Topic 20- Digestion
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
What are the four stages of food processing?
Ingestion, Digestion (mechanical and chemical), Absorption, Elimination.
What is the difference between mechanical and chemical digestion?
Mechanical breaks food into smaller pieces (chewing); chemical uses enzymes to hydrolyze macromolecules.
Where does digestion occur in single vs. multicellular organisms? (Single: 2; Multicellular: 3
Single: food vacuoles & lysosomes. Multicellular: extracellular digestion (e.g., gastrovascular cavity or alimentary canal).
What are accessory glands of the human digestive system? (4)
Salivary glands (3 pairs), pancreas, liver, gallbladder.
What is peristalsis?
Smooth muscle contractions that move food through the digestive tract.
What are sphincters?
Ring-like valves that regulate passage of food between compartments.
What happens in the oral cavity during digestion?
Teeth chew (mechanical), tongue shapes bolus, saliva adds amylase and mucins.
What does salivary amylase do?
Begins breakdown of starch into maltose (polysaccharide → disaccharide).
What prevents food from entering the airway during swallowing?
The epiglottis.
What is the function of the esophagus?
Uses peristalsis to move bolus to the stomach.
What is the function of the cardiac sphincter?
Regulates food entry from esophagus to stomach and prevents acid reflux.
What are the three types of cells in the gastric glands?
Mucus cells, parietal cells (HCl), chief cells (pepsinogen).
How is pepsin activated in the stomach?
HCl cleaves pepsinogen into active pepsin.
What does pepsin do?
Breaks proteins into smaller polypeptides.
What is chyme?
Acidic, semi-liquid mixture of food, enzymes, and gastric secretions.
What are the three parts of the small intestine?
Duodenum, jejunum, ileum.
What increases surface area in the small intestine? (2)
Villi and microvilli.
What does pancreatic juice contain? (2)
Bicarbonate (neutralizes acid) and digestive enzymes.
What is the function of bile, and where is it produced and stored?
Emulsifies fats (produced in liver, stored in gallbladder).
What is the function of the large intestine? (3)
Absorbs water, forms feces, houses microbiota.
What are feces composed of? (2)
~75% water and ~25% solid material.
Where are carbohydrates first digested?
In the mouth by salivary amylase.
What enzymes digest carbohydrates in the small intestine? (2)
Pancreatic amylase and disaccharidases.
What digests proteins in the stomach?
Pepsin.
What enzymes digest proteins in the small intestine? (5)
Trypsin, chymotrypsin (pancreas), and dipeptidase, carboxypeptidase, aminopeptidase (SI).
Where are nucleic acids digested?
Only in the small intestine by pancreatic nucleases, nucleosidases, and phosphatases.
How are lipids digested? (2)
Bile salts emulsify fats; pancreatic lipase breaks triglycerides into glycerol, fatty acids, and monoglycerides.
How are lipids absorbed? (4)
Diffuse into cells, reassembled into triglycerides, packaged into chylomicrons, transported via lacteals.
What is the hepatic portal vein?
Carries nutrient-rich blood from intestines to the liver for processing.
What are the liver’s roles in digestion? (4)
Makes bile, detoxifies substances, converts nutrients, stores glucose as glycogen (insulin-regulated).
What do gut bacteria in the large intestine do? (2)
Produce vitamins (K, B12, thiamine, riboflavin) and prevent pathogen colonization.
What helps regulate elimination at the anus?
Two sphincters: one voluntary, one involuntary.
