unit 2 chpt 7 attention and scene perception
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
attention
any of the very large set of selective processes in the brain
– To deal with the impossibility of handling all inputs at once,
the nervous system has evolved mechanisms that are able to
restrict processing to a subset of things, places, ideas, or
moments in time.
selective attention
The form of attention involved when processing
is restricted to a subset of the possible stimuli.
external attention
attending to stimuli in the world ex looking at slides in class
internal attention
attending to one line of thought over another or selecting one response over another. ex your thoughts and feeling
overt attention
directing a sense organ toward a stimulus, like turning your eyes or your head
covert attention
attending without giving an outward sign you are doing so
divided attention
splitting attention btw two diff stimuli
sustained attention
continuously monitoring some stimulus ex a lifeguard monitoring the pool to make sure no one drowns
inattentional blindness
a failure to notice- or at least to report- a stimulus that would be easily reportable if it were attended ex the gorilla crossing the screen while ppl throwing ball
change blindness
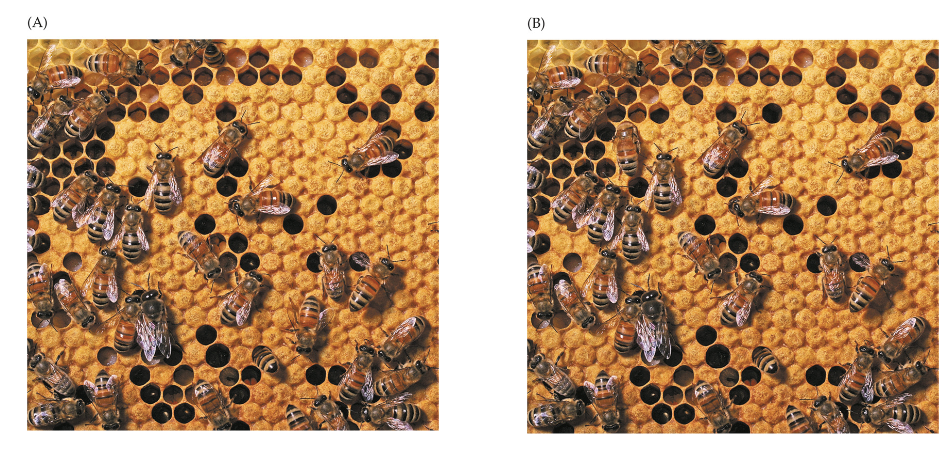

the failure to notice a change btw two scenes
bottom-up processing
automatic, stimulus-driven
top-down processing
controlled, goal-driven
interaction
working together in complementary roles
reaction time
a measure of the time from the onset of a stimulus to a response
cue
a stimulus that might indicate where (or what) a subsequent stimulus will be
stimulus onset asynchrony
the time btw the onset of one stimulus and the onset of another
“spotlight” model theory of attention
attention is restricted in space and moves from one point to the next. areas within the spotlight receive extra processing
“zoom lens” model theory of attention
the attended region can grow or shrink depending on the size of the area to be processed
visual search
looking for a target in a display containing distracting elements ex wheres waldo
guided search
attention is restricted to a subset of possible items based on info abt the items basic features (type of visual search) ex i knew what waldo looked like so i look for the striped shirt
inhibition of return
the relative difficulty in getting eyes to move back to a recently attended location ex during hide and seek i would hide in the place the seeker just looked bc they think they alr searched so they dont need to look again
serial self terminating search
a search from item to item, ending when a target is found. least efficient way of searching. ex looking at every single person in picture until you find waldo
feature search
efficient. search for a target defined by a single attribute, such as a salient color or orientation
salience
the vividness of a stimulus relative to its neighbors
parallel
in visual attention, referring to the processing of multiple stimuli at the same time
conjunction search
search for a target defined by the presence of two or more attributes
scene-based guidance
info in our understanding of scenes that helps us find specific objects in scenes ex. asked to find plate and you look on table bc thats where it would normally be
the binding problem
the challenge of tying diff attributes of visual stimuli, which are handled by diff brain circuits, to the appropriate objects so we perceive a unified object
feature integration theory
– a limited set of basic features can be processed in parallel
preattentively (automatically), but that other properties, including the correct
binding of features to objects, requires attention.
preattentive stage
the processing of a stimulus that occurs before selective attention is deployed to that stimulus
illusory conjunction
an erroneous combination of 2 features in a visual scene ex you remember there was a blue F in a picture but there was actually a blue A and an orange F
rapid serial visual presentation
an experimental procedure in which stimuli appear in a stream at one location at a rapid rate
attentional blink
the difficulty in perceiving and responding to the second of two target stimuli amid a rapid serial visual presentation stream of distracting stimuli
– The second target is often missed if it appears within 200 to 500 ms of the first target.
