AP United States History ID's 1 - 37
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Headright System (1618)
Who: Sir Edwin Sandys, Virginia Company
What: Land grants to settlers in exchange for populating colonies
Impact: Expanded colonies, created planter elite, increased indentured servitude, more Native conflicts

House of Burgesses (1619)
Who: Virginia colonists
What: First representative assembly in America
Impact: Early model of self-government & democracy

Indentured Servitude (1619)
Who: Poor settlers, colonial landowners
What: Worked for years to pay passage
Impact: Increased population; class tensions → shift to slavery

Puritans (1620)
Who: English religious reformers
What: Settled New England for religious freedom
Impact: Influenced politics, culture, education in New England
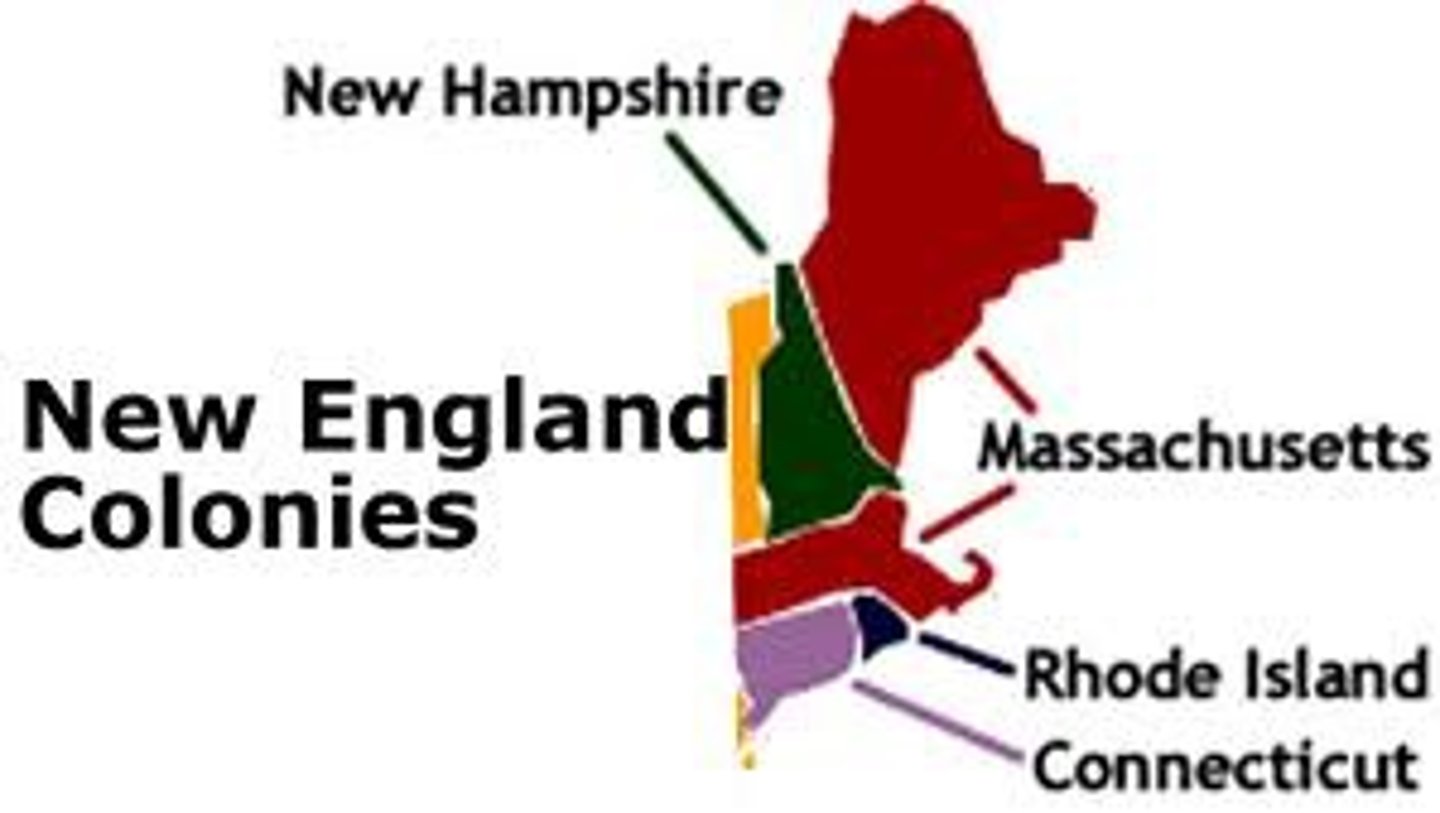
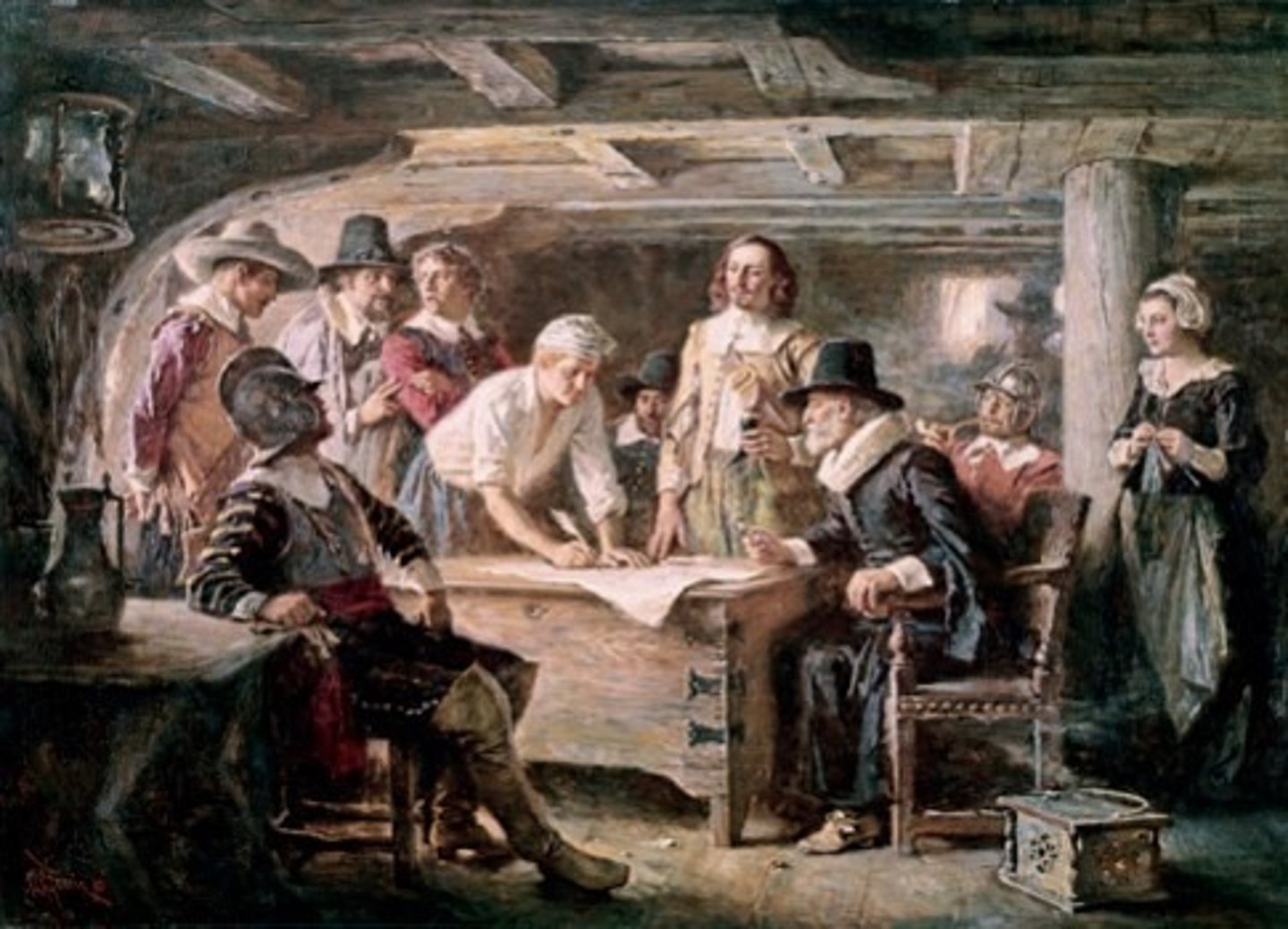
Mayflower Compact (Nov 11, 1620)
Who: Pilgrims on the Mayflower
What: Agreement for self-government in Plymouth
Impact: Early example of democracy