Sequence the stages of food processing in animals in 4 steps:

Compare and contrast the stages of food processing in animals in terms of their purpose and additional information: [ingestion, digestion, absorption, elimination]

Compare and contrast digestive compartment of animals:
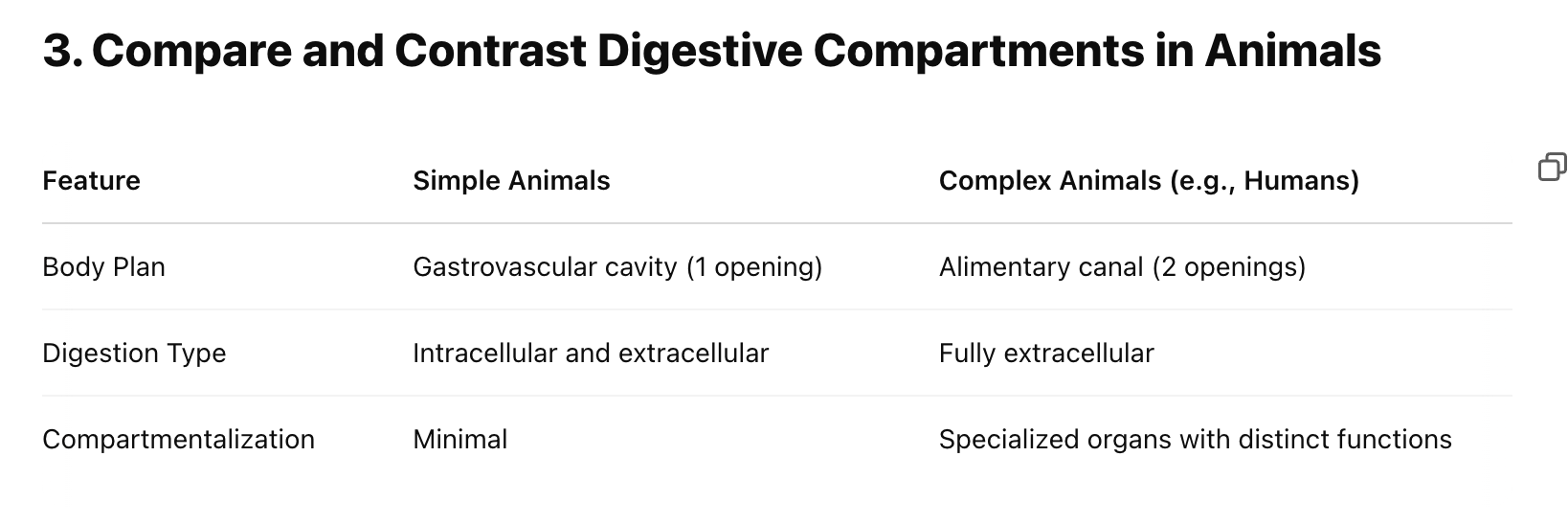
Compare and Contrast Human Digestive Compartments [oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, liver, gallbladder, pancreas]