– Reflects the limitations of the brain's processing capacity and the time needed to reset attention.
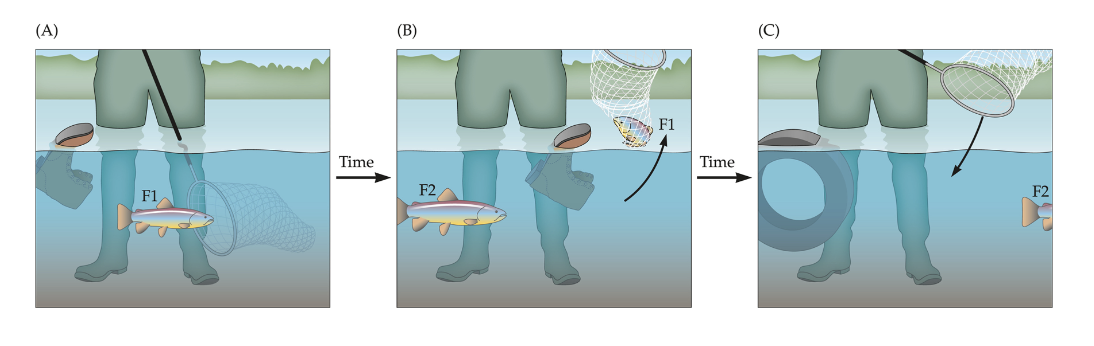
miss the second fish bc u caught the first
*three ways responses of a cell could be changed by attention*
response enhancement
sharper turning
altered tuning
visual-field defect
a portion of the visual field with no vision or with abnormal vision, typically resulting from damage to the visual nervous system
-damage to the parietal lobe can cause a visual field defect such that one side of the world is not attended to
neglect
in visual attention, the inability to attend to or respond to stimuli in the contralesional visual field
-typically, neglect of the left visual field after damage to the right parietal lobe
selective pathway
permits the recognition of one or of very few objects at a time. this pathway passes through the bottleneck of selective attention
nonselective pathway
contributes info abt the distribution of features across a scene as well as info abt te “gist” of the scene. this pathway does not pass through the bottleneck of attention
ensemble statistics
the nonselective pathway computes _ _
ensemble statistics
the avg distribution of properties, such as orientation or color, over a set of objects or a region in a scene
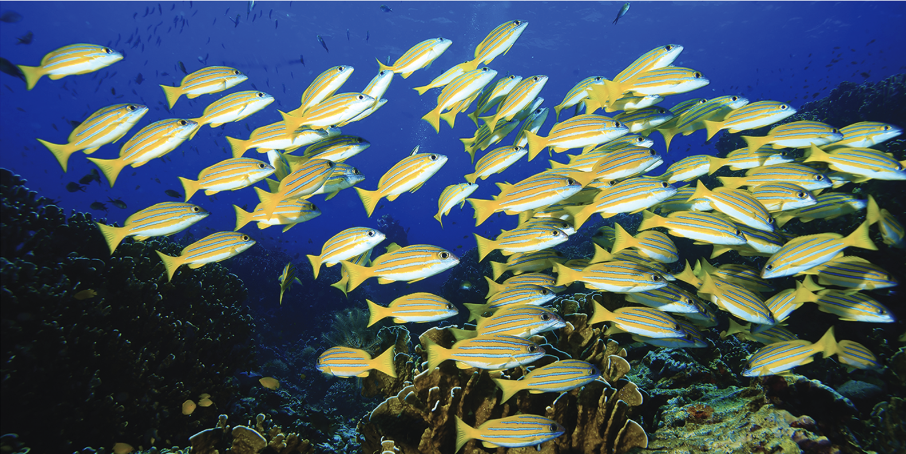

fish look horizontal overall
the nonselective pathway computes _ and _ very quickly
scene gist and layout
spatial layout
The description of the structure of a scene (e.g.,
enclosed, open, rough, smooth) without reference to the identity of
specific objects in the scene.