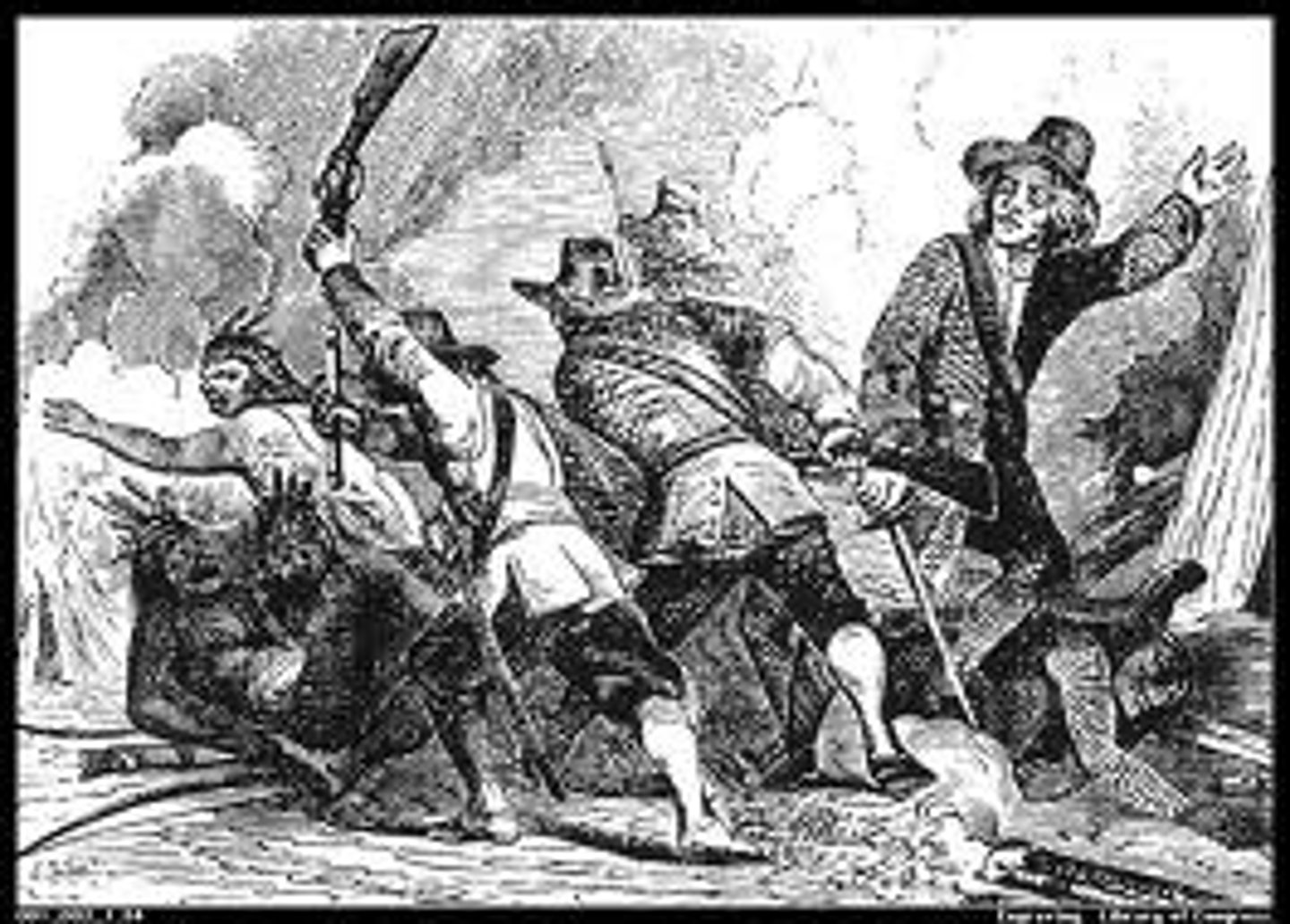
Pequot War (1637)
Who: Pequot tribe vs. New England colonists & Native allies
What: Conflict over land & trade
Impact: Pequot nearly wiped out; set precedent for violence

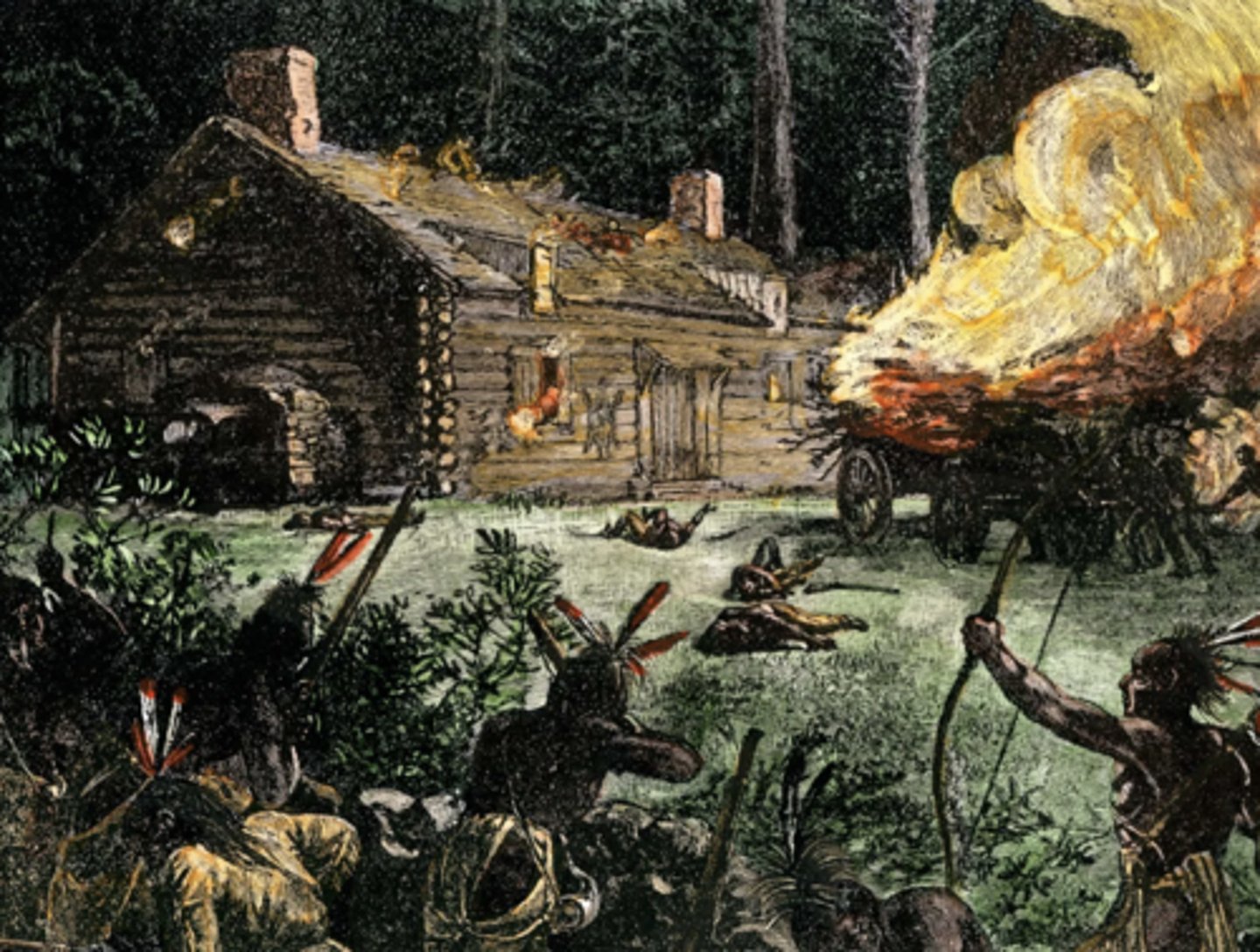
King Philip's War (1675)
Who: Metacom (King Philip) vs. New England colonists
What: Native uprising in New England
Impact: Destroyed Native power in New England

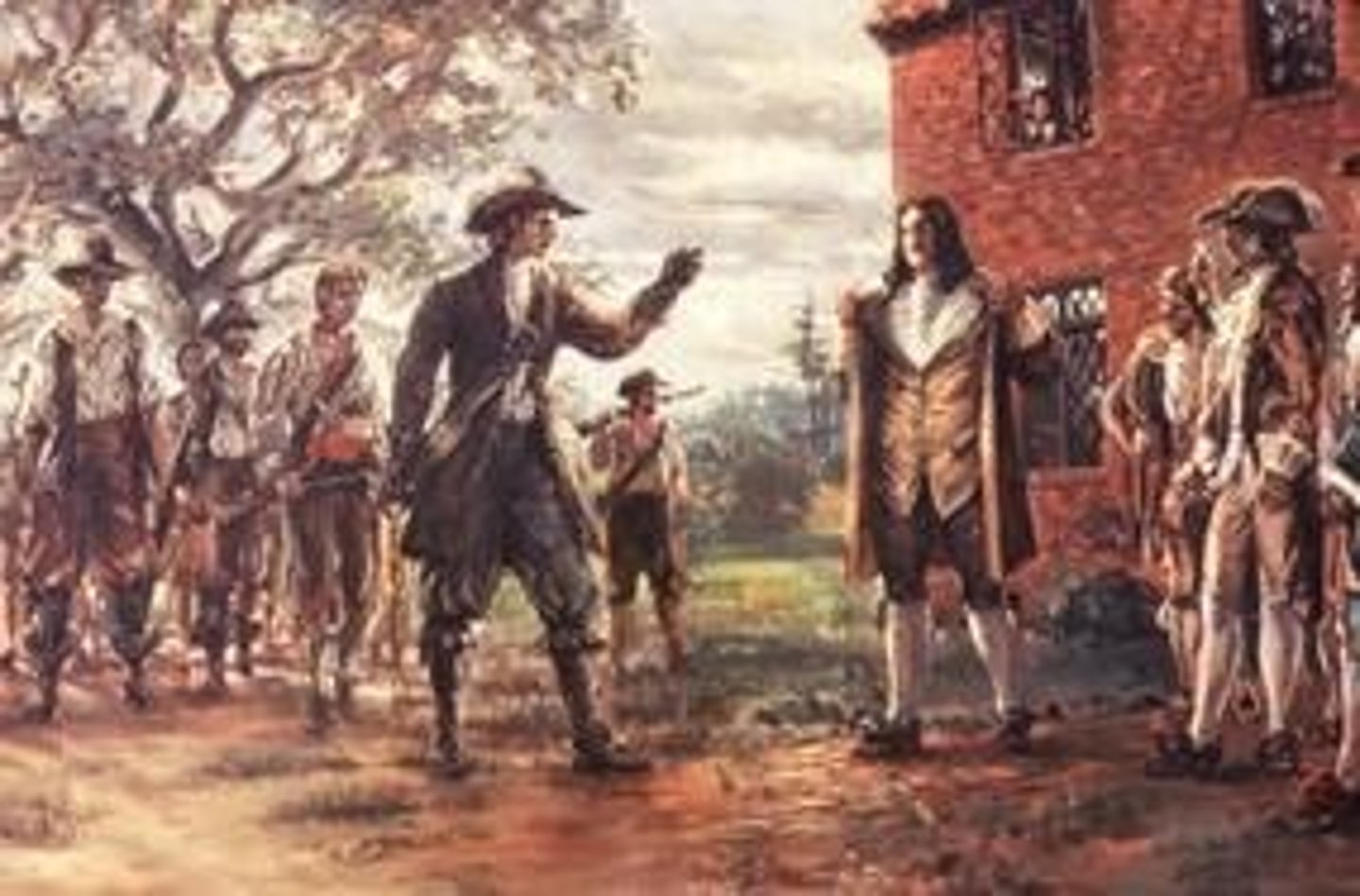
Bacon's Rebellion (June 6, 1676)
Who: Nathaniel Bacon vs. Gov. Berkeley
What: Frontier settlers rebelled over Native policy
Impact: Exposed class tensions; increased reliance on slavery

