Module 9: qualitative research
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What is qualitative research?
strategies that collect and analyze non-numerical data
Types of qualitative data
Primary qualitative data
Secondary qualitative data
Types of secondary data
company reports
blogs
press releases
When to use qualitative research
generate insights into less mature topics
inductive
Types of primary qualitative data
interviews
focus groups
observations
Types of interview
structured interview
unstructered interview
semi-structured interview → favored
Steps in designing semi-structured interview
setting the scene→ purpose, recording
warm-up questions → easy, non senstive
interview → per subtopic, open ended and probing questions (can you explain?)
summarize → interpretation
What to do with interview data?
Transcribe it immediately
Focus group
unstructered interview
by a moderator
small group oif participants (8-14)
free to speak
→ new products/ideas
role of moderator
everyone participate
no member dominates
Steps focus group
setting the scene → topics, purpose and recording
introductions → everyone
discussion→ topic guide
closing round
Focus group data consist of
recordings
notes moderator
transcripts
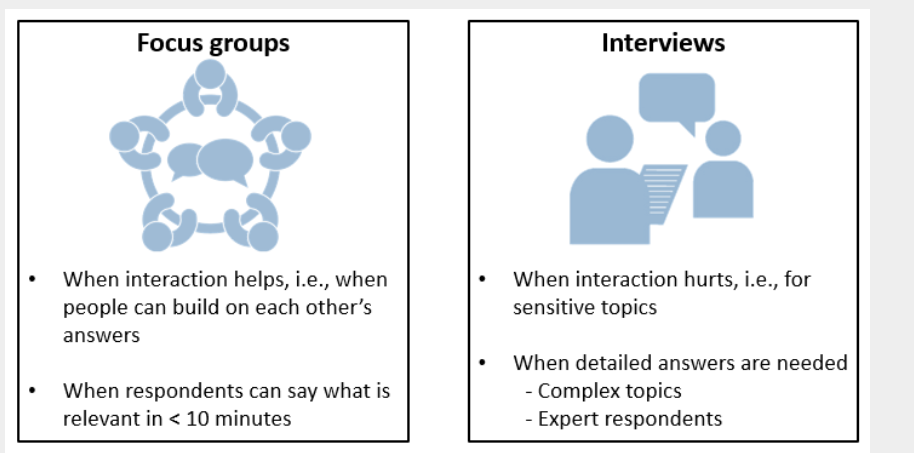
Choosing between focus group and interviews
Observational studies
-systematically
-recording behavior
-natural surrounding
Types of observational research
complete participant → is part and not revealed purpose
complete observer → doesn’t take part and not revealed purpose
participant as observer → takes part and reveal purpose
observer as participant→ doesn’t take part and reveals purpose
Observational data
primary observations → notes about what happened
experiental data → notens on your perceptions of the experience
contextual data → note setting
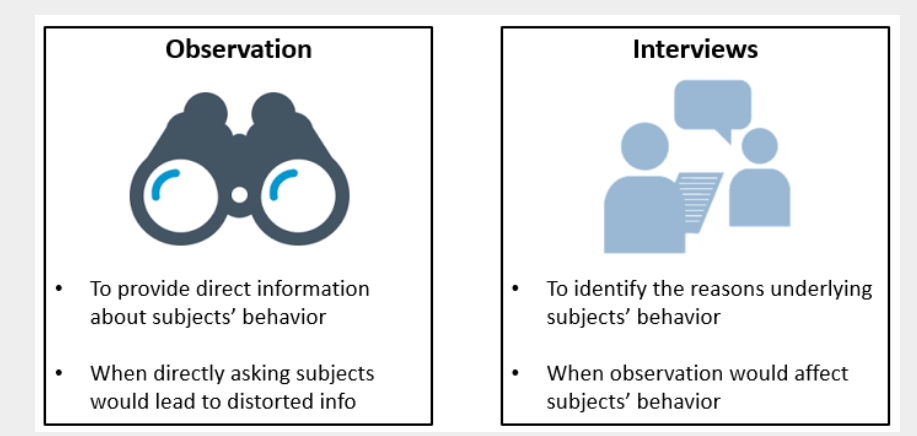
Choosing between observations and interviews
Threats to internal validty qualitative research
researcher bias → skews process towards specific research outcome → selective perception and interpretation
respondent bias
2 types of responden tbiases
authority bias
conformity bias
How to increase internal validity
triangulation → analyzing data through different angels (several mod, differen locations)
peer debriefing → peer debriefing → feedback from someone at a different stage
member checking
negative case anlysis → analyzing cases that don’t match the trends
Member checking
send transcripts for feedback
mail/verify interpretations
validation interview
External validity
The qualitative researcher can enhance generalizability by doing a thorough job of describing the research context and the assumptions that were central to the research. The person who wishes to “transfer” the results to a different context is then responsible for judging how sensible the transfer is.