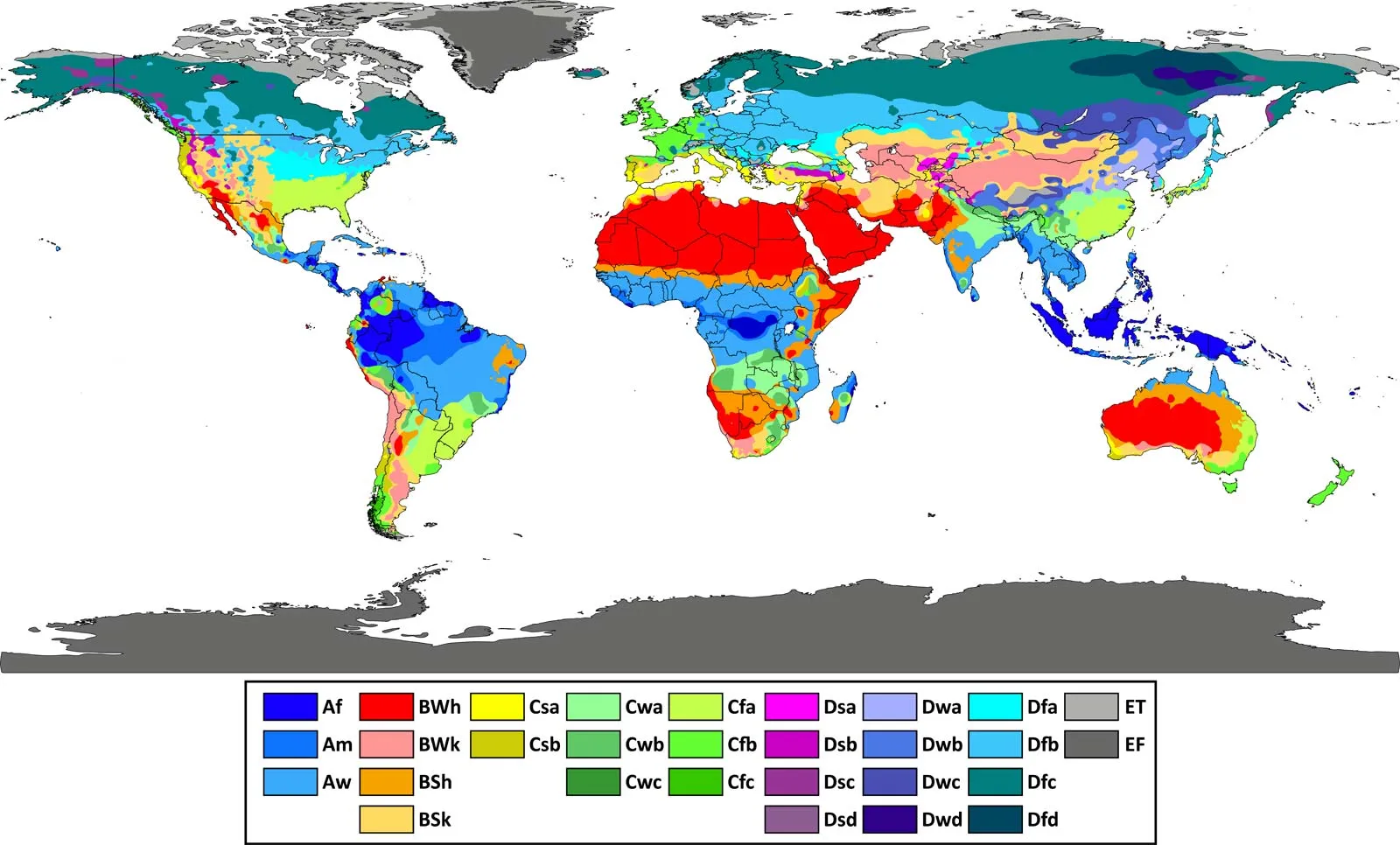
tropical climate
a climate characterized by consistently high temperatures, high humidity, and significant rainfall throughout the year
wheat belt
a geographical region in North America where wheat is the dominant crop grown
intensive agriculture
a farming practice that utilizes a small amount of land but requires a high input of labor and capital to maximize crop yield per unit area
extensive agriculture
a farming system that utilizes large areas of land with relatively low inputs of labor, capital, and technology per unit of land, often characterized by low yields but requiring large tracts of land to produce a substantial output
Market/commercial gardening/ truck farming
the large-scale production of fruits and vegetables for sale in distant markets
Plantation agriculture
a large-scale commercial farming practice where a single crop is grown on a vast area of land, primarily for export to other markets, often located in tropical climates and characterized by intensive labor requirements to produce a cash crop like coffee, sugar cane, cotton, or rubber; typically associated with historical colonial exploitation
Mixed crop and livestock
a type of agriculture where farmers cultivate crops AND raise livestock on the same land, with the crops often being used to feed the animals, creating a symbiotic relationship between the two components and allowing for more balanced income throughout the year
Nomadic herding
a type of subsistence agriculture where people move their livestock seasonally across large areas to find fresh grazing pastures
Shifting Cultivation (slash and burn)
a farming practice where farmers clear a plot of land, cultivate it for a short period, then abandon it to allow the soil to regenerate while they move to a new plot
Cluster settlement pattern
a type of rural settlement where houses and buildings are located close together, forming a dense grouping, often with fields surrounding the community, which allows for close proximity and shared resources among residents
Dispersed settlement pattern
a rural settlement where individual homes and farmsteads are scattered across a large area, with significant distances between each dwelling
Linear settlement pattern
a type of settlement where buildings and structures are arranged in a long, straight line, typically along a transportation route like a road, river, or canal, creating a ribbon-like appearance
Metes and Bounds
a method of describing land boundaries by using a detailed sequence of directions, distances, and reference points like natural features (rivers, trees) or man-made structures (roads, fences)
Long Lots
a land division system where parcels of land are long and narrow, typically with a narrow frontage along a river or road, giving each property access to a waterway while extending deep inland
Township and Range
a system of land surveying that divides land into a grid-like pattern using rectangular blocks called townships, which are further divided into smaller sections called ranges
First Agricultural Revolution/Neolithic revolution
the historical shift from a nomadic hunter-gatherer lifestyle to a settled, agricultural way of life, marked by the domestication of plants and animals, which allowed for the development of early civilizations and larger populations; essentially, the beginning of farming as a primary food source