Enlightenment (1685-1815)
Who: John Locke, Montesquieu, philosophers
What: Intellectual movement—reason, liberty, natural rights
Impact: Inspired Revolution & Constitution

Great Awakening (1730-1743)
Who: Jonathan Edwards, George Whitefield
What: Religious revival movement
Impact: Increased church membership, challenged authority, independence spirit

French & Indian War (1754-1763)
Who: Britain & colonists vs. France & Natives
What: War over North America
Impact: British victory; debt → colonial taxes; tension

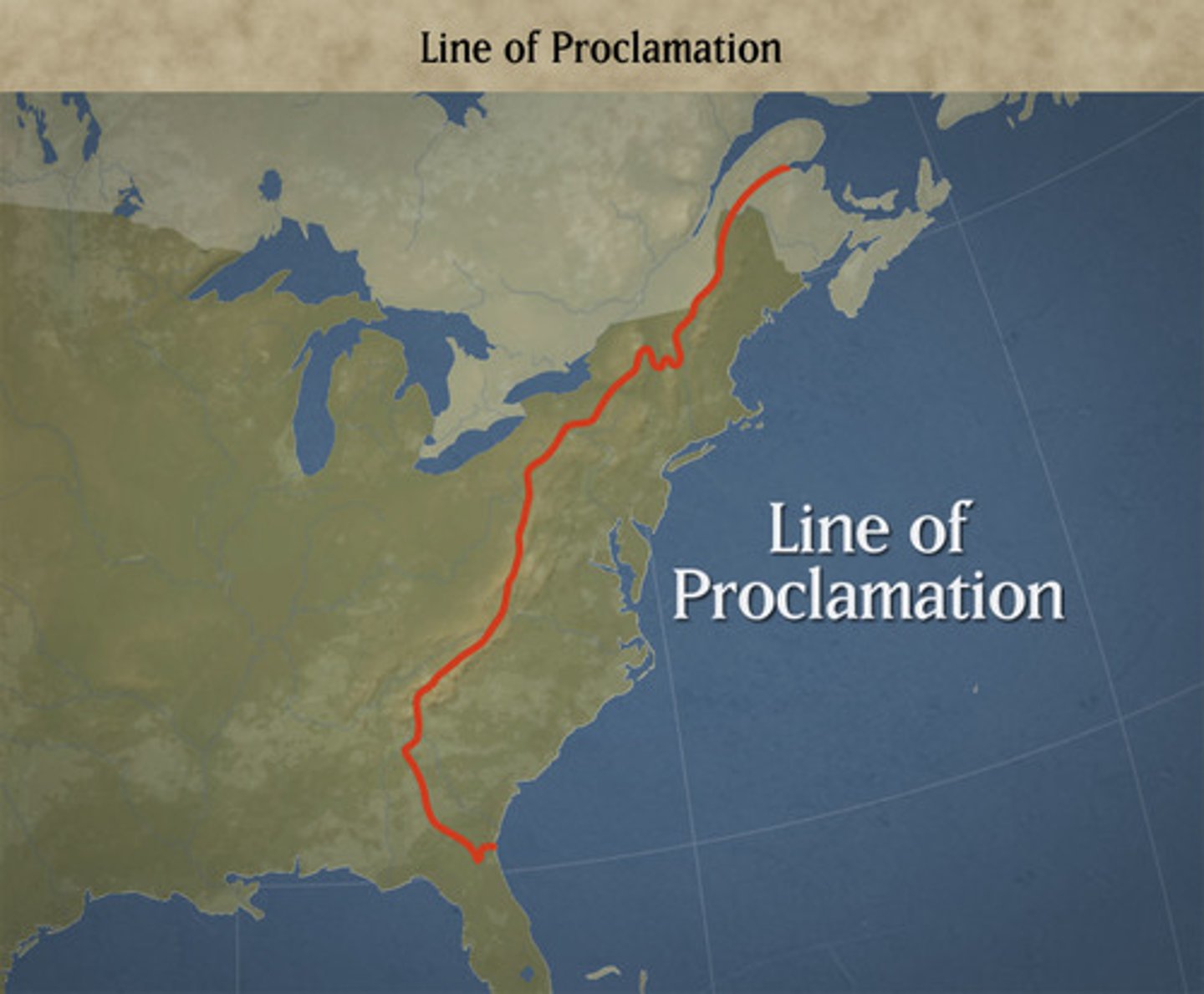
Proclamation of 1763 (Oct 7, 1763)
Who: King George III
What: Banned settlement west of Appalachians
Impact: Angered colonists; ignored
Salutary Neglect (1696-1763)
Who: British colonial policy
What: Loose enforcement of trade laws
Impact: Allowed self-rule; ended after French & Indian War

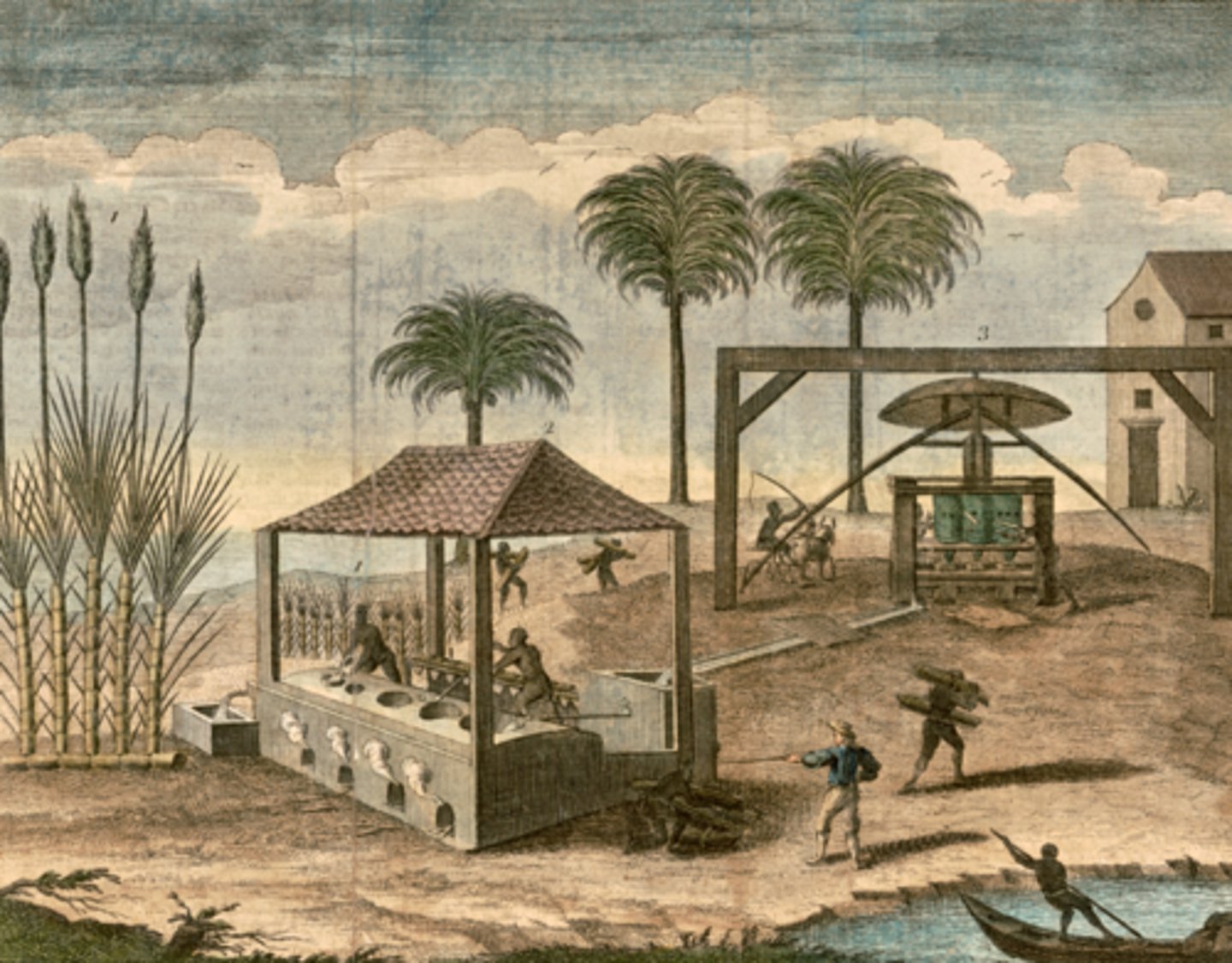
Sugar Act (April 7, 1764)
Who: British Parliament
What: Tax on imported sugar & molasses
Impact: Angered colonists; start of taxation resentment

