11.1 Economic Growth and the Economic Cycle
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
What is short-run economic growth
It is the annual percentage increase in a country’s real GDP, caused by increases in aggregate demand
What is long-run economic growth
It occurs when the productive capacity of the economy increases, caused by an increase in aggregate supply
What is potential output
The level of output an economy can produce if all resources are fully employed
What is an output gap
The difference between actual and potential levels of output
What characterises a negative output gap
Actual output is less than potential output, leads to unemployment and downward pressure on inflation
What characterises a positive output gap
Actual output is greater than potential output, resources are overused, causing upward pressure on inflation
What is the economic cycle
The fluctuations in economic growth over time, including booms and recessions
Draw the Economic Cycle
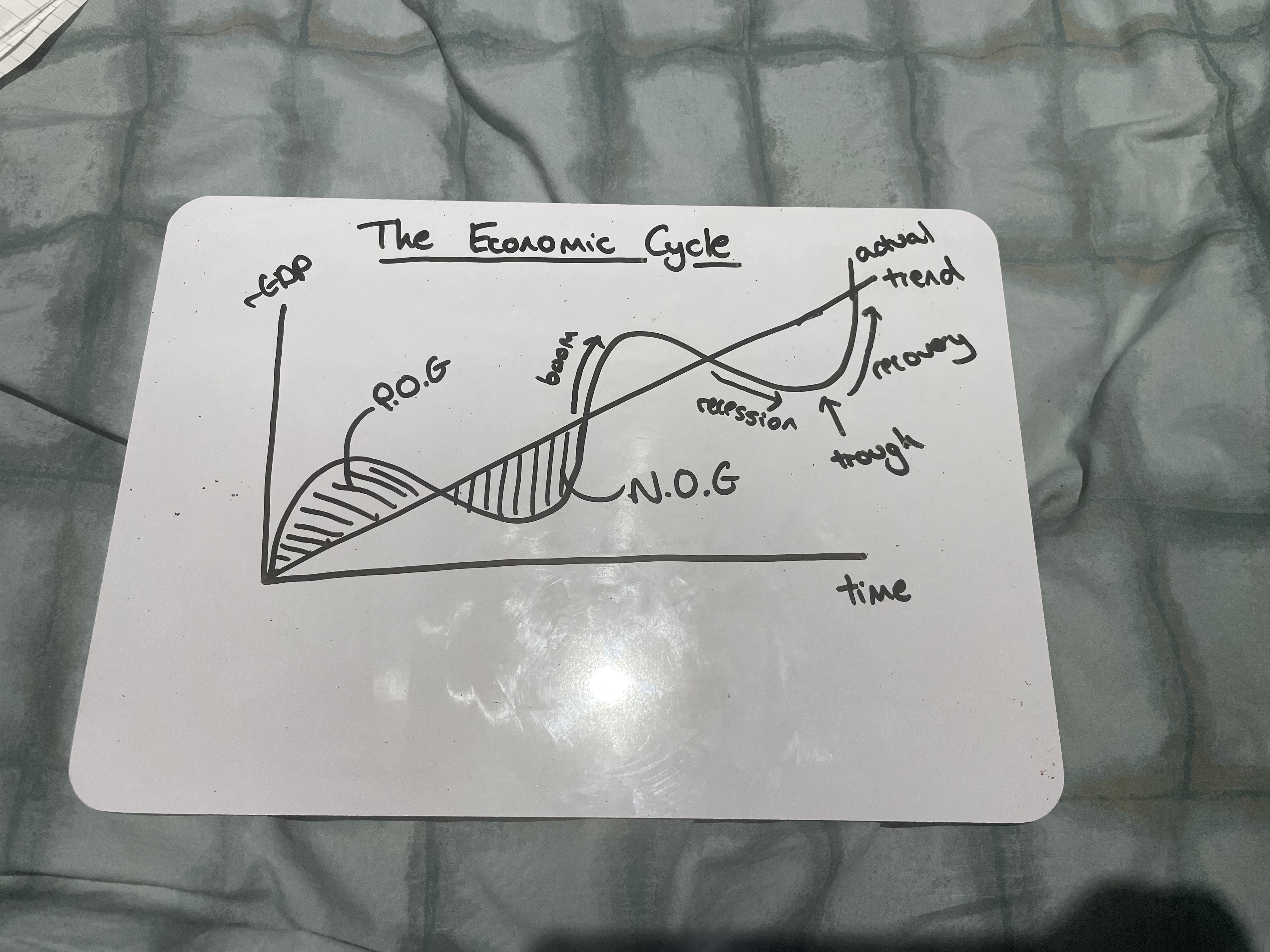
What happens during a boom
Fast economic growth, near full employment, positive output gaps, demand-pull inflation
What happens during a recession
Negative growth over two consecutive quarters, spare capacity, rising unemployment, and lower inflation
How might government respond to a recession
Increase spending, cut taxes, raise welfare benefits to stimulate demand
What benefits do consumers gain from economic growth
Growth increases confidence, leading to higher consumption and living standards
What are consumer costs of economic growth
Higher inflation, greater inequality
What benefits do firms gain from economic growth
Higher profits, investment, economies of scale, better export opportunities
What are menu costs
The costs to firms of changing prices frequently due to inflation
How does economic growth benefits the government
Increased tax revenues, reduced welfare spending which improves the budget