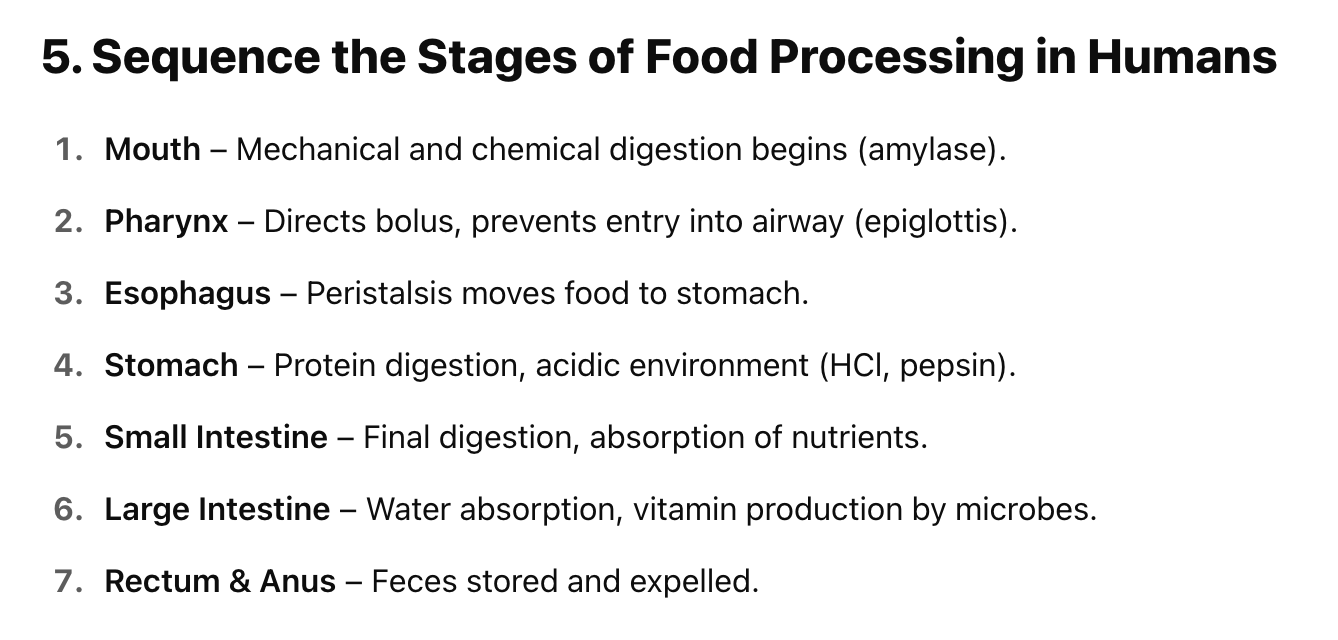
Sequence the Stages of Food Processing in Humans (7)
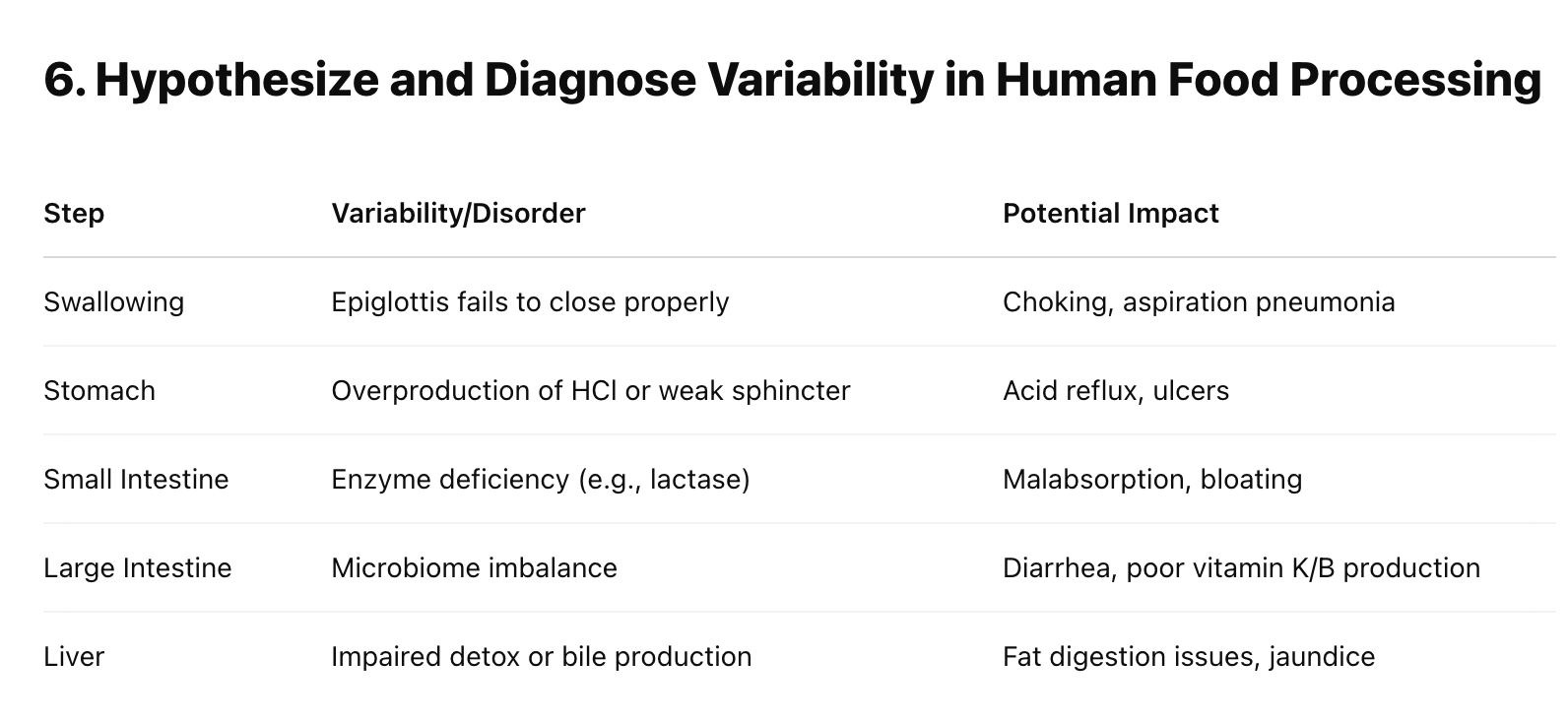
Hypothesize and Diagnose Variability in Human Food Processing
Sequence the Digestion of Carbohydrates, Proteins, Nucleic Acid, Lipids [Site of Digestion, Enzymes Involved]

Compare and Contrast the Digestion of Carbs, Proteins, Nucleic Acids, and Lipids. [Start where?, Enzymes used, Special processes (broken down to)]