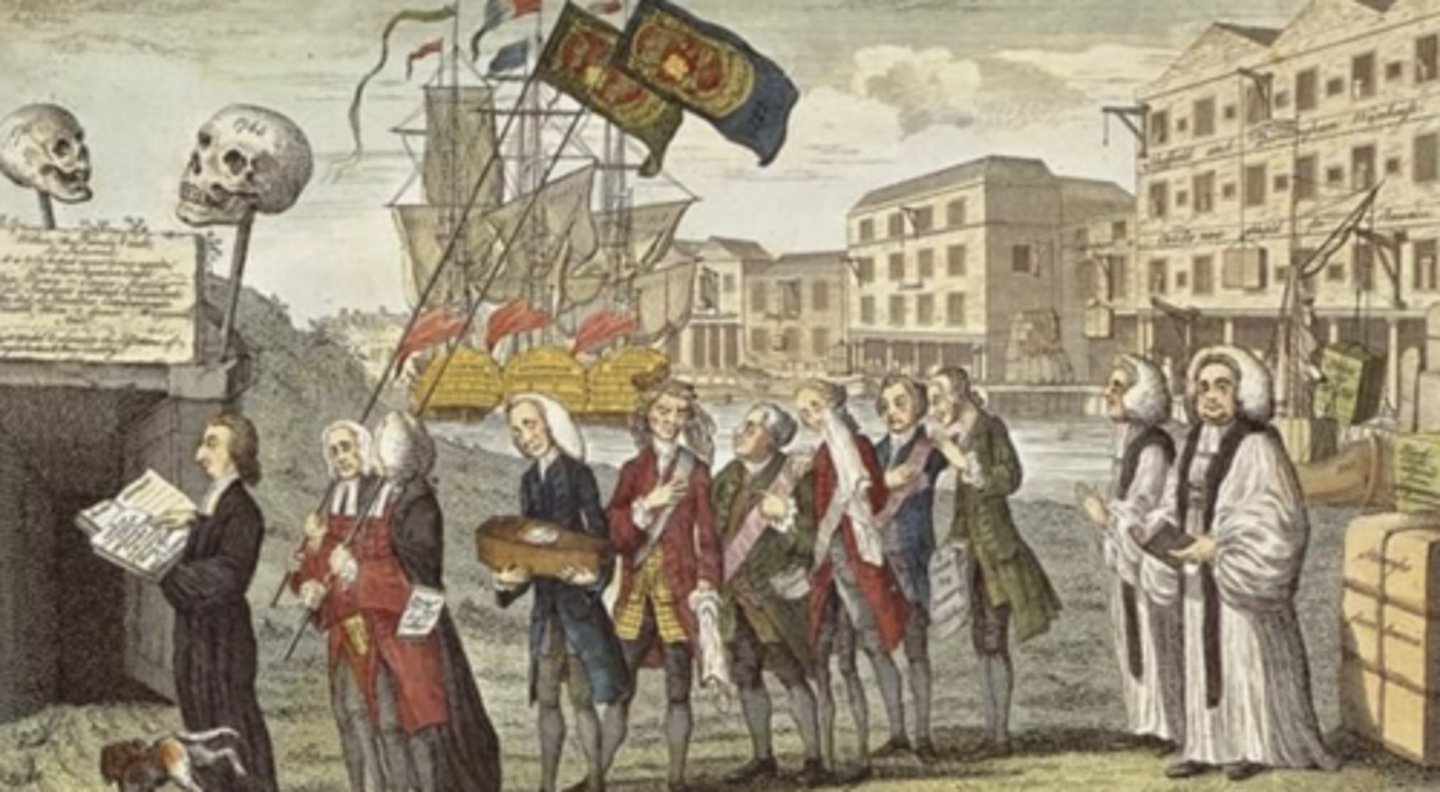
Stamp Act (March 22, 1765)
Who: British Parliament
What: Tax on printed materials
Impact: Protests, “No taxation without representation”

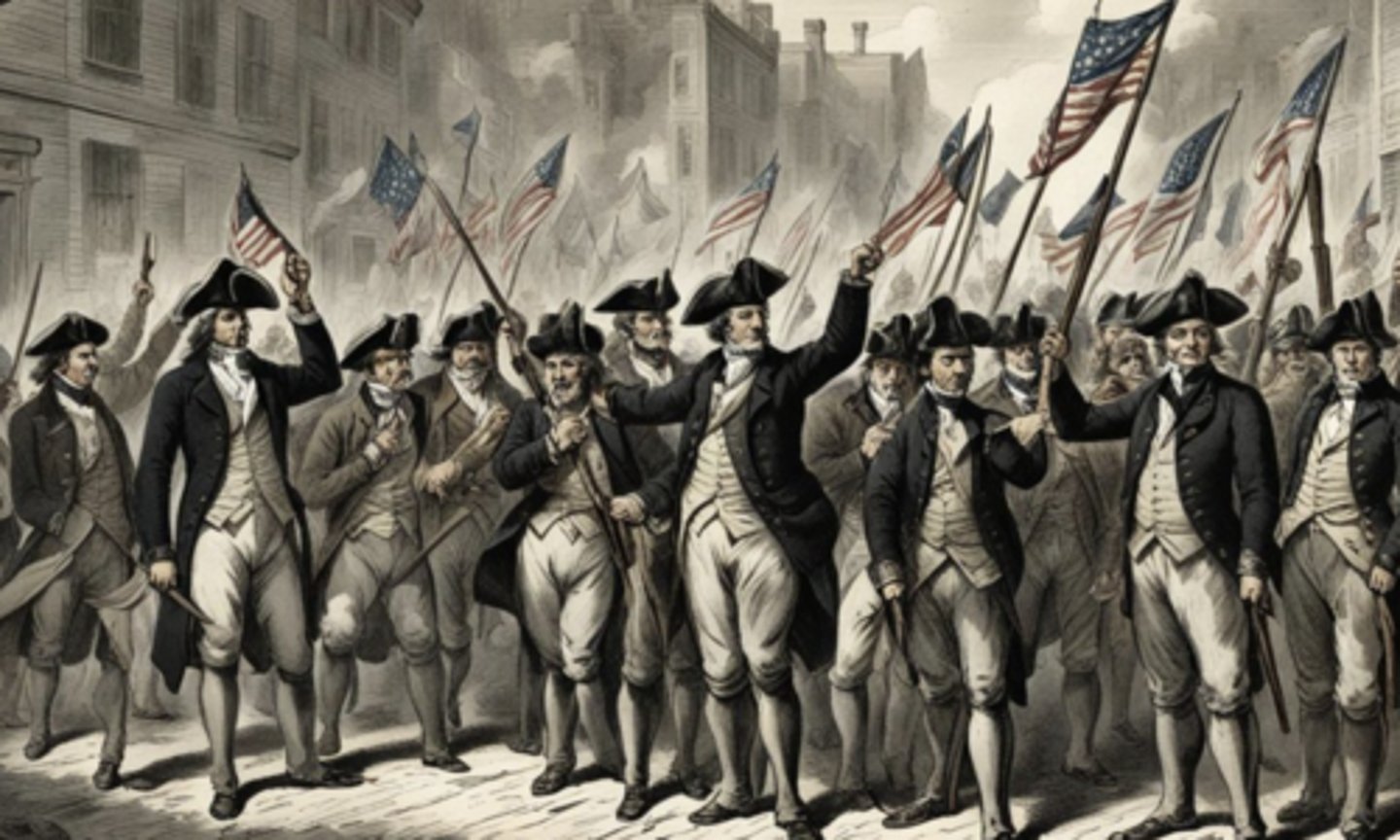
Sons of Liberty (Aug 14, 1765)
Who: Samuel Adams & colonists
What: Secret resistance group to oppose taxes
Impact: Organized protests, boycotts, Boston Tea Party

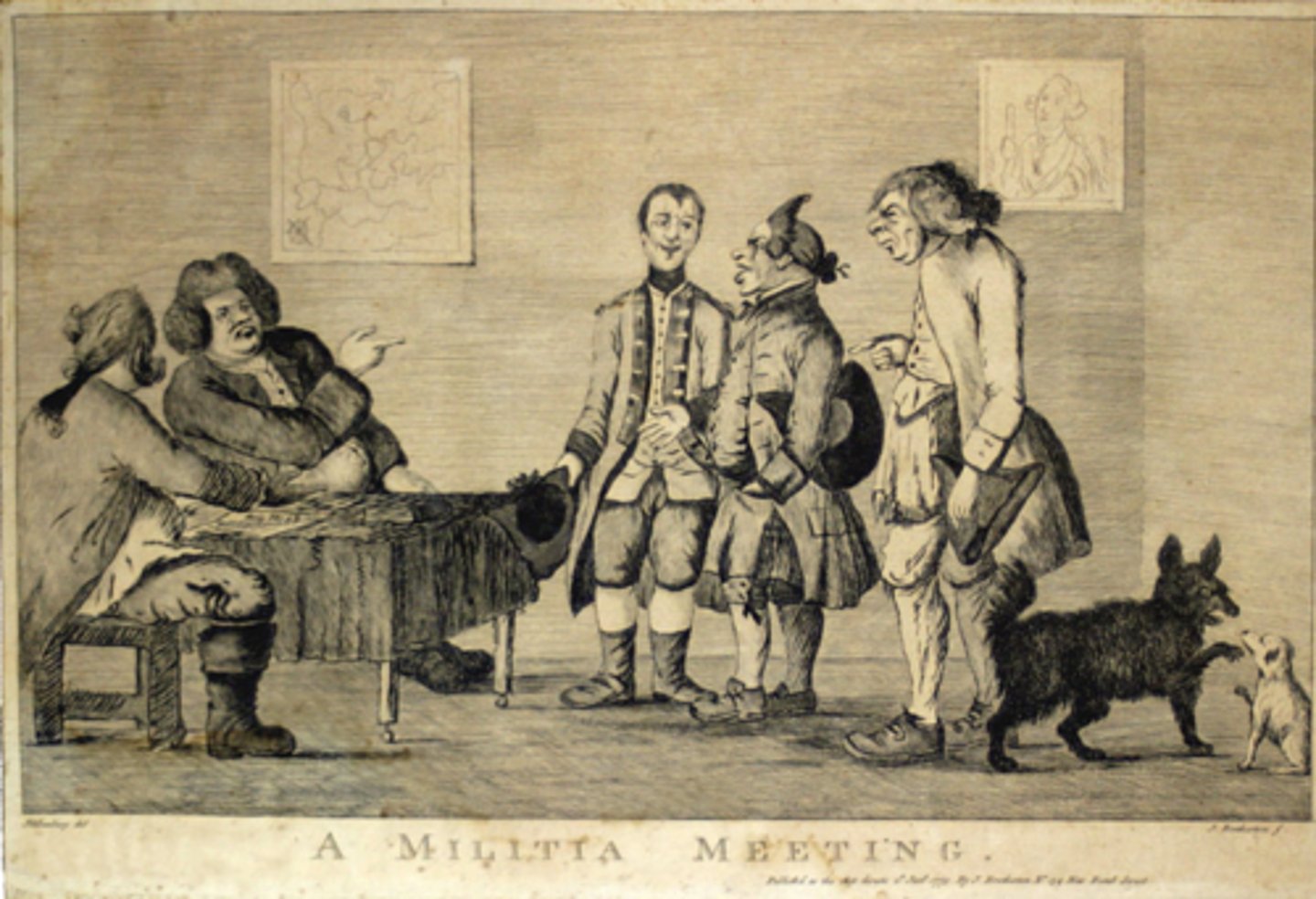
Townshend Acts (June 29, 1767)
Who: Charles Townshend, Parliament
What: Taxes on imports (glass, paint, tea, paper)
Impact: Colonial boycotts & resistance grew