Columbian Exchange
the widespread transfer of plants, animals, diseases, and technologies between the "Old World" (Europe, Asia, Africa) and the "New World" (Americas) following Christopher Columbus' voyages
Second Agricultural Revolution
a period between the 17th and 19th centuries where significant advancements in agricultural technology, like the mechanization of farming with tools like the seed drill and reaper, led to increased crop yields and food production
Green Revolution
a period of significant agricultural advancements, primarily focused on developing high-yield crop varieties through hybridization, increased use of fertilizers and pesticides, and improved irrigation technologies
Subsistence Agriculture
the practice of farming primarily to produce food for the farmer and their family's consumption
Commerical Agriculture
a type of farming where the primary goal is to produce cash crops and livestock for sale on the market to generate profit, rather than solely for the farmer's own consumption
Agribusiness
the commercial aspect of agriculture, encompassing the entire system of producing, processing, and distributing food products, including activities like seed production, farming, processing, distribution, and retail
Complex Commodity Chain
the intricate networks of production and distribution that connect raw materials to final consumer goods
monocropping
the agricultural practice of growing a single crop on the same plot of land year after year
ranching
a type of commercial agriculture where large herds of livestock, typically cattle, are raised on extensive tracts of land, usually grazing on natural pasture, with the primary focus on producing meat for market, often characterized by a relatively low labor input per unit of land used
Pastoral nomadism
a lifestyle where people move their herds of domesticated livestock seasonally across large areas to find fresh pasture and water, relying primarily on animal husbandry for their livelihood, typically found in arid (having little or no rain; too dry or barren to support vegetation) and semi-arid regions
fair trade
a system of trade that aims to ensure producers in developing countries receive a fair price for their goods, promoting sustainable and equitable trading practices by focusing on better wages, improved working conditions, and environmentally conscious production methods, often with a focus on transparency and accountability within the supply chain
urban farming
the practice of cultivating plants and raising animals within the boundaries of a city
community supported agriculture (CSA)
a farming model where consumers buy shares of a farm's harvest in advance, thus providing farmers with capital at the start of the growing season.
soil salinization
the process where excessive salt accumulates in the soil, typically due to irrigation in arid climates, causing the land to become infertile as the water evaporates, leaving behind salt deposits
food deserts
a geographic area where residents have limited access to affordable and nutritious food, particularly fresh fruits and vegetables, often due to a lack of nearby grocery stores or supermarkets, leaving them reliant on convenience stores with less healthy options