Sequence the Absorption of Water, sugars, amino acids, and lipids (table) [absorbed where, transport method]
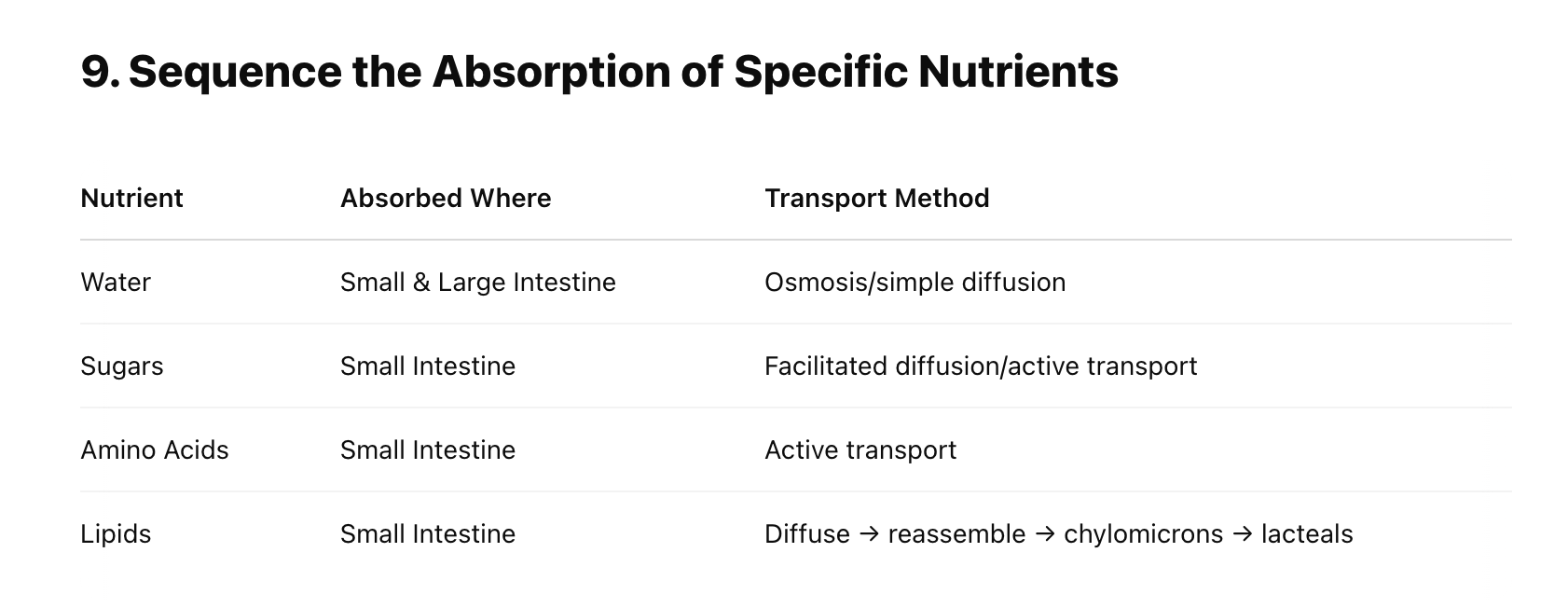
Compare and Contrast the Absorption of Carbs, Proteins, Lipid, and Water in terms of pathway and special features

Compare and Contrast Small Intestine, Large Intestine, and Liver in terms of structure and function