Letters from a Farmer in Pennsylvania (1767-1768)
Who: John Dickinson
What: Essays against taxation w/out representation
Impact: United colonists, spread resistance

Committees of Correspondence (1773)
Who: Samuel Adams, colonial leaders
What: Communication networks between colonies
Impact: Built unity, helped form Continental Congress

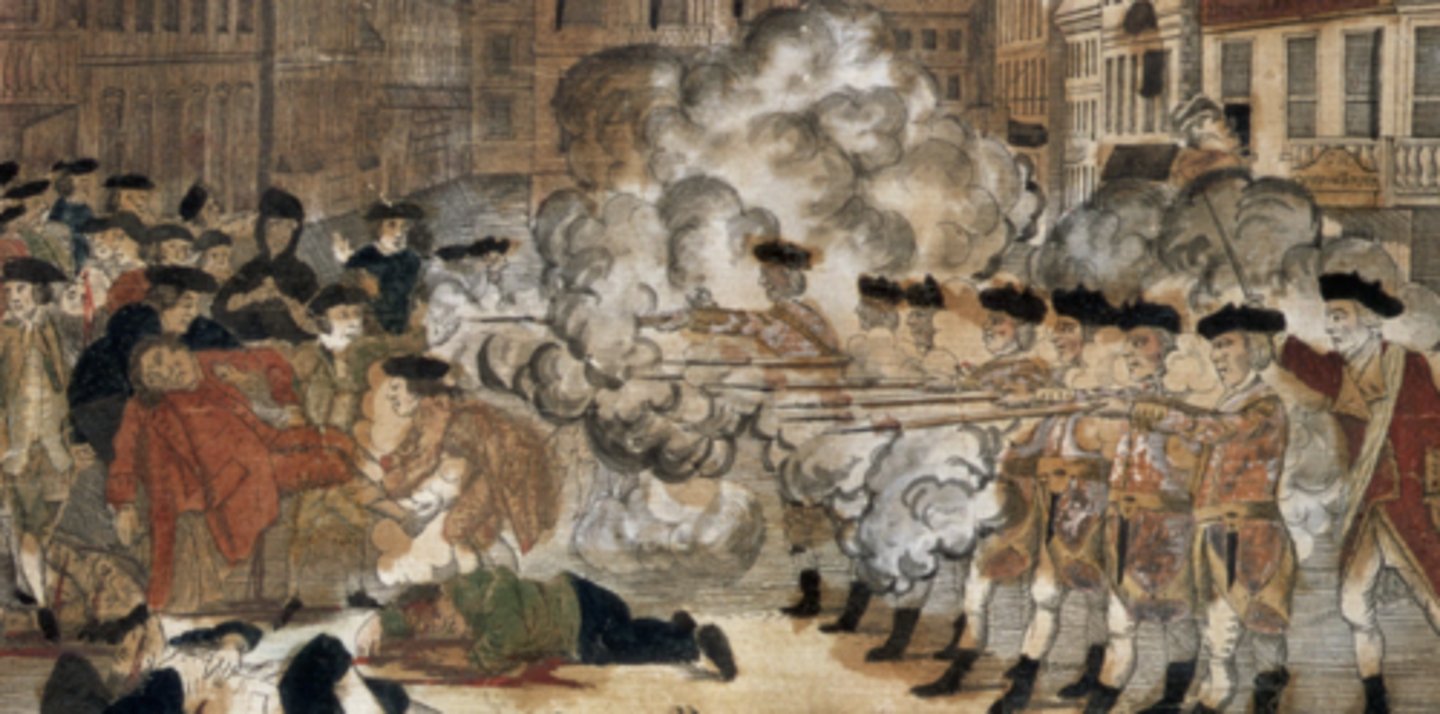
Boston Massacre (March 5, 1770)
Who: British soldiers vs. colonists
What: Troops fired on crowd, 5 killed
Impact: Patriot propaganda, fueled anger

Tea Act (May 10, 1773)
Who: Parliament, British East India Co.
What: Gave company monopoly on colonial tea sales
Impact: Led to Boston Tea Party
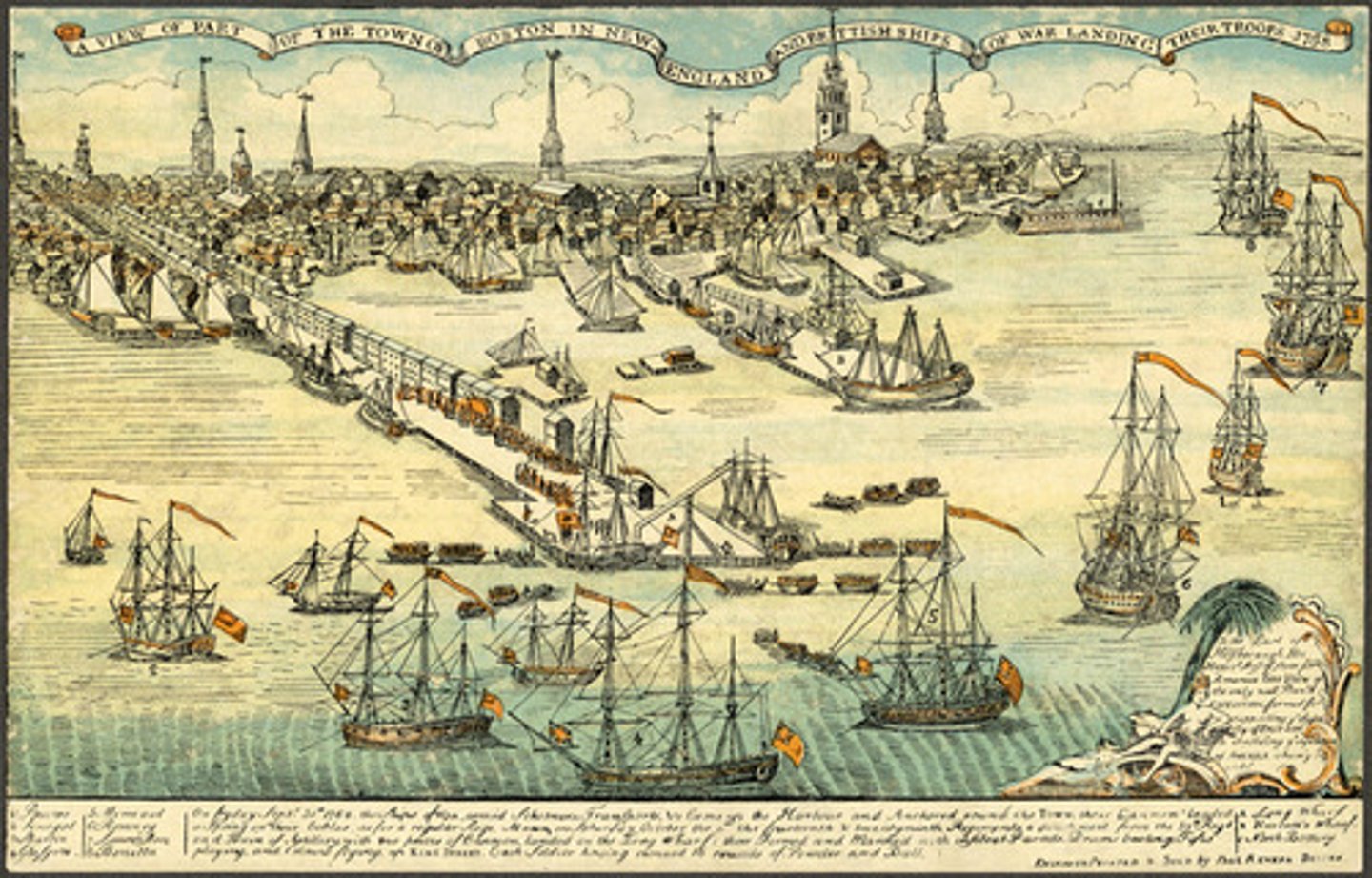
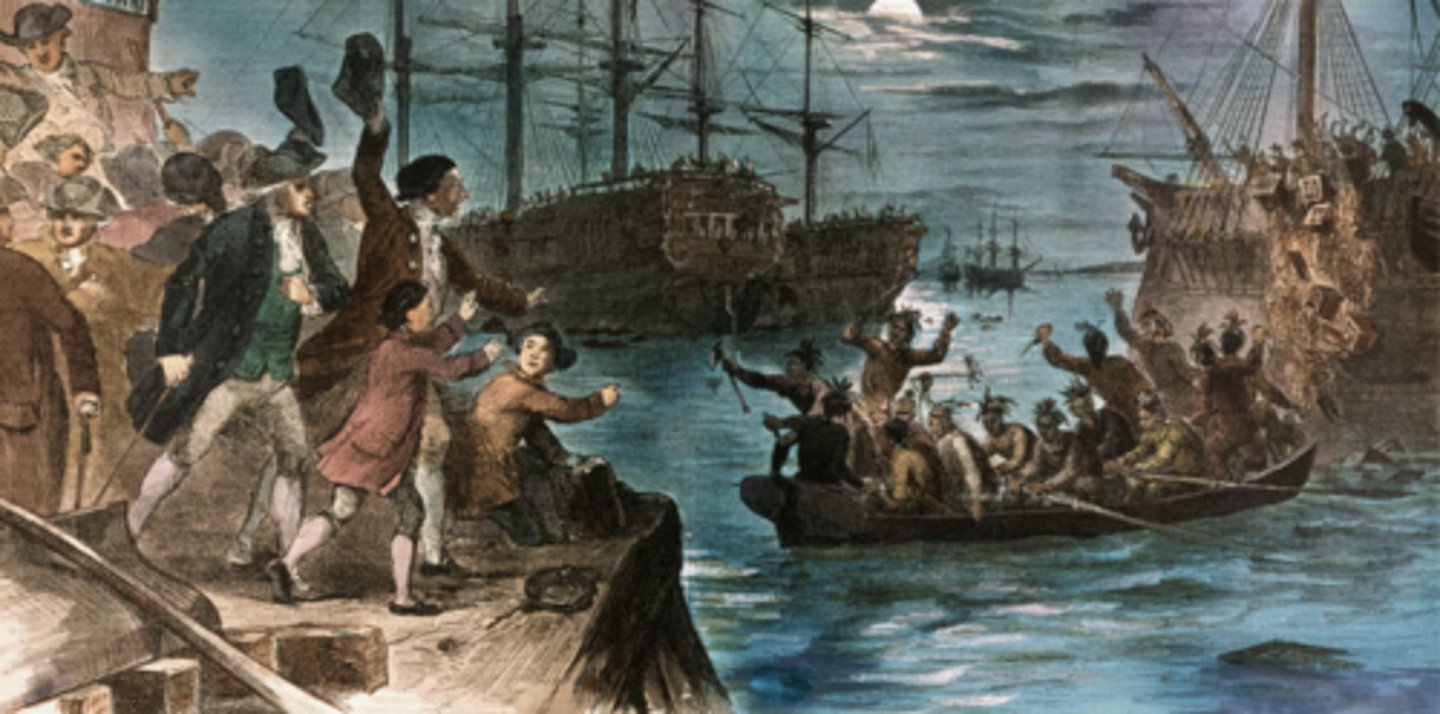
Boston Tea Party (Dec 16, 1773)
Who: Sons of Liberty
What: Dumped tea into Boston Harbor
Impact: Britain responded with Intolerable Acts

