Island Biogeography
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
What is island biogeography and what organisms does it refer to?
how species colonize, survive, and go extinct on islands. refers ONLY to species that originate on the mainland
How does size of an island affect the number of species on an island? (area effect)
larger size = more species
smaller size = fewer species
How does the distance of an island from the mainland affect the number of species on an island? (distance effect)
more distance = fewer species
shorter distance = more species
What are rates of colonization and extinction on an island related to?
number of species present, distance from mainland, and island area/size
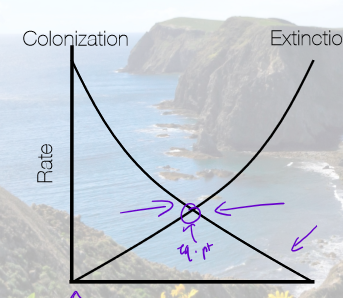
Where is the equilibrium point for rate of colonization and extinction on an island?
intersect between lines
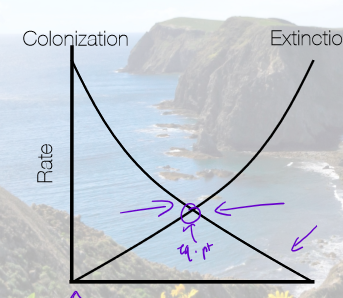
Explain why having more species on an island decreases colonization rates, and why having fewer species increases colonization rates.
more species = more interspecific competition for resources, fewer niches left
fewer species = more niches to fill, less interspecific competition for resources
In terms of colonization and extinction rates, what will happen on a smaller island at the same distance the mainland as a larger island, and why?
smaller island will have higher extinction rate because smaller islands can support fewer populations, increasing extinction rates. niches are filled more quickly and there are fewer resources.


In terms of colonization and extinction rates, what does the extinction and colonization rate for a small island look like compared to a normal-sized island the same distance from the mainland??
extinction rate is sharper, and fewer species are supported
colonization rate is the same
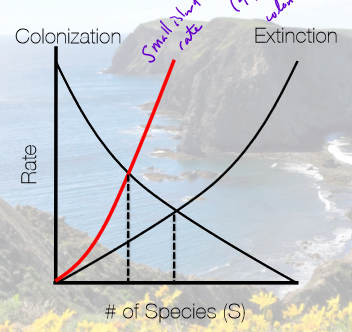
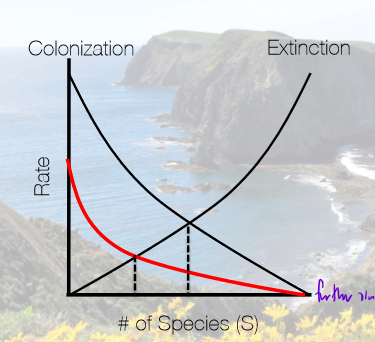
In terms of colonization and extinction rates, what does the extinction and colonization rate for a small island look like compared to a normal sized island?
colonization rate is the same
extinction rate is higher
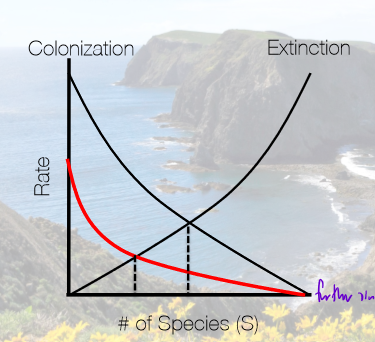
In terms of colonization and extinction rates, what will happen on an island of the same size but further from the mainland and why?
lower colonization rate, harder to reach
same extinction rate
Describe the Florida Keys experiment
counted the number of spider species on each island in the florida keys
theorized that, if size/distance theory is true, the same number of species should colonize each island after extermination all spider species
found that closer islands were colonized more quickly than distant islands
number of species returned to same number of species as before
species composition changed