Coercive/Intolerable Acts (May 20, 1774)
Who: Parliament, King George III
What: Punitive laws—closed Boston Harbor, restricted meetings
Impact: Pushed colonies to unite; led to First Continental Congress

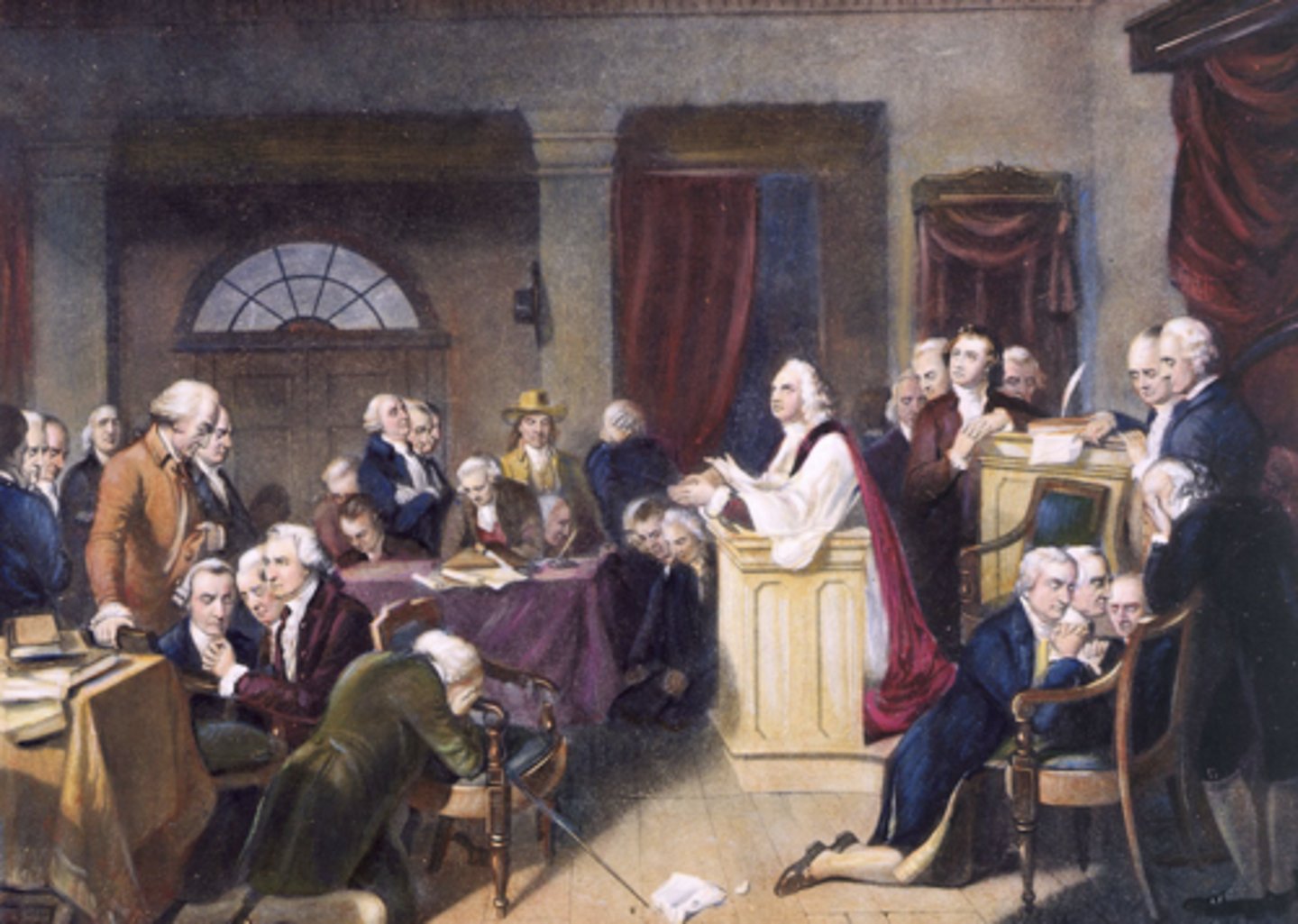
First Continental Congress (Oct 26, 1774)
Who: 12 colonies’ delegates
What: Response to Intolerable Acts; boycotts, petitioned king
Impact: Step toward independence & unity

Olive Branch Petition (July 8, 1775)
Who: 2nd Continental Congress
What: Final appeal to King for peace
Impact: Rejected by King George; war inevitable

Second Continental Congress (May 10, 1775)
Who: Delegates from 13 colonies
What: Managed war, created Continental Army under Washington
Impact: Declared independence; functioned as gov’t

Common Sense (Jan 9, 1776)
Who: Thomas Paine
What: Pamphlet calling for independence & republic
Impact: Inspired widespread support for independence

Lee's Resolution (June 7, 1776)
Who: Richard Henry Lee
What: Declared colonies independent
Impact: Led to Declaration of Independence

Battle of Bunker Hill (June 17, 1775)
Who: Colonial militia vs. British Army
What: Early major battle of Revolution
Impact: Boosted morale despite colonial defeat

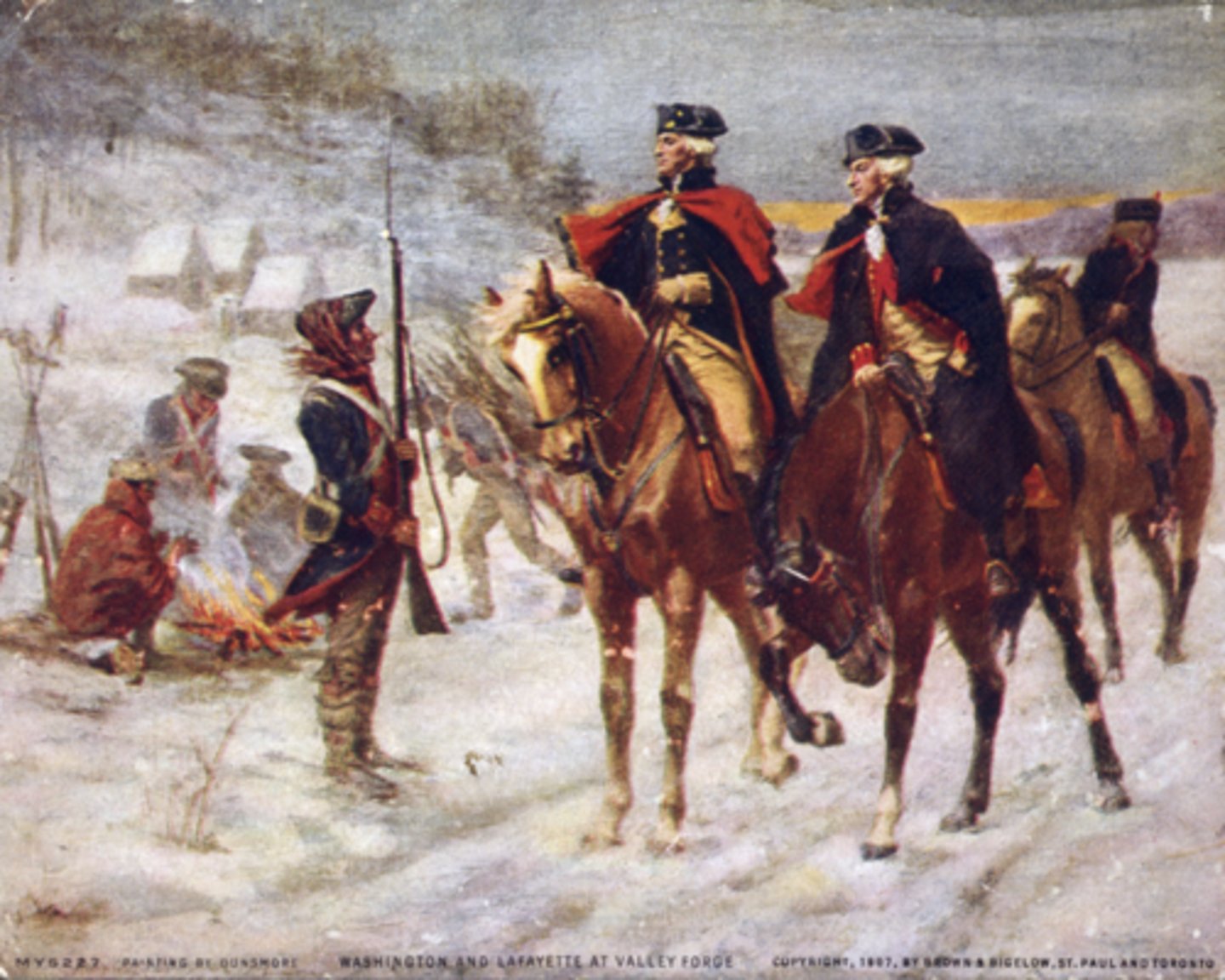
Valley Forge (Dec 1777-June 1778)
Who: Washington’s army, Baron von Steuben
What: Harsh winter camp, soldiers trained
Impact: Army emerged disciplined & stronger

Wealth of Nations (March 9, 1776)
Who: Adam Smith
What: Book on capitalism, free markets
Impact: Influenced American economic policy

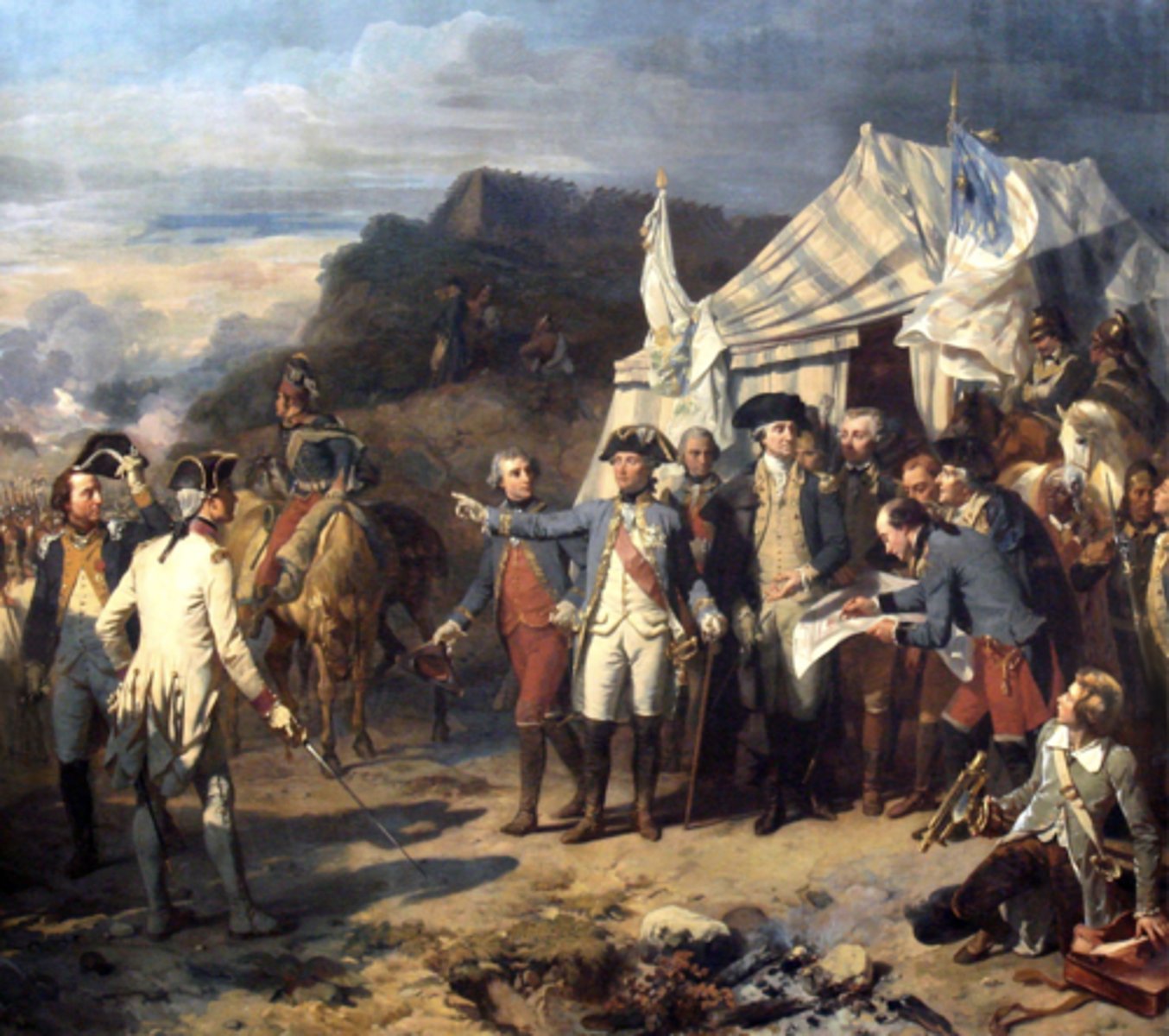
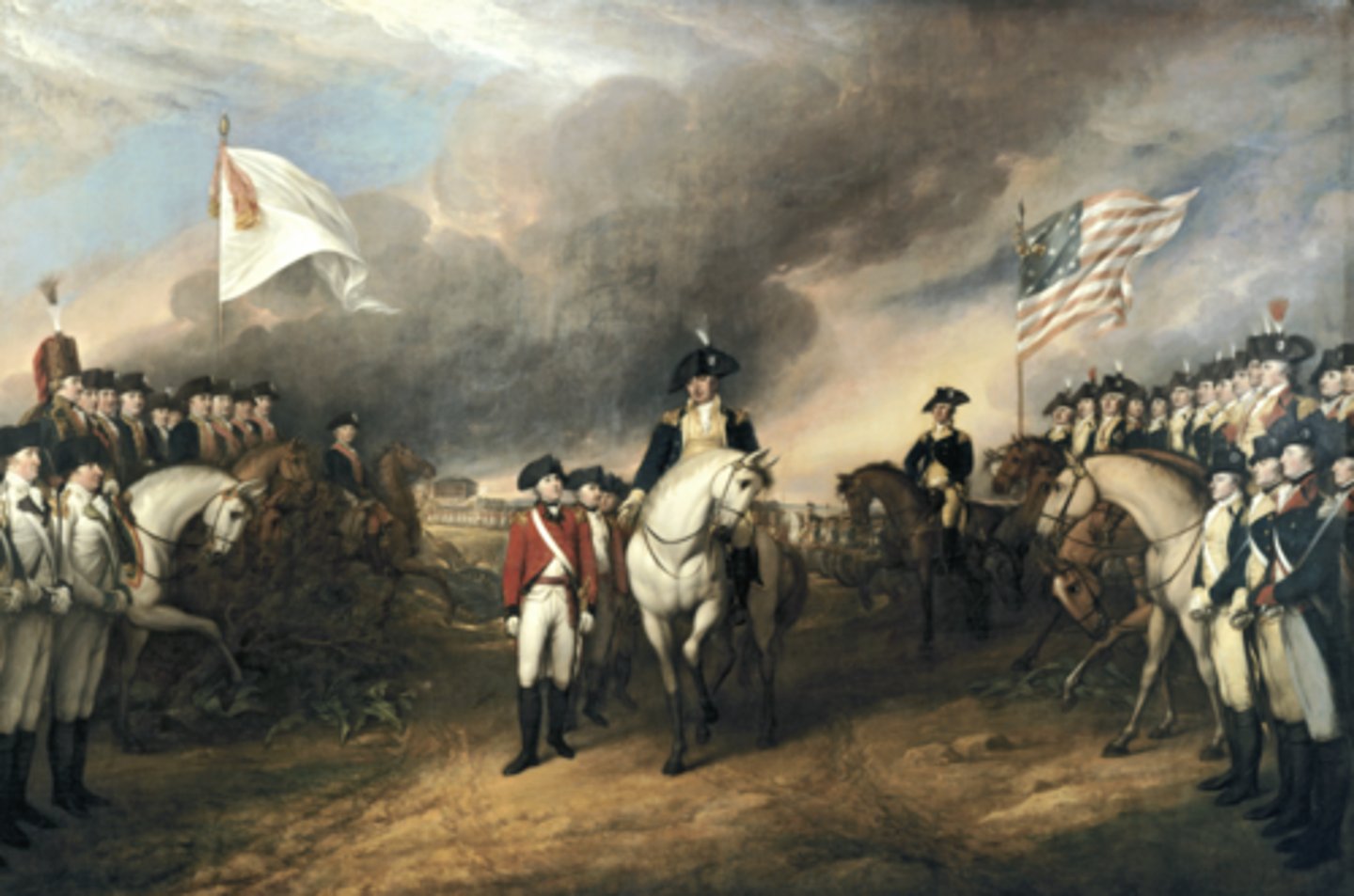
Battle of Yorktown (Sept 28-Oct 19, 1781)
Who: Washington, French allies vs. Cornwallis
What: Final battle of Revolution
Impact: British surrendered; war effectively ended

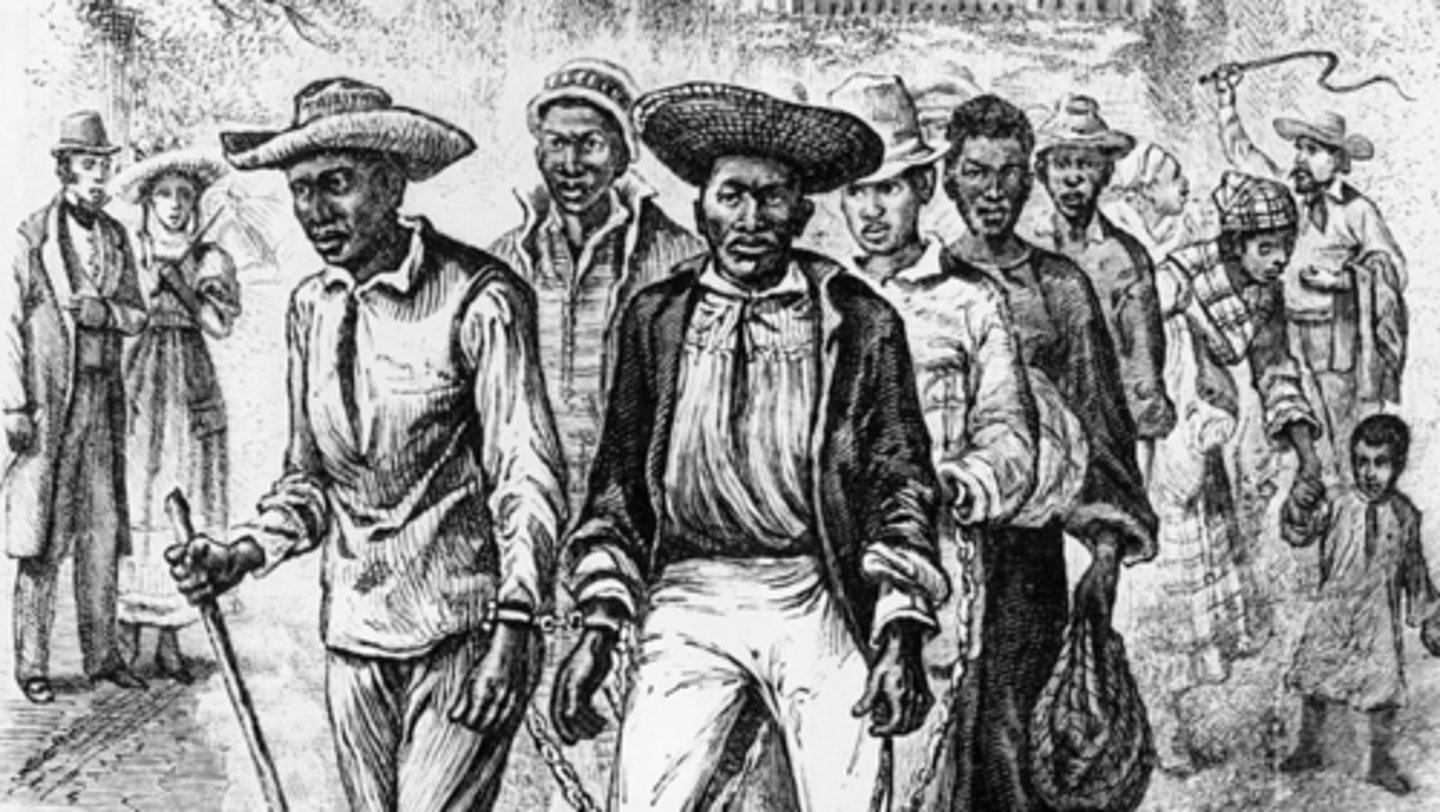
Stono Rebellion (Sept 9, 1739)
Who: Enslaved Africans in South Carolina
What: Slave revolt seeking freedom in Spanish Florida
Impact: Stricter slave codes in South

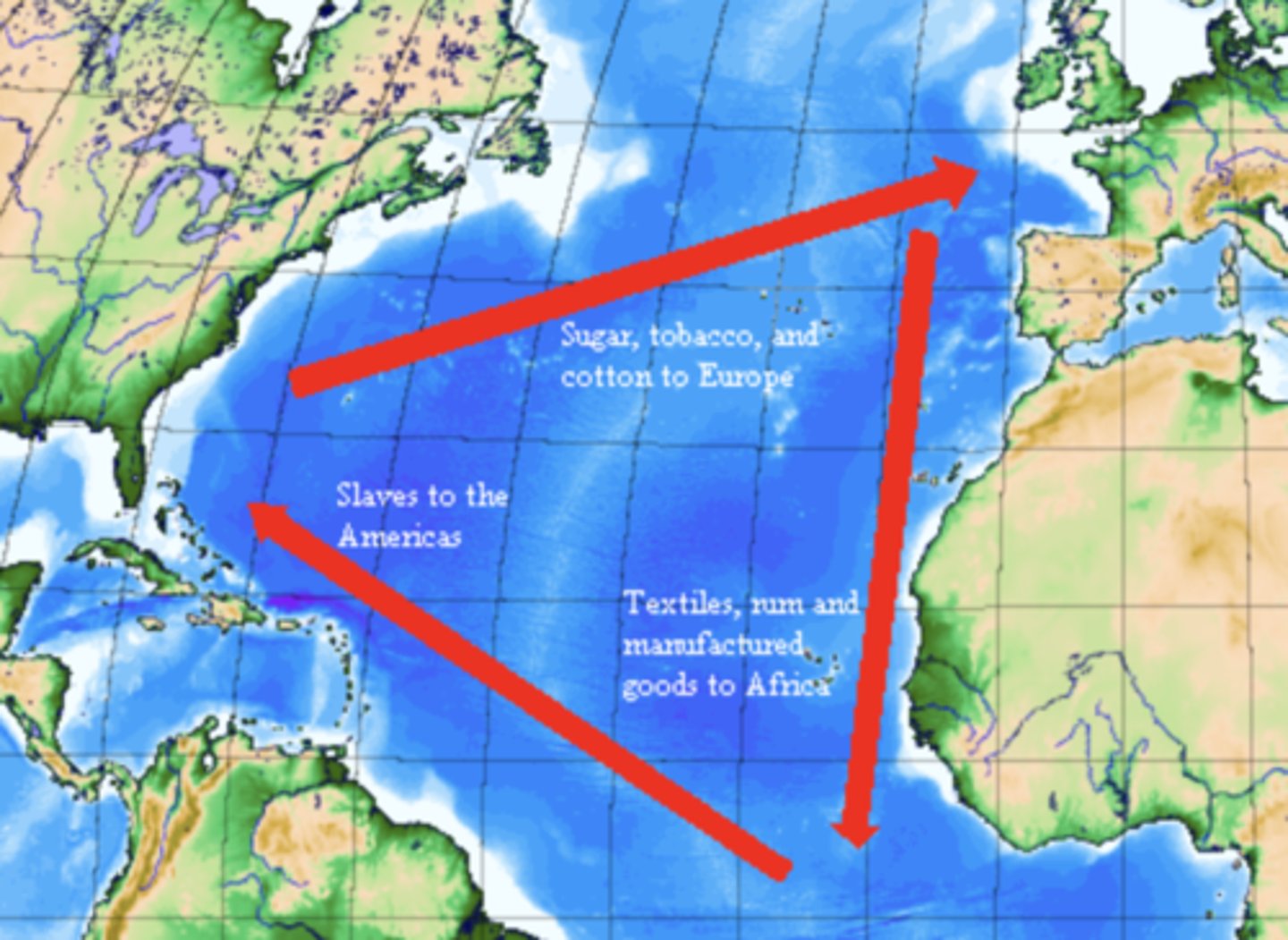
Triangular Trade (15th-16th centuries)
Who: Europe, Africa, Americas
What: Exchange of slaves, goods, raw materials
Impact: Fueled slavery, enriched colonies & Europe
Albany Plan of Union (July 10, 1754)
Who: Benjamin Franklin
What: Proposal for colonial unity in defense
Impact: Rejected, but early attempt at unity

Battle of Saratoga (Sept 19-Oct 17, 1777)
Who: American forces vs. British
What: American victory in New York
Impact: Turning point; French alliance secured
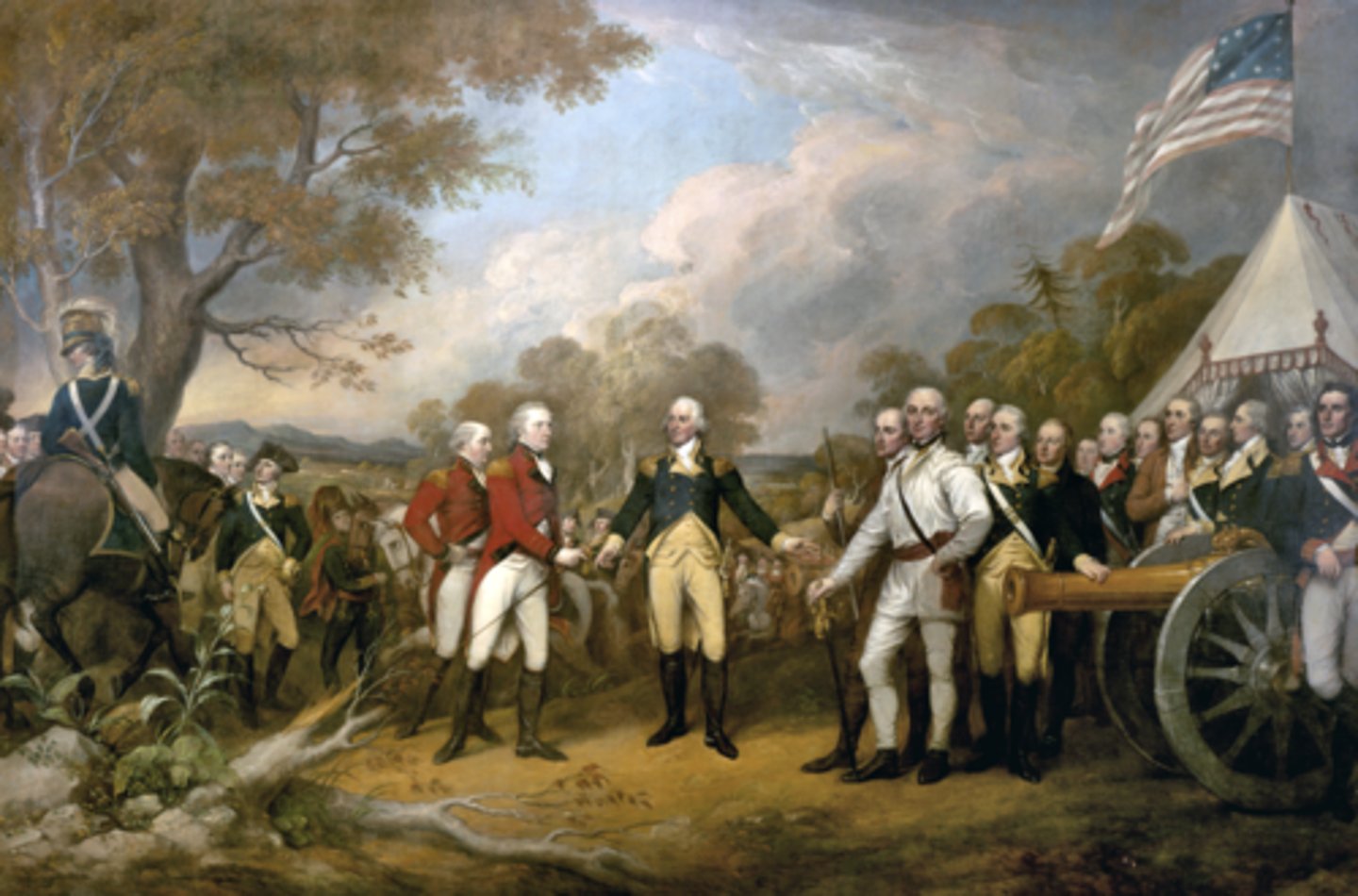

Treaty of Paris (Sept 3, 1783)
Who: U.S., Britain, France, Spain
What: Ended Revolutionary War, recognized U.S. independence
Impact: Gained land to Mississippi; secured peace
